Method for improving corrosion resistance and coercive force of sintered neodymium-iron-boron magnet
A NdFeB, corrosion-resistant technology, applied in the manufacture of permanent magnets, inductors/transformers/magnets, coatings, etc., can solve the problem of reducing magnet remanence and energy product, poor corrosion resistance and temperature stability. And other problems, to achieve the effect of improving coercive force, shortening heat treatment time, and improving corrosion resistance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
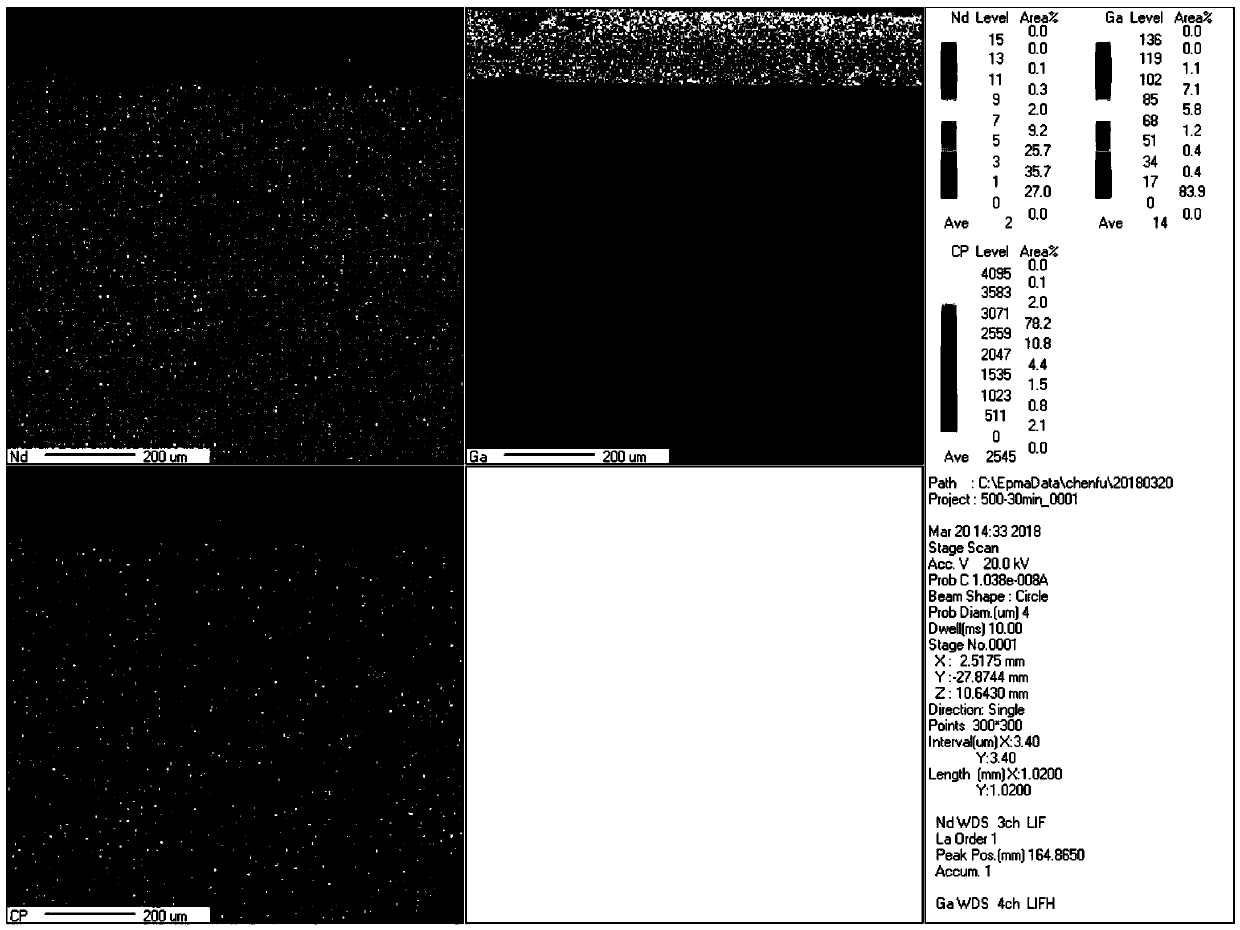
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0018] 1) Take a sintered NdFeB magnet with an external dimension of 10mm*10mm*4mm, denoted as A0, and perform surface polishing on it;
[0019] 2) Place an appropriate amount of the pretreated magnet and solid Ga in the crucible;
[0020] 3) Place the crucible in a vacuum heat treatment furnace, heat treatment at 500°C for 0.5h, and the vacuum degree is greater than 10 -2 Pa;
[0021] 4) After the heat treatment, take out the crucible, heat it to 30°C in the air, and then take out the magnet from the molten Ga, and record it as A1;
[0022] 5) Take the original magnet A0 and the magnet A1 that has been infiltrated with Ga, respectively, and polish them on six sides, and then put them in an autoclave at the same time, and perform corrosion at high temperature and high pressure (temperature 121 °C, 2 atmospheres) for 55 hours. , take out the magnet after the corrosion is over, and calculate the weight loss.
[0023] Table 1 Comparison of corrosion resistance between A1 and A...
Embodiment 2
[0029] 1) Take a sintered NdFeB magnet with an external dimension of 10mm*10mm*4mm, denoted as B0, and perform surface polishing on it;
[0030] 2) Place an appropriate amount of the pretreated magnet and solid Ga in the crucible;
[0031] 3) Place the crucible in a vacuum heat treatment furnace, heat treatment at 600°C for 0.5h, and the vacuum degree is greater than 10 -2 Pa;
[0032] 4) After the heat treatment, take out the crucible, heat it to 30°C in the air, and then take out the magnet from the molten Ga, denoted as B1;
[0033] 5) Take the original magnet B0 and the magnet B1 that has been infiltrated with Ga, respectively, and polish six sides of them, and then put them in an autoclave at the same time, and perform high-temperature and high-pressure corrosion (temperature is 121 ° C, 2 atmospheres) for 55 hours. , take out the magnet after the corrosion is over, and calculate the weight loss.
[0034] Table 3 Corrosion resistance comparison between B1 and B0
[00...
Embodiment 3
[0039] 1) Take a sintered NdFeB magnet with an external dimension of 10mm*10mm*4mm, denoted as C0, and perform surface polishing on it;
[0040] 2) Place an appropriate amount of the pretreated magnet and solid Ga in the crucible;
[0041] 3) Place the crucible in a vacuum heat treatment furnace, heat treatment at 400°C for 1 hour, and the vacuum degree is greater than 10 -2 Pa;
[0042] 4) Take out the crucible after the heat treatment, heat it to 30°C in the air, then take out the magnet from the molten Ga, and record it as C1;
[0043] 5) Take the original magnet C0 and the magnet C1 that has been infiltrated with Ga, respectively, and polish them on six sides, and then put them in an autoclave at the same time, and perform high-temperature and high-pressure corrosion (temperature is 121 ° C, 2 atmospheres) for 55 hours. , take out the magnet after the corrosion is over, and calculate the weight loss.
[0044] Table 5 Comparison of corrosion resistance between C1 and C0 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com