A kind of nickel-titanium alloy stent surface treatment method
A nickel-titanium alloy and surface treatment technology, applied in the field of surface engineering technology and biomaterials, can solve problems such as safety doubts, prone to corrosion, and achieve the effect of enhancing adhesion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0018] A method for treating the surface of a nickel-titanium alloy stent is characterized in that it comprises the steps of:
[0019] (1) The nickel-titanium alloy bracket is first polished with water-grinding paper to remove the initial roughness of the surface, then cleaned in acetone and deionized water, and dried to obtain a bright surface;
[0020] (2) Use anodic oxidation technology to remove nickel in nickel-titanium alloy;
[0021] (3) Using the magnetron sputtering method, using the auxiliary effect of the electro-acoustic transducer, magnetron sputtering titanium nitride film layer on the surface of the nickel-titanium alloy support.
Embodiment 2
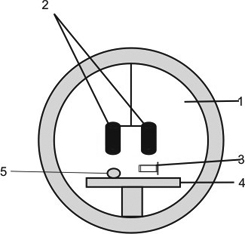
[0023] The working state of the composite magnetron sputtering deposition table: the mother deposition table 4 is fixed below the interior of the vacuum chamber 1, and the position is directly below the magnetron sputtering device 2, and the sub-deposition table 5 is connected to the top of the mother deposition table 4 through a motor device , and the table top of the sub-deposition table 5 can rotate horizontally, the metal wire is fixed on the bracket and placed on the surface of the sub-deposition table 5, and the sub-deposition table 5 rotates in the horizontal direction under the control of the motor, so that the sputtered metal is evenly deposited on the surface of the wire .
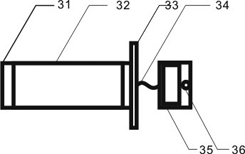
[0024] The electro-acoustic transducing device 3 is fixed on the parent deposition platform 4 and is level with the surface of the sub-deposition platform 5 . The electro-acoustic transducing device 3 is fixed on the mother deposition table 4 through the connecting piece 33, the acoustic waveguid...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com