Method for improving hydrogen resistance of iron-nickel-based alloy by increasing special grain boundary ratio
An iron-nickel-based alloy and special grain boundary technology, which is applied in the field of iron-nickel-based alloys, can solve problems such as cracking and hydrogen resistance degradation, achieve optimal room temperature mechanical properties, increase initiation and expansion resistance, and improve hydrogen damage resistance. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] In this embodiment, the J75 alloy plate with a thickness of 3.0mm is subjected to thermomechanical treatment, and the proportion of special grain boundaries reaches 75%, which improves the hydrogen damage resistance of the alloy. The specific implementation process is:
[0034] 1. The J75 alloy sheet is a hot-rolled sheet, and the chemical composition of the hot-rolled sheet meets the requirements of GJB 5724-2006 "Specification for Hydrogen-Resistant Steel Bars". The J75 alloy plate is placed in a heat treatment furnace, kept at 970-990°C (980°C in this embodiment) for 0.5-2h (1h in this embodiment), and taken out for water quenching;
[0035] 2. Using a four-roll cold rolling mill, the J75 alloy plate after solution treatment in step 1 is subjected to 4-6% (4.3% in this embodiment) cold rolling deformation.
[0036] 3. The J75 alloy plate after the cold rolling and deformation in step 2 is subjected to heat preservation treatment. The method is to keep warm for 20 to...
Embodiment 2
[0049] The difference from Example 1 is that the thickness of the J75 alloy plate used is 3.8mm, the pre-deformation is 6%, and the holding time is 1000°C and 40min, the proportion of special grain boundaries in the alloy is 72.4%.
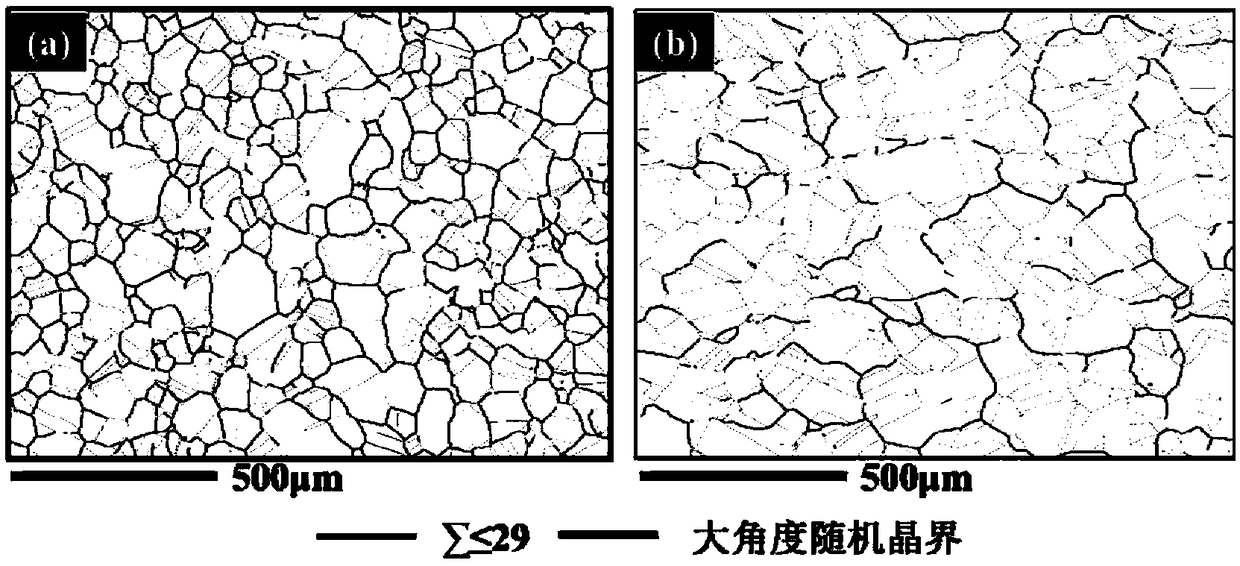
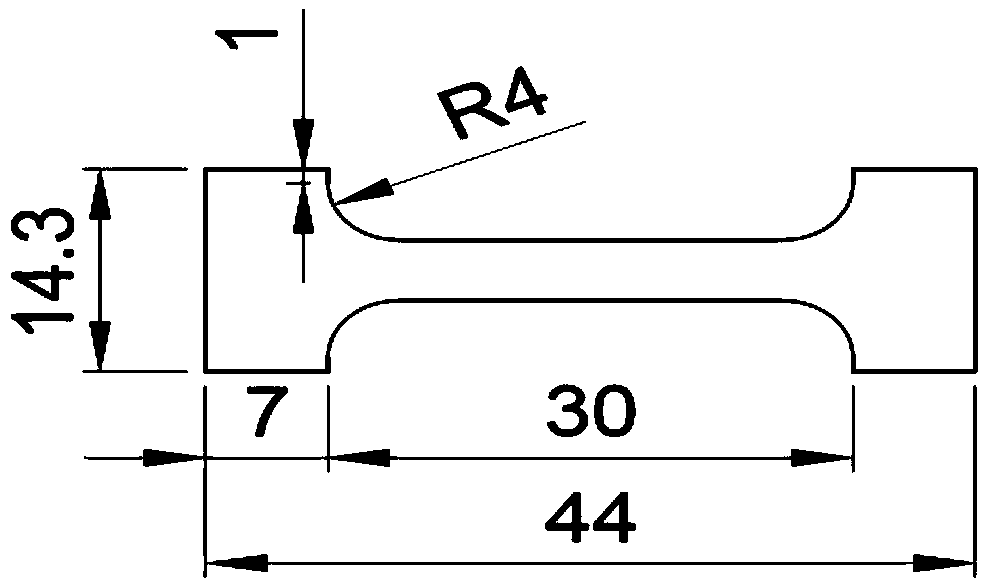
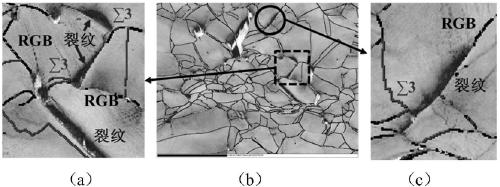
[0050] A 3.8 mm thick J75 alloy hot-rolled plate with the same chemical composition as in Example 1 was used for thermomechanical treatment. Heat preservation at 980°C for 1 hour, followed by water quenching; after 6% cold rolling deformation, heat preservation treatment at 1000°C for 40 minutes, and then water cooling to room temperature. The samples after thermomechanical treatment were kept at 720°C for 16h, and then air-cooled to room temperature. EBSD was used to analyze the grain boundary structure, and the results showed that the proportion of special grain boundaries in the alloy reached 72.4%, and the connectivity of large-angle random grain boundaries was interrupted. The J75 alloy plate according to figure 2 Process the tensile speci...
Embodiment 3
[0058] The difference from Example 1 is that the selected J75 alloy sheet has a thickness of 4mm, 5% pre-deformation, and heat preservation treatment at 1000°C for 25 minutes, and the proportion of special grain boundaries is 77.4%.
[0059] A 4 mm thick J75 alloy hot-rolled plate with the same chemical composition as in Example 1 was used for thermomechanical treatment. Insulate at 980°C for 2 hours, then water quenching; after 5% cold rolling deformation, perform heat preservation at 1000°C for 25min, then take out the water and cool to room temperature. The samples after thermomechanical treatment were kept at 720°C for 16h, and then air-cooled to room temperature. EBSD was used to analyze the grain boundary structure, and the results showed that the proportion of special grain boundaries in the alloy reached 77.4%, and the connectivity of large-angle random grain boundaries was interrupted. The J75 alloy plate according to figure 2 Process the tensile specimens, and per...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| yield strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| yield strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com