Patents
Literature
832results about How to "Uniform discharge" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
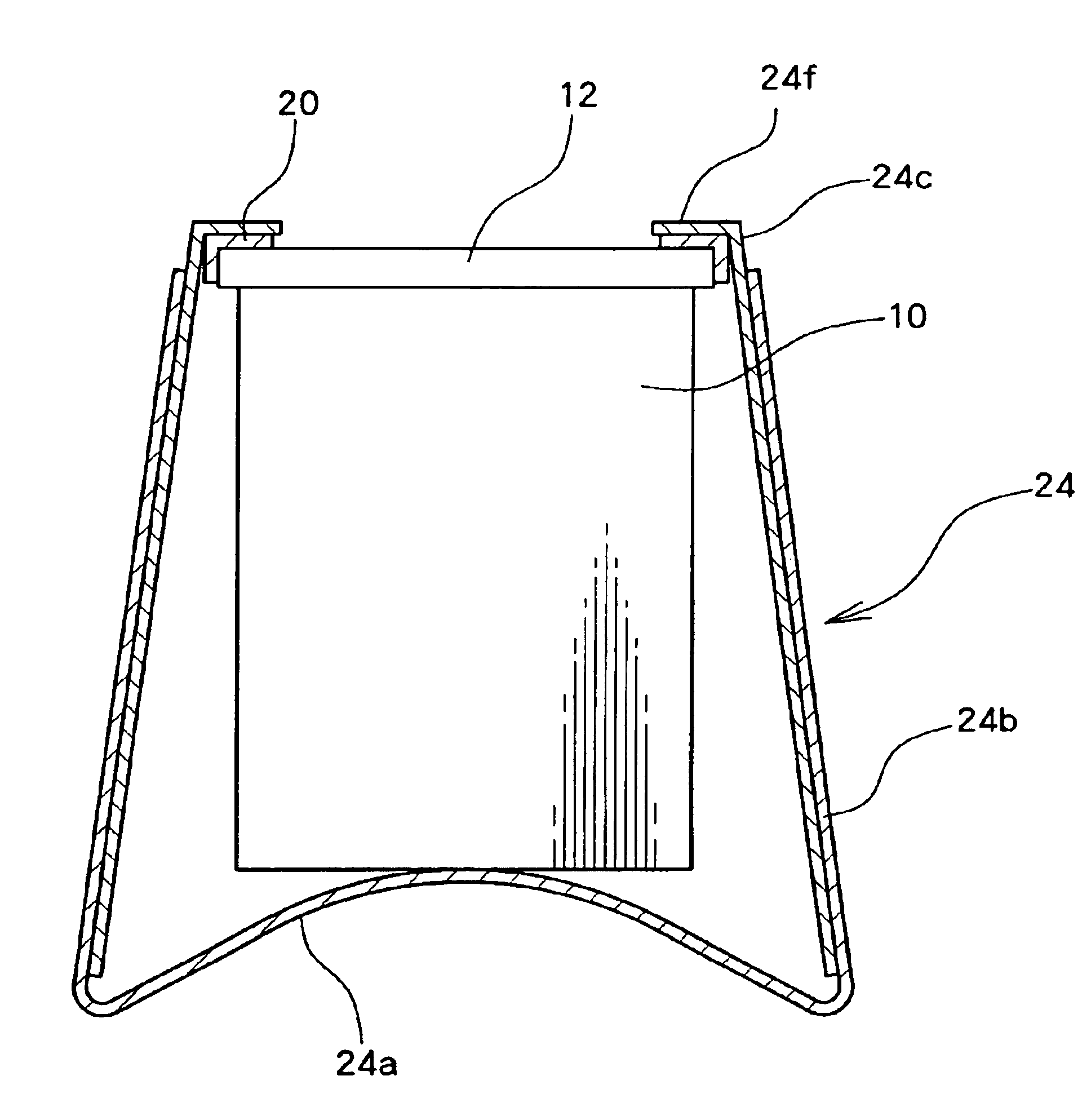
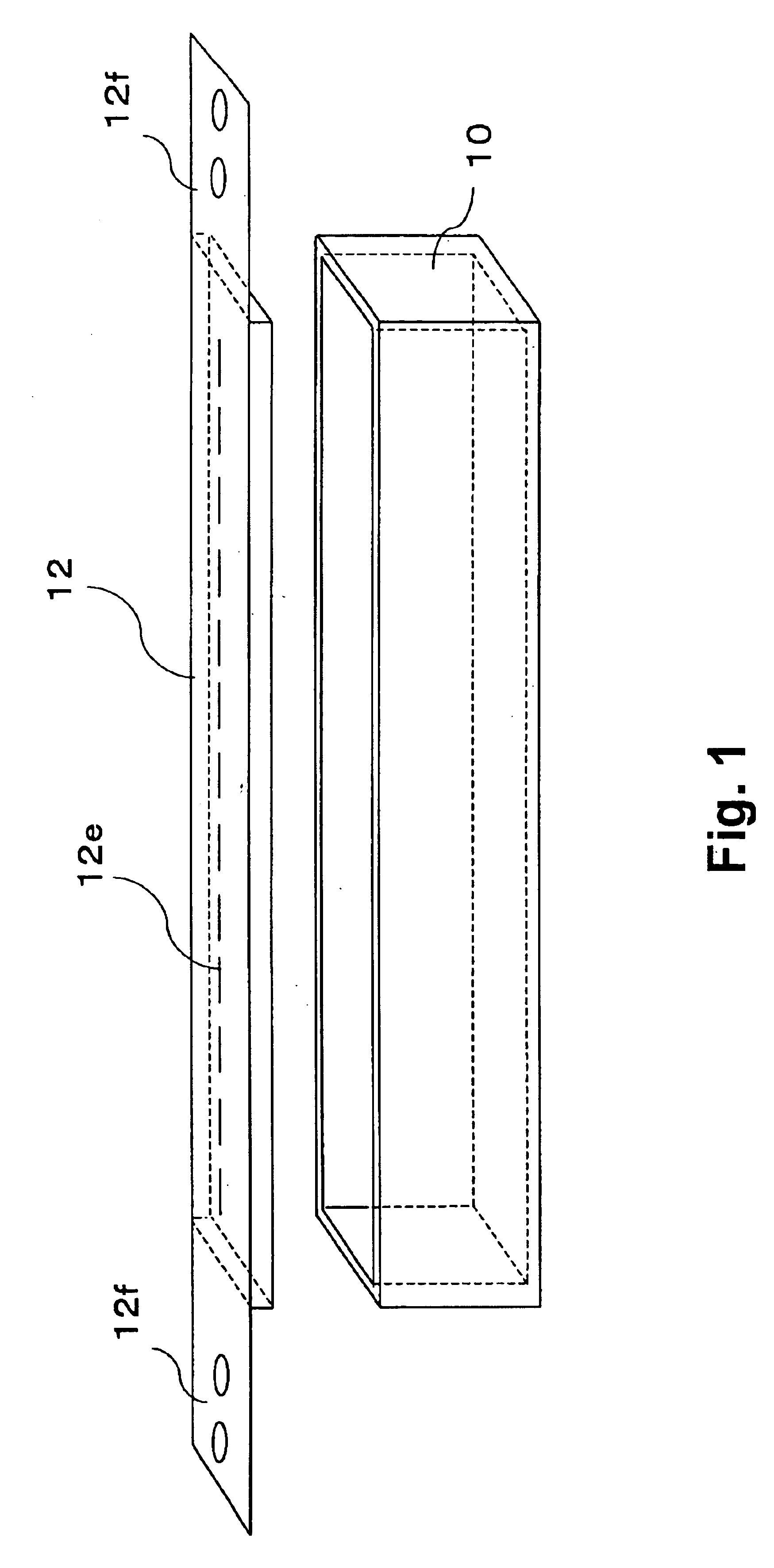
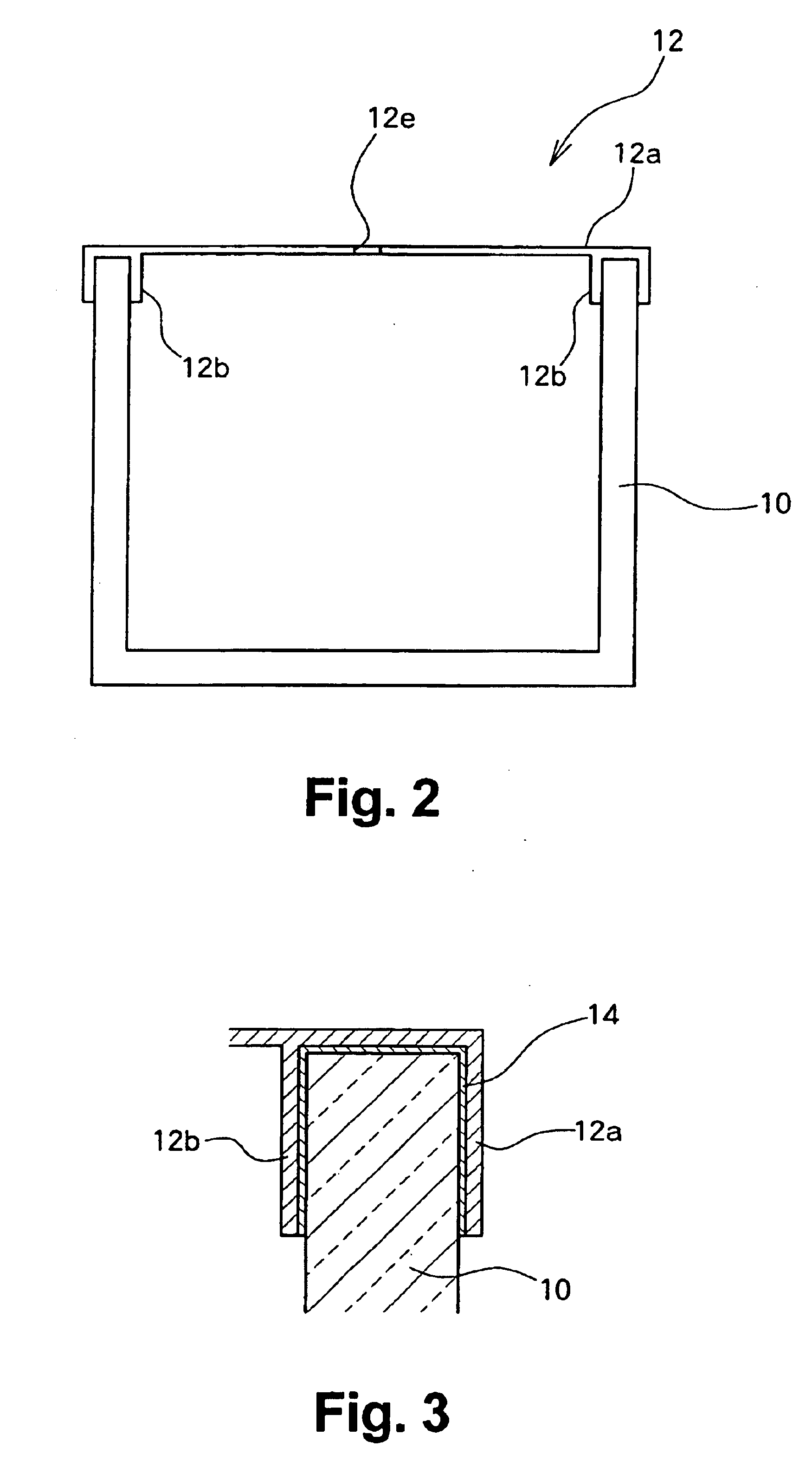
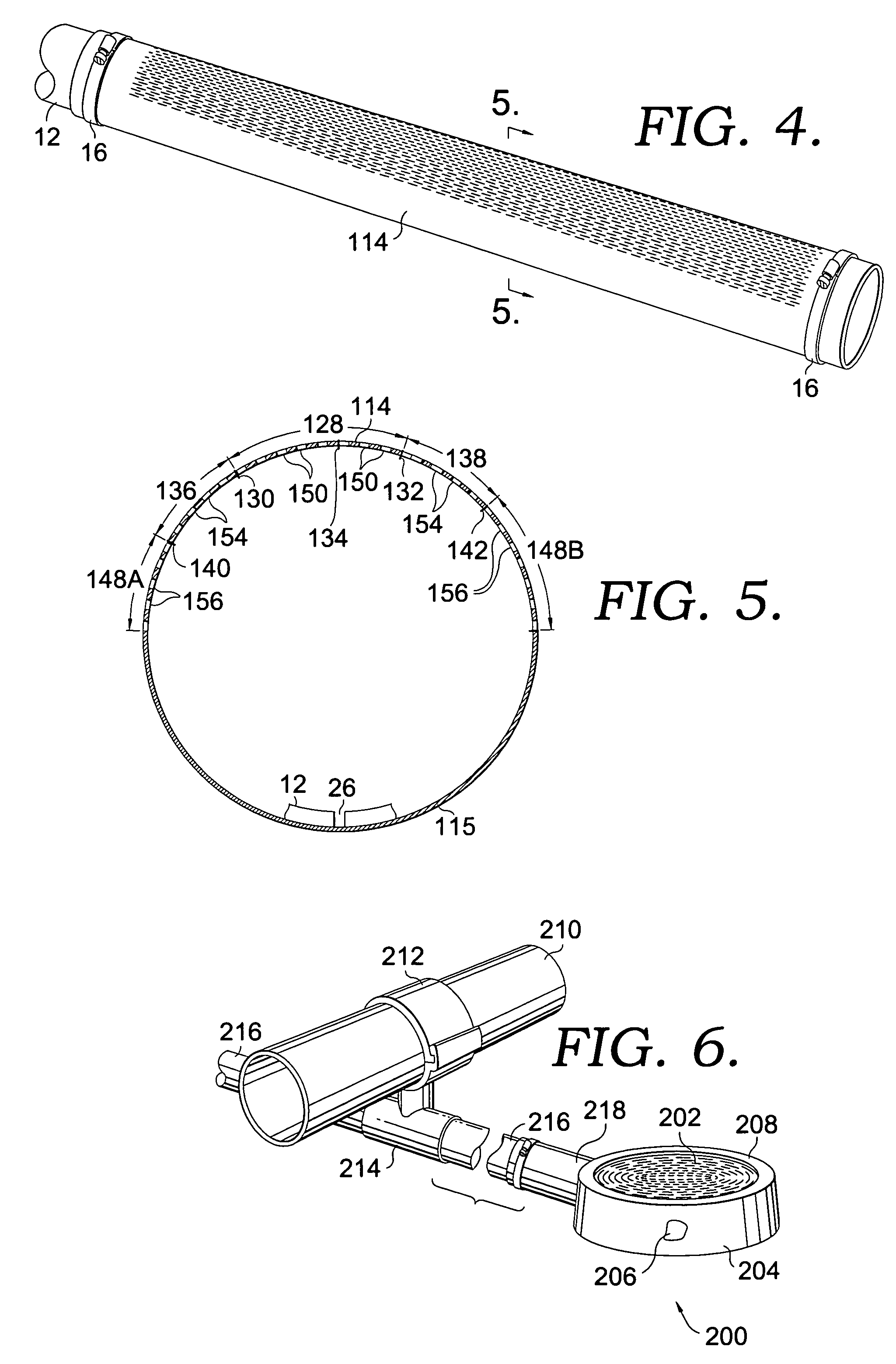
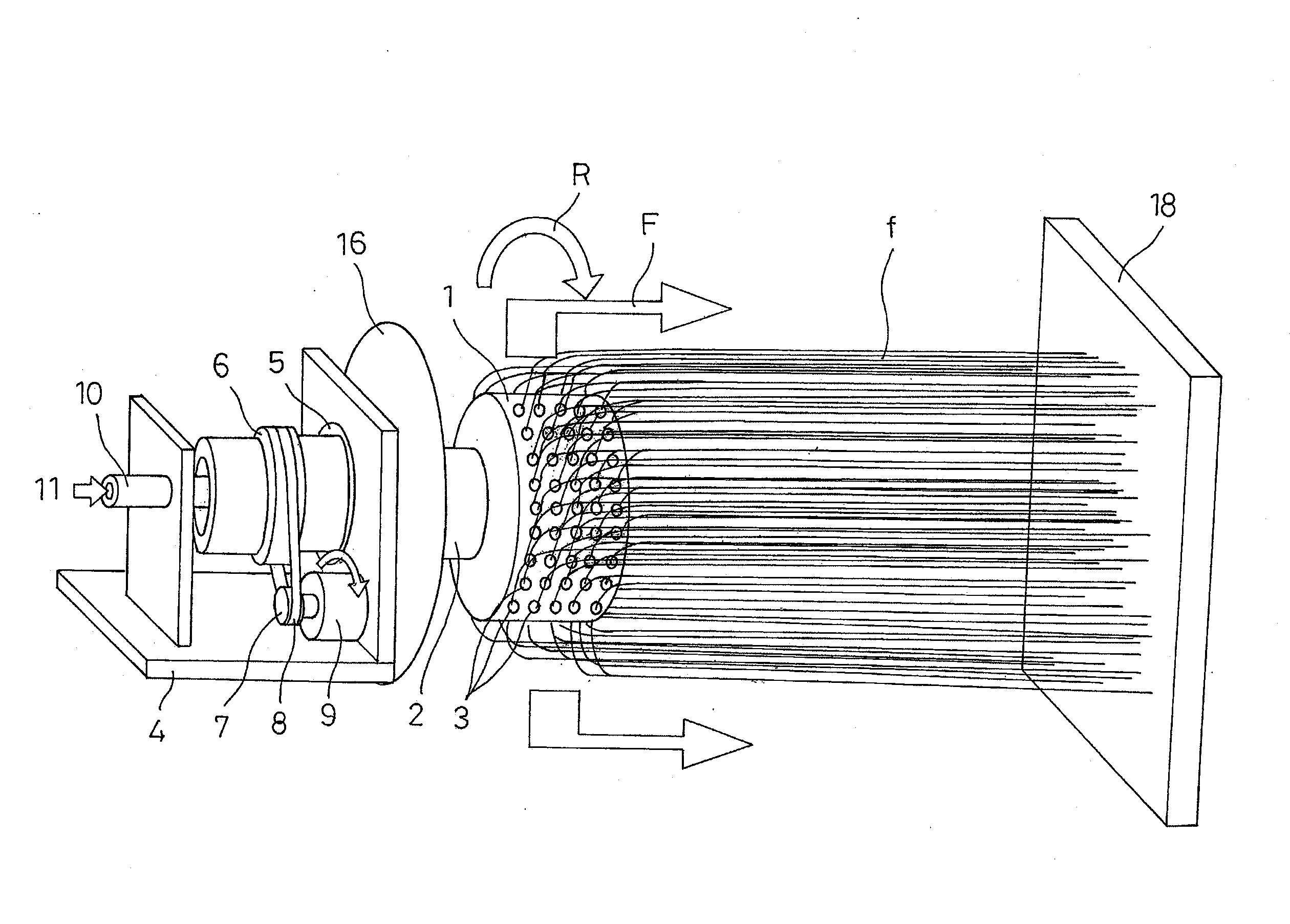
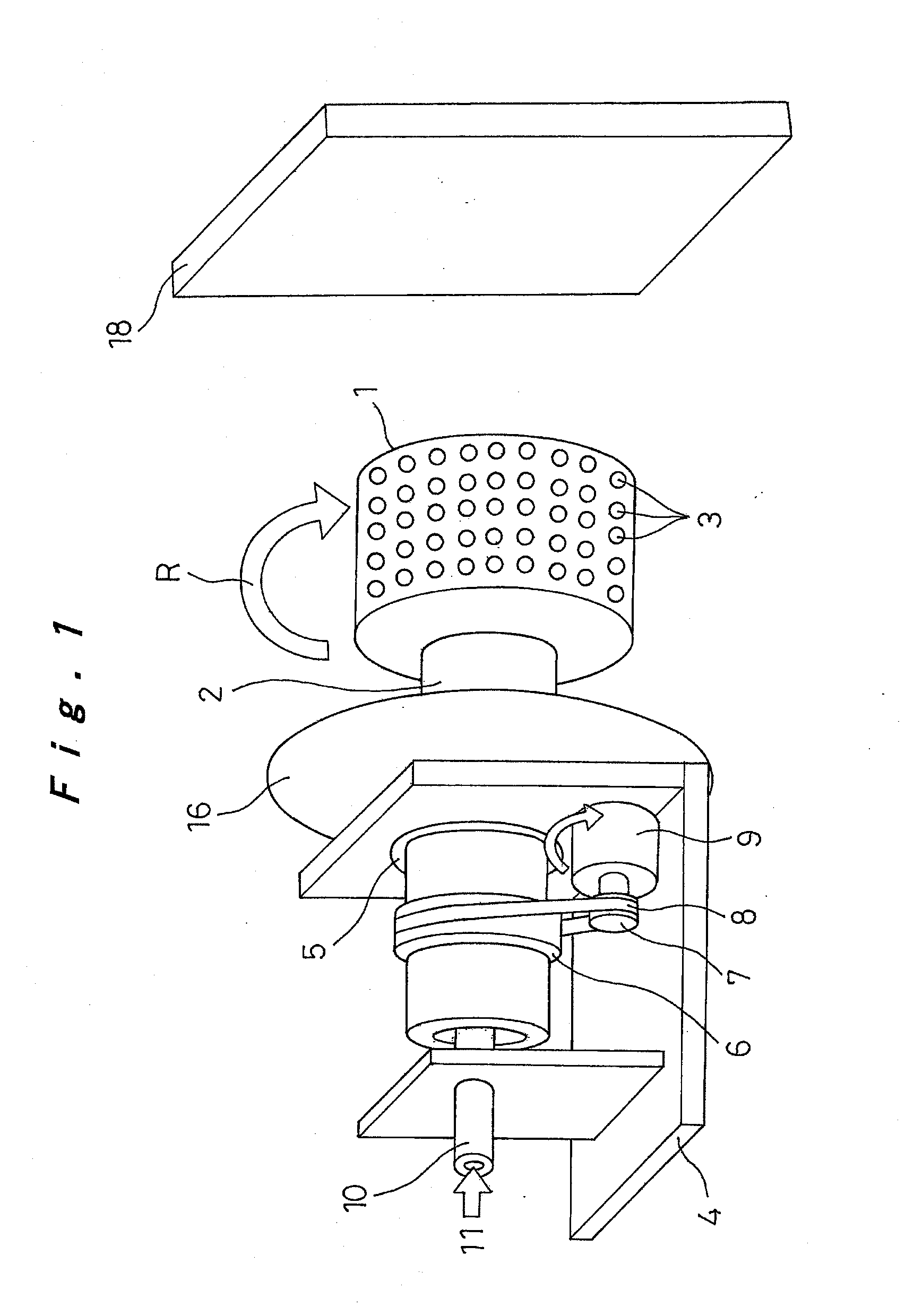
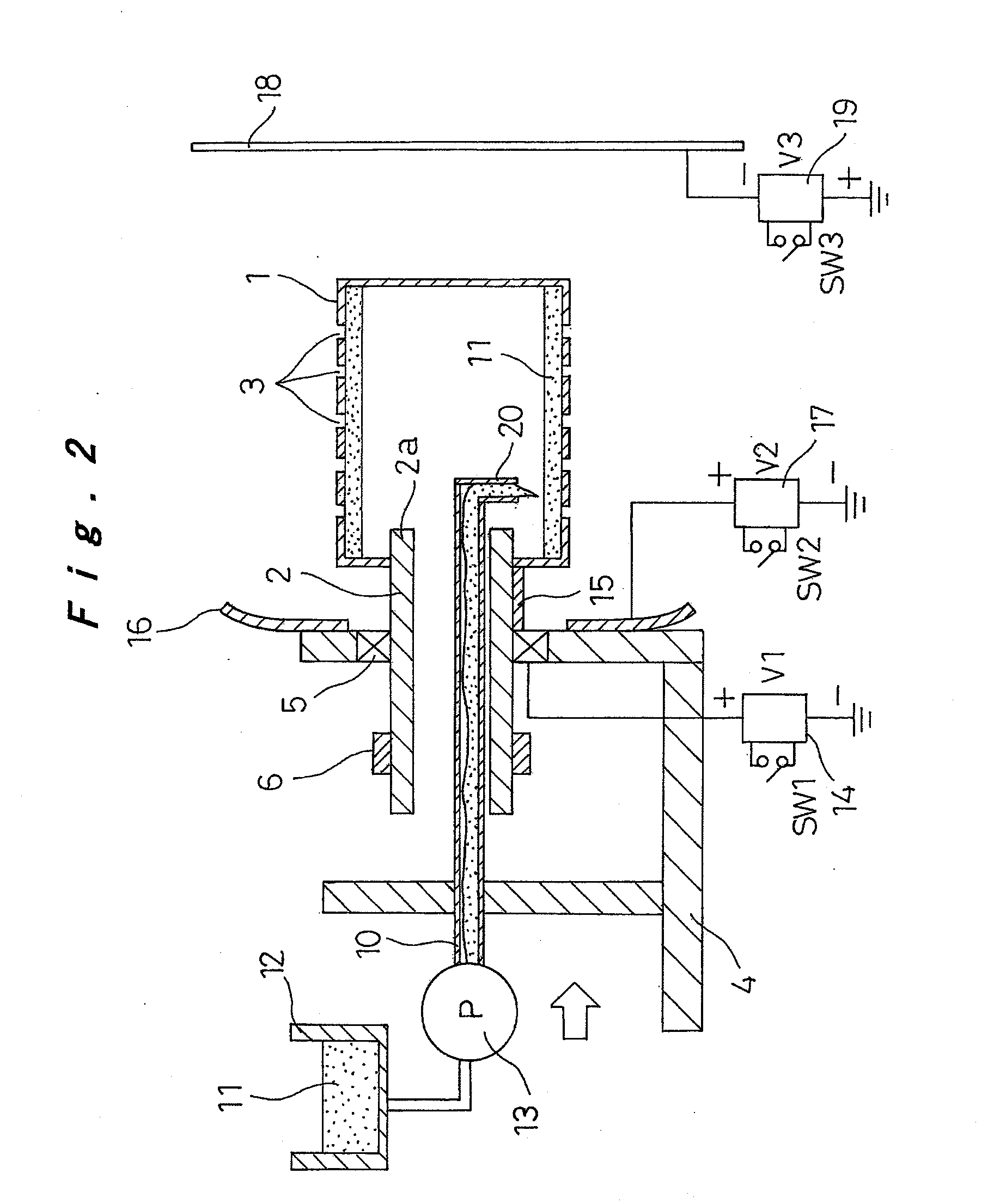
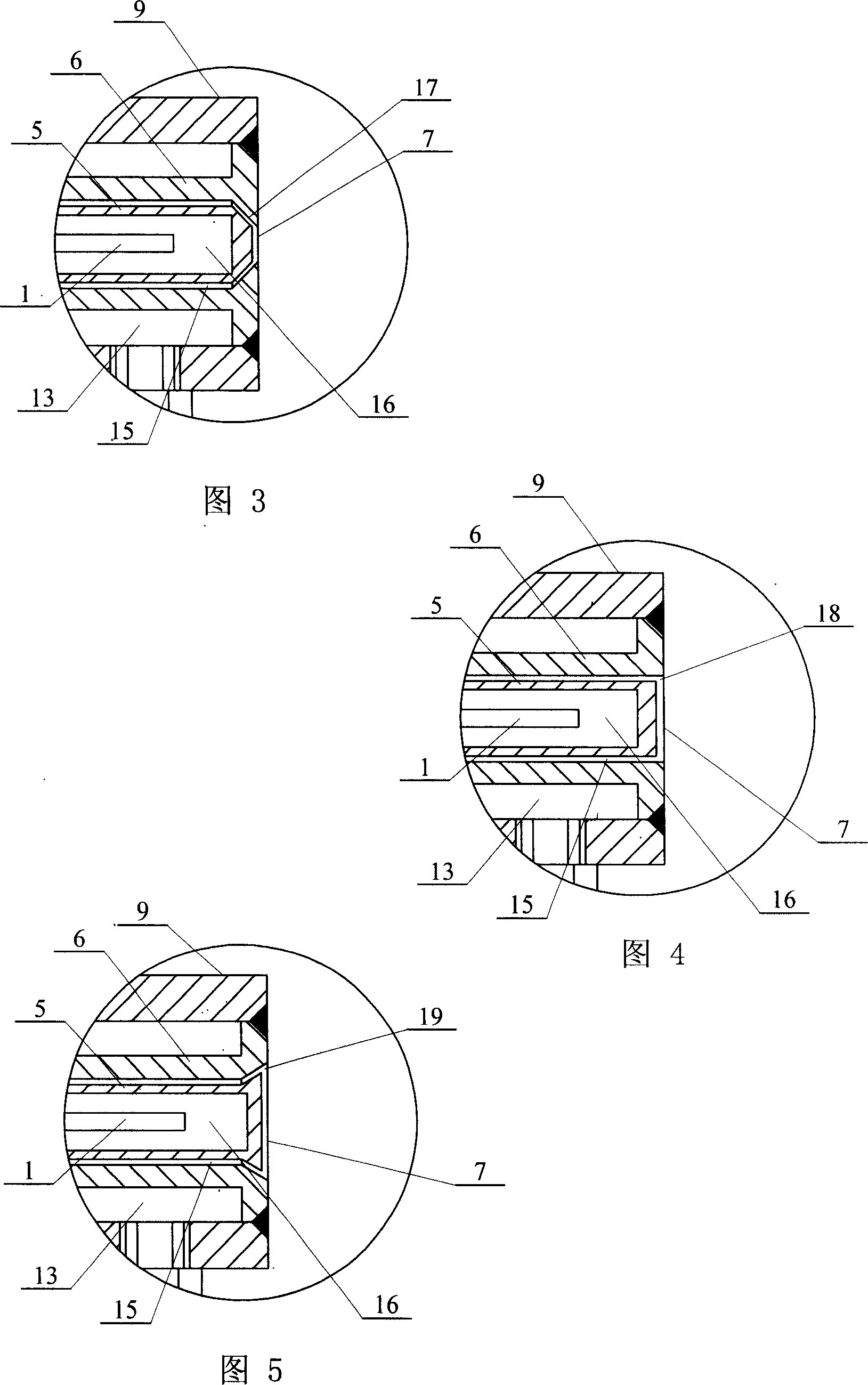
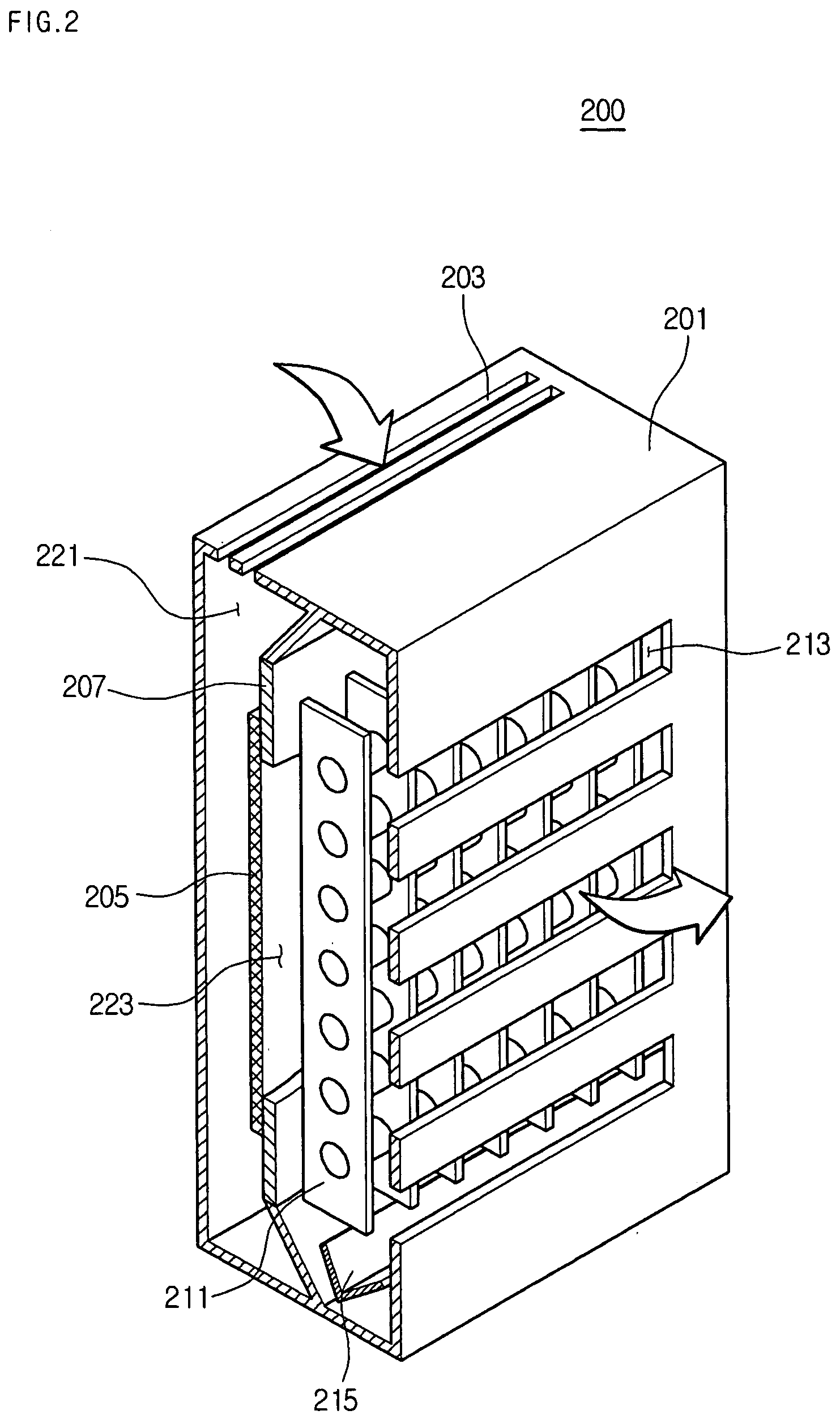
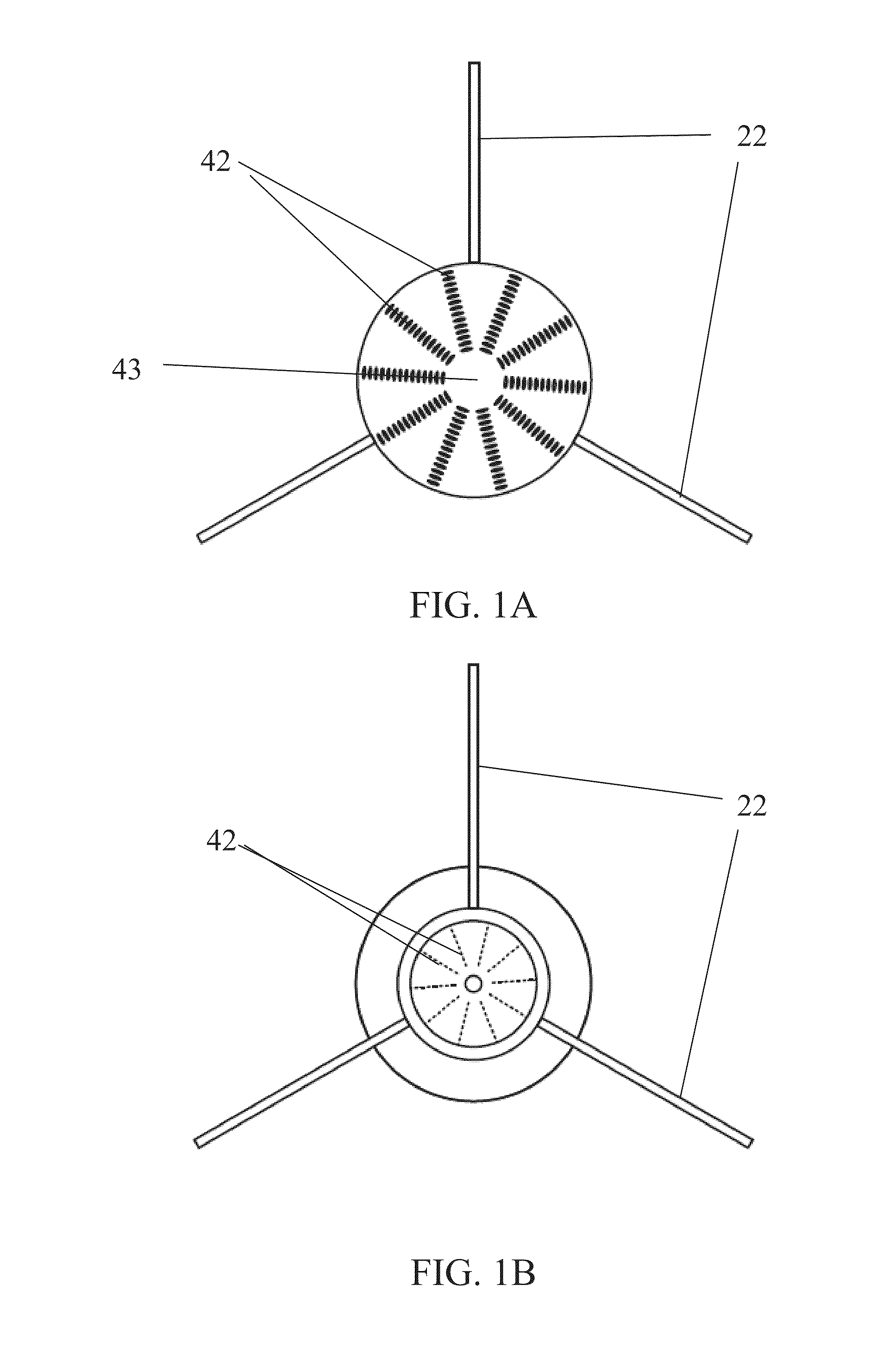
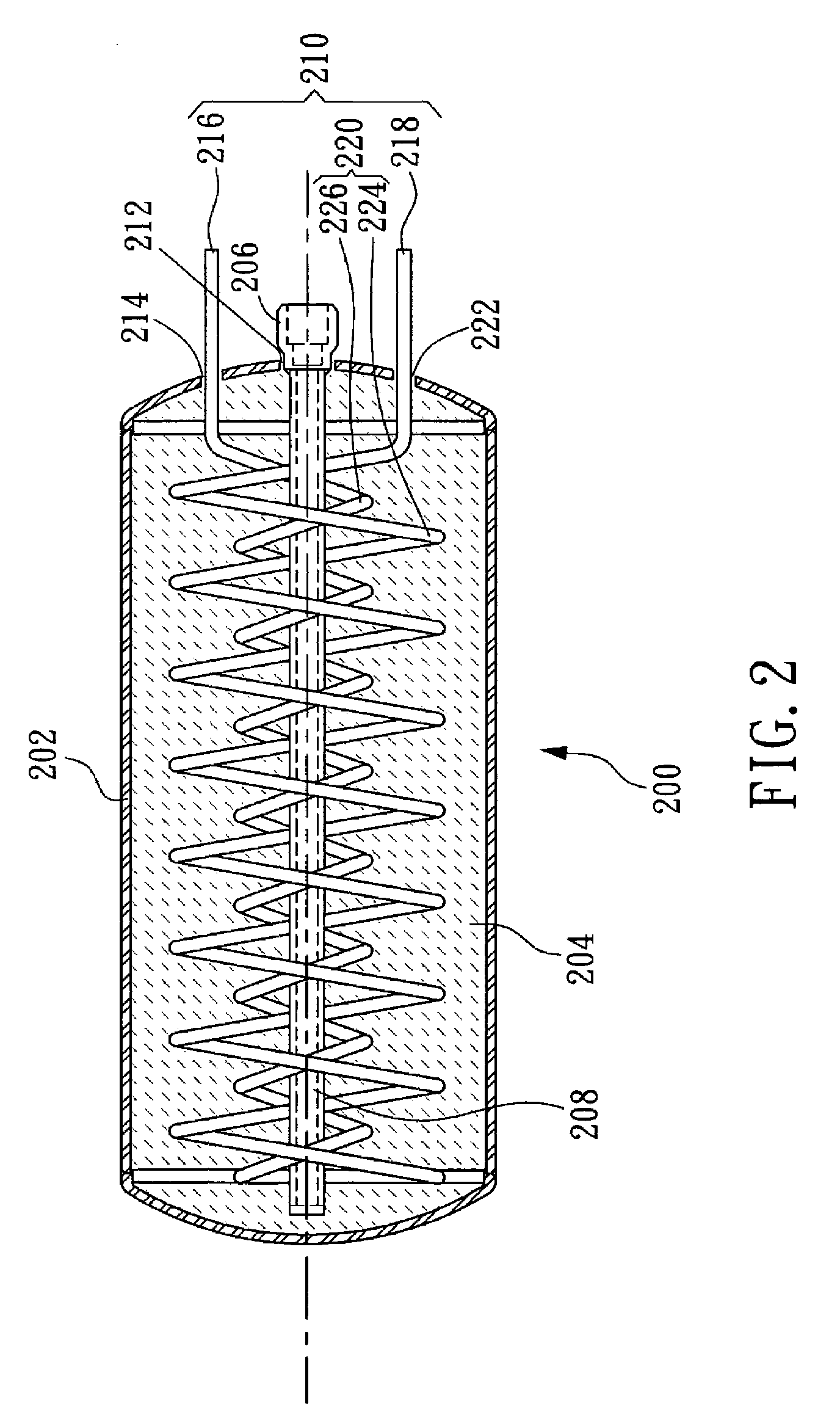
Fixing member for evaporation apparatus
InactiveUS6881271B2Uniform dischargeEfficient heatingSnap fastenersElectric lighting sourcesCrucibleEvaporation
An electric heater is placed so as to cover an upper opening of a crucible. Then, a plurality of angle members are disposed along the side portions of the electric heater and are pressed and fixed by clamps. The clamp includes, at its bottom, a curved portion formed by bending a plate-like spring member into a convex shape, and generates pressing force between the curved portion and corresponding claw portions at the upper edge, thereby clamping the crucible.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
Electrostatographic imaging member
InactiveUS6303254B1Improve thickness uniformityReduces undesirable dirtElectrographic process apparatusMicrometerPolymer chemistry
An electrostatographic imaging member including: a flexible supporting substrate; an imaging layer having an optional adjacent ground strip layer coated on one side of the substrate; and an anti-curl backing layer coated on the other side of the substrate which layer is comprised of a film forming polymer binder, an optional adhesion promoting polymer, and a dispersion of polytetrafluoroethylene particles which dispersion has particles with a narrow diameter particle size distribution of from about 0.19 micrometer to about 0.21 micrometer, and an average diameter particle size of about 0.20 micrometer. The optional ground strip layer can include the same dispersion of polytetrafluoroethylene particles as the anti-curl backing layer.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Method of polishing normal pressure plasma
The normal pressure plasma polishing method is provided. The normal pressure plasma polishing method includes providing plasma gas and reaction gas in the volume ratio of 4-1000; and starting RF power source and increasing power gradually while controlling the reflected power to zero, with the initial effective power being 180-240 W, normal power being 400-1200 W, and maximum power being 1500 W. The present invention realizes super smooth surface machining by means of plasma chemical reaction at normal pressure, and has no need of vacuum chamber, low cost, wide application range, high machining efficiency, no surface damage and contamination, and high surface smoothness up to 1nm Ra.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
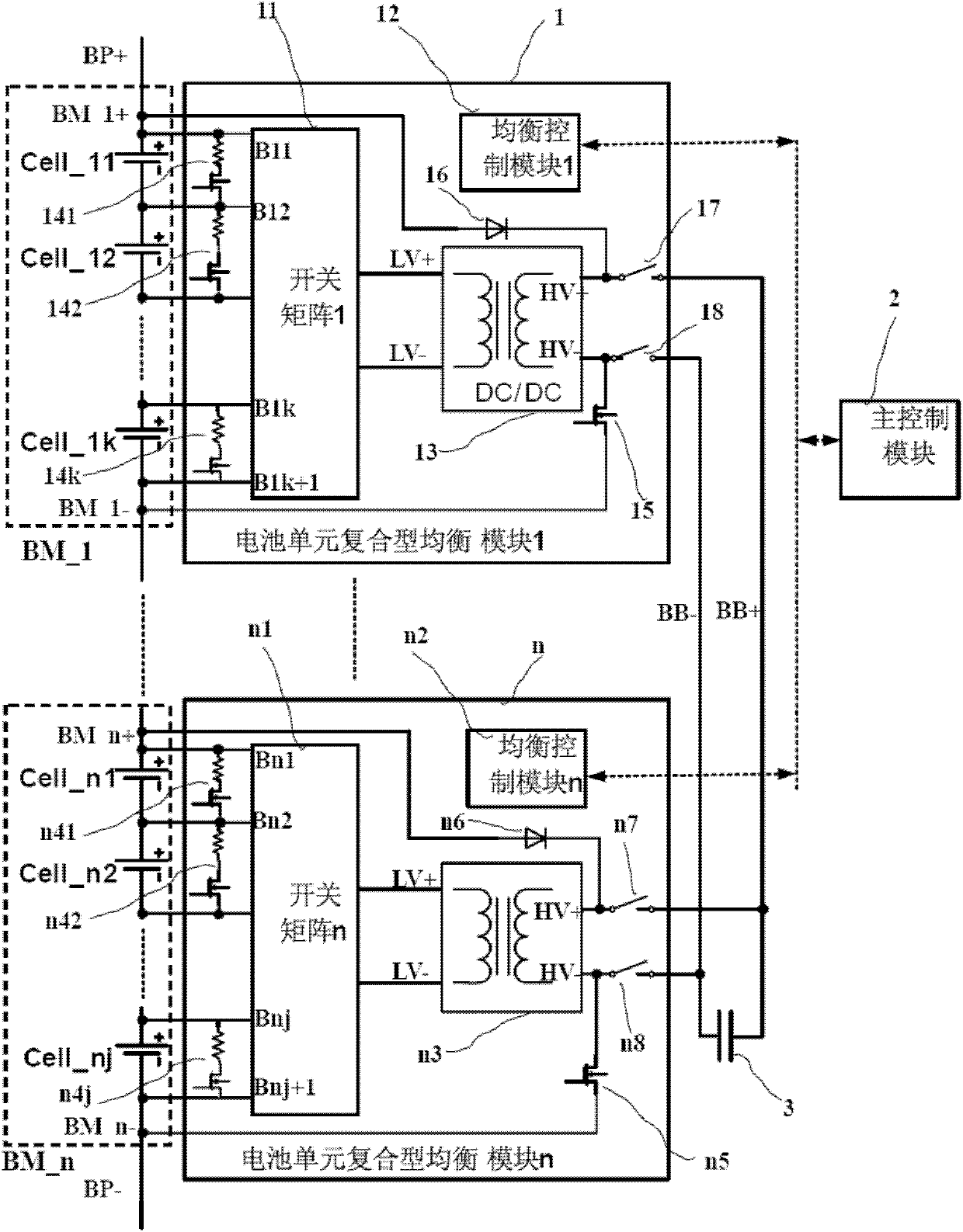
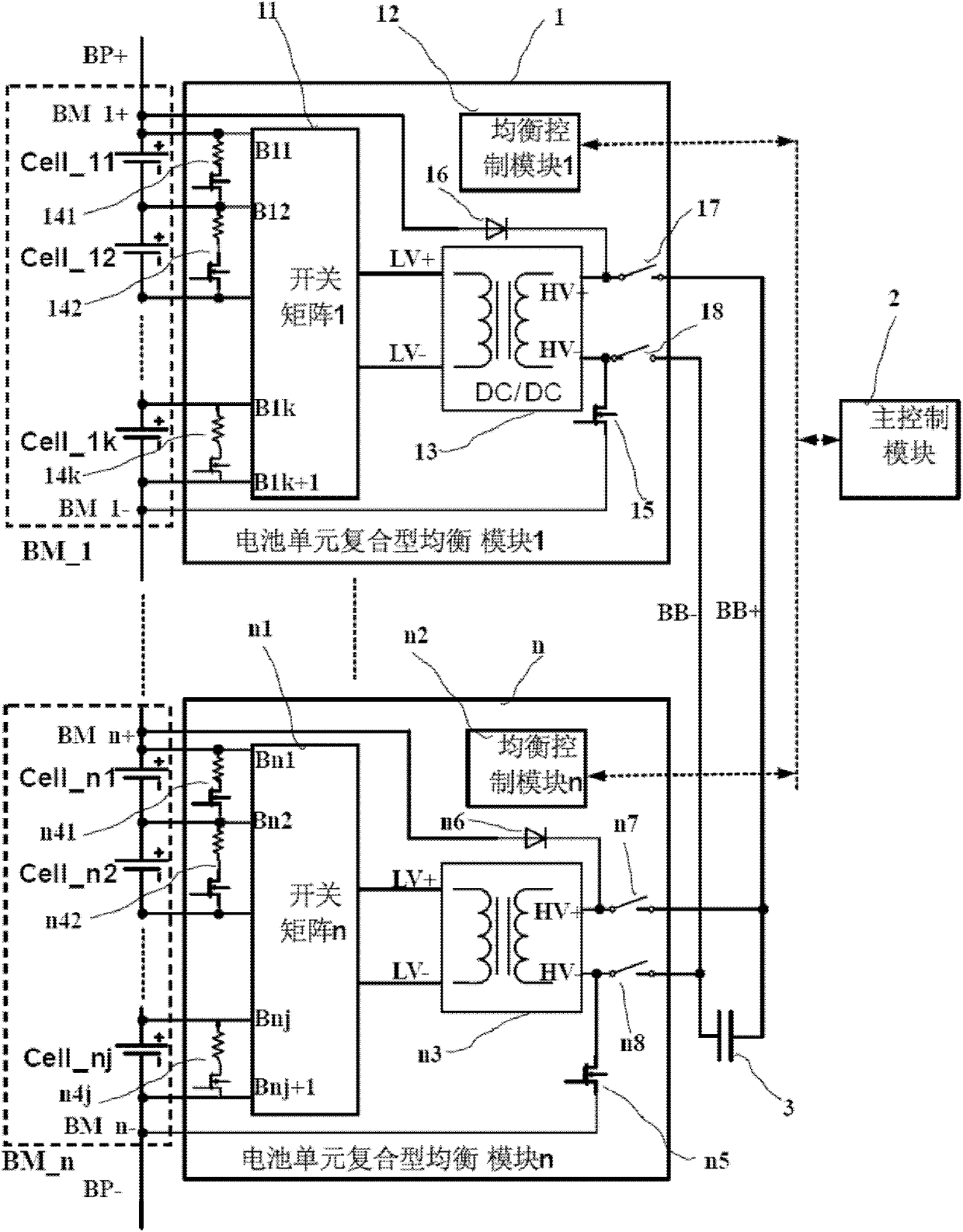
Equalization circuit of battery pack and equalization method
InactiveCN103326439AGood balance control effectBalanced time-sharing chargingBatteries circuit arrangementsElectric powerCapacitanceManagement unit
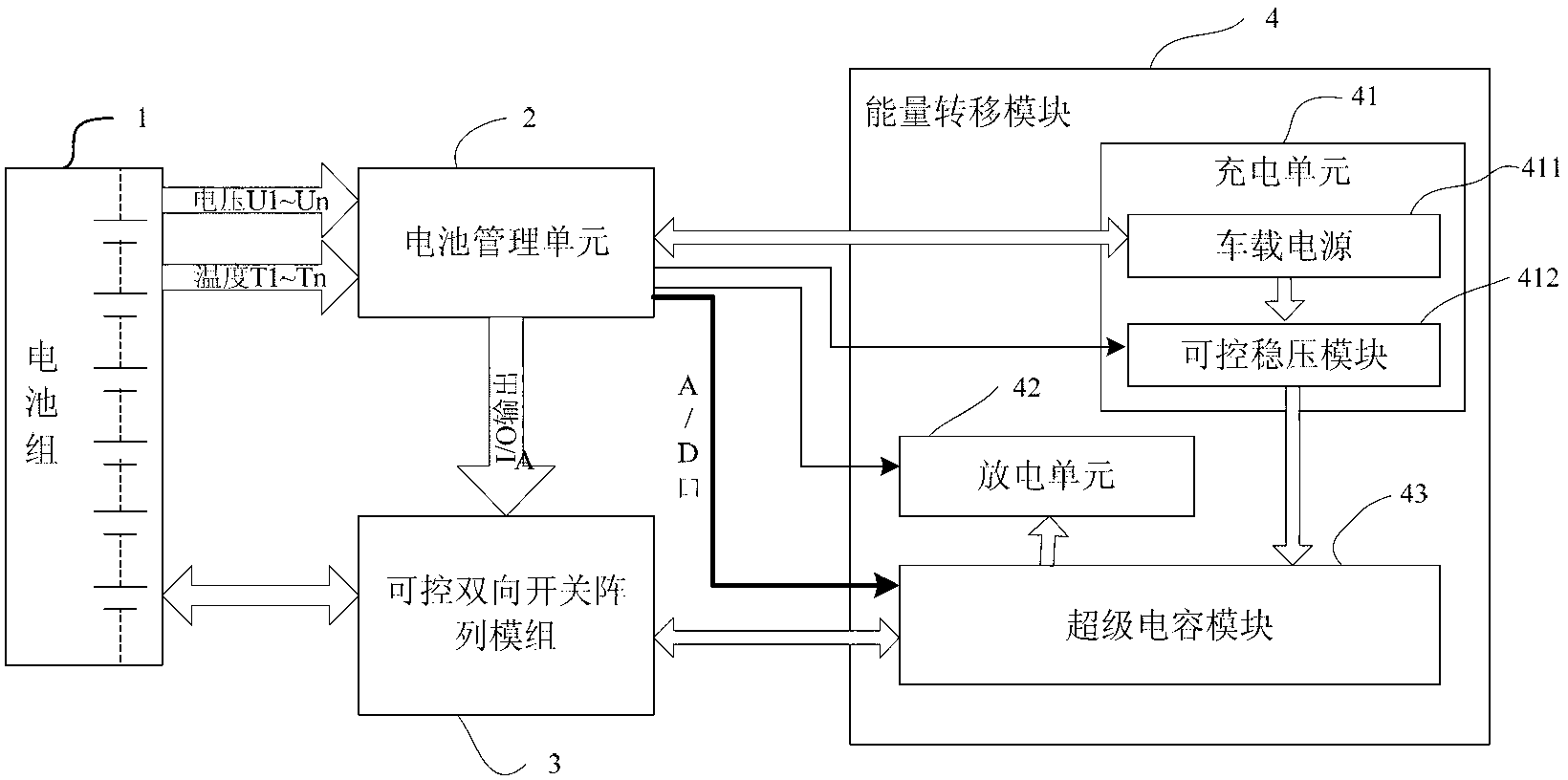
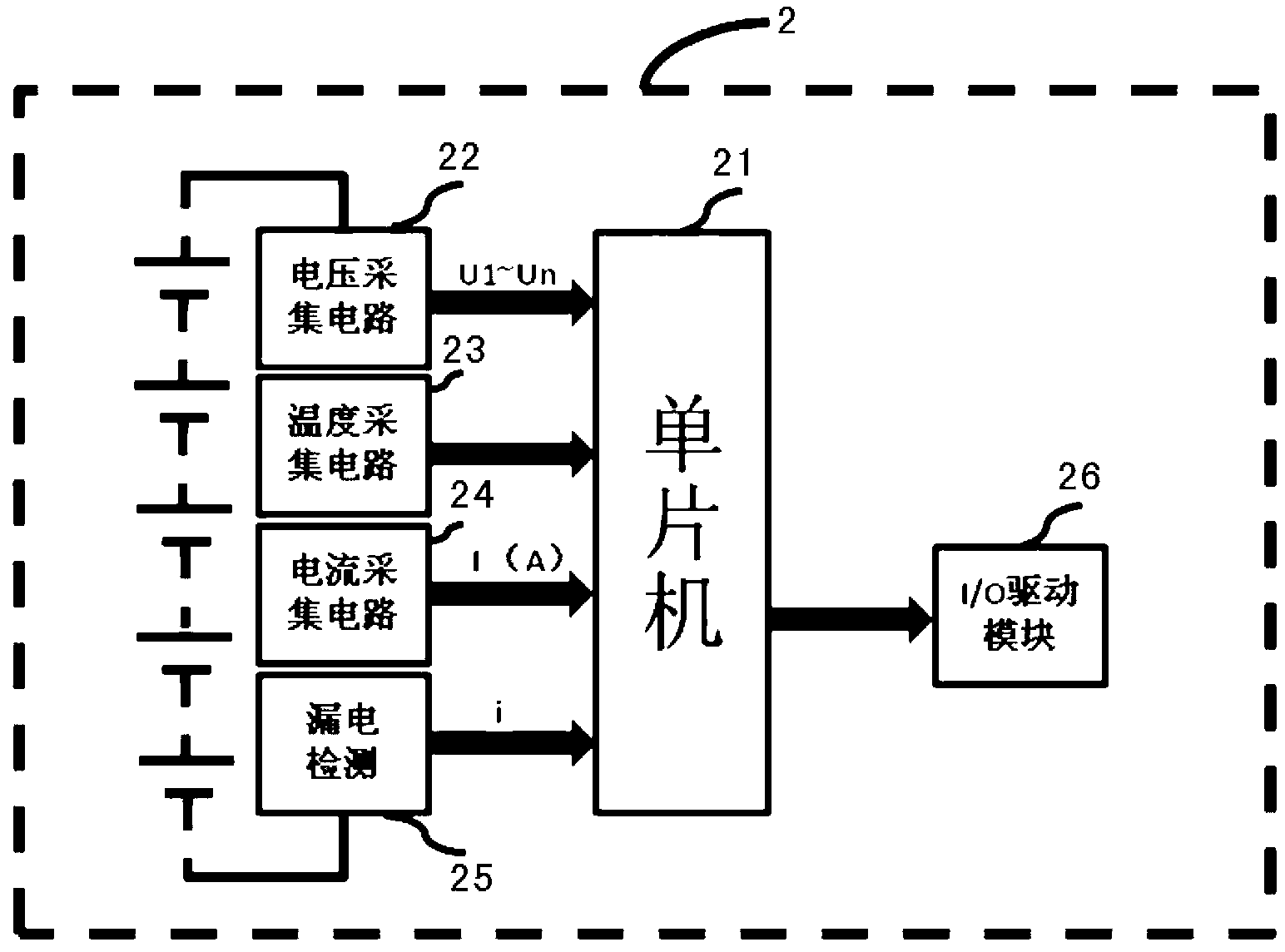
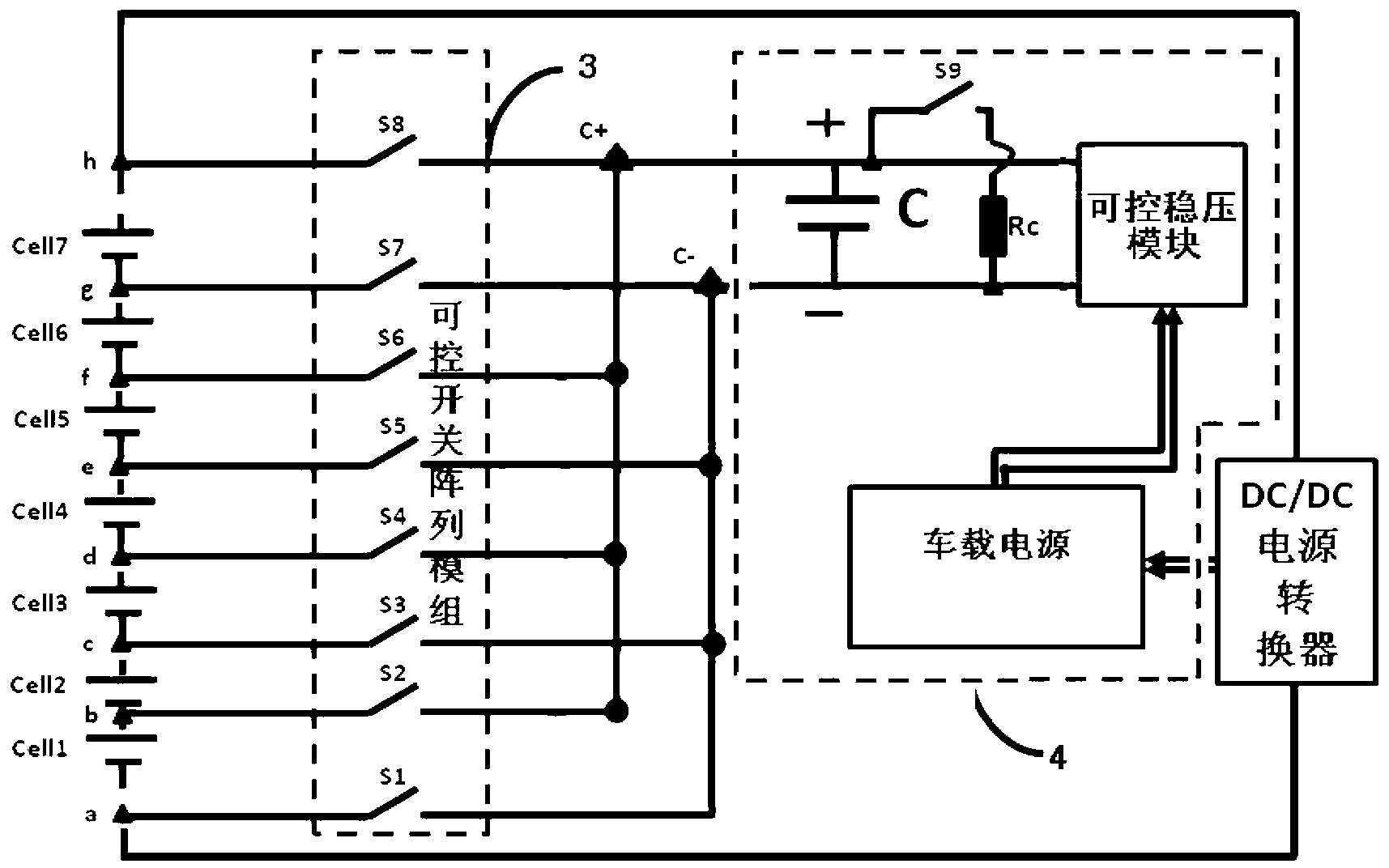
The invention provides an equalization circuit of a battery pack and an equalization method. The equalization circuit comprises the battery pack, a battery management unit, a controllable bidirectional switch array module and an energy transfer module, the energy transfer module comprises a charging unit, a discharging unit and a super capacitor module; the controllable bidirectional switch array module is used for switching on or switching off the electric connection between battery cells and the super capacitor module according to an equalization control command of the battery management unit; the super capacitor module is used for charging and discharging the battery cells which meet equalization conditions; the battery management unit is used for controlling the voltage of the super capacitor module, making the voltage of the super capacitor module to be equal to the average voltage of the battery pack and sending the equalization control command to the controllable bidirectional switch array module to charge and discharge the battery cells which meet the equalization conditions. By means of the equalization circuit of the battery pack, the battery cells in the battery pack are equalized, and the equalization circuit of the battery pack has the advantages of being efficient, low in heat, long in service life and the like.
Owner:珠海市安吉名能源科技有限公司
Plasma display panel
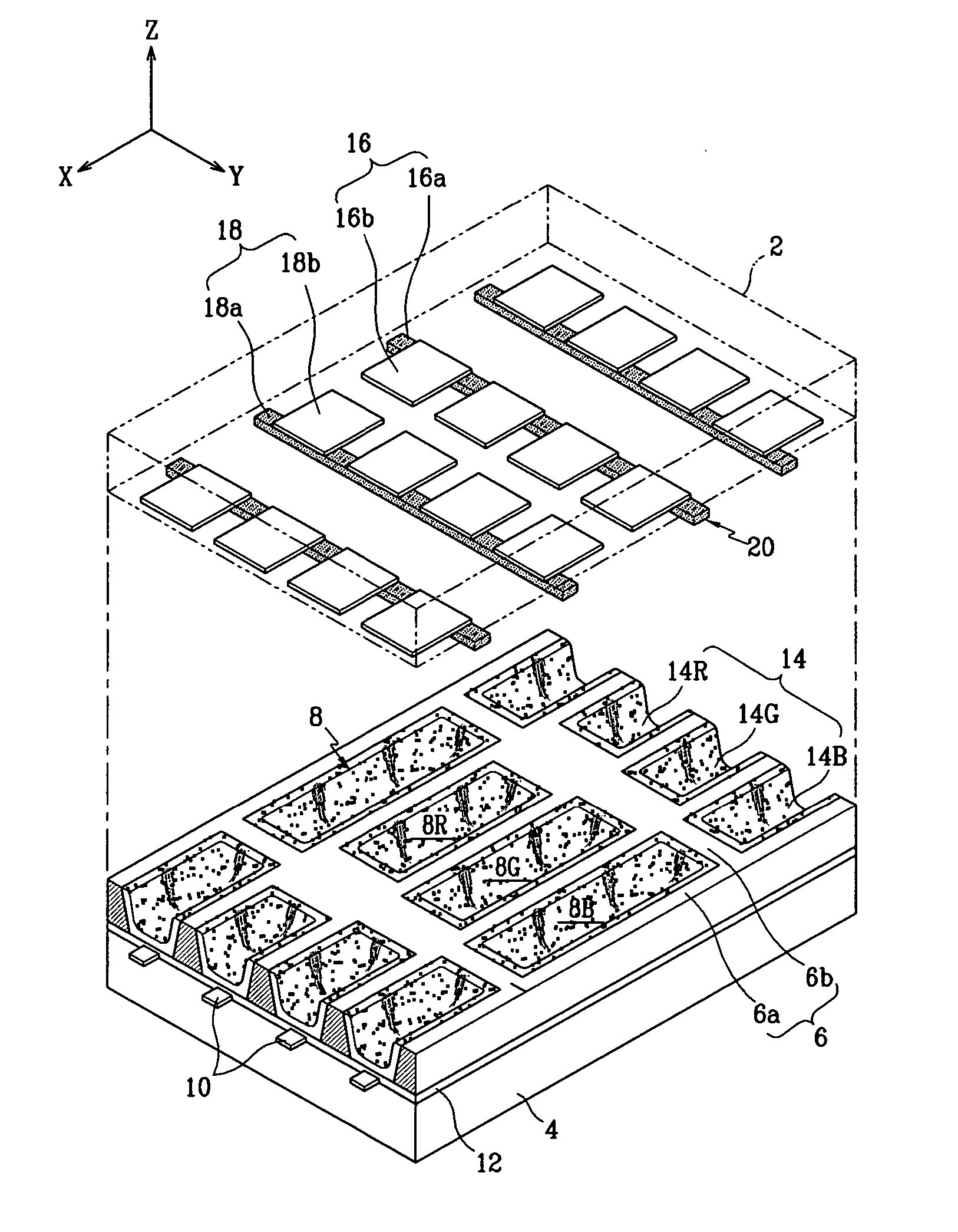
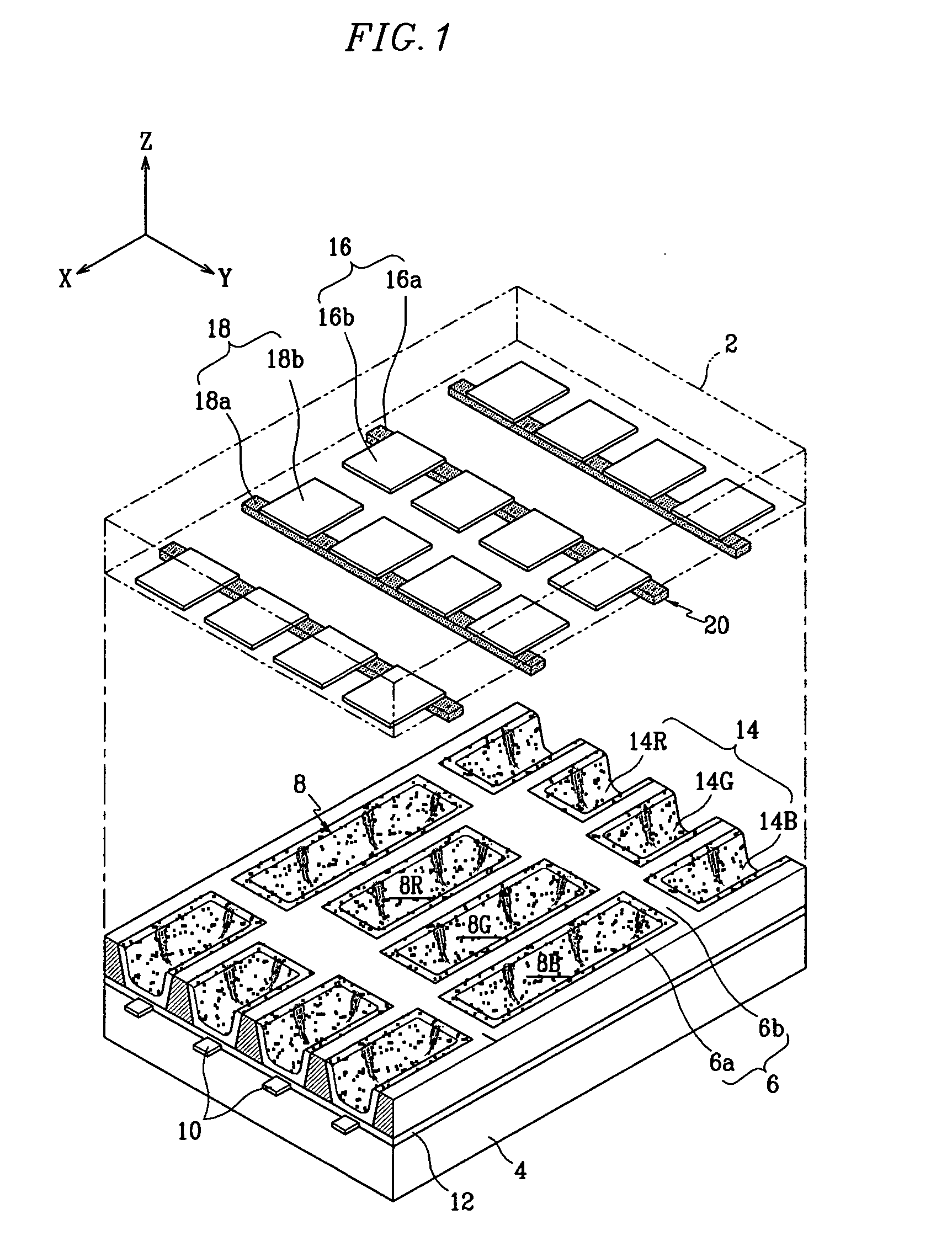
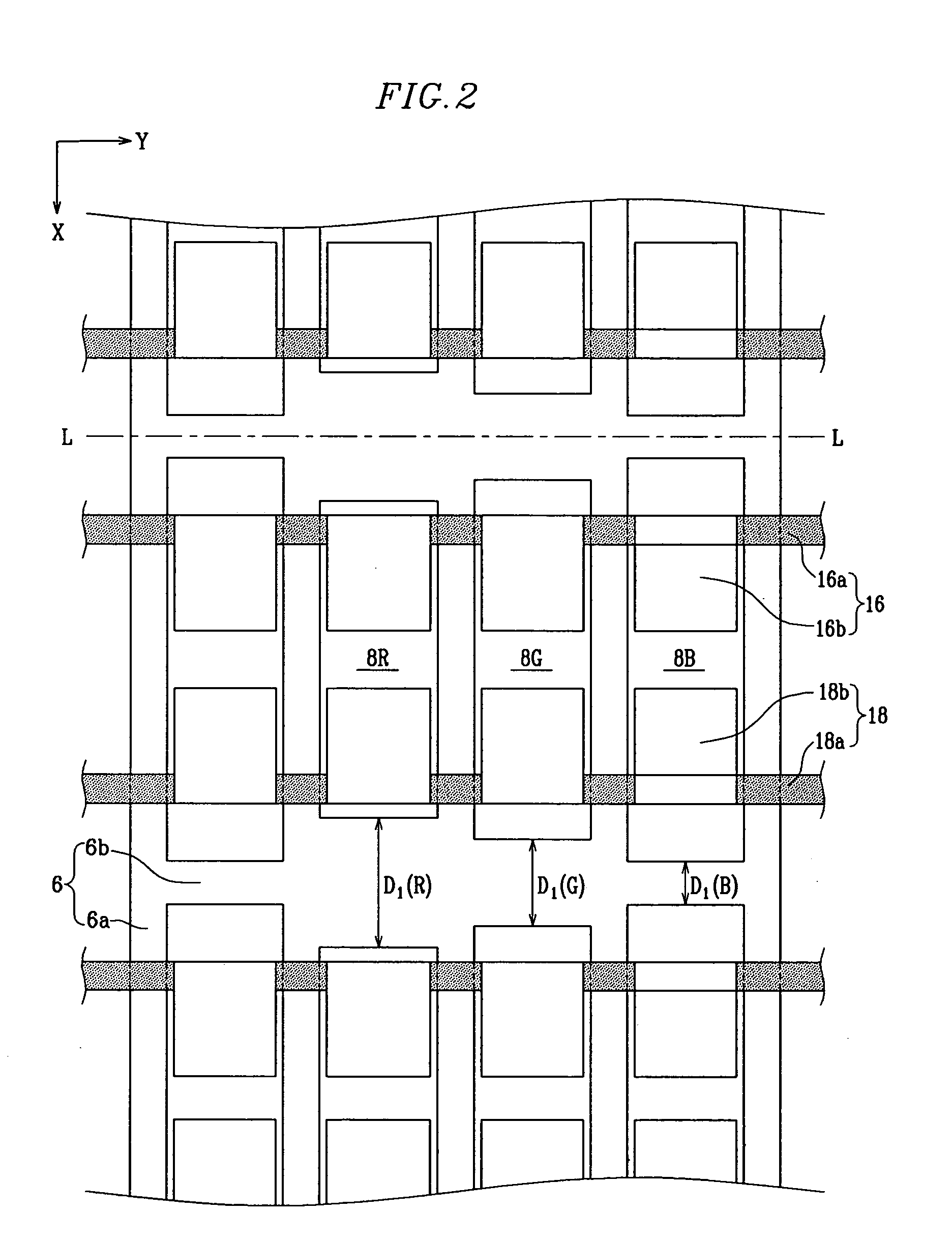
InactiveUS20050017637A1Improve efficiencyUniform dischargeSustain/scan electrodesStatic indicating devicesEngineeringPlasma display
A plasma display panel. A first substrate and a second substrate are provided opposing one another with a predetermined gap therebetween. Address electrodes are formed on the second substrate. Barrier ribs are mounted between the first substrate and the second substrate, the barrier ribs defining a plurality of discharge cells. Also, red, green, and blue phosphor layers are formed within each of the discharge cells. Discharge sustain electrodes are formed on the first substrate. The barrier ribs comprise first barrier rib members formed substantially parallel to the direction of the address electrodes, and second barrier rib members obliquely connected to the first barrier rib members and intersecting over the address electrodes. The second barrier rib members are formed to different widths according to discharge cell color such that red, green, and blue discharge cells have different volumes.
Owner:SAMSUNG SDI CO LTD
Membrane diffuser with uniform gas distribution
InactiveUS7044453B2Improve distribution uniformityImprove transmission efficiencyCarburetting airTransportation and packagingMembrane surfaceMaterial Perforation
A flexible diffuser membrane is provided with a unique system of perforations arranged to result in uniform distribution of gas even though the membrane deflects to different extents or the submergence varies in different parts of the membrane. The perforations are arranged to provide less perforation area per unit of perforated membrane surface area in the membrane parts that deflect the most or are submerged least and greater perforation area in membrane parts that deflect the least or are submerged most. The perforations can be slits arranged in parallel rows on a tubular membrane, in concentric circles or another pattern on a disk membrane, or in still a different pattern on a flat panel diffuser membrane. The slit length or separation can be varied between different zones on the membrane surface or the spacing between rows or circles can be varied.
Owner:ENVIRONMENTAL DYNAMICS INC
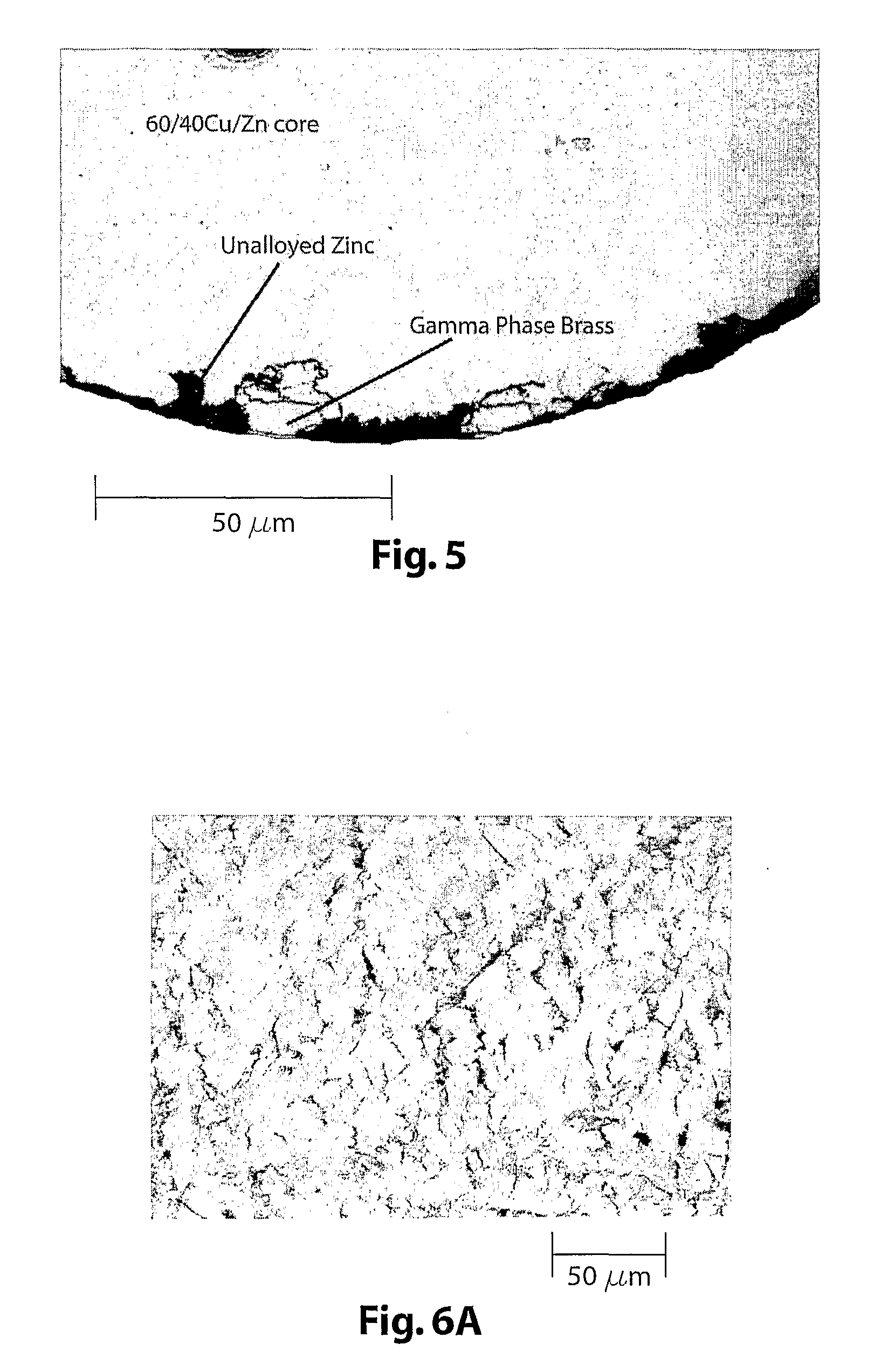
EDM wire
An EDM wire having an outer coating of gamma phase brass with an overlayer of continuous unalloyed zinc or ductile epsilon phase brass entrapping the gamma phase and a process for manufacturing the EDM wire is provided. A second process for synthesizing a ductile epsilon phase brass coating on the aforementioned and other substrates is also provided. The first process includes coating a copper bearing metallic core with zinc. The zinc coating is then converted to gamma phase brass via a diffusion anneal and subsequently re-coated with zinc prior to being cold drawn to its finish diameter.
Owner:THERMOCOMPACT
Method for manufacturing ultrafine carbon fiber and field emission element
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Low-temperature coal carbonization kiln
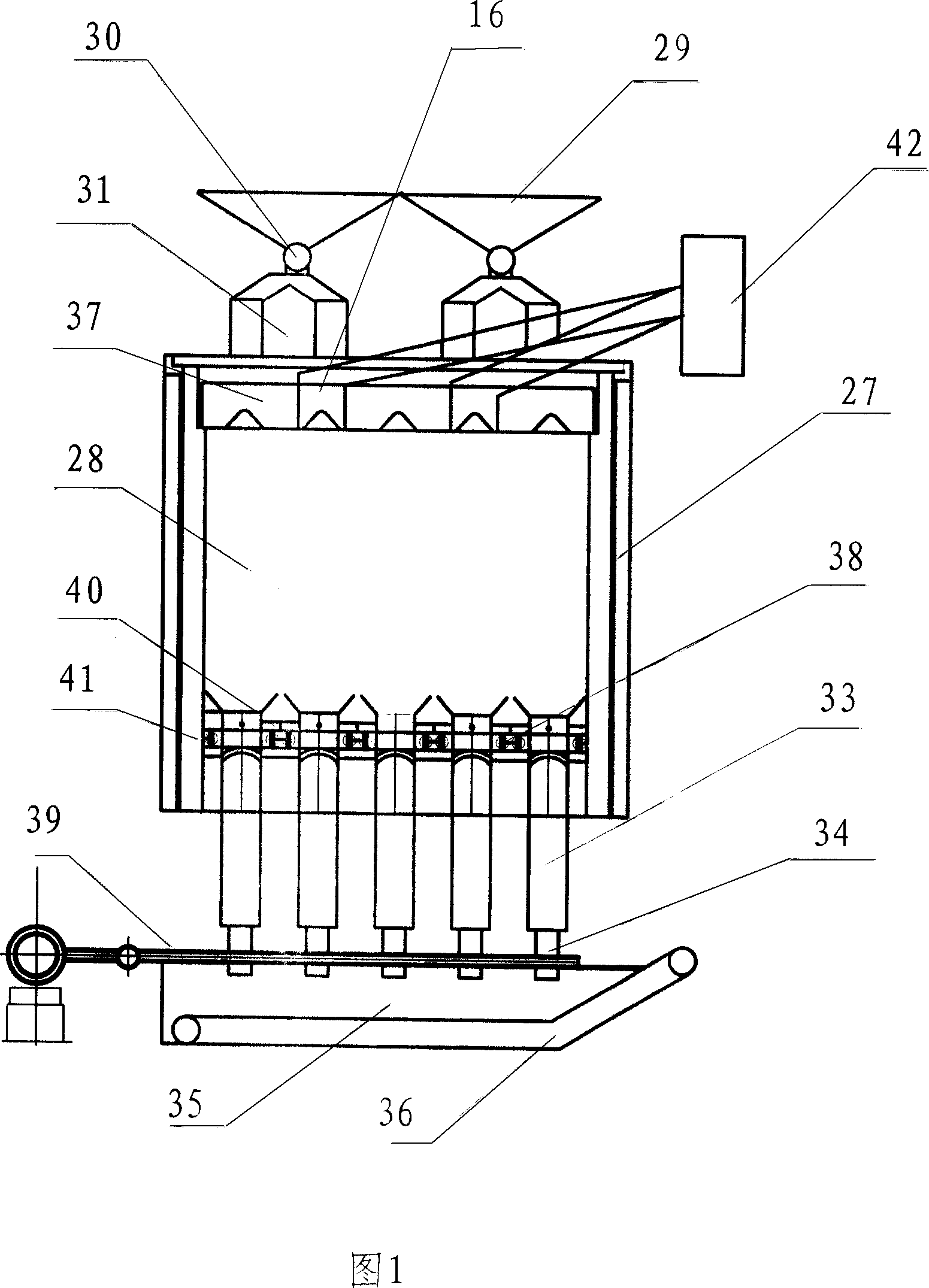
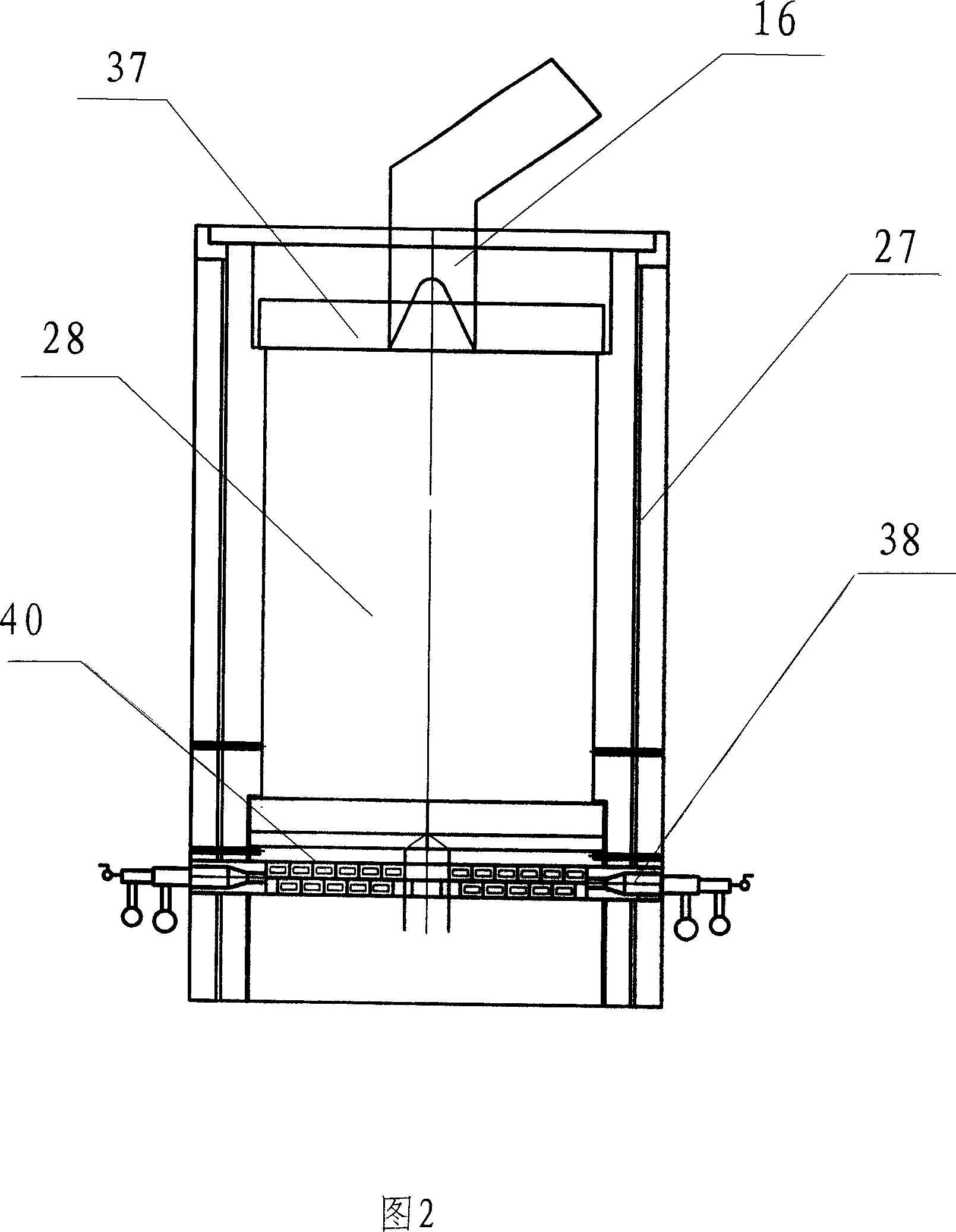
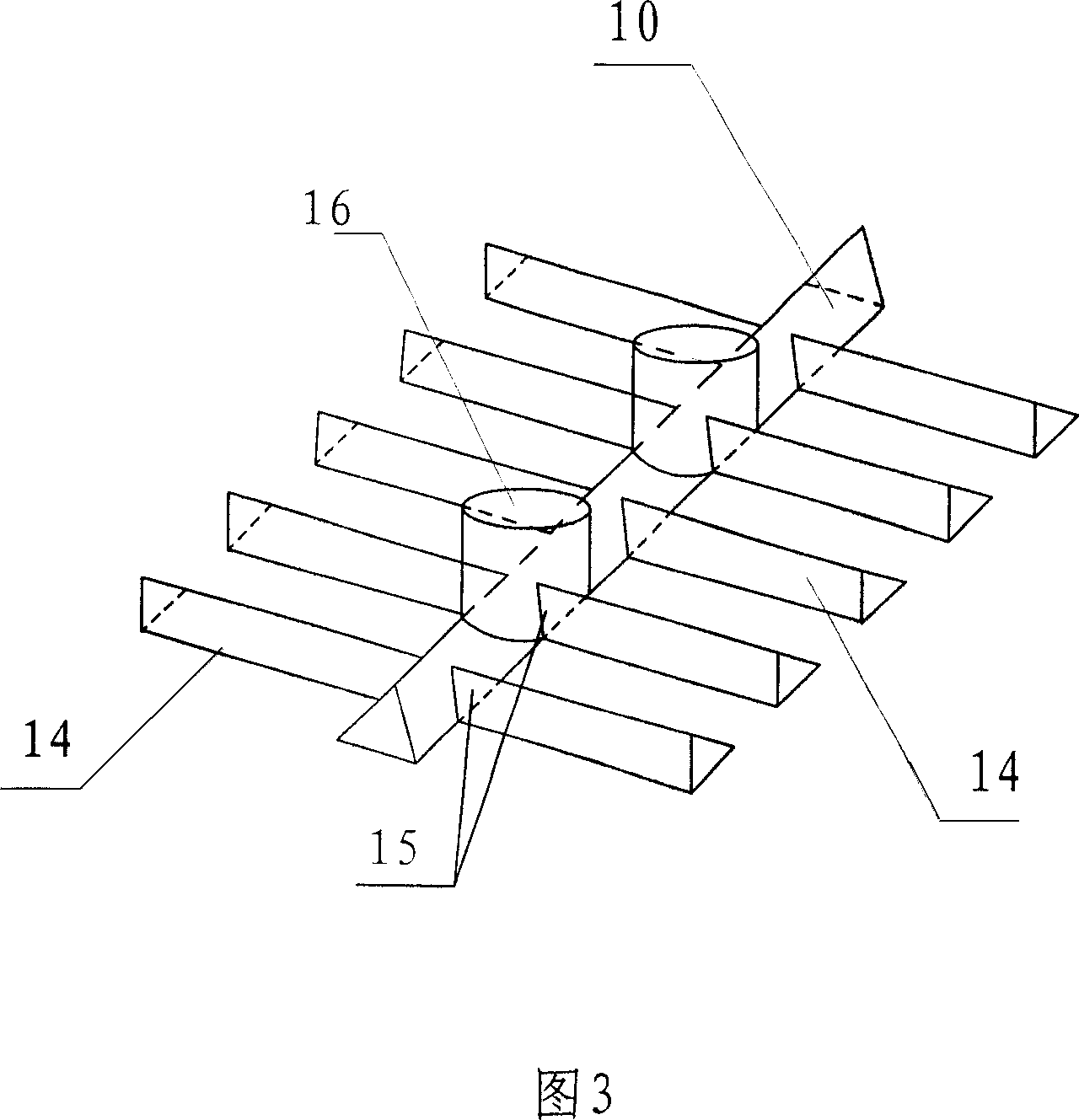
ActiveCN1966609AIncrease effective volumeHigh yieldRetortsDischarging devicesAutomatic controlCarbonization
The invention disclosed a kind of low temperature coal dry distillating square stove which includes stove body, coal cup, dant-pushing machine and branch admixer. On the top of the hearth there is installed the gas collecting umbrella, inside the stove it is cavity structure; on the bottom of the cavity there are installed several rows of emitting gas walls, every row of emitting gas wall is parallel to the interval between two side umbrella of the gas collecting umbrella; the consecutive emitting gas walls are pedestalled by arch wall; on both sides of the emitting gas walls there are two branch admixer respectively; the bottom of the stove connects the dant discharging box, the bottom of which connects the dant leading slot; the bottom of the dant leading slot is dant-pushing machine, the bottom of which is aqua sealing slot, in the slot there is scraper machine. The invention adopts the heating scheme of endo-burnning and calor internus which can heat uniformly. The gas collecting umbrella and accessory coalbox can make the material and gas-collecting uniformly while the dant-pushing machine can make the product uniform. The advantage of the invention: it can bring into full play of the producing ability and decrease the investment as well as increase the benefits; besides, it is easy to operate, it needs less people and can be controlled automatically.
Owner:SHAANXI SHENMU SAN JIANG COAL CHEM
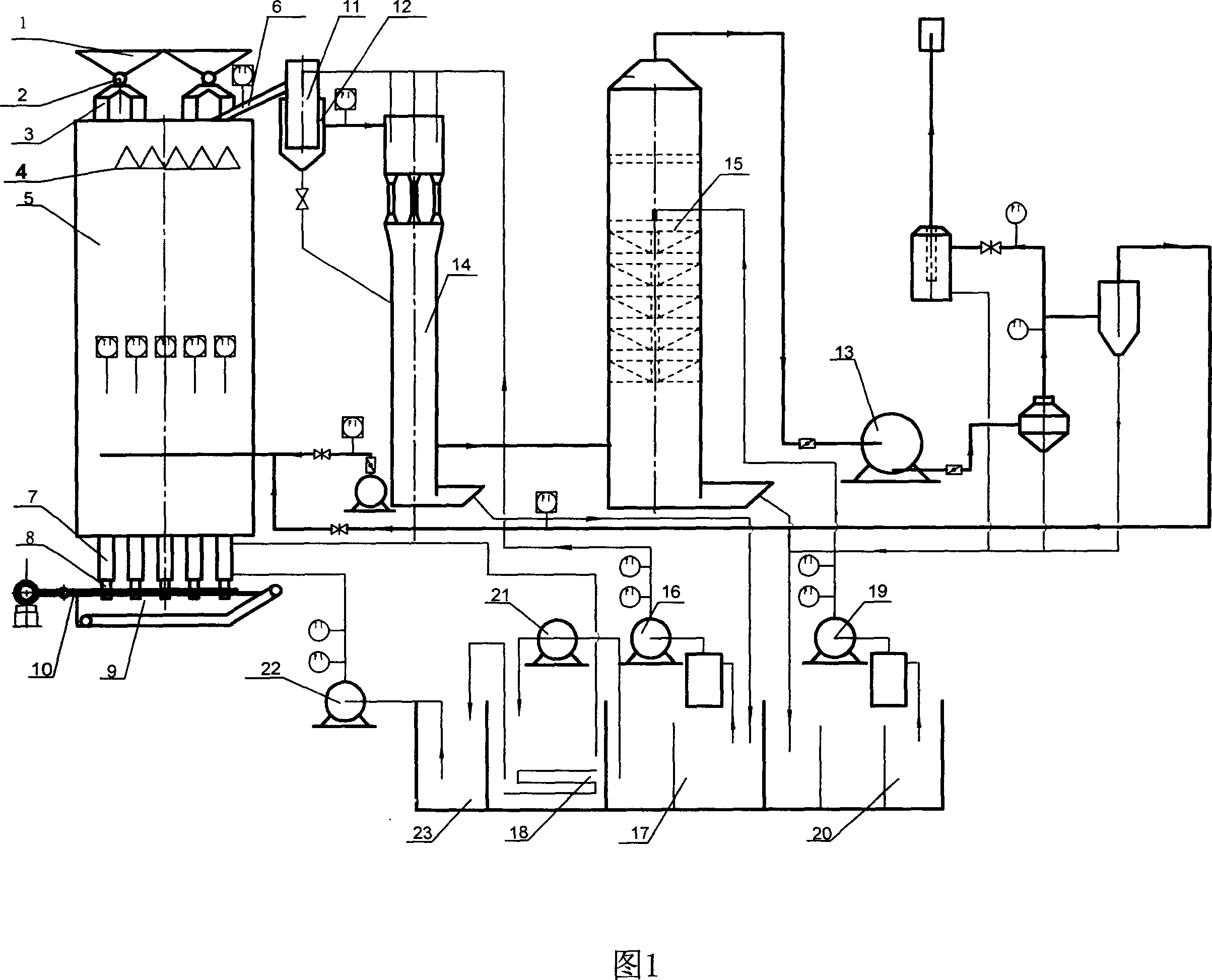
Low-temperature coal carbonization manufacturing technique
ActiveCN1966612AGive full play to the maximum capacityIncrease productionIndirect heating destructive distillationTemperature controlCarbonization
The invention disclosed a low temperature coal dry distillating process which includes the following steps: choosing the material coal; the coal goes through coal cup, roller, and assistant coalbox to get into collecting umbrella and being separated; pre-heating the coal in the drying stage; dry-distillating at 100-550DEG C for about 4h, the temperature of heating region is 700-800DEG C to decrease the content of semi-coal to less than 6%; cooling the semi-coal through the water-cooling jacket box. The heat in the stove is all absorbed by the coal in the invention. It needs less time to dry distillate the coal and it's quite direct and simple. The invention adopts big containing space, the heating gas is provided uniformly to the bottom of the stove so the stove throughput is 3 times more than the traditional stove; it can heat the material more uniformly and it need less temperature control; the tar yield has been increased and the recovery rate has been increased from less than 50% to 80% or more.
Owner:SHAANXI SHENMU SAN JIANG COAL CHEM
Composite automatic synchronous energy transfer equalization circuit and equalization method for series battery pack
InactiveCN102437609AHigh speedImprove efficiencyBatteries circuit arrangementsElectric powerCapacitanceMode control
The invention discloses a composite automatic synchronous energy transfer equalization circuit and an equalization method for a series battery pack. The circuit comprises n composite two-way battery unit energy transfer equalization modules, a master control module and equalization buses, wherein the composite two-way battery unit energy transfer equalization modules are arranged according to the number of battery units in the series battery pack; n is more than or equal to 1; the composite two-way battery unit energy transfer equalization module corresponds to a battery module consisting of k battery units which are connected in series; k is more than 1; and the composite two-way battery unit energy transfer equalization module consists of a switch matrix, an equalization control module, a two-way direct current (DC)-DC module, k discharge equalization circuits and a mode control switch. The composite automatic synchronous energy transfer equalization circuit and the equalization method for the series battery pack are high in reliability, low in cost, small in volume, light in weight, functionally comprehensive and easy to manufacture and use in large scale, and can be applied in the fields of electric vehicles, rail transit, wind-driven power generation and the like by which the series battery pack and a series capacitor bank are required.
Owner:SHANGHAI 01 POWER TECH
Membrane diffuser with uniform gas distribution
InactiveUS20050151281A1Improve distribution uniformityIncrease gas transfer efficiencyCarburetting airMixing methodsCircular discMembrane surface
A flexible diffuser membrane is provided with a unique system of perforations arranged to result in uniform distribution of gas even though the membrane deflects to different extents or the submergence varies in different parts of the membrane. The perforations are arranged to provide less perforation area per unit of perforated membrane surface area in the membrane parts that deflect the most or are submerged least and greater perforation area in membrane parts that deflect the least or are submerged most. The perforations can be slits arranged in parallel rows on a tubular membrane, in concentric circles or another pattern on a disk membrane, or in still a different pattern on a flat panel diffuser membrane. The slit length or separation can be varied between different zones on the membrane surface or the spacing between rows or circles can be varied.
Owner:ENVIRONMENTAL DYNAMICS INC
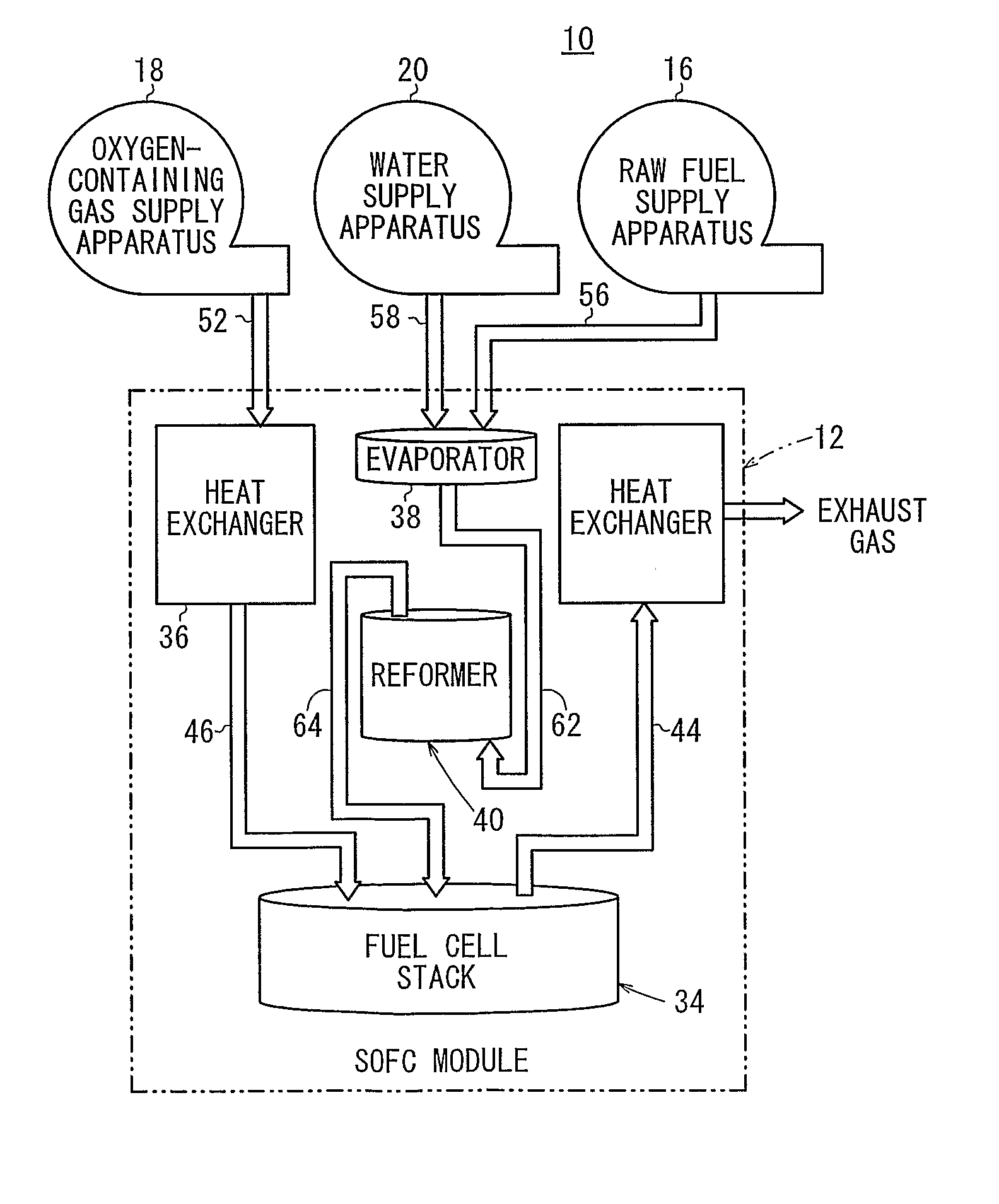
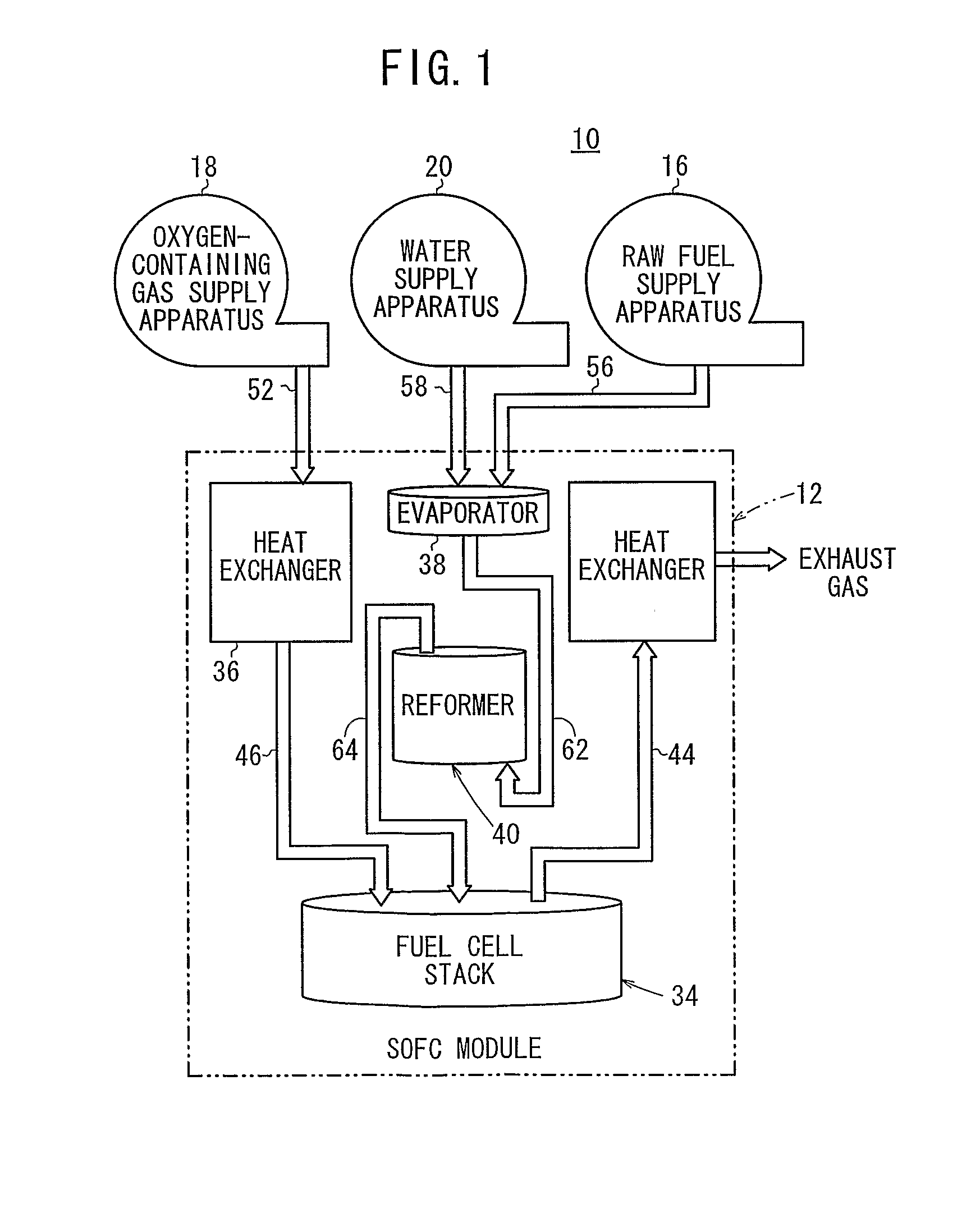
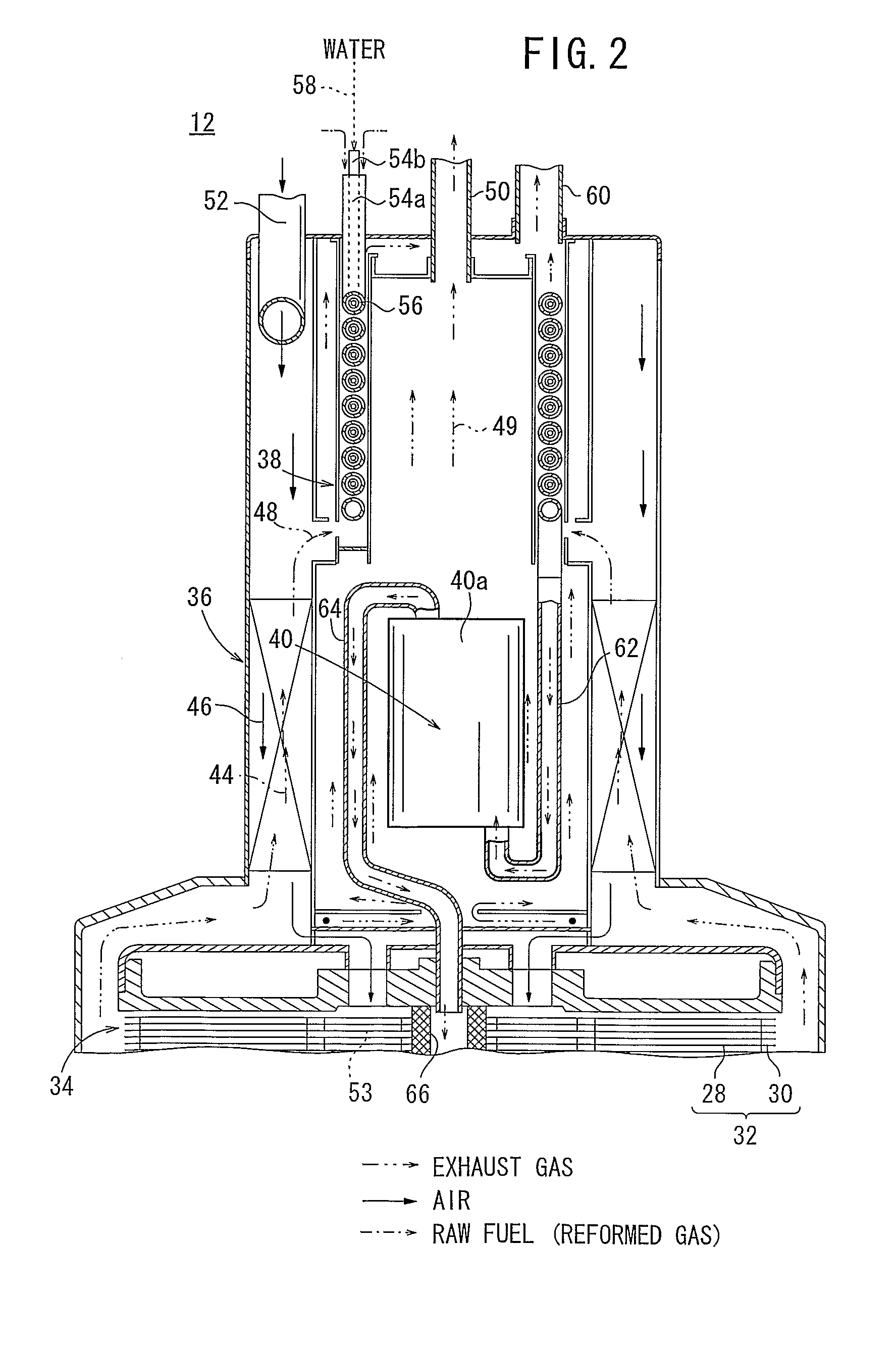
Reformer
ActiveUS20110165483A1Simple structureSmall sizeHydrogenGaseous chemical processesEngineeringWaste management
A reformer includes a reforming chamber having a raw fuel passage through which a raw fuel flows, the reforming chamber being filled with or carrying a reforming catalyst, a supply chamber disposed upstream of the reforming chamber, for uniformly supplying the raw fuel to the raw fuel passage, and a discharge chamber disposed downstream of the reforming chamber, for uniformly discharging the raw fuel from the raw fuel passage. The raw fuel passage has first and second reversers for reversing the direction in which the raw fuel flows. The raw fuel passage has a cross-sectional area which is smaller in a downstream portion thereof than in an upstream portion thereof.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Method and apparatus for producing nanofibers and polymer web
ActiveUS20100072674A1Efficient and stable productionEnsure efficient flowElectric discharge heatingFilament/thread formingProduction rateNanofiber
Nanofibers are formed from a polymer material by rotating a conductive rotating container having a plurality of small holes while supplying a polymer solution formed by dissolving a polymer material in a solvent into the rotating container, charging the polymer solution discharged from the small holes of the rotating container by charging means, and drawing the discharged filamentous polymer solution by centrifugal force and an electrostatic explosion resulting from evaporation of the solvent. The nanofibers from this production step are oriented and made to flow from one side toward the other side in a shaft center direction of the rotating container by a reflecting electrode and / or blowing means, or those nanofibers are deposited, to produce a polymer web. The nanofibers and the polymer web using these nanofibers can be produced uniformly by a simple configuration with good productivity.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Double-point coating production line for hot-melt adhesive padding cloth
InactiveCN102697213APrevent flutteringAvoid wrinklesInspecting textilesGarmentsProduction linePulp and paper industry
The invention provides a double-point coating production line for hot-melt adhesive padding cloth, and the double-point coating production line comprises a cloth reception device, a wind shielding screen, a size discharging roller, a holt-melt rubber powder blowing / sucking device, a drying oven, a cooling device, an ultraviolet lamp perching device and a rolling device which are arranged in sequence from front to back, wherein the cloth reception device comprises a cloth reception underframe, a lower pressing mould which is arranged on the cloth reception underframe and an upper pressing mould which is arranged on the cloth reception underframe and matched with the lower pressing mould in a lifting manner to crimp padding cloth; the wind shielding screen comprises a screen underframe and a screen plate which is arranged on the screen underframe; the size discharging roller comprises a discharging roller main body and a discharging hole which is formed in the discharging roller main body; and a scraper is arranged in the discharging roller main body. According to the double-point coating production line for hot-melt adhesive padding cloth, the unrolling speed of the padding cloth is increased, the continuous production is realized, the work efficiency is improved, the production cost is reduced and the quality of the padding cloth is improved.
Owner:HANGZHOU AOKE GARMENT ACCESSORIES
Normal atmosphere plasma burnishing device
The invention relates to an atmospheric plasma buffing attachment. The invention aims to overcome shortcomings in normal mechanical buffing process and solve problems of low efficiency, damage for surface and semi-surface and hardness for clean in process of preparing ultra-smooth surface with fragile material such as silicon carbide. The main components comprise: sealed working capsule (51), plasma torch (53), the first linked system (52), the second linked system (57), the first flow quantity controller (60), the second flow quantity controller (65), reacting gas bottle (61), plasma gas bottle (62), and gas recycle treating device (63); the plasma torch is installed on the first linked system. The ultra-smooth surface is realized under normal pressure through plasma chemical reaction, which can reduce device cost and enlarge application range. The working efficiency is ten times than that of traditional method, and there is no surface damage and no surface pollution.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
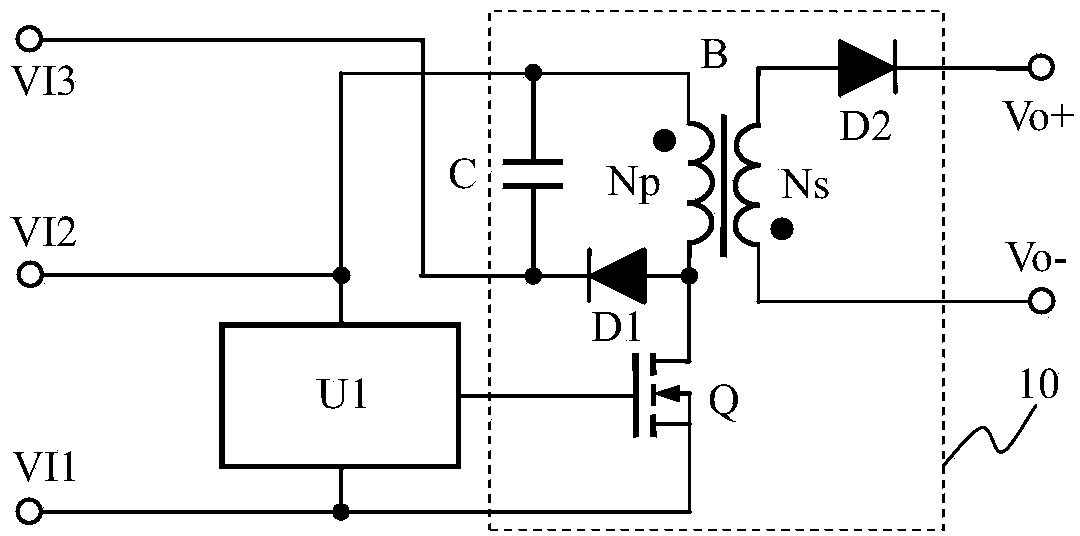
Equalizing charge circuit and battery pack
ActiveCN104201744AReduce power consumptionReduce heat consumptionBatteries circuit arrangementsElectric powerOxide semiconductorCapacitance
An equalizing charge circuit comprises a first input end, a second input end, a third input end, an output plus end, an output minus end, a detection circuit U1 and a flyback DC-DC converter 10. The junction of a drain of an N-MOS (N-channel metal oxide semiconductor) transistor Q and a primary winding NP of a transformer B is further connected with an anode of a diode D1, a cathode of the diode D1 is connected with the third input end, and a capacitor C is parallelly connected between the second input end and the third input end. The output plus end is connected on the anode of the batter pack, and the output minus end is connected on the cathode of the battery pack. When the detection circuit detects that voltage of a battery cell is larger than a set value, the converter 10 starts working, charge current to the battery cell is extracted and returned to charge the chatter pack, energy generated by leakage inductance of the flyback converter can be used for charging a previous battery cell, and accordingly equalizing charge of the battery pack is realized; when the detection circuit U1 composed of a single chip microcomputer is utilized, an infrared receiving head is added to synchronously adjust a set value, and equalizing discharge can be realized. The flyback circuit is high in reliability, simple in composition, low in cost, high in efficiency and easy to maintain.
Owner:MORNSUN GUANGZHOU SCI & TECH
Ozone generating apparatus
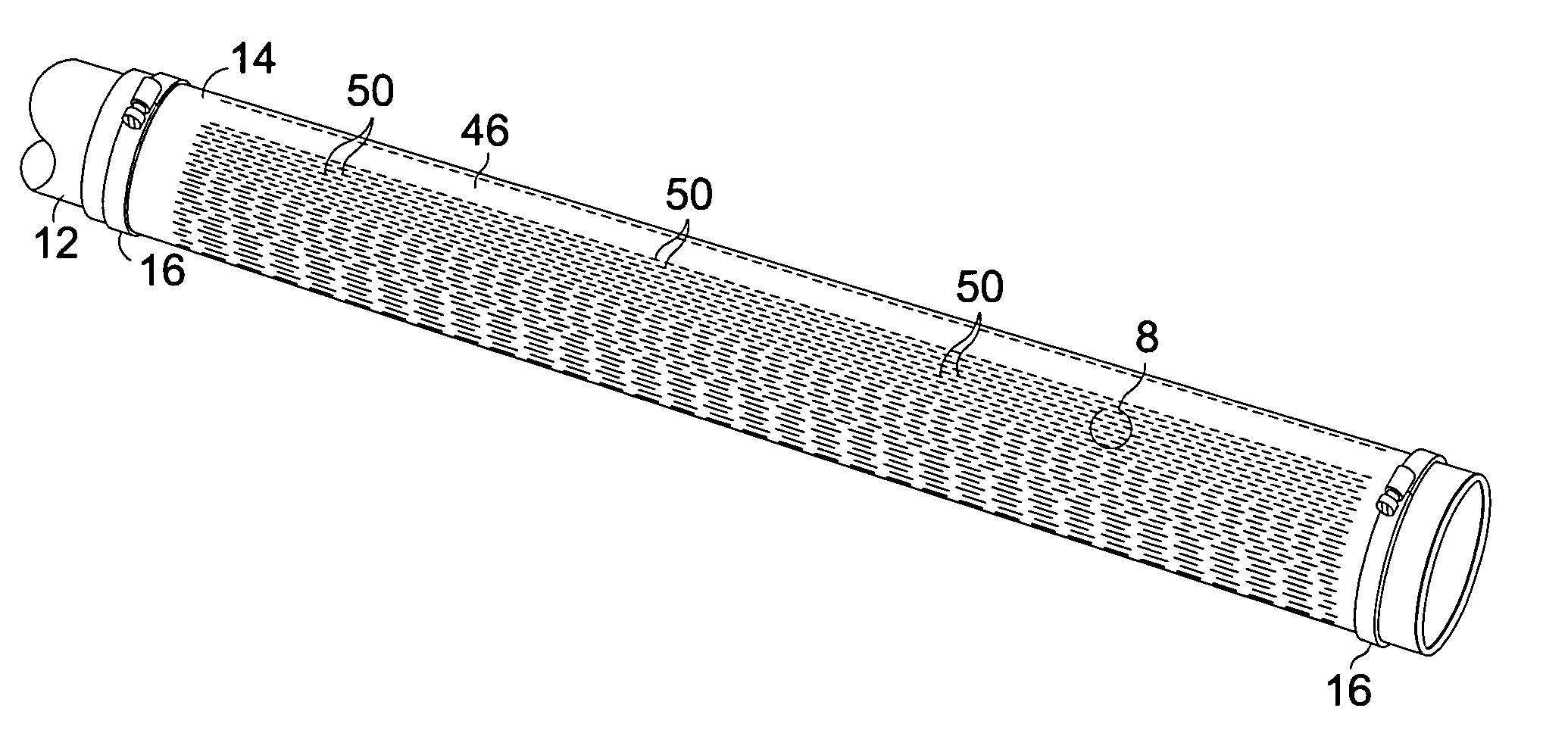
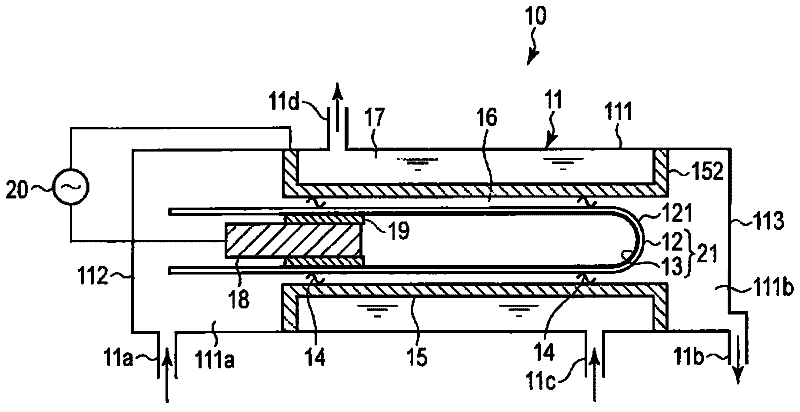
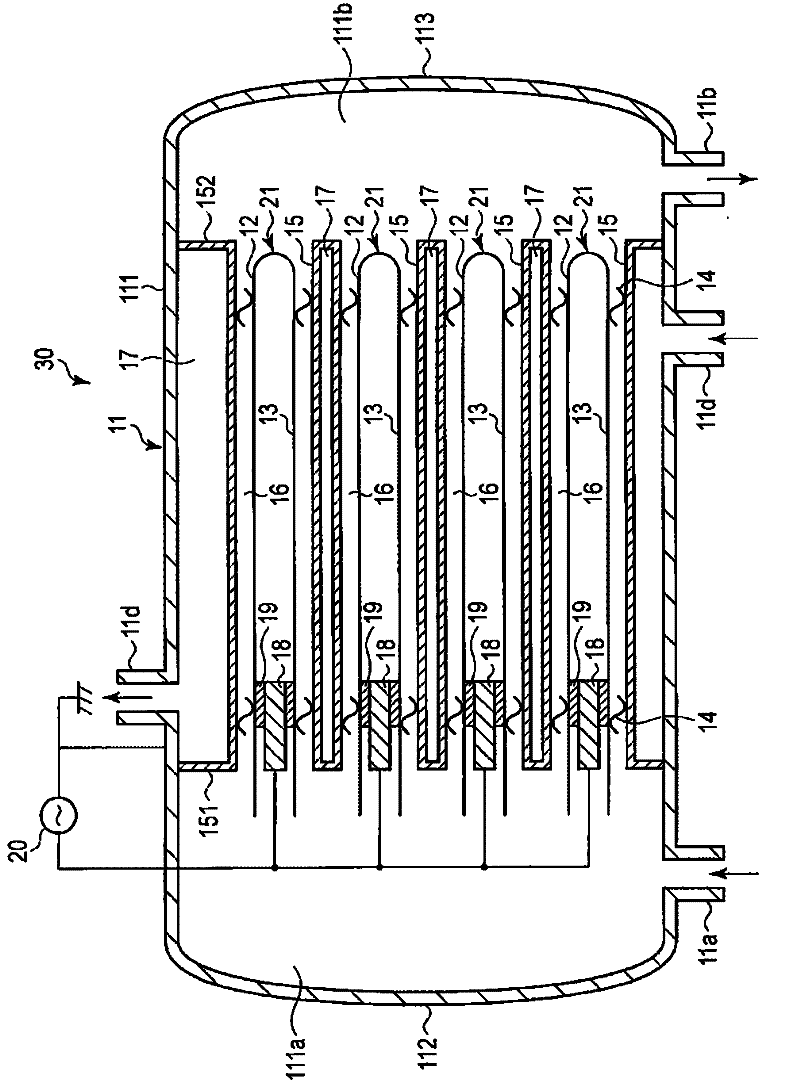
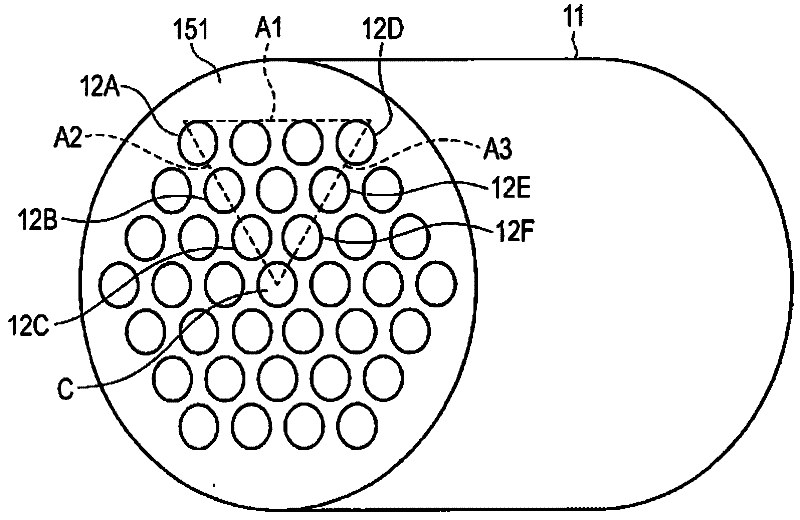
InactiveCN102530879AUniform dischargeUniform discharge gapElectrical discharge ozone preparationVoltage sourceWater jacket
An ozone generating apparatus according to one embodiment includes a hollow cylindrical sealed container provided with an inlet for a feed gas containing oxygen gas and an outlet for an ozonized gas. A discharge tube including a dielectric tube arranged within the container and a first electrode arranged within the dielectric tube is provided in the container. A second electrode is arranged within the container and surrounds the first electrode, spaced apart from the dielectric tube to form a discharge gap between the second electrode and the dielectric tube. The apparatus further includes a discharge voltage source configured to apply a discharging voltage across the first and second electrodes, and a cooling water jacket surrounding the second electrode. The dielectric tube has an outer diameter of 12 mm or more, but 19 mm or less.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Long life high capacity bipolar-type pole plate lead acid battery for electric automobile
InactiveCN101202355AImprove corrosion resistanceReduce the likelihood of feverFinal product manufactureSmall-sized cells cases/jacketsElectrical batteryEngineering
The invention provides a dual-pole polar plate lead-acid accumulator with long service life and high capacity used for an electric vehicle. A polar plate group consists of a dual-pole polar plate, an upper end polar plate, a lower end polar plate and a clapboard; the polar plate group is arranged in a battery frame which presses the polar plate group and gives a suitable pressure to active matter. The invention is technically characterized in that one surface of an anode of a baseplate of the dual-pole polar plate is provided with a conductive needle and one surface of a cathode is provided with a conductive column; furthermore, electrode modification is carried out for the baseplate and the conductive needle. After the modification, the specific capacity of the battery is 45-50Wh / kg, which is improved by 20%-30% compared with the existing normal battery. The design service life is 3-8 years, which is improved 2-3 times compared with the normal battery. The battery is mainly used for electric vehicles, electric bicycles, etc., as power supplies, and can be also used for all sites where the existing normal lead-acid batteries are applied.
Owner:夏振明
Waveguided laser channels for a gas laser
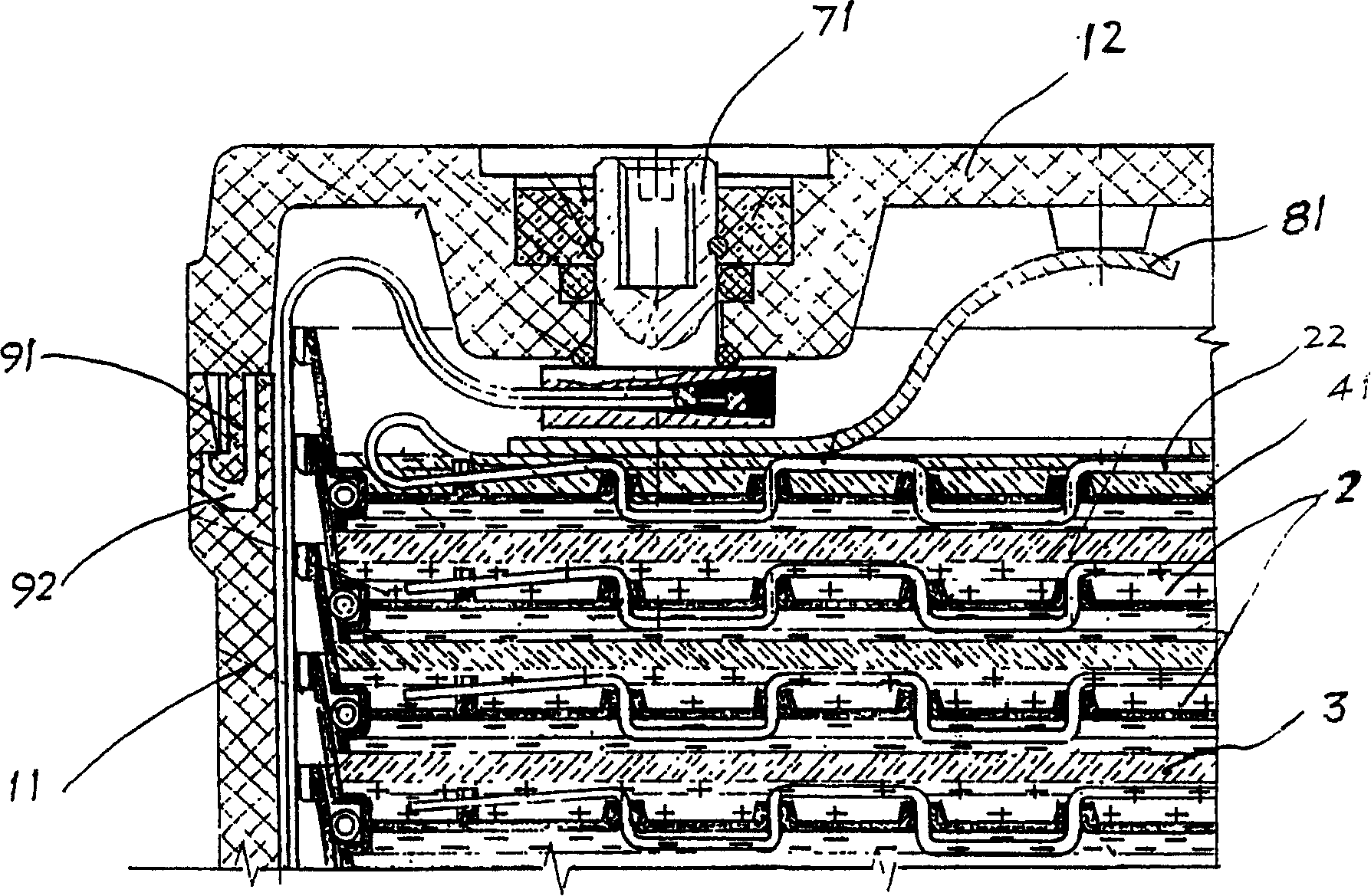
ActiveUS7570683B1Eliminate distortionGood plasma breakdownActive medium materialLaser cooling arrangementsDielectricOptical axis
An RF-excited waveguide laser module comprises a first electrode having a first elongate surface defining in part a waveguide laser channel extending along an optical axis, the first elongate surface having a substantially linear cross-section normal to the optical axis. A second electrode has a second elongate surface defining in part the waveguide laser channel extending along the optical axis. The second elongate surface has a non-linear cross-section normal to the optical axis. A dielectric insert may be provided between the electrodes defining in part the waveguide laser channel. A lengthwise gap may extend essentially an entire length of the waveguide laser channel between one of the first and second electrodes and the dielectric insert. The gap provides fluid communication between the waveguide laser channel and a volume outside the waveguide laser channel.
Owner:EPILOG CORP
High-efficiency agitation device for chemical production
InactiveCN106378029AQuality assuranceQuality improvementTransportation and packagingRotary stirring mixersHelical bladeIron removal
The invention discloses a high-efficiency agitation device for chemical production. The high-efficiency agitation device comprises an agitation barrel, wherein the left end of the upper side of the agitation barrel is provided with a material feeding hopper; the lower side of the material feeding hopper is connected with an iron removal cavity; an iron removal rotating shaft is horizontally arranged in the center of the interior of the iron removal cavity; the outer wall of the iron removal rotating shaft is provided with permanent magnet sheets in a longitudinal symmetry manner. By using a high-efficiency pre-crushed chemical material agitator, the iron removal can be carried out on a raw material of a chemical material; in an agitation process, the scraping and the washing can be carried out on the chemical material, which is adhered to an inner wall, by a scraping and washing hairbrush; the waste which is caused as the chemical material is adhered to the inner wall is avoided; the material discharge can be carried out when a helical blade positively rotates; the agitation and the mixing can be carried out on the chemical material at a bottom when the helical blade negatively rotates; the agitation effect and efficiency are improved; the automatic and quantitative water addition can be realized; the quality of the material is guaranteed; the effective shock absorption can be realized by a spring pillar; further, the movement is more convenient and quicker; the practicability and the convenience are high.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
Slim-type air conditioner
InactiveUS20050257561A1Reduce thicknessSmall footprintLighting and heating apparatusPumpsEngineering
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Dispense point isolation device
ActiveUS20140305967A1Improve mixing and dispensingPromote downward mobilityLiquid transferring devicesLiquid dispensingContaminationBiomedical engineering
Devices for dispensing beverages, particularly multiple differing beverages from a dispensing nozzle, are provided herein. In an exemplary embodiment, a multiple beverage dispensing device includes a dispensing array attached to a dispense point isolation device within a dispensing nozzle, the dispensing array facilitates flow of a beverage base and at least one beverage additive into the dispensing nozzle and the dispense point isolation device isolating discharge of beverage additive to prevent cross-contamination and color-carryover caused by the residual traces of beverage additive often associated with conventional dispensing devices. In many embodiments, the dispense point isolation device further includes one or more isolation features, including any or all of a recess, trough, notch, raised ridge or tubular projection around an exit orifice of the beverage additive flow channel so as to further isolate release of the beverage additive and further inhibit cross-contamination and color-carryover.
Owner:AUTOMATIC BAR CONTROLS
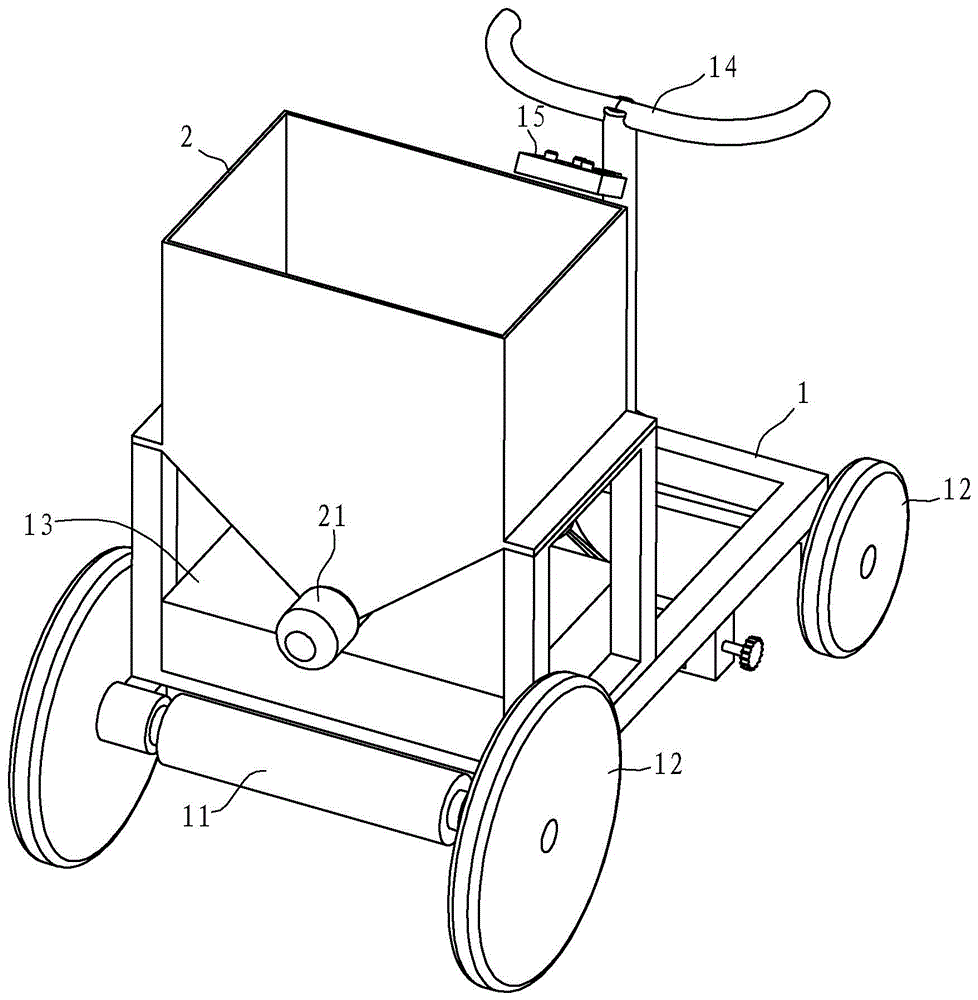
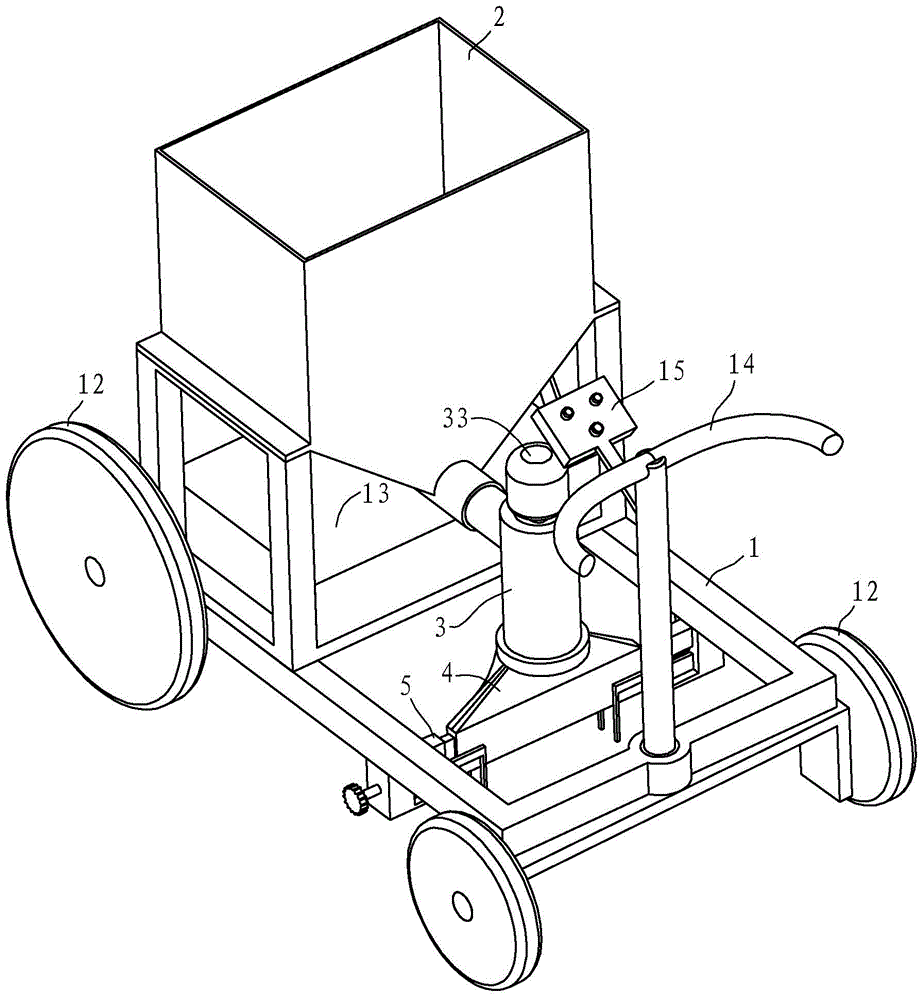
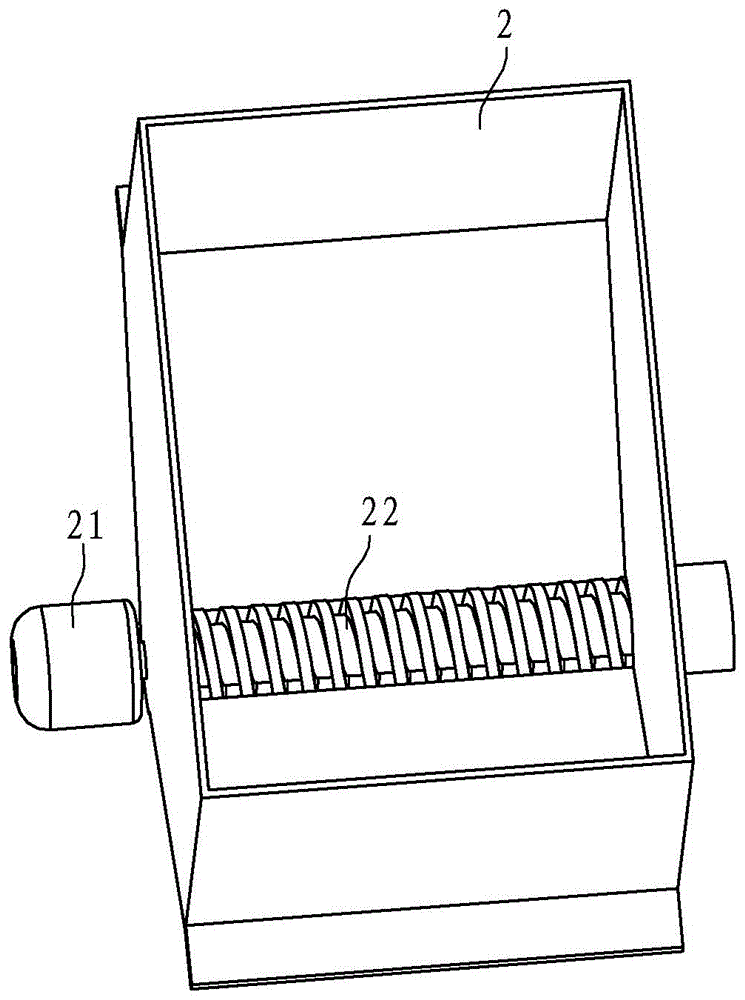
Extrusion type marker
The invention discloses an extrusion type marker which comprises a frame, a coating barrel, a discharging box, an extrusion screw rod and an adjusting mechanism. The coating barrel is in a funnel shape, is provided with a discharge opening and is arranged at the front end of the frame; the discharging box is communicated with the discharge opening of the coating barrel through a conveying pipeline, and a marking opening is formed in the bottom; the extrusion screw rod is arranged in the conveying pipeline, and the power input end of the extrusion screw rod is connected with the output end of an extrusion motor; the adjusting mechanism can adjust the length of the marking opening. Compared with the prior art, the extrusion type marker has the advantages that a screw rotary extrusion mode is adopted, the coating is extruded from an extrusion pipe into the discharging box through the conveying pipeline and is discharged through the marking opening of the discharging box, the discharging is uniform, caking is avoided, the on / off of discharging can be realized by opening and closing the extrusion screw rod, and the marker is convenient to control.
Owner:NINGBO MUNICIPAL ENG CONSTR GROUP
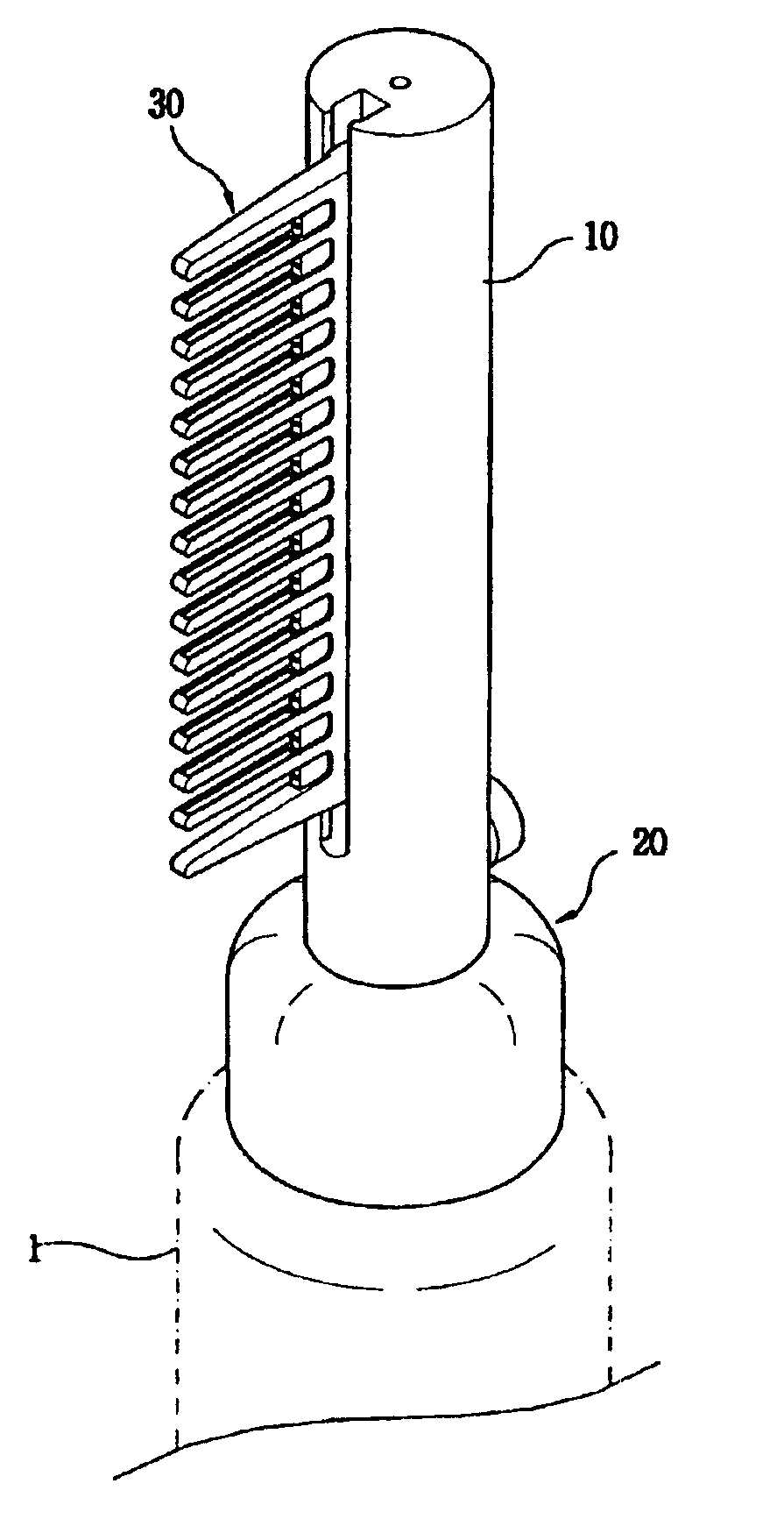
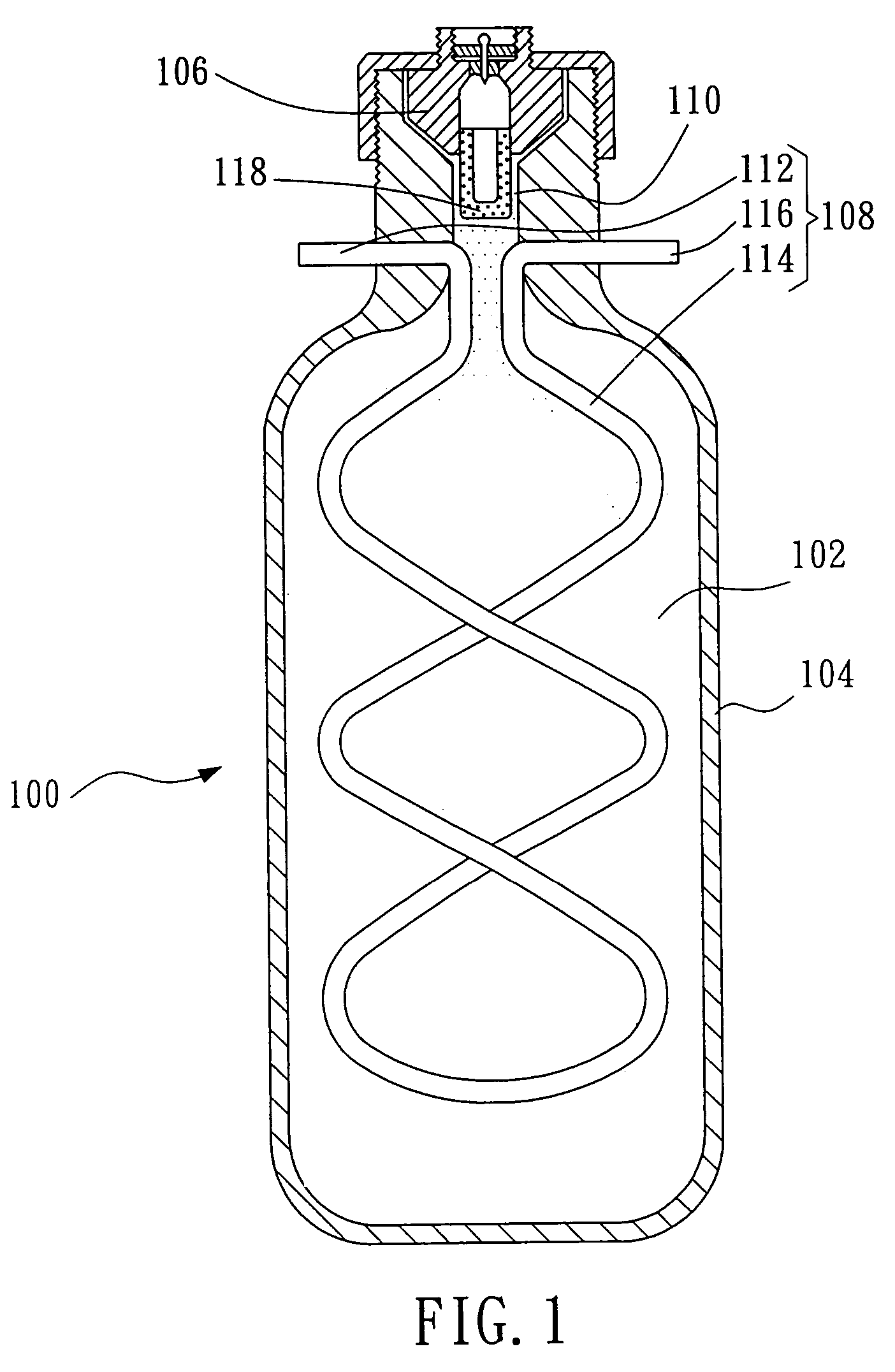
Hair setting device
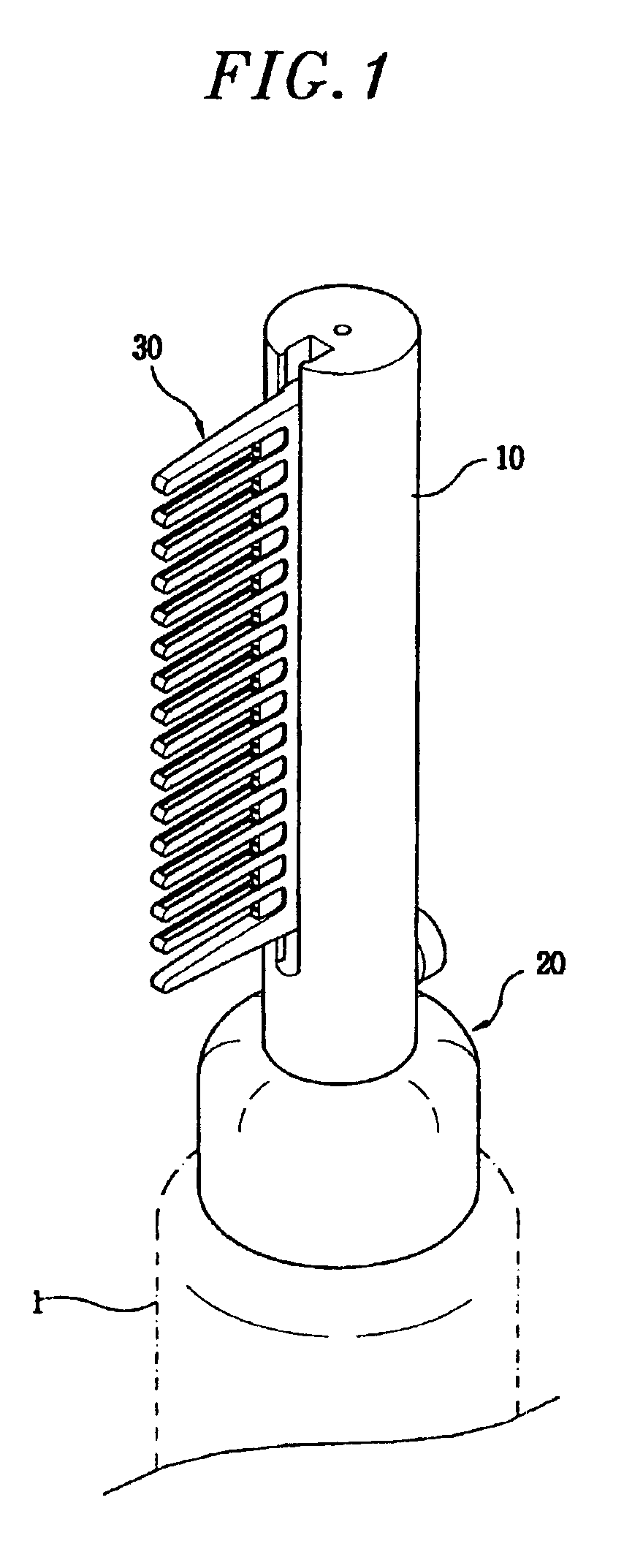
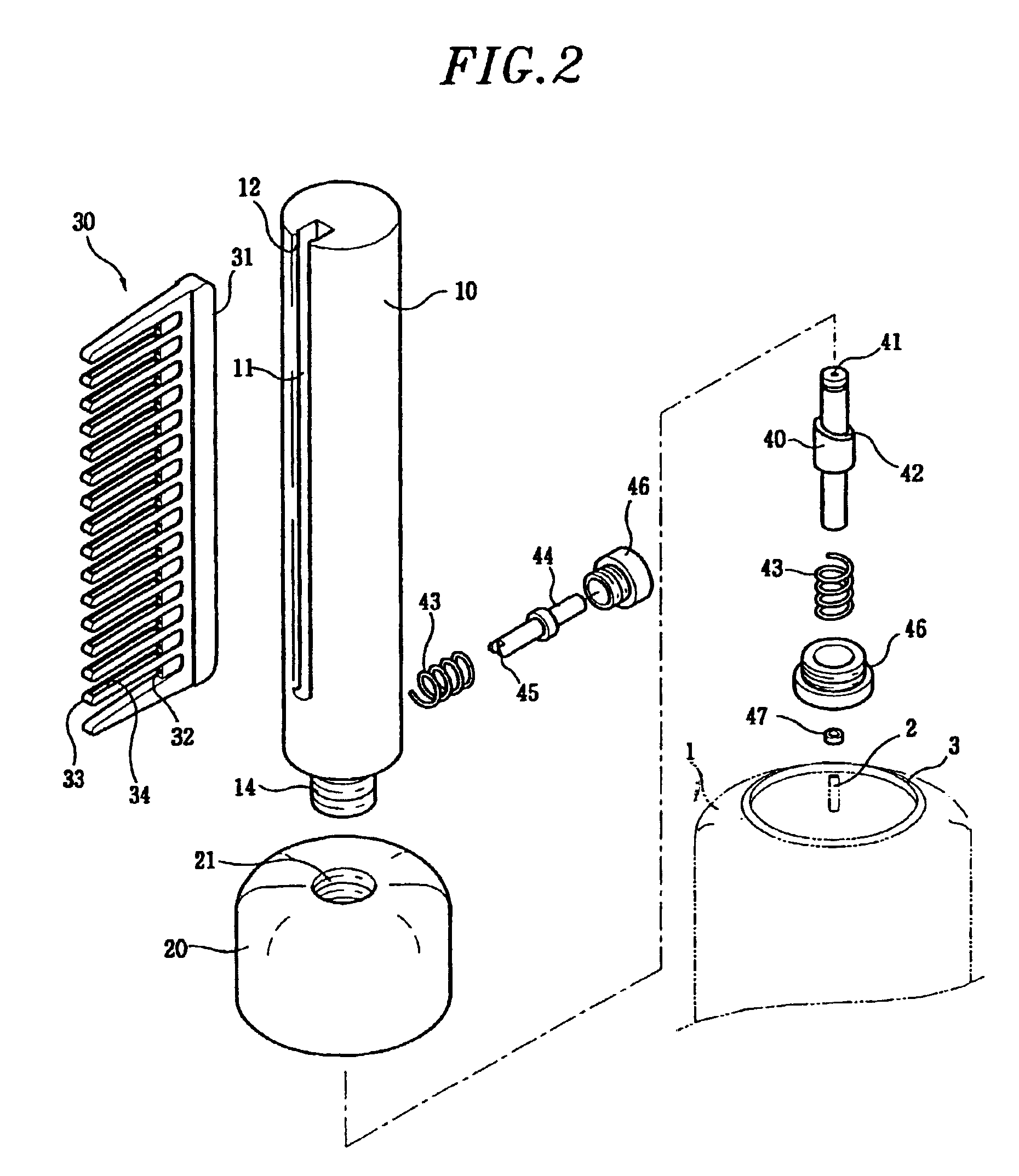
InactiveUS6915807B2Uniform applicationUniform dischargeCurling devicesHair combsInterior spaceComing out
A hair setting device comprises a setting material supply for storing hair setting material, a hollow pipe-shaped body including a guide groove formed along a lengthwise direction of the body and a slit formed at a bottom of the guide groove, the slit communicating with an inside space of the hollow pipe-shaped body, a base for fixing the hollow pipe-shaped body to the setting material supply, the base communicating with the inside space of the hollow pipe-shaped body and including an inner surface enclosing a nozzle of the setting material supply, an operating valve, including a setting material guide hole at a center portion of the operating valve, the operating valve being supported by a first spring inside the hollow pipe-shaped body, a bottom end portion of the operating valve being in contact with the nozzle of the setting material supply, a push button installed at a bottom portion of the hollow pipe-shape body in a radial direction thereof and supported by a second spring, wherein the push button is in contact with the operating valve in such a way that the operating valve is moved toward the nozzle of the setting material supply when the push button is pressed, and a comb including a base portion which is detachably engaged with the guide groove of the body and a plurality of outlets arranged in a regular interval for allowing the hair setting material to come out from the slit.
Owner:CHOI YONG SIK +1
Systems and methods for aerial seeding
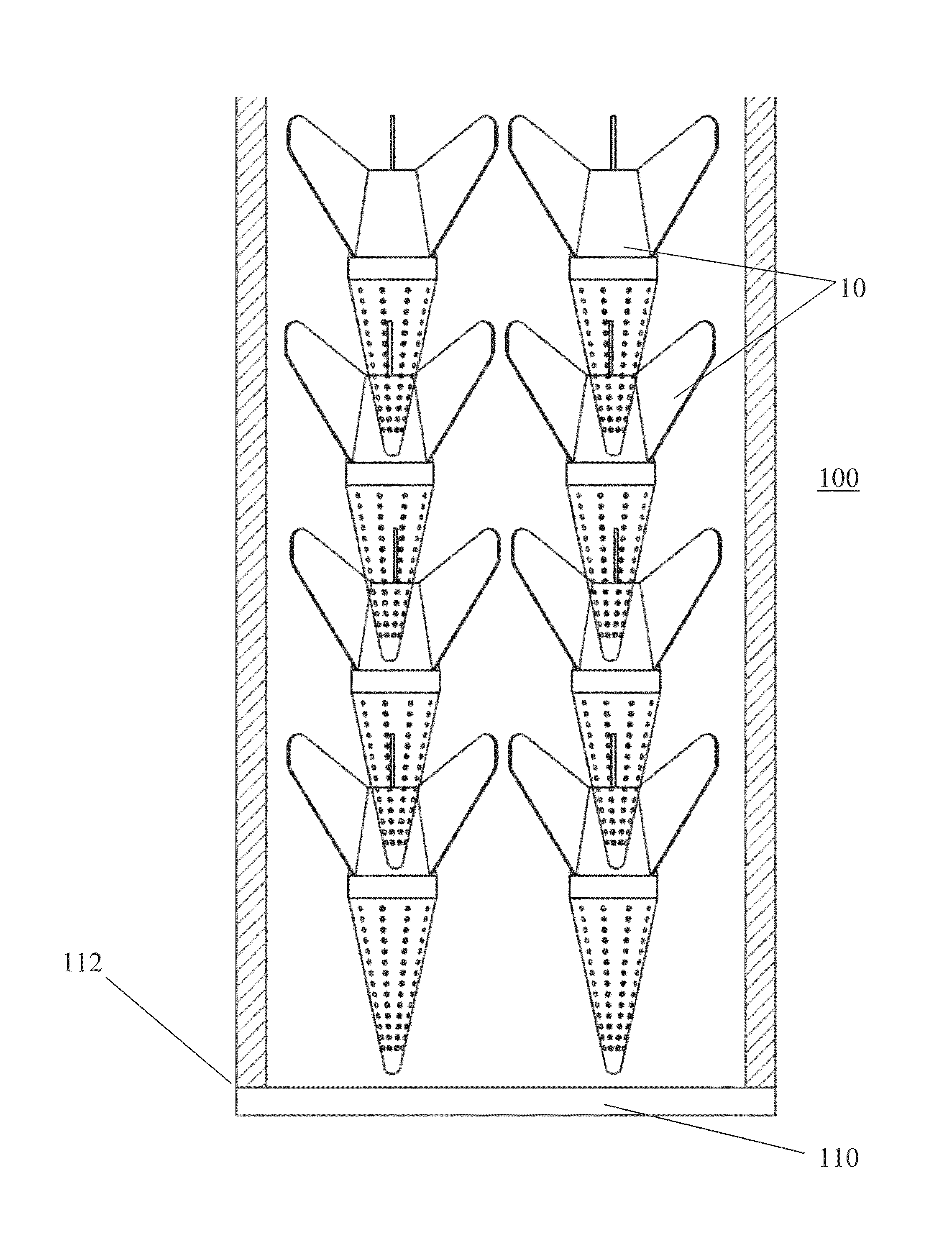
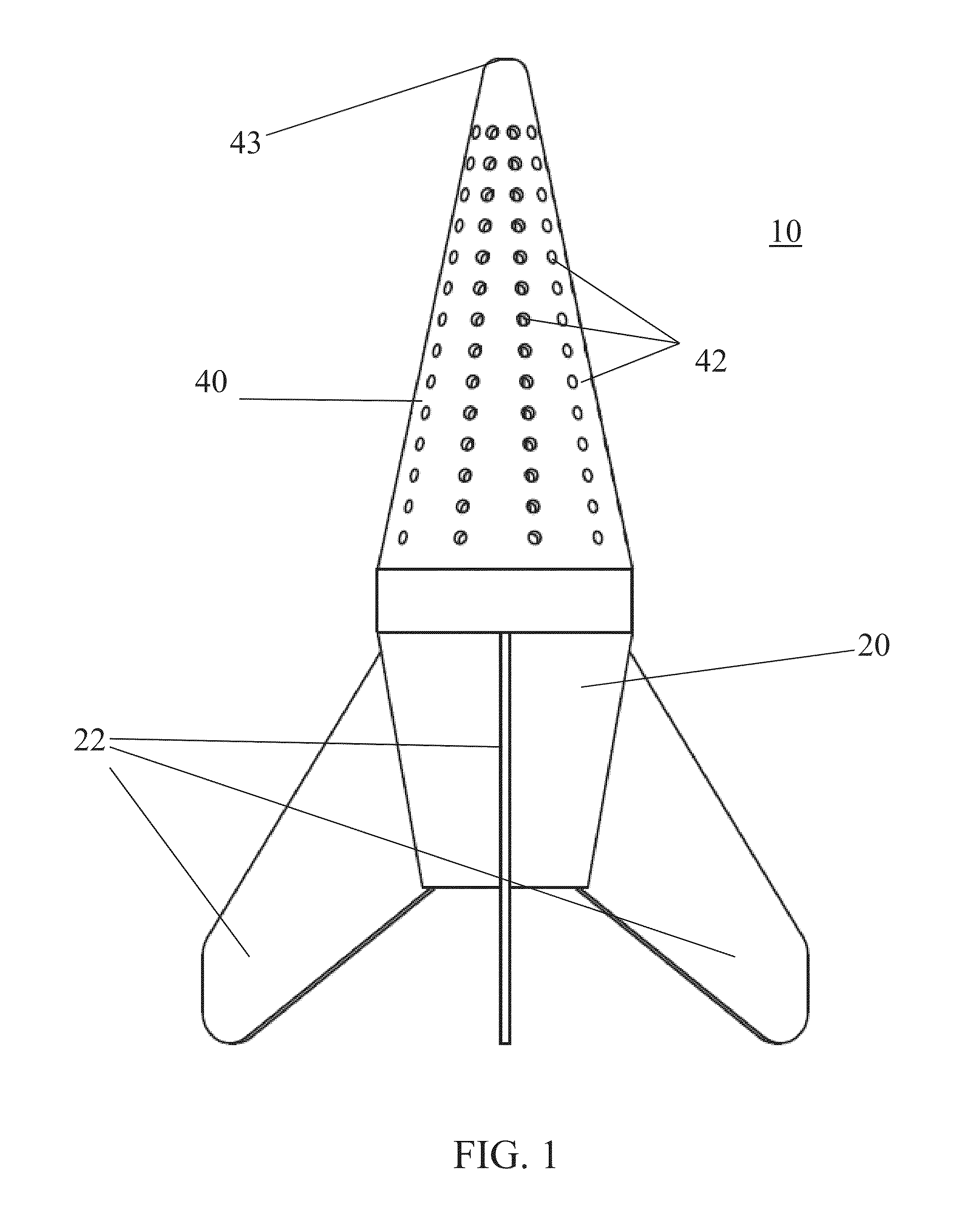
ActiveUS20160234997A1Efficient ground penetrationReduce mortalityAircraft componentsClimate change adaptationFlight vehicleSeedling
Reforestation capsules composed of biodegradable materials are operable to be used in aerial reforestation operations. Capsules may contain one or more seedlings, compacted fertilizer, soil, and / or nutrients. Capsules include a flight platform component and cone tip component. The capsule structure survives impact and may serve as additional nutrient for the seedling(s). A housing unit sized and configured to contain and dispense capsules can be mounted or otherwise housed in an aircraft to deliver capsules.
Owner:NEW JERSEY INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Temperature controlled and pressure controlled formation method of lithium ion battery
ActiveCN108598593APrevent oxidationPromote formationFinal product manufactureSecondary cells charging/dischargingTemperature stressTemperature control
The invention provides a temperature controlled and pressure controlled formation method of a lithium ion battery. The method comprises the step of performing a liquid injection and formation method on an assembled battery under the condition of controlling the temperature and pressure. The temperature controlled and pressure controlled formation method comprises multi-stage formation technologiesof low pressure formation, normal temperature formation and high temperature formation. The lithium ion battery acquired by the method is good in cycling life and high temperature stability.
Owner:星恒电源(滁州)有限公司
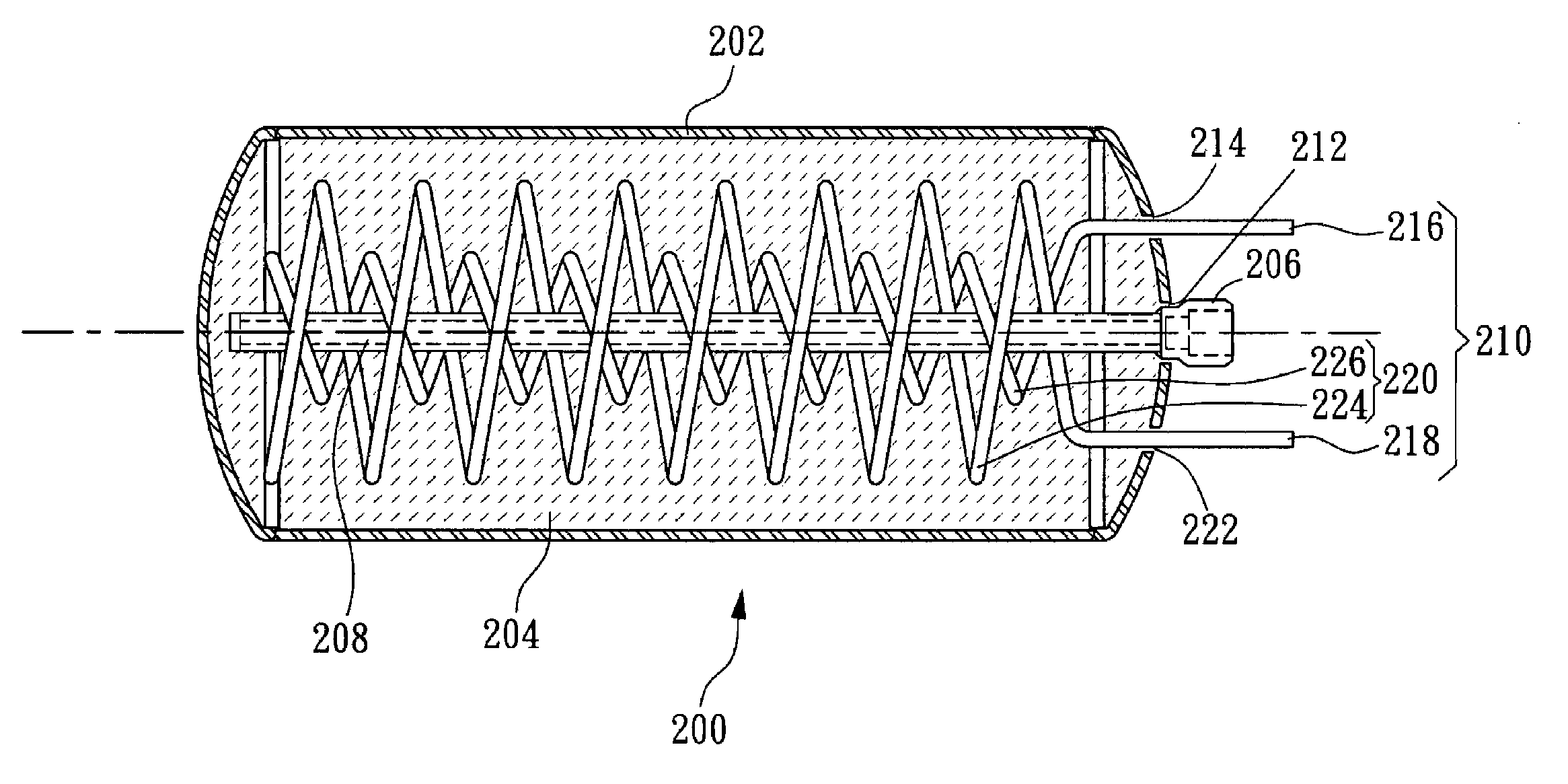
Metal hydride canister apparatus
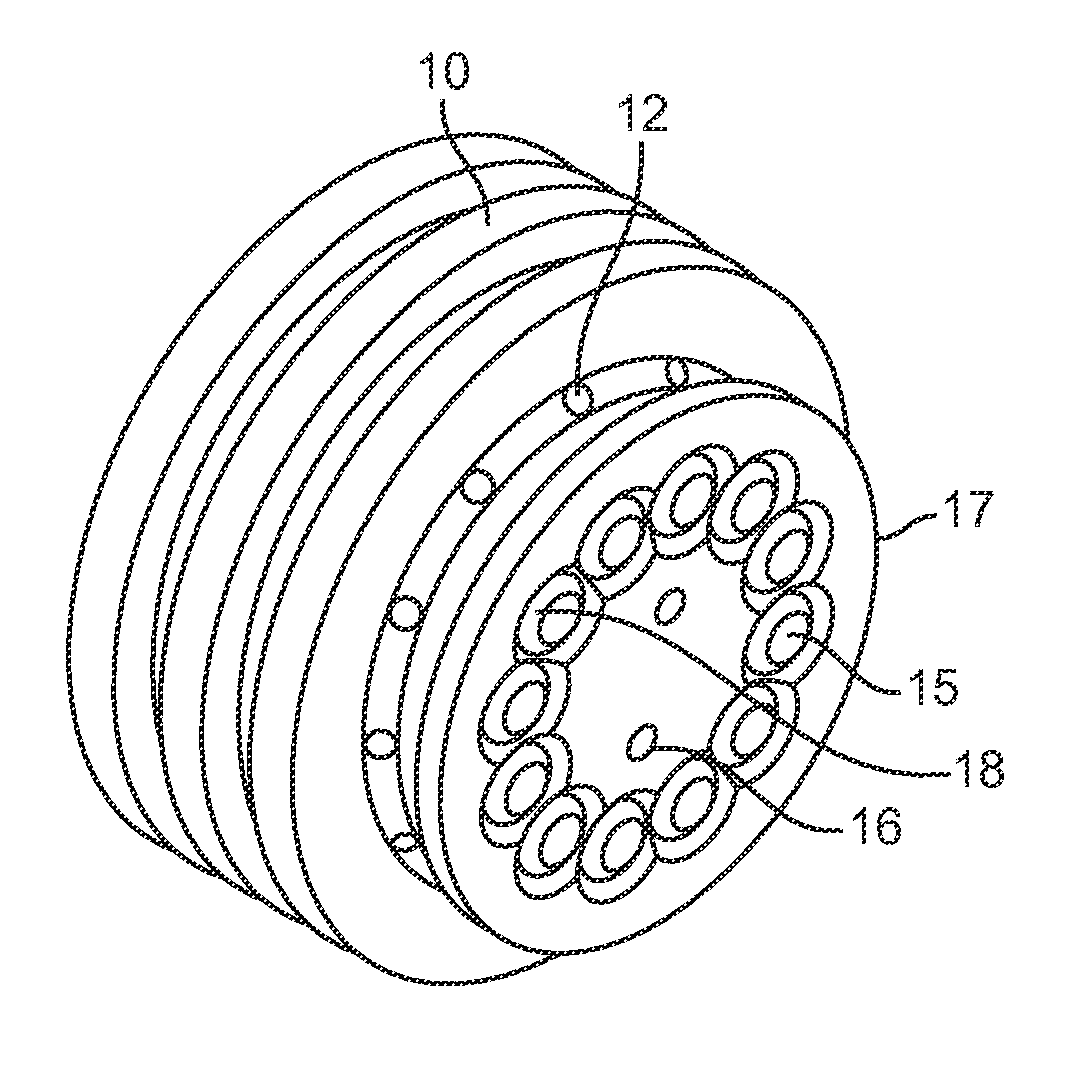
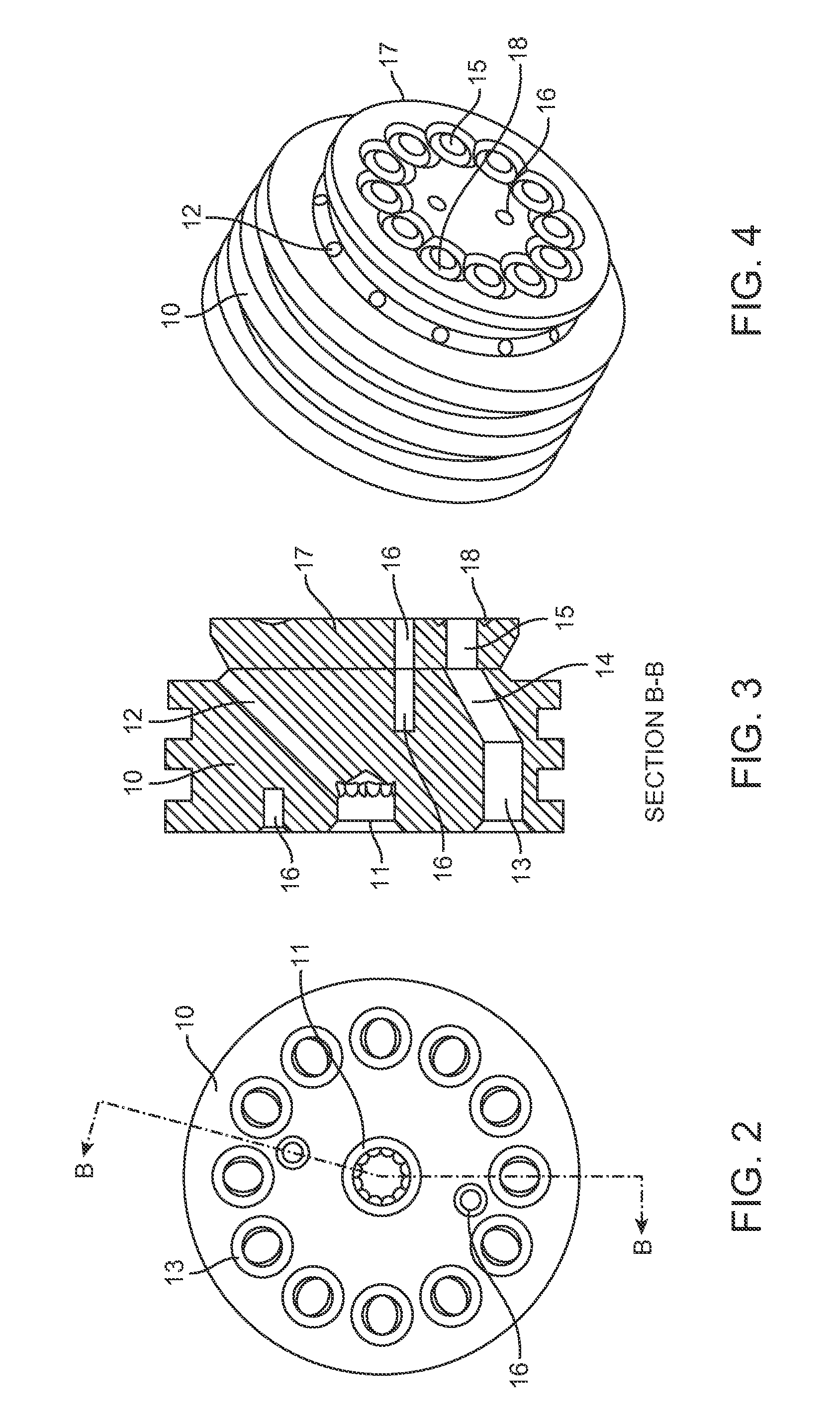
ActiveUS7241331B2Prevent leakageUniform dischargeReversible hydrogen uptakeFuel cell auxillariesEngineeringHydride
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Tyre rubber slitter
ActiveCN101229642AEasy to force feedImprove ergonomicsMetal working apparatusWebs handlingRubber materialDrive motor
The invention provides a vertical cutting machine for tyre rubber, which comprises a feed-in transporting mechanism, a vertical cutting mechanism and a discharging transporting mechanism, wherein, an end of a feed inlet of the vertical cutting mechanism is provided with a hydraulic forced conveying mechanism so as to provide convenience to convey ultra-thick rubber matrix into the vertical cutting mechanism by force and raise work efficiency with safety and reliability. The vertical cutting mechanism comprises a frame, an upper cutter axle, a lower cutter axle, an upper rubber shoveling plate, a lower rubber shoveling plate, a drive motor and a reducer, wherein, the upper and lower cutter axles are arranged on a bottom seat of the frame through two bearing seats at both ends of the axles; a plurality of cylindrical cutter discs are positioned on the upper and lower cutter axles in a staggered way through interval sleeves; the upper and lower cylindrical cutter disc groups conduct pressing and cutting for the tyre rubber and can continuously cut the rubber materials with different types of thickness, hardness and viscosity into a plurality of rubber material strips at a time, with uniform discharging and high cutting efficiency. As the rubber material with the length of 10-15 meters can be cut per minute and the labor intensity is reduced, the work efficiency is greatly improved with labor and time saved as well as low loss and uneasy wear.
Owner:尹家旺
Electrostatic air conditioner cleaner and electric discharge device
ActiveCN102430479AImprove bindingIncrease discharge voltageExternal electric electrostatic seperatorElectrode constructionsElectric dischargeEngineering
The invention provides an electrostatic air conditioner cleaner for a central air-conditioning system and an electric discharge device arranged in the electrostatic air conditioner cleaner. The electrostatic air conditioner cleaner comprises a shell, an air inlet, an air outlet, an electric discharge assembly and an ionization dust collecting assembly, wherein the electric discharge assembly comprises an electric discharge anode assembly which is of an acicular structure and an electric discharge cathode assembly, the acicular structure is firm, can be used for improving an electric discharge voltage, can be washed without any chemical agent or a soaking process and can be directly flushed with a pressure water pistol, the electric discharge anode assembly passes through the center of the ionization dust collecting assembly and extends out of the tail end of the ionization dust collecting assembly, and the ionization dust collecting assembly consists of honeycomb six-wall type ionization dust connecting plates, thus the dust collecting space is increased and the overall size of the cleaner is reduced; and the overall performance of the cleaner is improved, and the cleaning period is prolonged. Compared with a medium-efficiency band filter, the cleaner has the advantages that the production of nondegradable solid pollutants can be reduced and the effects of environmental friendliness, energy conservation and emission reduction are achieved truly.
Owner:杨全辉
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com