Method for rapid and highly-selective detection of hypochlorous acid
A technology for qualitative detection of hypochlorous acid, applied in chemical instruments and methods, measuring devices, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as insufficient sensitivity, insufficient selectivity, complex synthesis, etc., and achieve simple synthesis, good stability, and reaction. responsive effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033]
[0034] (Scheme 1) Dissolve 290mg (1mmol) of azenobutyl-4-chloro-1,8-naphthalimide in 15mL of acetonitrile, then add 110mg (1mmol) of p-aminophenol, then add 326mg (1mmol) of cesium carbonate and reflux for 2h , and then use a high-pressure pump to carry out suction filtration to obtain a filtrate, which becomes our crude product. If a purer product is desired, the filtrate can be separated by column chromatography with a mixed system of dichloromethane and methanol (for example, v / v, 100:1) to obtain a pure product, and 200 mg of a yellow pure product is obtained with a yield of 50%.
[0035] (Scheme 2) Dissolve 290mg (1mmol) of azetyl-4-chloro-1,8-naphthalimide in 15mL of acetonitrile, then add 220mg (2mmol) of p-aminophenol, then add 652mg (2mmol) of cesium carbonate to reflux 4h, and then use a high-pressure pump to carry out suction filtration to obtain a filtrate, which becomes our crude product. If a purer product is to be obtained, the filtrate can be purif...
Embodiment 2
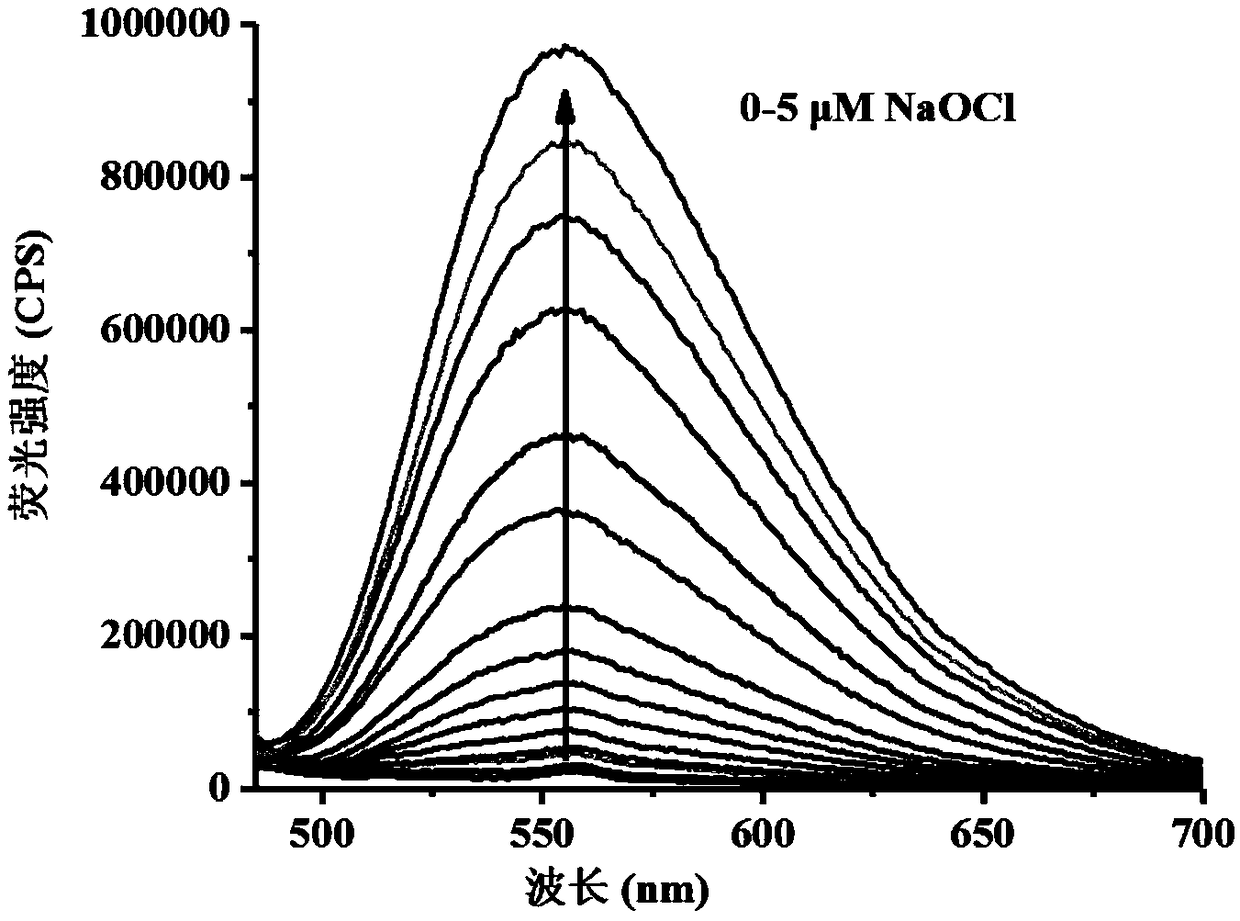
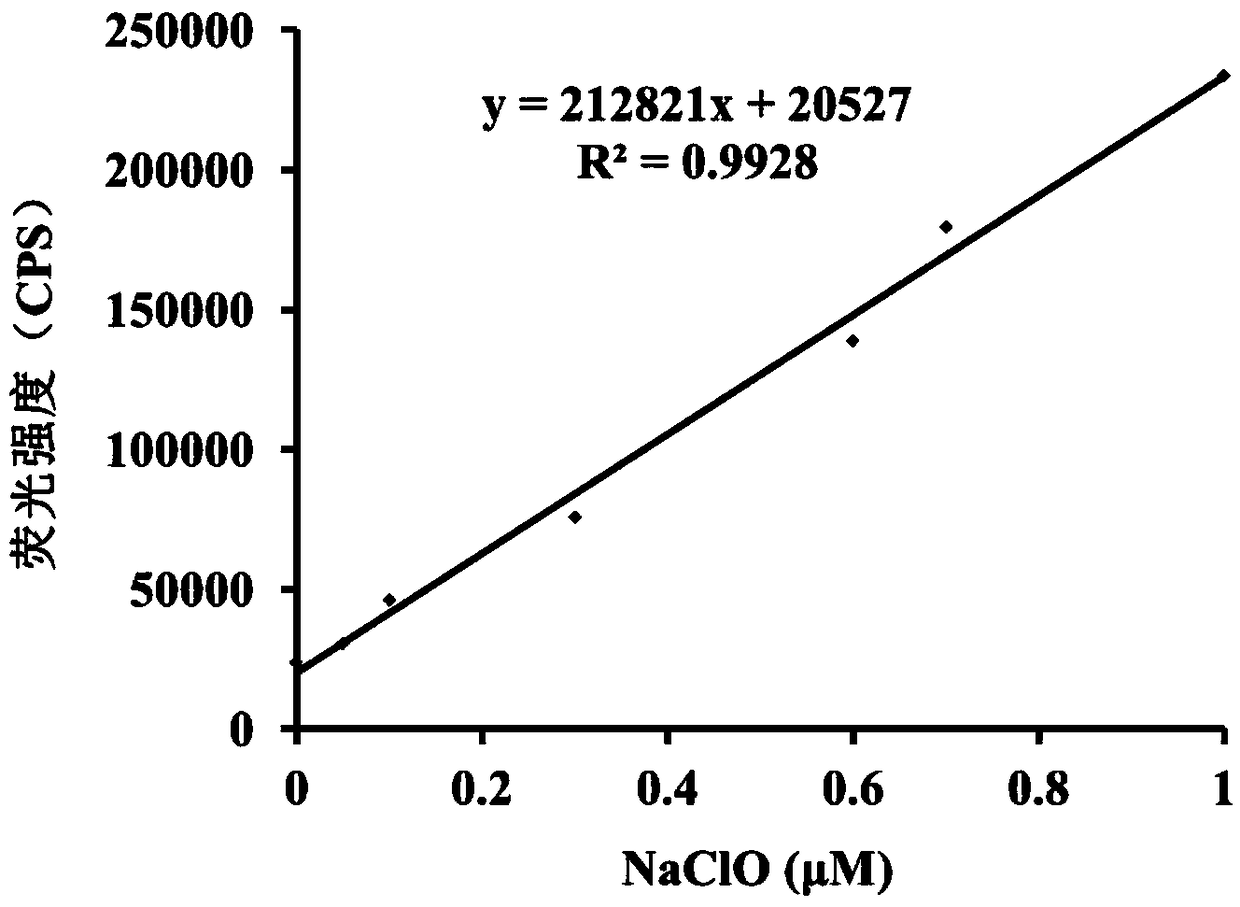
[0040] Figure 1a It is the change graph of the fluorescence spectrum of the hypochlorous acid fluorescent probe (5 μM) added to the hypochlorous acid (0-5 μM). Figure 1b It is a linear relationship graph of different concentrations of hypochlorous acid (0-1 μM) to probe (5 μM).
[0041] Configure multiple parallel samples with a probe concentration of 5 μM in a 10mL colorimetric tube, then add different concentrations of hypochlorous acid into the test system, shake it evenly and let it stand for 2 minutes. The above determinations were carried out in pure water (5mM PBS, pH 7.4), the probe used was the probe prepared in Example 1, and all spectral tests were measured at 25°C.
[0042] Fluorescence intensity changes were measured with a fluorescence spectrometer, from Figure 1a It can be clearly seen that with the increase of the concentration of hypochlorous acid added, the fluorescence intensity at 557 nm gradually increases. And, by inserting Figure 1b It can be seen ...
Embodiment 3
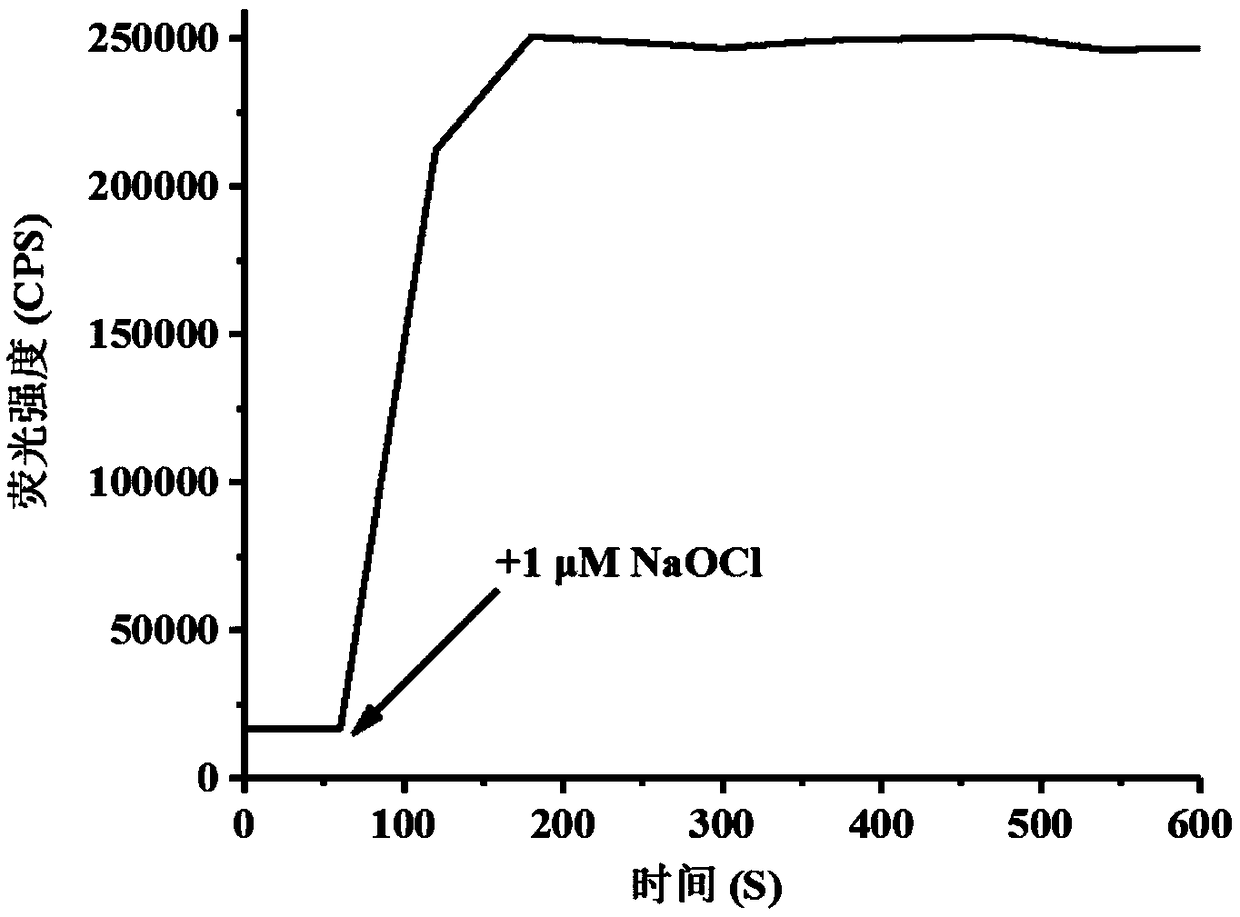
[0044] figure 2 is the response time of the probe (5 μM) after adding hypochlorous acid (5 μM). Take 50 μL from the probe mother solution and place it in a 10 mL test system, then add 5 μM hypochlorous acid into the test system, shake it evenly, and measure the change of its fluorescence intensity with a fluorescence spectrometer immediately. The above determinations were carried out in pure water (5mM PBS, pH 7.4), the probe used was the probe prepared in Example 1, and all spectral tests were measured at 25°C.
[0045] It can be clearly seen from the figure that after the addition of hypochlorous acid, the fluorescence intensity reaches the maximum value and remains unchanged after about 2 minutes of detection, which shows that the probe reacts rapidly with hypochlorous acid and can provide a rapid solution for the determination of hypochlorous acid. analysis method.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com