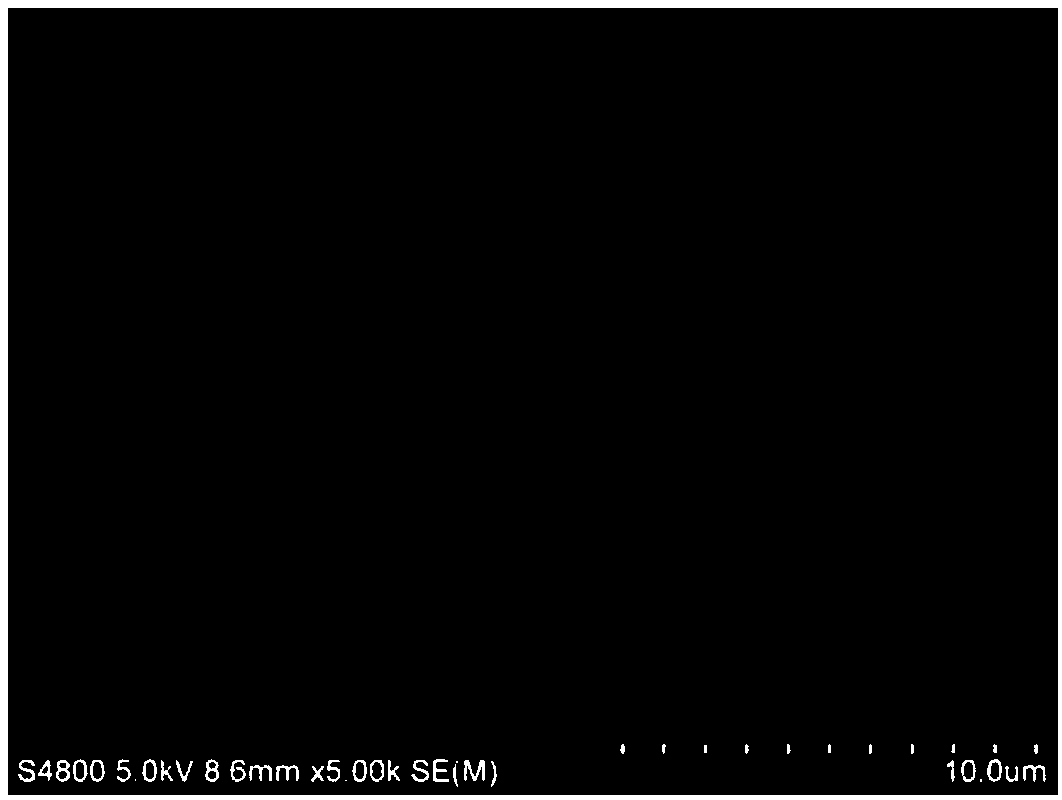
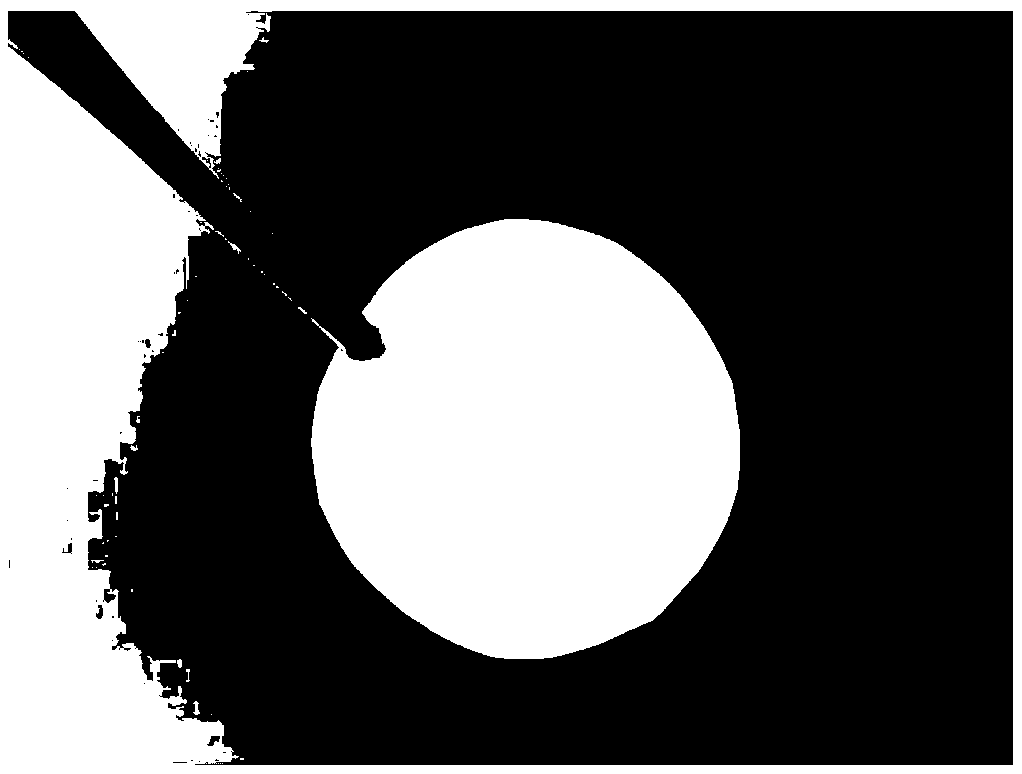
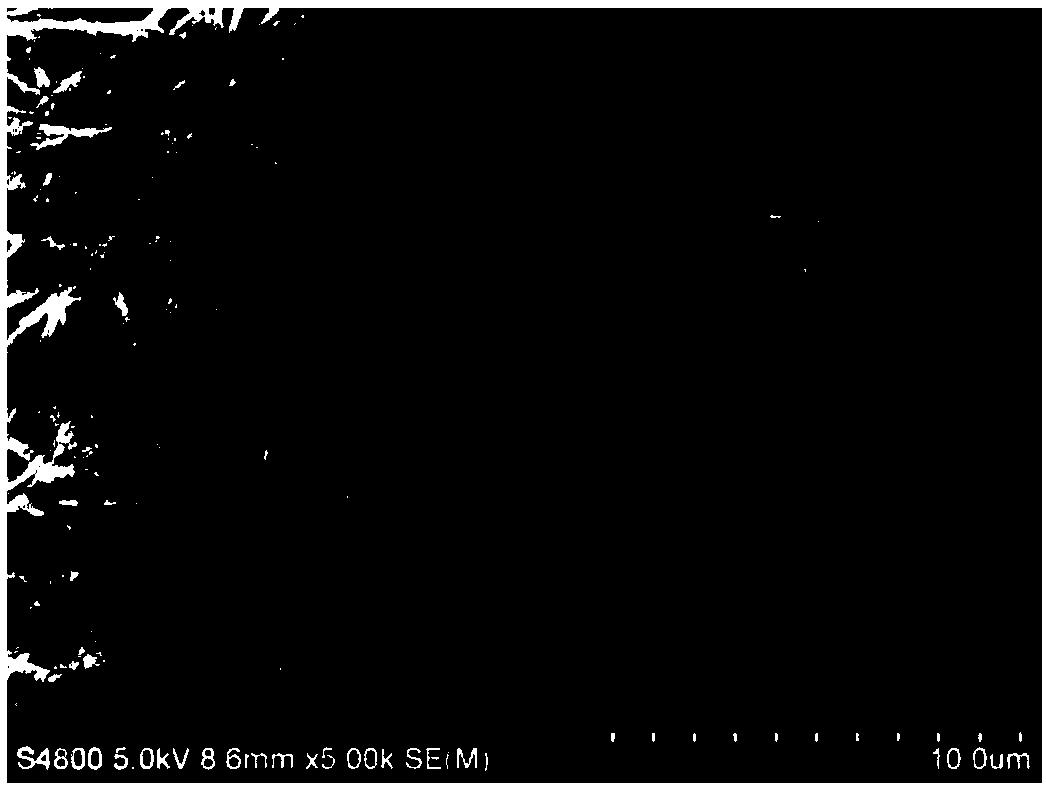
Method for preparing positive osmosis membrane with reserved draw solute and double active layers
A forward osmosis membrane, dual-active technology, applied in the field of membrane separation to achieve the effect of improving permeation flux
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0041] The preparation method of the double active layer forward osmosis membrane with reserved solute absorption is as follows:
[0042] Step A: Rinse the support layer with a pore size range of 50-1000nm and a porosity range of 20-98% with deionized water, and dry it at 40-60°C for 1-60 minutes for later use;
[0043] Step B: Dissolve the polyamine in deionized water to form a polyamine solution of 1 to 7 wt%;
[0044] Step C: adding the drawn solute to the polyamine solution obtained in step B, and the drawn solute has a concentration of 0-15 wt% to prepare a mixed solution;
[0045] Step D: Dissolve polybasic acid chloride in n-hexane solution to form a 0.01-1wt% polybasic acid chloride solution;
[0046] Step E, soak the support layer in the solution obtained in step C for 1-30 minutes, so that the drawn solute remains in the support layer;
[0047] Step F. After taking it out, use filter paper to absorb the residual solution on the surface of the support layer, place it in a suctio...
Embodiment 1
[0050] (1) Wash the base of the polyacrylonitrile fiber support layer with a pore size of 200nm and a porosity of 90% with deionized water, and dry it at 40°C for 10 minutes for use;
[0051] (2) Dissolve m-phenylenediamine in deionized water to prepare a 2wt% m-phenylenediamine solution;
[0052] (3) Add sodium chloride to a 2wt% m-phenylenediamine solution, wherein the concentration of sodium chloride is 3wt%, to prepare a mixed solution;
[0053] (4) Dissolve trimesoyl chloride in n-hexane solution to form a 0.2wt% trimesoyl chloride solution;
[0054] (5) Soak the polyacrylonitrile fiber support layer in a solution containing 2wt% of m-phenylenediamine (containing 3wt% of NaCl) for 2 minutes;
[0055] (6) Take out the polyacrylonitrile fiber support layer reserved for extraction solute (NaCl), absorb the excess water with filter paper, and place it in a suction filter device, so that the single layer is soaked in 0.2wt% trimesoyl chloride / n-hexane 30s in alkane to obtain a polyamid...
Embodiment 2
[0062] (1) Rinse the polyvinylidene fluoride support layer with a pore size of 100nm and a porosity of 80% with deionized water, and dry it at 50°C for use;
[0063] (2) Dissolve m-phenylenediamine in deionized water to prepare a 3wt% m-phenylenediamine solution;
[0064] (3) Add sodium chloride to the 3wt% m-phenylenediamine solution, wherein the concentration of sodium chloride is 3.5wt%, to prepare a mixed solution;
[0065] (4) Dissolve trimesoyl chloride in the n-hexane solution to form a 0.2wt% trimesoyl chloride solution;
[0066] (5) Soak the polyvinylidene fluoride support layer in a solution containing 3wt% m-phenylenediamine (containing 3.5wt% NaCl) for 2 minutes;
[0067] (6) Take out the polyvinylidene fluoride support layer reserved for the extraction solute (NaCl), absorb the excess water with filter paper, and place it in a suction filter device, so that the single layer is soaked in 0.2wt% trimesoyl chloride / n-hexane 30s in alkane to obtain a polyamide active layer, re...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Aperture | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Water flux | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Water flux | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com