Carbon-fixing rhodococcus and application thereof
A rhodococcus and carbon source technology, applied in the field of rhodococcus, can solve the problems of unknown microbial functions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] Example 1 Isolation and identification of bacterial strain 201806YC01
[0024] Taking the soil at the southwestern edge of the Mu Us Sandy Land in Inner Mongolia as the target soil, the specific screening scheme is as follows:
[0025] 1. Collect the soil at a depth of 0-20cm, take 1.0g of the collected soil, add it to 9mL sterilized water, and shake it for 10min to make a soil solution. Then, take another 1 mL of soil suspension and put it in 9 mL of sterilized water to dilute the soil solution. Repeat this operation. According to previous research experience, the soil solution was diluted to 10 -3 times. Take 100 μL of the soil dilution, inoculate it into inorganic salt MSM medium, and culture it at 25°C for 7 days. The composition of MSM medium is: Na 2 HPO 4 2H 2 O, 7.8g / L; KH 2 PO 4 , 6.8g / L; Na 2 S·9H 2 O, 0.187g / L; MgSO 4 , 0.2g / L; Ca(NO 3 ) 2 4H 2 O, 0.05g / L; NH 4 NO 3 , 0.085g / L; FeSO 4 ·7H 2 O, 0.4g / L; trace element solution, 1mL / L; NaHCO 3...
Embodiment 2
[0028] Example 2 The process of producing carbonate by bacterial strain 201806YC01
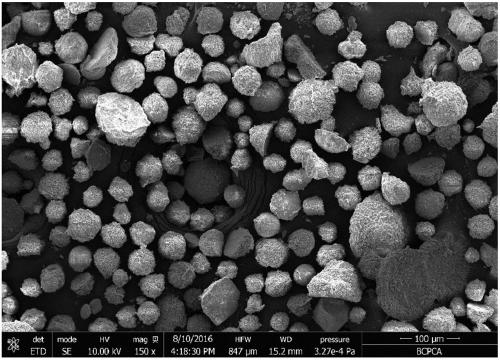
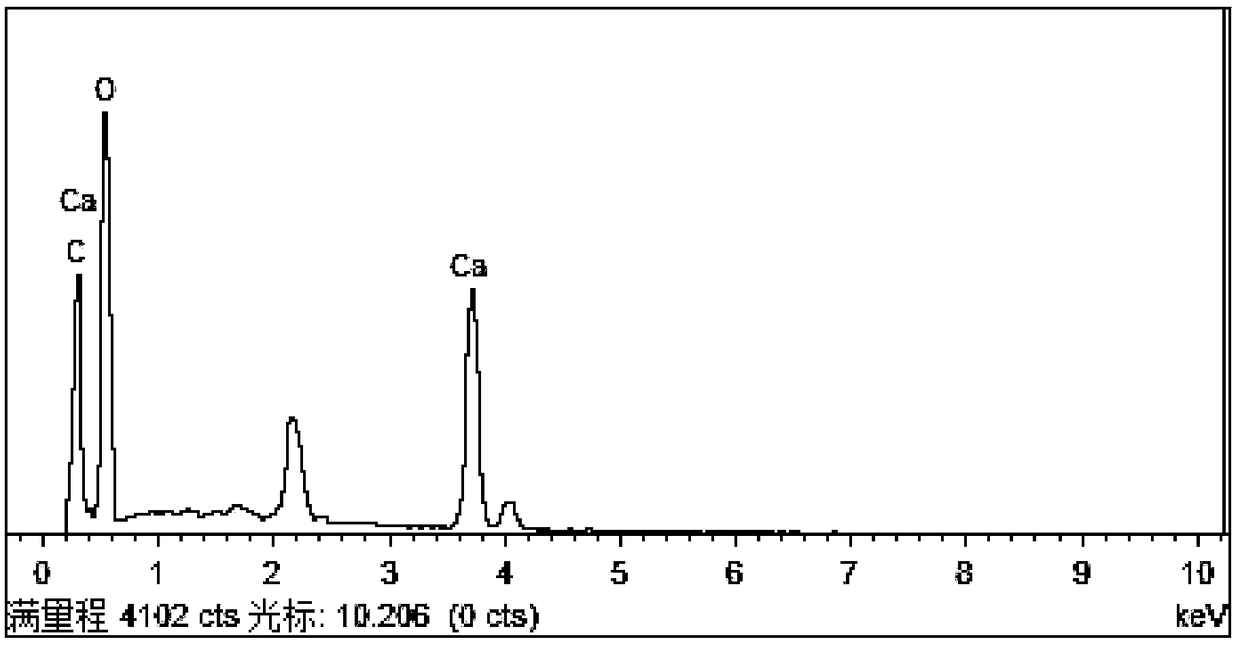
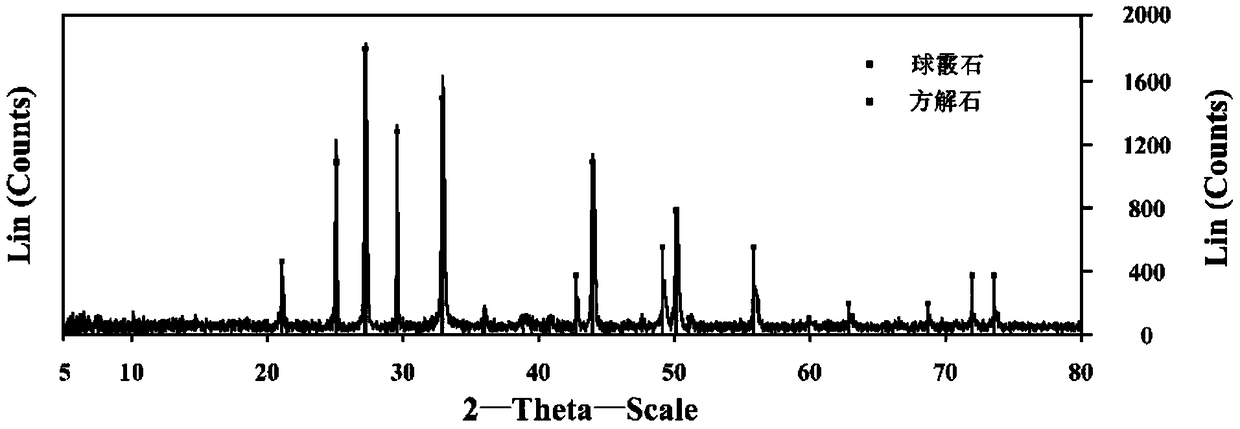
[0029] The process of producing carbon-containing minerals by Rhodococcus sp.201806YC01 strain was tested by using organic carbon source medium. Firstly, 100 mL of liquid medium was prepared and placed in a 250 mL Erlenmeyer flask, and sterilized by moist heat method, that is, sterilized at 121° C. for 15 minutes. The composition of the liquid medium is: yeast extract 5g / L, peptone 10g / L, sodium chloride 5g / L, calcium chloride 2g / L. Then, the bacterial strain was inoculated into a liquid culture medium with an inoculation needle, placed at 25° C., and cultivated under the condition of avoiding light. It was observed every 3 days whether there was precipitation, and the fifth observation found that there was precipitation. In order to obtain sufficient precipitation for subsequent analysis, the process was co-cultivated for 30 days. After the cultivation, the generated precipitates were colle...
Embodiment 3
[0033] Example 3 Verification experiment of bacterial strain 201806YC01 precipitating atmospheric carbon dioxide
[0034] The operation method of Example 2 was adopted to prepare culture medium and inoculate bacterial strains. A total of 6 culture flasks were set up for the experiment, and 3 were placed in 13 CO 2 cultured in the environment to label atmospheric CO 2 the whereabouts of; three put in nothing 13 CO 2 cultured in a labeled environment as a control. After the cultivation, the precipitate was treated with hydrogen peroxide solution, the organic matter was oxidized and removed, and then the inorganic precipitate was measured. 13 C abundance value.
[0035] The result is as Figure 4 shown in 13 CO 2 carbonaceous minerals 13The C abundance value was 953.00‰, which was significantly higher than -11.52‰ in the control group, indicating that part of the C in the carbon-bearing minerals in the marked group was derived from atmospheric CO 2 . showed that the s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com