Group of laminaria japonica base morphology QTLs and breeding application thereof
A technology of kelp and base, which is applied in the direction of recombinant DNA technology, microbial measurement/inspection, DNA/RNA fragments, etc., can solve the problems of less research on kelp QTL genetic analysis, fewer primer sequences, and molecular breeding, etc., to achieve enrichment Effect of Screening Breeding Resources
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0052] Embodiment 1: Construction of genetic population
[0053] Cross the female gametophytes of S. longissima (S. longissima) with the male gametophytes of S. japonica. After the F1 generation of kelp is bred at sea, select individuals with excellent traits and both parental traits for indoor collection of spores and self-breeding f 2 generation.
Embodiment 2
[0054] Embodiment 2: the construction of genetic map
[0055] (1) Using the CTAB method to extract the parents and 102 F 2 Separate the genomic DNA of the population, and dilute the qualified DNA to 50ng / μL, and use 1% agarose gel electrophoresis to detect the purity and integrity of the DNA;
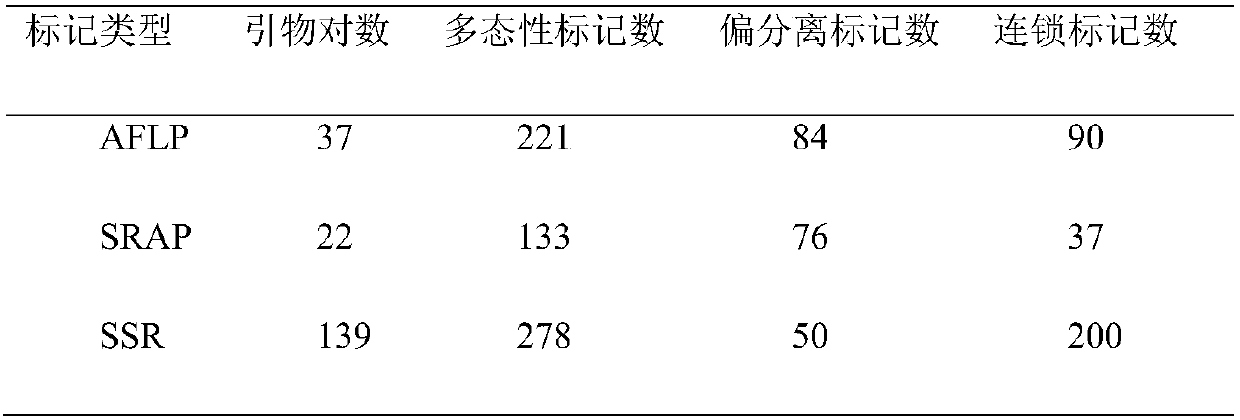
[0056] (2) Using 49 pairs of AFLP, 88 pairs of SRAP and 1546 pairs of SSR primers developed in the laboratory, the parents and randomly selected F 2The two individuals of the isolated group were used as templates for PCR amplification, and the products were electrophoresed in denatured polyacrylamide gels. After staining and developing, the size of the bands was judged, and 37 pairs of polymorphic AFLP primers, 22 pairs of polymorphic AFLP primers, and 22 pairs of polymorphic primers were screened out. Morphic SRAP primers and 139 pairs of polymorphic SSR primers;
[0057] (3) Using polymorphic primers for 102 F 2 The isolated population was analyzed for molecular markers to obtain g...
Embodiment 3
[0062] Embodiment 3: QTL analysis of kelp base morphology
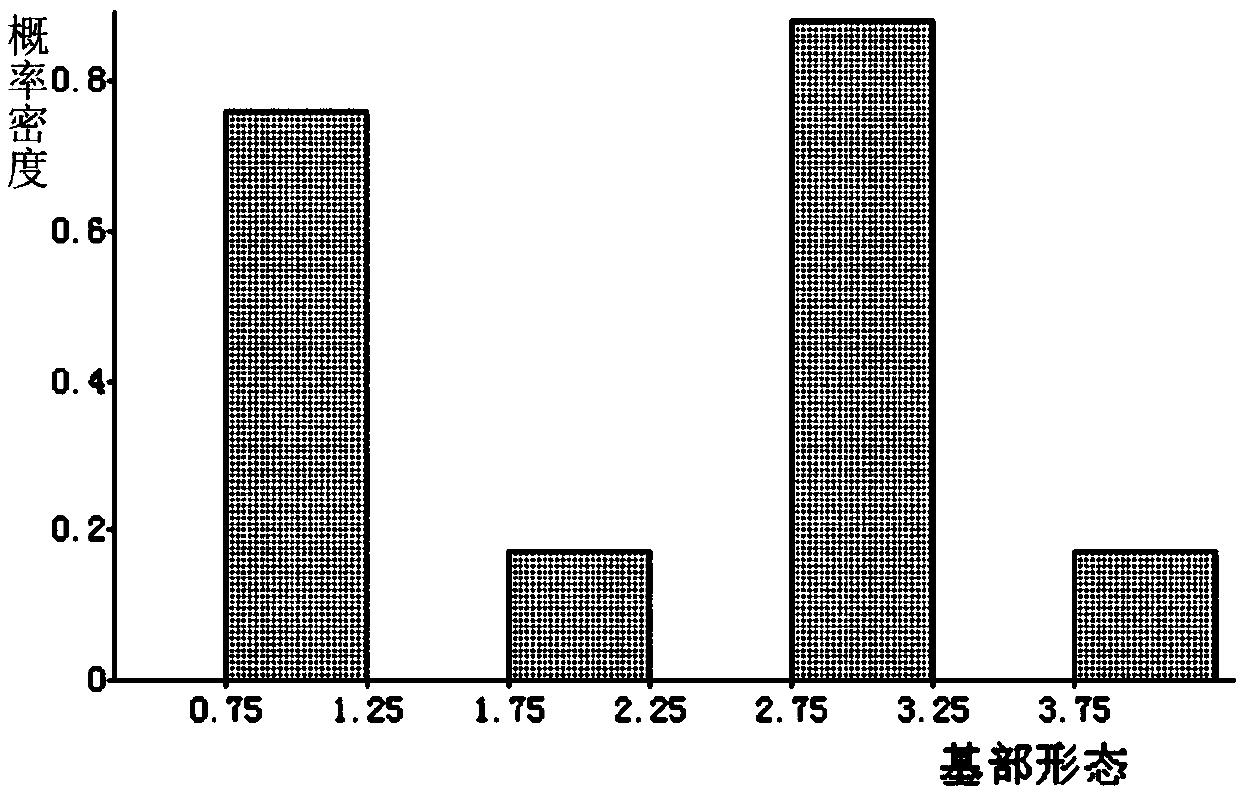
[0063] combined parent and F 2 The phenotypic data was analyzed by using the Composite Interval Mapping (CIM) of the software MapMaker for QTL analysis, and the results are shown in Table 2.
[0064] Table 2 Analysis results of QTLs for basal morphology of Laminaria
[0065]
[0066]
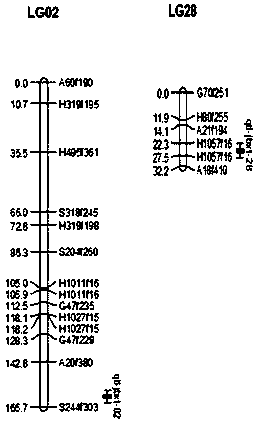
[0067] The inventor obtains a group of basal morphological QTLs of Laminaria qtl-jbxt-02 and qtl-jbxt-28 (such as figure 2 shown).
[0068] The above qtl-jbxt-02 is located in the linkage group LG02; the molecular markers adjacent to the above qtl-jbxt-02 are A20f380-S244f303, which are located by molecular markers A20f380 and S244f303.
[0069] The above qtl-jbxt-28 is located in the linkage group LG28; the molecular markers adjacent to the above qtl-jbxt-28 are H1057f16-A18f410, which are located by molecular markers H1057f16 and A18f410.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com