Application of tris(2,2'-bipyridyl)ruthenium(II) chloride hexahydrate as catalyst
A technology of hexahydrate and trichloride, applied in the direction of organic compound/hydride/coordination complex catalyst, physical/chemical process catalyst, catalytic reaction, etc. The effect of reaction cost, reduction of reaction energy consumption and raw material consumption, and broad application prospects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
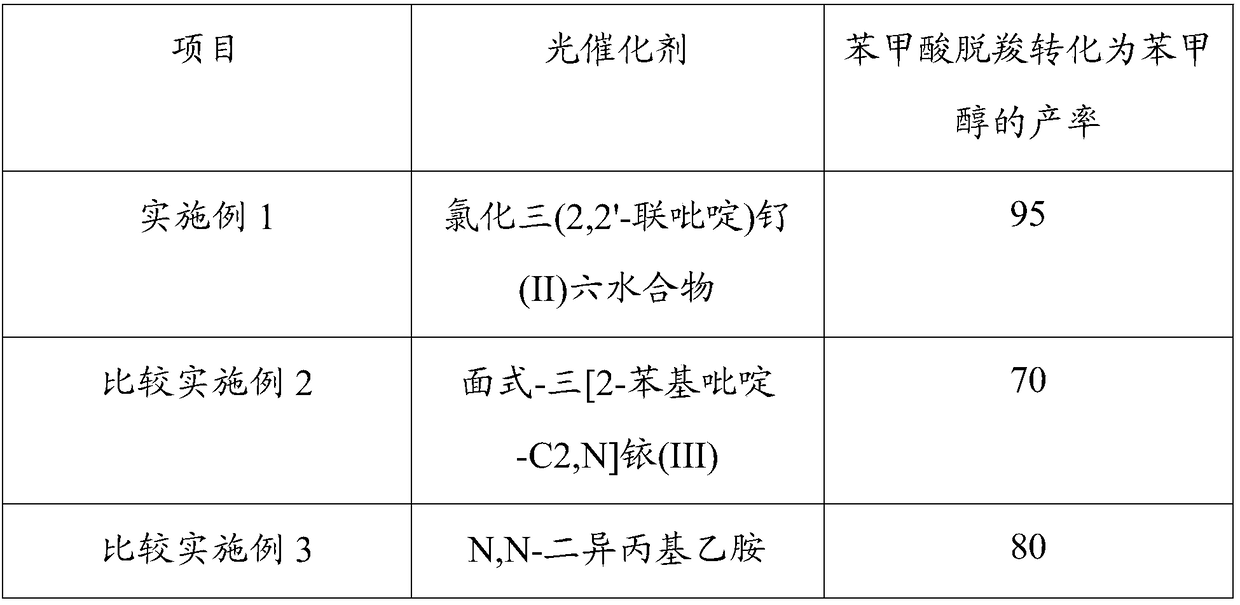
[0025] Example 1: Application of three (2,2'-bipyridyl) ruthenium (II) chloride hexahydrate as a catalyst in the preparation of benzyl alcohol from benzoic acid decarboxylation
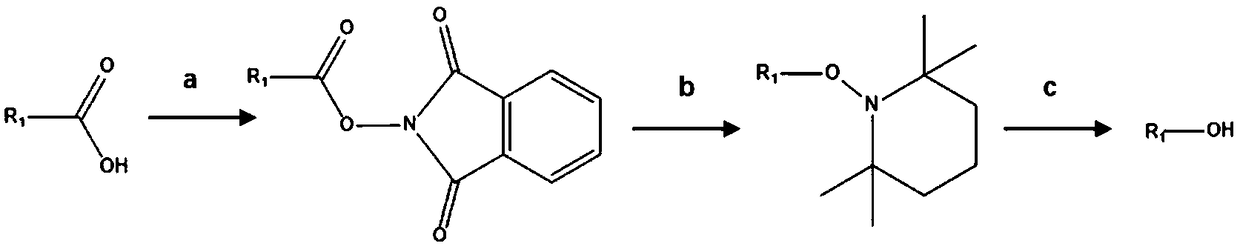
[0026] Step a, add benzoic acid to N-(hydroxyl)phthalimide, 4-dimethylaminopyridine, and dichloromethane in a three-necked flask and mix evenly, then add dicyclohexylcarbodiimide at 25°C After the reaction is completed, the reaction is carried out by washing and purifying to obtain phenyl N-(acyloxy)phthalimide.
[0027] Wherein the molar weight (mol) of benzoic acid in step a: the molar weight (mol) of N-(hydroxyl) phthalimide: the molar weight (mol) of 4-dimethylaminopyridine: the mole of dichloromethane Amount (mol): Molar amount (mol) of dicyclohexylcarbodiimide=1:1.1:0.1:0.1:0.1.
[0028] Step b, dissolving the phenyl N-(acyloxy)phthalimide obtained in step a in the solvent N,N-dimethylformamide in a three-necked flask, adding reducing agents 2, 2, 6 , 6-tetramethylpiperidine nitroxide radical ...
proportion Embodiment 4~7
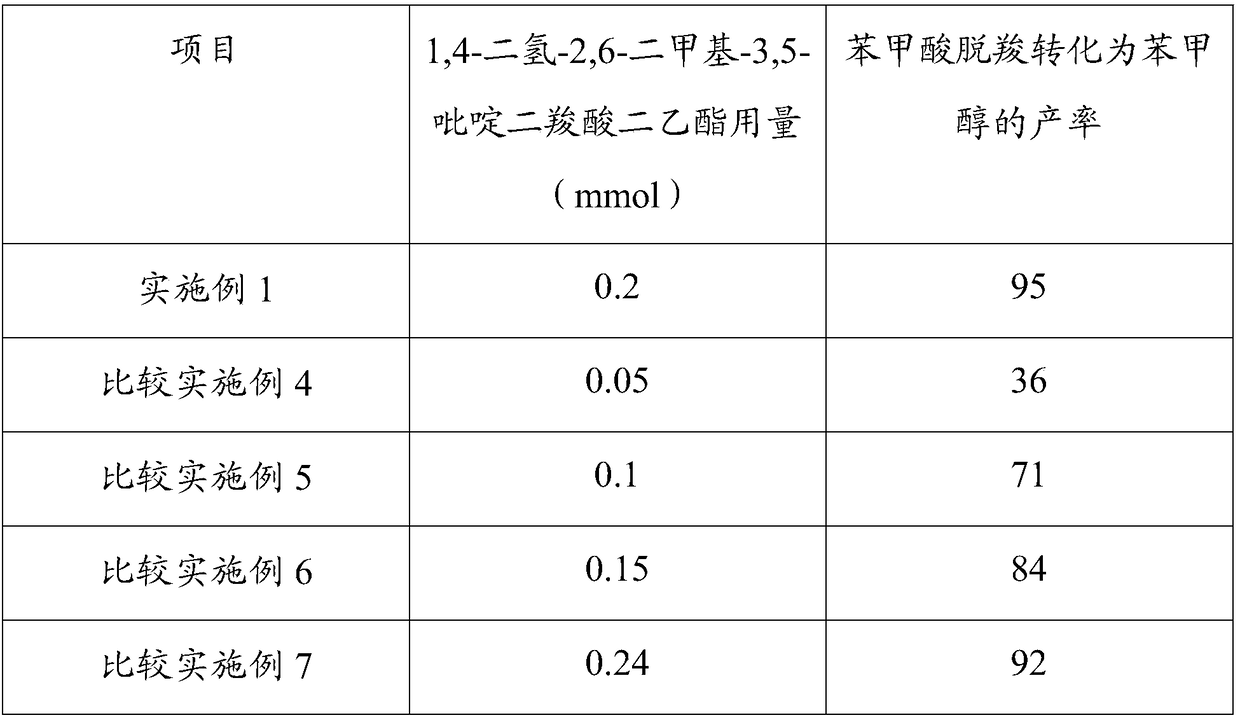
[0035]Ratio Examples 4-7: Application of tris(2,2'-bipyridyl)ruthenium(II) chloride hexahydrate as a catalyst in the preparation of benzyl alcohol by decarboxylation of benzoic acid
[0036] Step a and step c process reaction conditions of embodiment 4~7 are consistent with embodiment 1. In step b of Examples 4-7, when other reaction conditions are consistent with Example 1, by adjusting the reducing agent 1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-3,5-pyridinedicarboxylate The consumption of acid diethyl ester, the productive rate that benzoic acid decarboxylation is converted into benzyl alcohol is as follows:
[0037]
[0038] Under the same reaction conditions, when the amount of reducing agent 1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-3,5-pyridinedicarboxylate diethyl ester was 0.2 mmol, the decarboxylation of benzoic acid was converted into the product of benzyl alcohol The highest rate reached 95%.
Embodiment 8
[0039] Example 8 Application of tris(2,2'-bipyridyl)ruthenium(II) chloride hexahydrate as a catalyst in the decarboxylation of hexadecanoic acid to prepare pentadecyl alcohol
[0040] Step a, add hexadecanoic acid to N-(hydroxyl)phthalimide, 4-dimethylaminopyridine, dichloromethane and mix well in a three-necked flask, then add dicyclohexylcarbodiimide at 25°C The reaction is carried out under conditions, and after the reaction is completed, washing and purification are carried out to obtain pentadecyl N-(acyloxy)phthalimide.
[0041] Wherein the molar weight (mol) of hexadecanoic acid in step a: the molar weight (mol) of N-(hydroxyl) phthalimide: the molar weight (mol) of 4-dimethylaminopyridine: dichloromethane Molar weight (mol): molar weight (mol) of dicyclohexylcarbodiimide=1:1.1:0.1:0.1:0.1.
[0042] Step b, dissolve the pentadecyl N-(acyloxy)phthalimide obtained in step a in the solvent N,N-dimethylformamide in a three-necked flask, add reducing agent 2,2, 6,6-tetrame...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com