Medical hydrophilic fiber dressing
A fiber and cellulose fiber technology, which is applied in the field of medical hydrophilic fiber dressings, can solve the problems of low liquid absorption, low fiber tensile strength, and low product performance.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
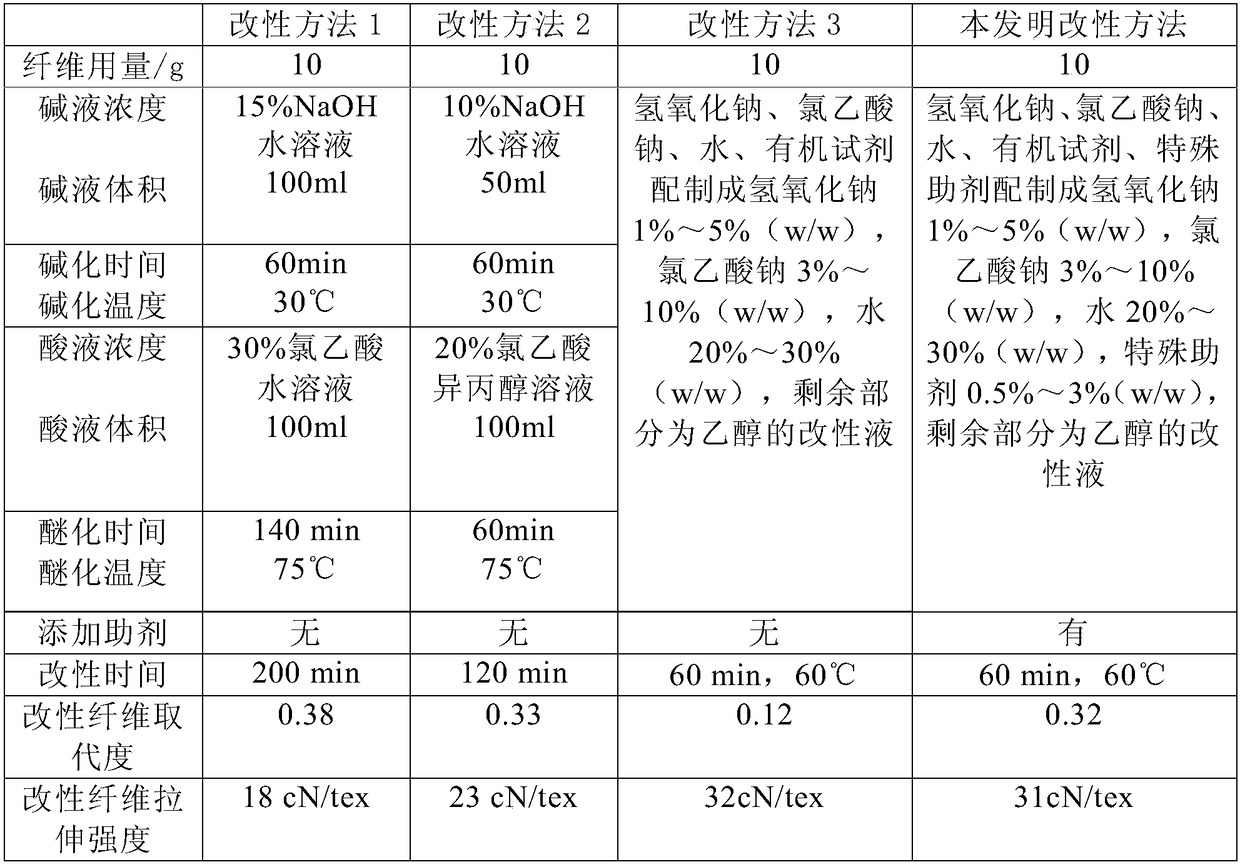
[0111] Embodiment 1 fiber modification (cellulose fiber selects lyocell fiber for use, and special auxiliary agent selects Tween 80 for use)
[0112] Modification method 1: Immerse 10g fiber in 100ml 15% NaOH aqueous solution, basify at 30°C for 60min, then add 100ml 30% chloroacetic acid aqueous solution, etherify at 75°C for 140min, then neutralize the modified fiber with acetic acid, 60% ethanol solution Wash 5 times, wash 2 times with 100% ethanol, and dry in a 40°C oven. The measured substitution degree of the modified fiber is 0.38, and the tensile strength is 18cN / tex.
[0113] Modification method 2: Cellulose fiber, soak 10g fiber in 50ml 10% NaOH aqueous solution, alkalinize at 30°C for 60min, then add 100ml 20% chloroacetic acid isopropanol solution. After etherification at 75°C for 60 minutes, the modified fiber was neutralized with acetic acid, washed five times with 60% ethanol solution, twice with 100% ethanol, and dried in an oven at 40°C. It is measured that ...
Embodiment 2
[0118] Example 2 Fiber moisture content and auxiliary agent content detection
[0119] After the fiber modified by the method of the present invention is subjected to drying and humidity-conditioning treatment, the moisture content test is carried out according to the measurement method of weight loss on drying in the third part of the "People's Republic of China 2015 edition", and the first part of the test method of "yy 0472.1-2004 medical nonwoven compress" - Test the content of additives in fibers by the method in "Nonwoven Fabrics for Compression Production". The test results are shown in Table 2.
[0120] Table 2
[0121]
[0122]
Embodiment 3
[0123] Embodiment 3 prepares dressing
[0124] The fiber modified by modification method 1 in Example 1 was prepared by non-woven process to obtain finished dressing C1. The dry strength of dressing C1 was measured to be 1.2 N / cm, and the wet strength was too low to be measured. After the fiber modified by method 2 was prepared into finished dressing C2 by non-woven process, the dry strength of dressing C2 was measured to be 1.8 N / cm, and the wet strength was too low to be measured. After the fiber modified by method 3 was prepared into finished dressing C3 by non-woven process, the dry strength of dressing C3 was measured to be 1.9 N / cm, and the wet strength was too low to be measured.
[0125] The test data of this example shows that the dry strength of the finished dressing 1 modified by the method of the present invention is 10.7N / cm, and the wet strength is 0.5N / cm, which proves that the method of the present invention can effectively reduce fiber proofing damage after ad...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Liquid absorption | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com