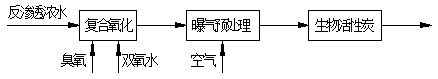
Compound oxidation-biological active carbon technology for removing coking reverse osmosis concentrated water organic matters
A technology of reverse osmosis concentrated water and biological activated carbon, which is applied in the direction of water pollutants, biological water/sewage treatment, oxidized water/sewage treatment, etc., can solve problems affecting the normal operation of the system, low treatment efficiency, and damage to membrane components, etc., to achieve The effect of improving the removal rate of organic matter
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] The COD of reverse osmosis concentrated water in a coking plant is 152mg / L. The wastewater enters the composite oxidation tower first, and the dosage of hydrogen peroxide is 200mg / L. When the residence time is 40min, the COD decline rate is less than 0.4mg / L·min After oxidation, the COD of wastewater is reduced to 87mg / L, and the effluent enters the aeration tank, and the residence time is 1h to remove residual ozone and hydrogen peroxide. Activated carbon, wherein the particle size of activated carbon is in the range of 0.5-3mm, and the hydraulic retention time is 0.5h. Before the start-up of the biological activated carbon unit, the activated carbon is bio-coated first, and the high-efficiency salt-tolerant biological bacteria agent is used for coating and domestication. The dosage of the high-efficiency salt-tolerant bacteria agent is 100mg / L, and the effluent of the biological activated carbon process is 46mg / L.
Embodiment 2
[0035] The COD of reverse osmosis concentrated water in a coal chemical plant is 193mg / L. The wastewater first enters the composite oxidation tower, and the dosage of hydrogen peroxide is 400mg / L. When the residence time is 60min, the COD decline rate is less than 0.4mg / L·min. After compound oxidation, the COD of the wastewater is reduced to 101mg / L, the effluent enters the aeration tank, the residence time is 2h, and the residual ozone and hydrogen peroxide are removed. Load activated carbon, wherein the particle size of activated carbon is in the range of 0.5-3mm, and the hydraulic retention time is 1h. Before the start-up of the biological activated carbon unit, the activated carbon is bio-filmed first, and the high-efficiency salt-tolerant biological bacteria is used for coating and domestication. The dosage of the high-efficiency salt-tolerant bacteria is 200mg / L, and the effluent of the biological activated carbon process is 55mg / L.
Embodiment 3
[0037] The COD of reverse osmosis concentrated water in a paper mill is 241mg / L. The wastewater enters the composite oxidation tower first, and the dosage of hydrogen peroxide is 600mg / L. After compound oxidation, the COD of the wastewater is reduced to 112mg / L, the effluent enters the aeration tank, the residence time is 3h, and the residual ozone and hydrogen peroxide are removed. The dissolved oxygen content in the effluent is 4mg / L, and the effluent enters the biological activated carbon unit in the form of a filter Load activated carbon, wherein the particle size of activated carbon is in the range of 0.5-3mm, and the hydraulic retention time is 2h. Before the start-up of the biological activated carbon unit, the bio-filming of the activated carbon is carried out first, and the high-efficiency salt-tolerant biological bacteria agent is used to coat the film and domesticate. The dosage of the high-efficiency salt-tolerant bacteria agent is 300mg / L, and the effluent of the b...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com