Phytate nanoparticle coated stain-removal compound abradant and preparation method and application thereof
A nanoparticle and phytate technology, applied in the field of toothpaste for removing stains and abrasives for toothpaste, can solve the problems of complicated toothpaste ingredients and the inability to fully exert the stain removal effect of phytic acid, so as to improve the stain removal effect and increase the overall concentration , the effect of reducing wear
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
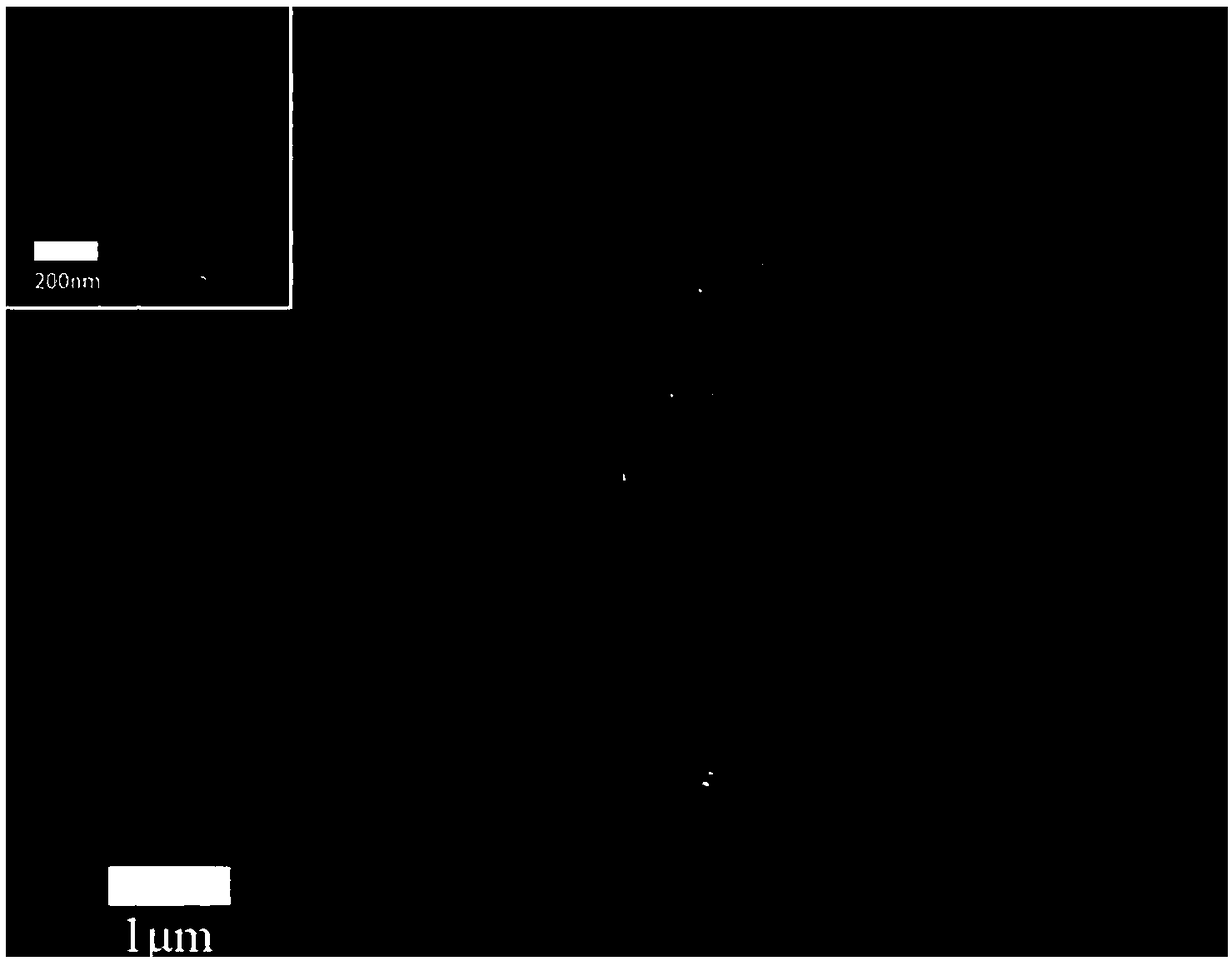
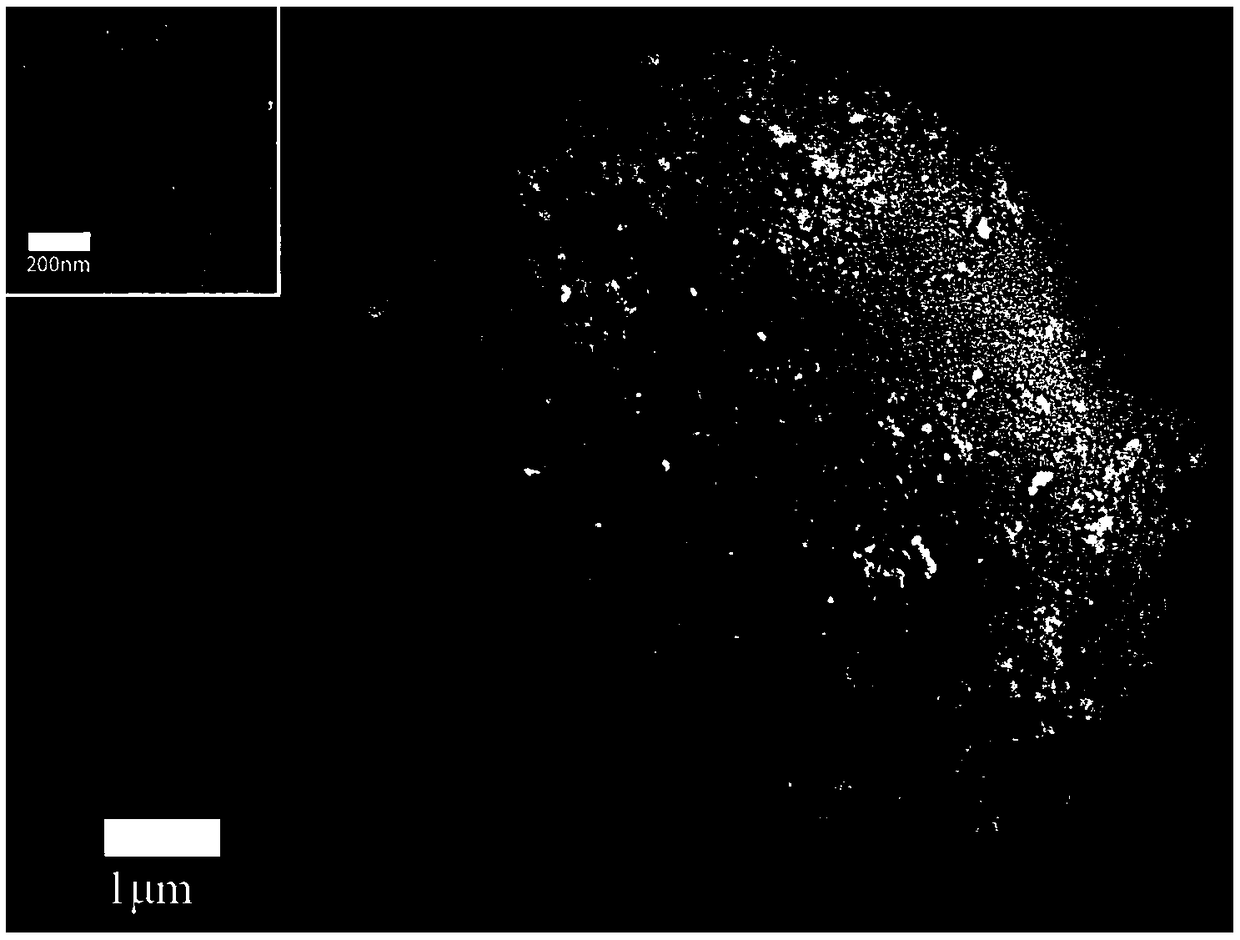
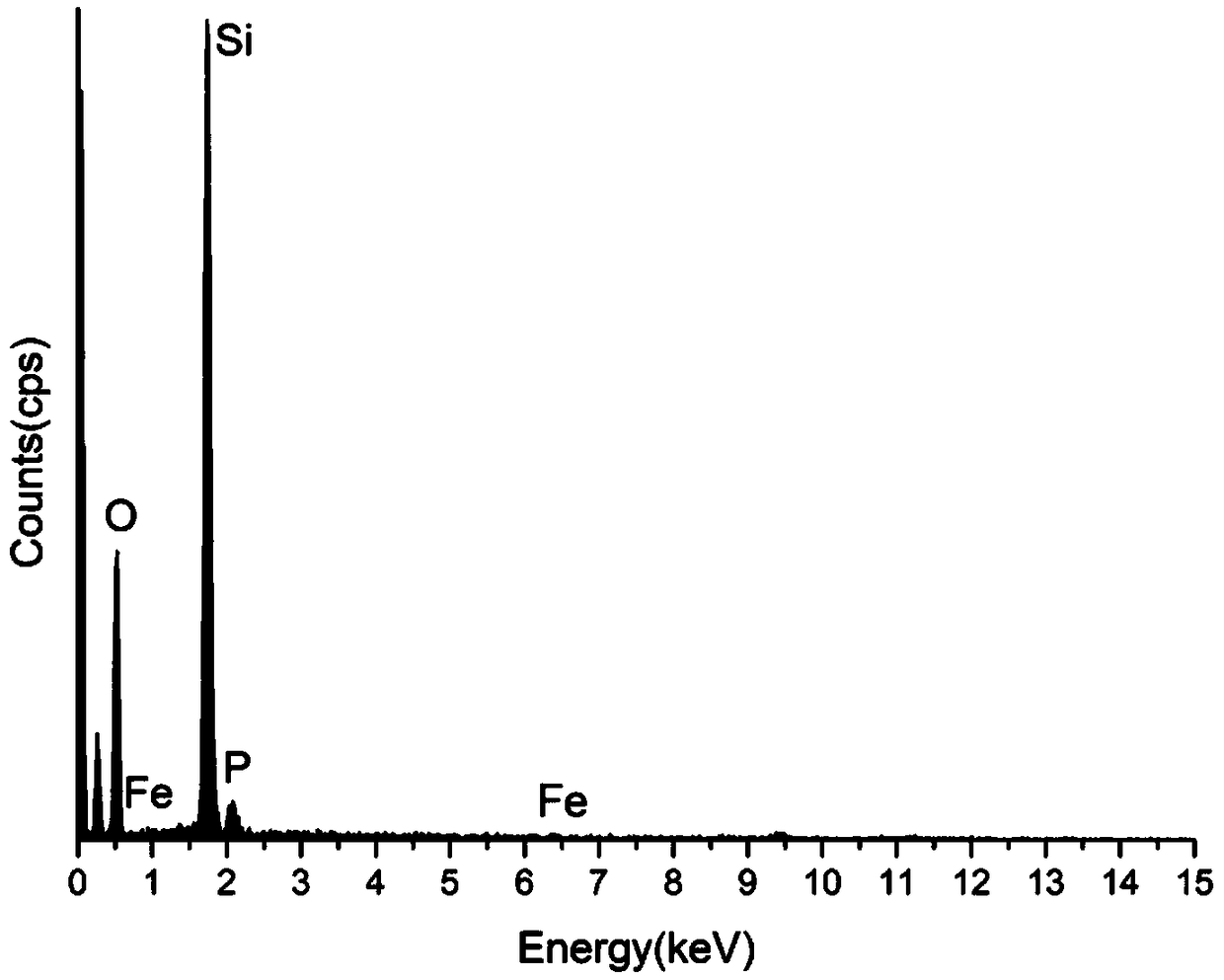
[0039] 150g abrasive silicon dioxide (SiO 2 ) soaked in 4L of phytic acid (PA) solution with a concentration of 0.08mol / L, and stirred for 5 minutes to make the surface of the abrasive adhere to phytic acid molecules; The concentration is 0.1mol / L ferric chloride (FeCl 3 ) in the solution and stirred for 5 minutes, utilize phytic acid to chelate iron ions, react on the surface of the silicon dioxide abrasive, and deposit insoluble iron phytate particles on the surface of the silicon dioxide abrasive; after filtering, washing and drying, A silicon dioxide composite friction agent for toothpaste whose surface is coated with insoluble ferric phytate nanoparticles is obtained. figure 1 The photo of the surface of the silica composite friction agent coated with insoluble ferric phytate nanoparticles observed by scanning electron microscope (Hitachi‐SU8220), figure 2 It is the surface of uncoated silica composite friction agent. From figure 1 It can be seen that a large number ...
Embodiment 2
[0045] 150g abrasive silicon dioxide (SiO 2 ) soaked in 4L 0.12mol / L phytic acid (PA) solution, stirred for 5 minutes, so that phytic acid molecules were attached to the surface of the friction agent; / L Zinc nitrate (Zn(NO 3 ) 2 ·6H 2 (2) Stir in the solution for 5min, utilize phytic acid to the chelation of zinc ions, react on the surface of the silicon dioxide abrasive, and deposit insoluble zinc phytate particles on the surface of the silicon dioxide abrasive; filter, wash, and dry , to obtain the silicon dioxide composite friction agent for toothpaste whose surface is coated with insoluble zinc phytate nanoparticles. The comparative analysis of the weight of the silica abrasive grains before and after coating shows that the coating amount of the iron-zinc phytate grains on the silica abrasive grains is 6.9% (mass percentage).
Embodiment 3
[0047] 150g abrasive silicon dioxide (SiO 2 ) soaked in 4L 0.22mol / L phytic acid (PA) solution, stirred for 5 minutes, so that phytic acid molecules were attached to the surface of the friction agent; / L cerium nitrate (Ce(NO 3 ) 3 ·6H 2 (2) Stir in the solution for 5min, utilize phytic acid to the chelation of cerium ions, react on the surface of the silica abrasive, and deposit insoluble cerium phytate particles on the surface of the silica abrasive; filter, wash, and dry , to obtain the silicon dioxide composite friction agent for toothpaste whose surface is coated with insoluble cerium phytate nanoparticles. The comparative analysis of the weight of silica abrasive grains before and after coating shows that the coating amount of cerium phytate nanoparticles on silica abrasive grains is 6.8% (mass percentage).
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com