Method for extracting vanadium from waste vanadium catalyst
A waste vanadium catalyst and extraction method technology, which is applied in the field of vanadium extraction, can solve the problems of low adsorption and resolution rate, complex vanadium extraction production process, and low product purity, so as to improve the adsorption effect, facilitate vanadium precipitation operations, and simplify the process flow Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
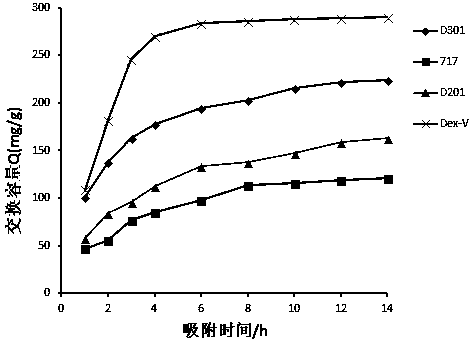
[0034] Embodiment 1: Dex-V resin carries out static adsorption of vanadium
[0035] (1) Grind the particle size of the spent vanadium catalyst to 300-370 μm, add water according to the ratio of solid-liquid mass ratio of 1:2.5, soak in water at 100°C for 1.5 hours, and filter to obtain the water-leaching filtrate and water-leaching filter residue , washing the water immersion filter residue with clear water until neutral to obtain the water leaching residue, combining the water immersion filtrate and the washing liquid to obtain the water immersion liquid, collecting the water leaching residue and the water immersion liquid respectively for subsequent use;
[0036] (2) Add H with a mass percentage concentration of 11% to the water leaching residue obtained in the upward step at a liquid-solid ratio of 2.5ml: 1g 2 SO 4 , carrying out reducing acid leaching under the condition that sodium sulfite is the reducing agent, filtering to obtain the reducing acid leaching solution and...
Embodiment 2
[0044] Embodiment 2: Dex-V resin carries out vanadium static adsorption
[0045] The difference from Example 1 is:
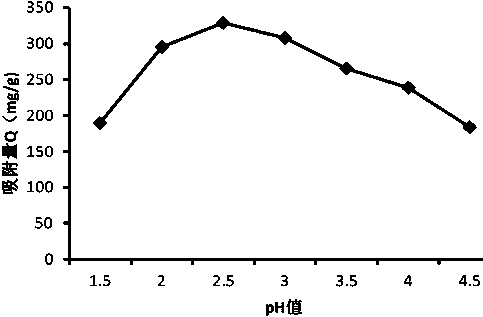
[0046] Grinding the waste vanadium catalyst, immersing in water, reducing acid leaching and oxidation to obtain raw material liquid; adjusting its pH value to 2.0, 2.5, 3.0;
[0047] Soak and wash the Dex-V anion exchange resin with deionized water until there is no brown and foam, then soak the Dex-V anion exchange resin with 5% NaOH solution for 12 hours, filter, and wash with deionized water until the effluent is neutral; then Soak the Dex-V anion-exchange resin with 5% HCl solution for 12h and filter it, wash it with deionized water until the effluent is neutral, and finally soak it with a saturated sodium chloride solution to obtain the pretreated Dex-V anion-exchange resin, spare.
[0048] Mix 150ml of raw material solution with 1g of pretreated Dex-V anion exchange resin, and magnetically stir at room temperature for 5h to perform adsorption.
[0049] ...
Embodiment 3
[0052] Embodiment 3: Dex-V resin carries out static adsorption of vanadium
[0053] The difference from Example 1 is:
[0054] Grinding the spent vanadium catalyst, immersing in water, reducing acid leaching and oxidation to obtain a raw material liquid, wherein the content of vanadium is 5.1g / L; adjust its pH value to 2.5;
[0055] Soak and wash the Dex-V anion exchange resin with deionized water until there is no brown and foam, then soak the Dex-V anion exchange resin with 5% NaOH solution for 12 hours, filter, and wash with deionized water until the effluent is neutral; then Dex-V anion exchange resin was soaked in 5% HCl solution for 12 hours, filtered, washed with deionized water until the effluent was neutral, and finally soaked in saturated sodium chloride solution to obtain pretreated Dex-V anion exchange resin.
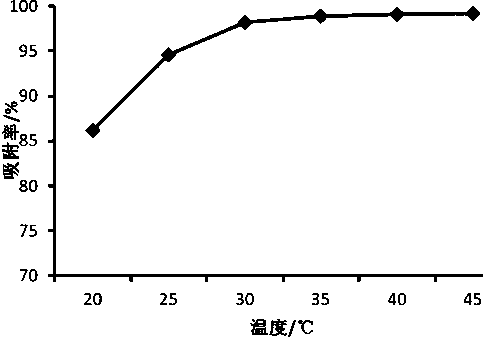
[0056] 150ml of the raw material solution was mixed with 1.0g of the pretreated Dex-V resin, and magnetically stirred at 30°C and 35°C for 5h for adsorptio...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com