New method for KRAS gene mutation detection
A new method, a technology for connecting probes, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, DNA/RNA fragments, recombinant DNA technology, etc., can solve the problems of poor specificity, low sensitivity, and high cost of mutation detection, achieving low cost and high sensitivity , Simple and convenient operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0018] Construction of fluorescent biosensors and detection of KRAS mutations
[0019] 1. Materials and methods
[0020] 1.1 Materials
[0021] Taq DNA ligase and Bst DNA polymerase were purchased from NEB (Beijing) Co., Ltd. deoxynucleotide solution mixture (dNTPs) was purchased from Bao Biological Engineering (Dalian) Co., Ltd. Nuclease-free Water was purchased from Thermo Fisher Scientific (China) Co., Ltd. Paraffin-embedded tissue DNA rapid extraction kit was purchased from Tiangen Biochemical Technology (Beijing) Co., Ltd. The DNA strands purified by HPLC were synthesized and modified by Sangon Bioengineering (Shanghai) Co., Ltd. The clinical specimens used in the experiment came from the First Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University.
[0022] 1.2 Testing instruments
[0023] The ligation reaction was completed using a BIO-RAD PCR instrument, and the real-time fluorescence intensity was monitored by an Applied Biosystems real-time fluorescent quantitativ...
Embodiment 2
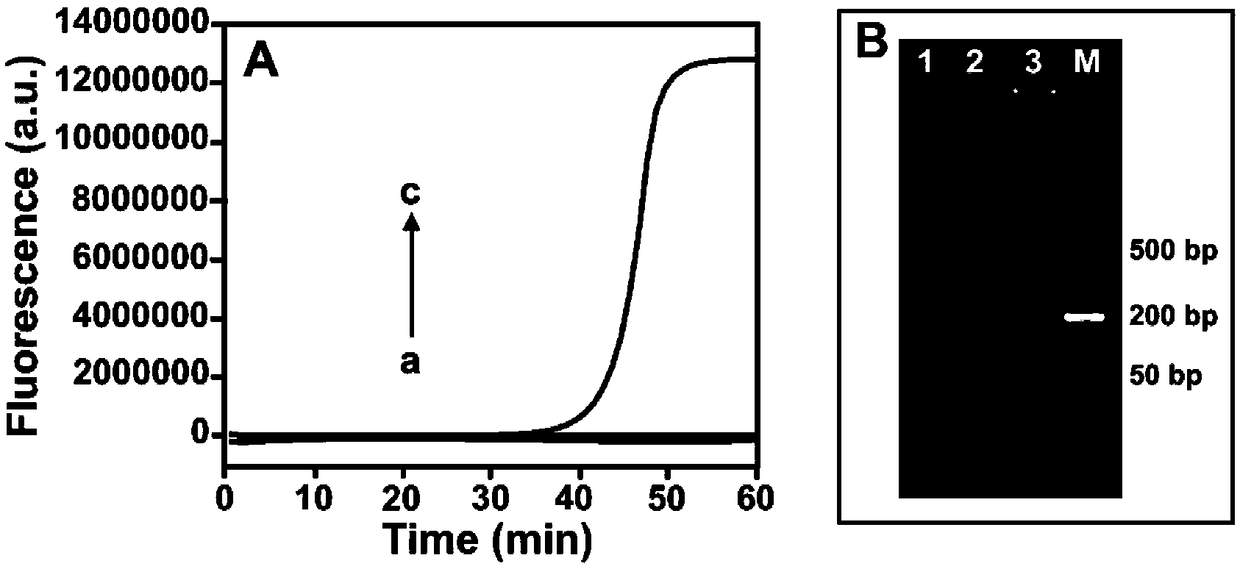
[0040] Validation of the feasibility of a ligation-based loop-mediated isothermal amplification method for detecting KRAS mutations
[0041] 1. Verification of the generation of dumbbell-shaped templates in ligation reactions
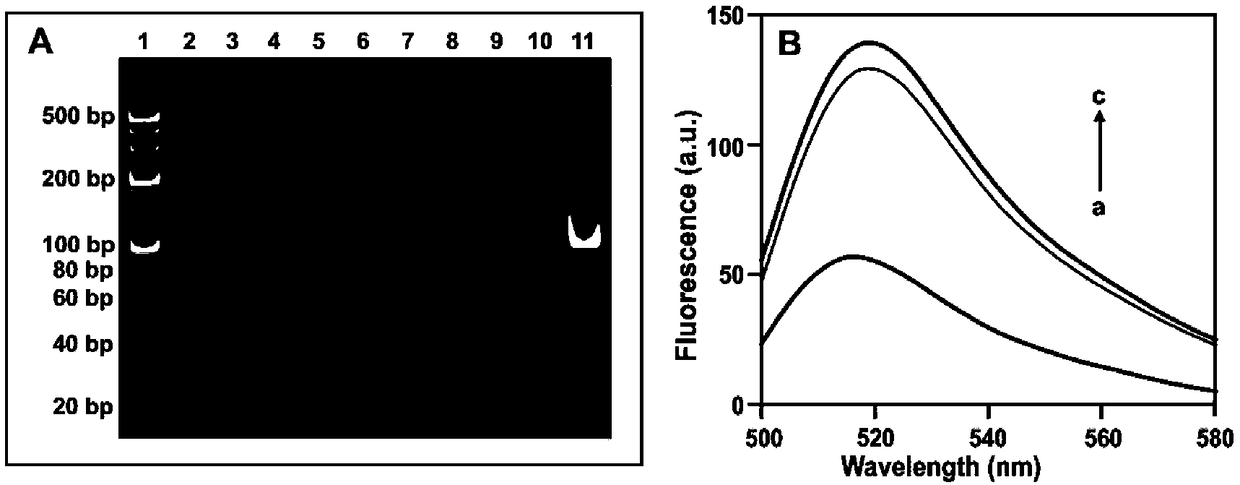
[0042] The connection product obtained in Example 1 is analyzed and verified by PAGE electrophoresis and fluorescence method, such as figure 1 The electrophoresis band in A shows that the ligation can only be performed under the conditions of the simultaneous presence of SLS1 (ligation probe 1), SLS2 (ligation probe 2), target sequence (MutDNA) and Taq ligase, resulting in a nucleic acid chain of about 110bp bring. figure 1 It can also be seen in B that the connection probe can be connected only in the presence of MutDNA, and the fluorescent groups and quenching groups respectively marked on the two connection probes are quenched due to the closer distance. Produces a lower fluorescent signal.
[0043] Such as figure 1 A: Band 1 is the DNA Marker of 5...
Embodiment 3
[0047] Fluorescence Biosensor and Optimization of Its Application Conditions
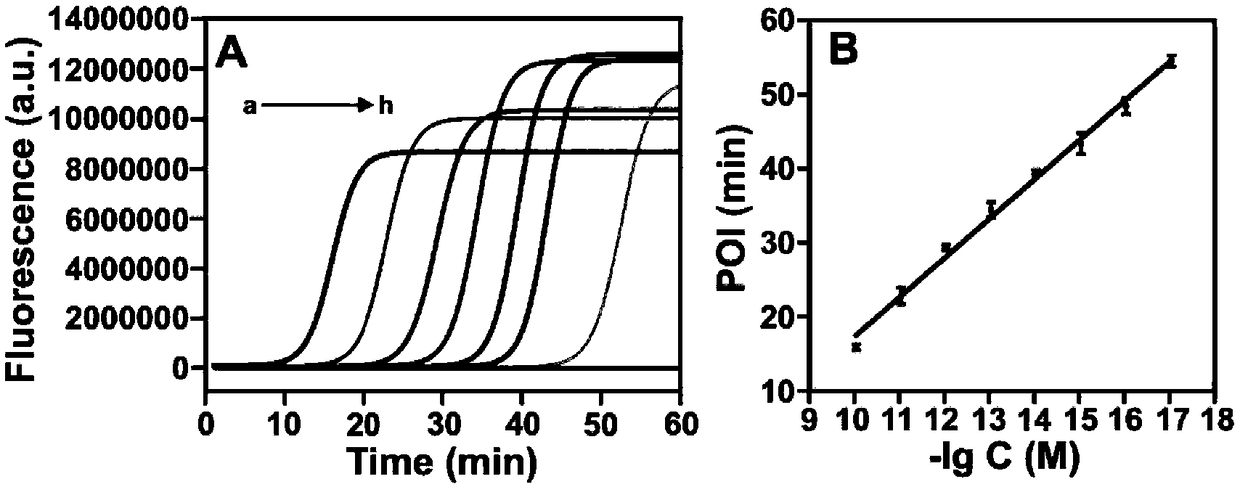
[0048] We also optimized the important conditions in the experimental process, namely, the mismatched base sites, the temperature of the ligation reaction, the number of cycles of the ligation reaction, the amount of Bst enzyme, and the temperature of the loop-mediated isothermal amplification. An optimized condition selected blank, WtDNA and different concentrations of MutDNA for a series of experiments.
[0049] 1. In order to investigate the influence of the mismatching sites in the junction probe SLS2 on the results of the fluorescent sensor with KRAS mutation, different mismatching sites were used in this experiment to construct the fluorescent sensor. The ratio of MutDNA to WtDNA POI (time corresponding to the point with the largest slope of the real-time fluorescence curve, the lower the POI value, the higher the amplification efficiency.) varies with different mismatched sites. When the mism...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com