Method and equipment for detecting cytoplasmic inheritance
A cytoplasmic and sample technology, applied in the field of cytoplasmic genetic detection, can solve problems such as misjudgment and achieve the effect of flexible sampling
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0062] Arabidopsis thaliana mitochondrial DNA genetic mode detection, including the following steps:
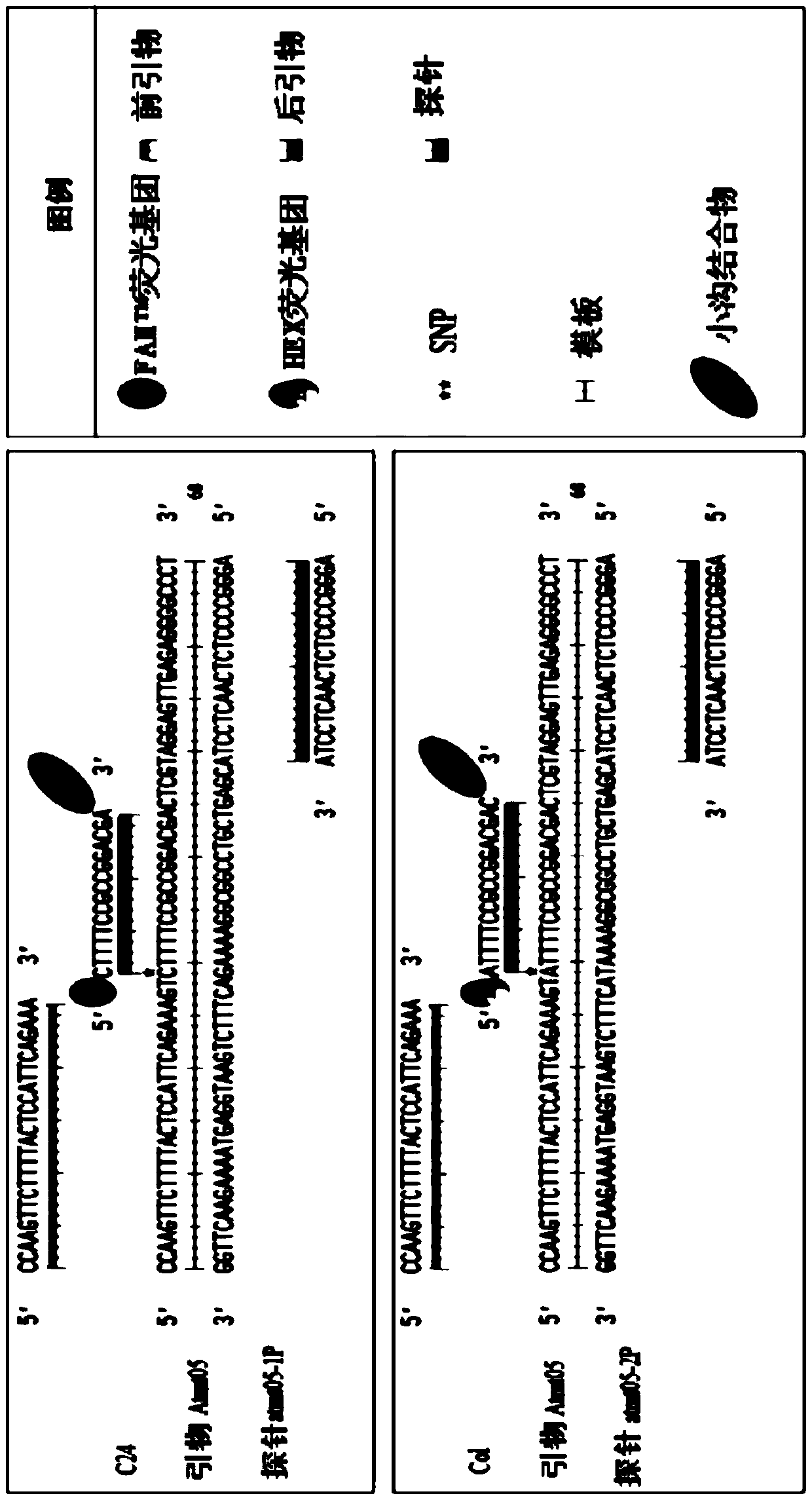
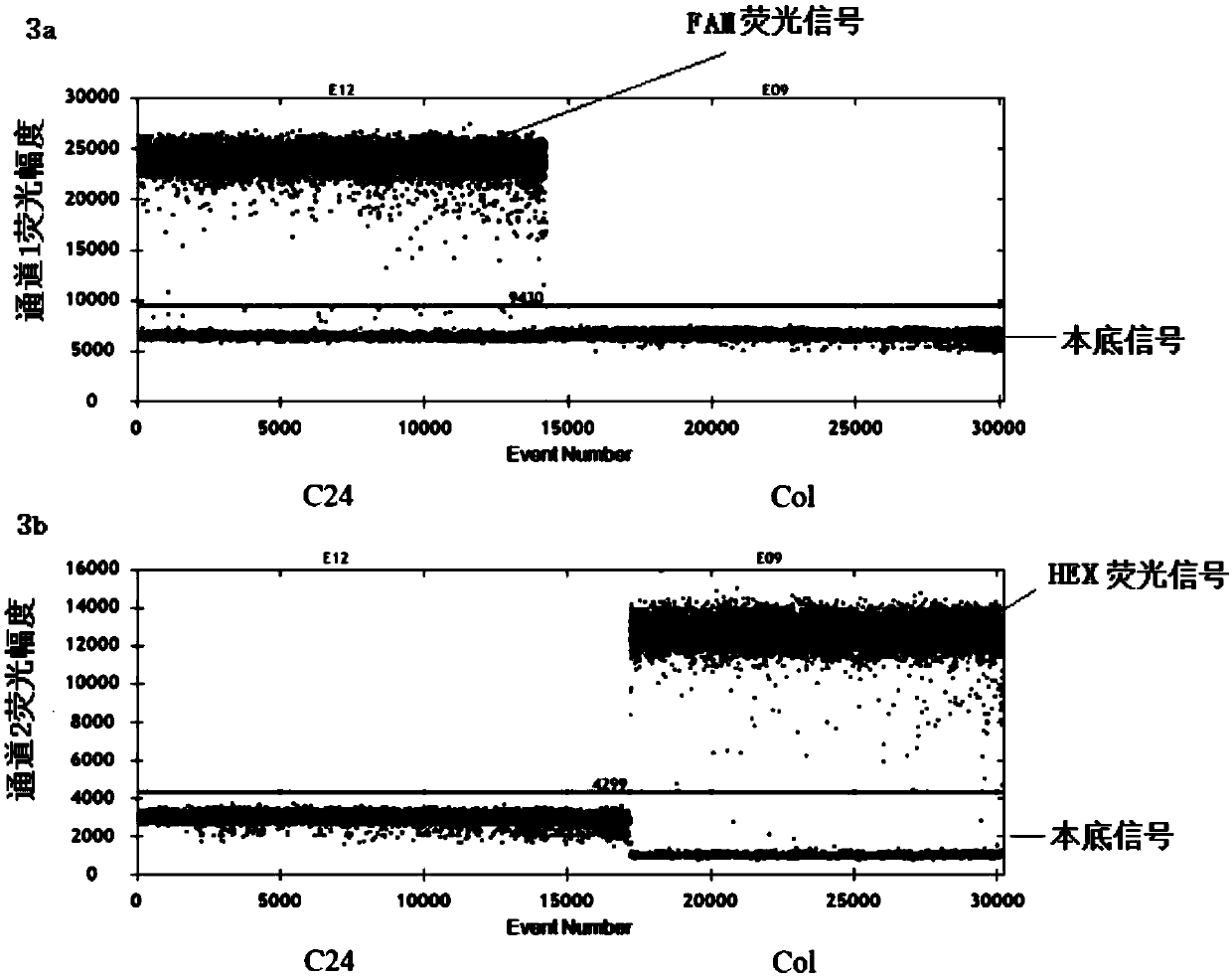
[0063] (1) According to literature reports (Matsushima et al., 2011), Arabidopsis ecotypes C24 and Col have a SNP site in the genome sequence of the mitochondrial gene matR. Therefore, for this SNP site, use Primer Express3.1 software, based on TaqMan MGB Allelic Discrimination mode, design primers and probes for paternal and maternal materials.
[0064] Wherein, the obtained mitochondrial genome sequences of C24 and Col are respectively shown as SEQ ID NO: 1 and SEQ ID NO: 2, and there is a SNP (SNP.C29A) at 29 bp compared with the two.
[0065] The front and back primer sequences of the two parents designed for this sequence are consistent, as shown in SEQ ID NO: 3 and SEQ ID NO: 4, the sizes are 26 and 20 bp respectively, and the size of the amplified fragment is 68 bp.
[0066] The specific probe sequence designed for C24 is shown in SEQ ID NO:5, the first one at the 5' ...
Embodiment 2
[0076] The detection of the mode of inheritance of cucumber mitochondrial DNA comprises the following steps:
[0077] (1) Comparatively analyze the mitochondrial genome polymorphisms of the parent materials '9930' and 'B', find suitable polymorphic sites, and then design synthetic primers and probes for the polymorphic sites, and the probes span the polymorphisms sites and labeled with FAM and HEX fluorophores, respectively. Among them, the parental materials 9930 and B are inbred line materials kept in the laboratory, and their mitochondrial genome sequences were respectively obtained by next-generation sequencing, and compared with the published reference mitochondrial genome of cucumber 'Calypso' by software Bowtie 2, bam files were generated , and load the bam file into IGV 2.4.5, and compare the sequencing results to find effective polymorphic sites. Then, using Primer Express 3.1 software, based on the TaqManAllelic Discrimination model, primers and probes for the pater...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com