A kind of method for catalyzing synthesis of biotin by a palladium-carbon catalyst with high mechanical activity
A palladium-carbon catalyst and synthetic biology technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, physical/chemical process catalysts, metal/metal oxide/metal hydroxide catalysts, etc. problem, to achieve the effect of reducing poisoning, superior performance and high activity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
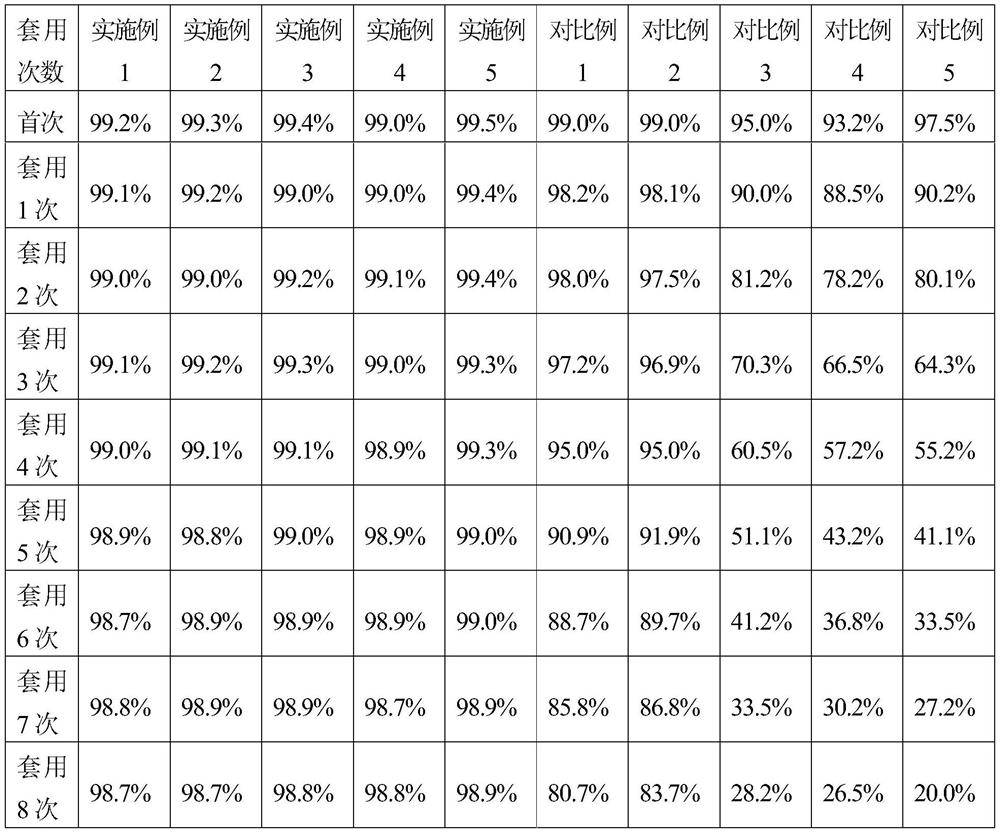
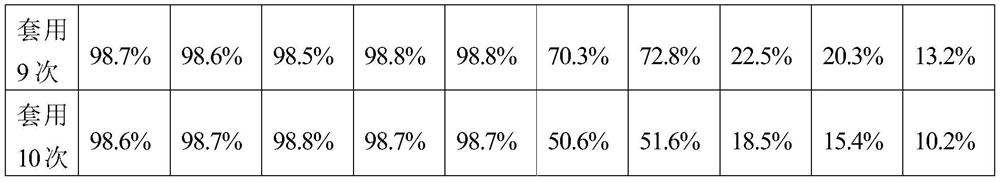
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0020] 1. Roast the activated carbon in a tube furnace at 400°C for 6 hours under an ammonia atmosphere. Weigh 10 g of the obtained activated carbon and add it to 100 mL of hydrogen peroxide with a volume concentration of 5%. Stir at room temperature for 24 hours and then filter. Put the filtered wet carbon in an oven Dry at 150°C to constant weight; obtain pretreated activated carbon.
[0021] 2. Dilute 10mL of 0.1g / mL chloropalladium acid aqueous solution (the molar weight of palladium is 9.4mmol) to 150mL with deionized water, then add 1.44g (9.4mmol) of dopamine, reflux and stir in a water bath at 90°C for 2h, Cool to room temperature to obtain a palladium precursor solution.
[0022] 3. Add 9g of pretreated activated carbon to 200mL of ethanol aqueous solution with a volume concentration of 5% for beating, then add 150mL of palladium precursor solution dropwise to the carbon slurry under stirring conditions, and add aqueous sodium carbonate solution to control pH = 7, dro...
Embodiment 2
[0025] 1. Roast the activated carbon in a tube furnace at 450°C for 5 hours under an ammonia atmosphere. Weigh 10 g of the obtained activated carbon and add it to 100 mL of hydrogen peroxide with a volume concentration of 10%. Stir at room temperature for 24 hours and then filter. Put the filtered wet carbon in an oven Dry at 150°C to constant weight; obtain pretreated activated carbon.
[0026] 2. Dilute 10mL of 0.1g / mL chloropalladium acid aqueous solution (the molar weight of palladium is 9.4mmol) to 150mL with deionized water, then add 2.26g (37.6mmol) urea, reflux and stir in a 90°C water bath for 2h, Cool to room temperature to obtain a palladium precursor solution.
[0027] 3. Add 9g of pretreated activated carbon to 200mL of ethanol aqueous solution with a volume concentration of 20% for beating, then add 150mL of palladium precursor solution dropwise to the carbon slurry under stirring conditions, and add aqueous sodium hydroxide solution to control pH = 11.2, Stir f...
Embodiment 3
[0030] 1. Roast the activated carbon in a tube furnace at 500°C for 5 hours under an ammonia atmosphere. Weigh 10 g of the obtained activated carbon and add it to 100 mL of hydrogen peroxide with a volume concentration of 10%. Stir at room temperature for 24 hours and then filter. Put the filtered wet carbon in an oven Dry at 150°C to constant weight; obtain pretreated activated carbon.
[0031] 2. Dissolve 1.67g of soluble palladium chloride (the molar weight of palladium is 9.4mmol) in 150mL deionized water, then add 1.29g (4.69mmol) trisodium nitrilotriacetate, reflux and stir in a water bath at 90°C for 2h, and cool to room temperature to obtain a palladium precursor solution.
[0032] 3. Add 9g of pretreated activated carbon to 200mL of ethanol aqueous solution with a volume concentration of 50% to make a slurry, then add 150mL of palladium precursor solution dropwise to the carbon slurry under stirring conditions, and add ammonia water to control pH = 9, dropwise After ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| quality score | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| quality score | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com