Nonwoven fabric separator for lead storage battery and lead storage battery using the same
A lead-acid battery and separator technology, applied in the field of non-woven separators, can solve the problem of not disclosing synthetic fiber structure and raw materials, etc., and achieve the effects of excellent ion permeability, excellent processing suitability, and long cycle life
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
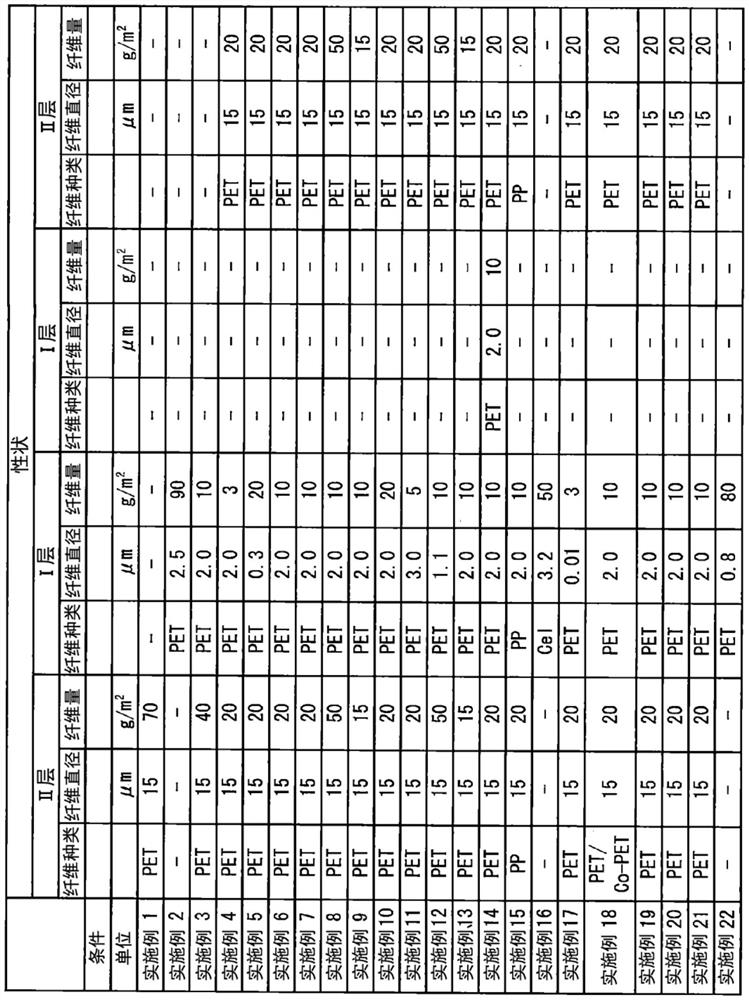
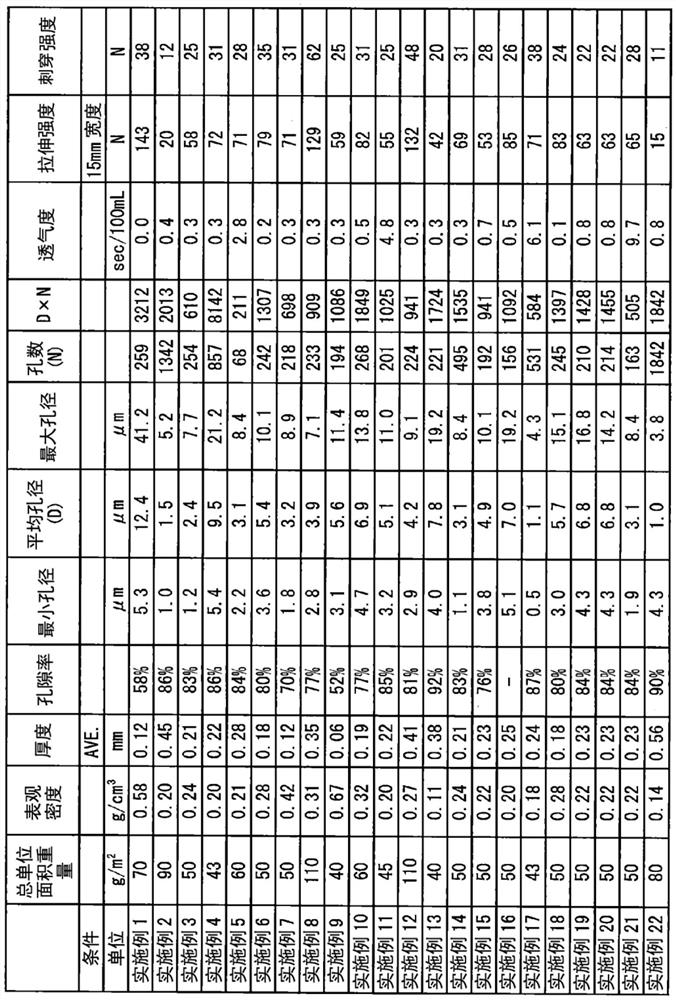
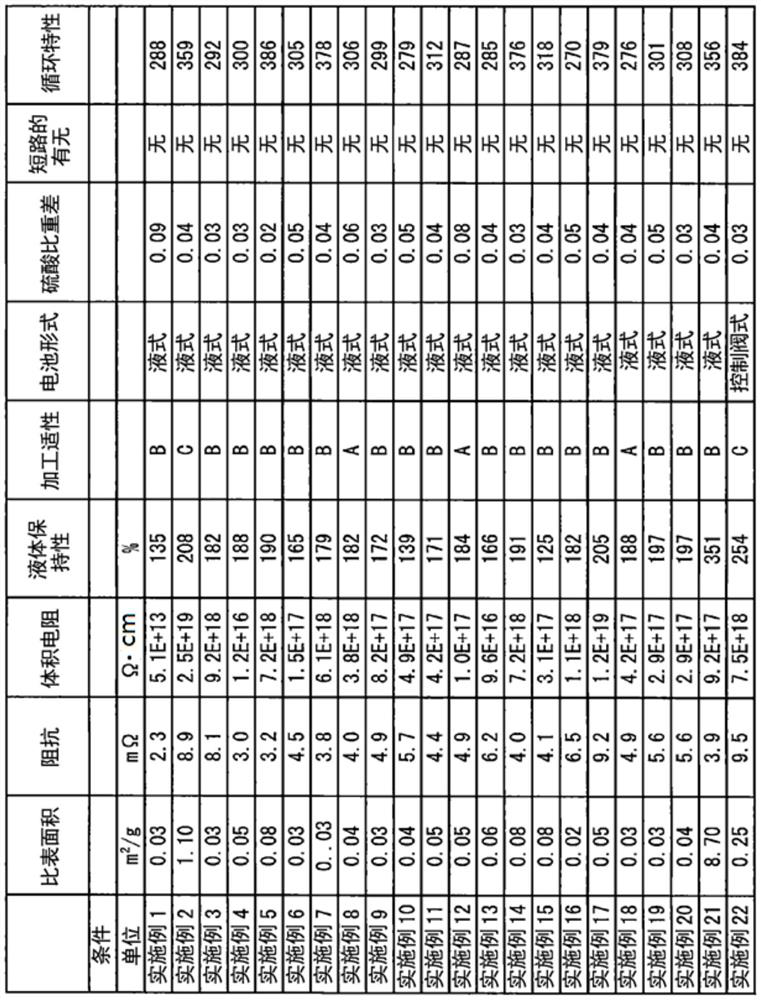
[0197] A nonwoven fabric layer (layer II) made of thermoplastic resin fibers is formed. Specifically, a solution (having a solution viscosity measured at a temperature of 35° C. using o-chlorophenol (OCP) as a solvent: ηsp / c = 0.67) using a general-purpose PET (as a thermoplastic resin) (the solution viscosity passed a temperature of 35 The viscosity tube in the constant temperature water tank of ℃ is measured. The following is the same), through the spunbonding method, at the spinning temperature of 300 ℃, the filament group is extruded towards the moving catch net surface, and spun at a spinning speed of 4500m / min . Next, by corona charging, the filament group is charged at about 3 μC / g to fully open the filament group, and a thermoplastic resin filament web is formed on the collecting net. The adjustment of the fiber diameter was performed by changing the drawing conditions to obtain a non-woven fabric separator.
Embodiment 2
[0199] As the superfine fiber non-woven fabric layer (layer I), a solution of PET (having a solution viscosity measured at a temperature of 35°C using OCP as a solvent: ηsp / c=0.50) was used at a spinning temperature of 300°C under heating Air 1000Nm 3 Under the condition of / hr / m, it is spun by melt blowing method and sprayed onto the above-mentioned thermoplastic resin long fiber web. At this time, the distance from the melt blowing nozzle to the thermoplastic resin long fiber web was set to 100 mm, the suction force in the collecting surface directly below the melt blowing nozzle was set to 0.2 kPa, and the wind speed was set to 7 m / sec. The fiber diameter and crystallinity were adjusted by adjusting the amount of heated air to obtain a nonwoven fabric separator including a nonwoven fabric layer (layer I) made of ultrafine fibers.
Embodiment 3
[0201] A PET-SM structure is formed by directly laminating the mesh sheet on the continuous long-fiber nonwoven fabric produced by the spunbond method by the same melt blown method as above. Furthermore, the nonwoven separator was obtained by adjusting the thickness and the apparent density to a desired thickness while integrating the calender rolls.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com