High-strength ancient building ceramic capable of resisting quick cooling and quick heating and preparation method thereof
An ancient ceramics, quench-resistant technology, applied in the field of ceramics, can solve the problem of extreme temperature resistance, and achieve the effect of reducing sintering temperature, improving drying performance, reducing drying shrinkage and deformation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
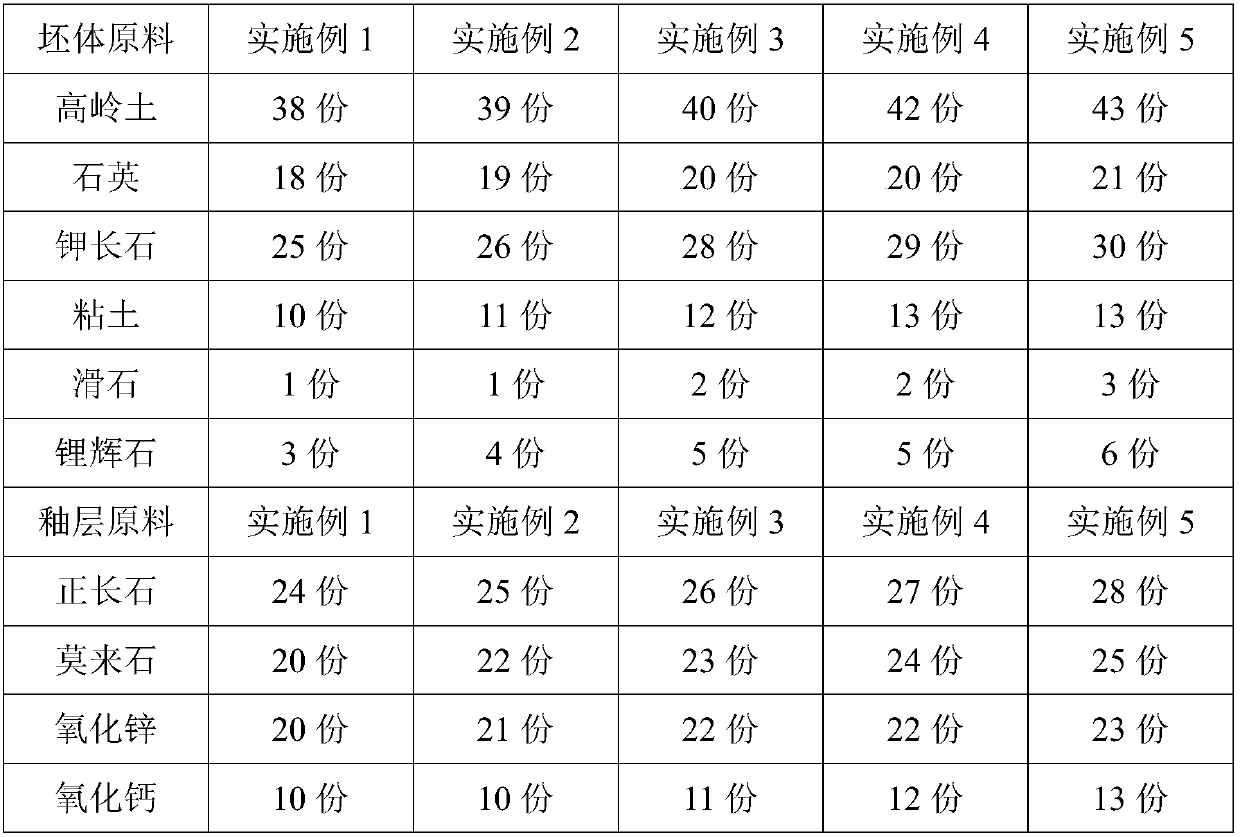
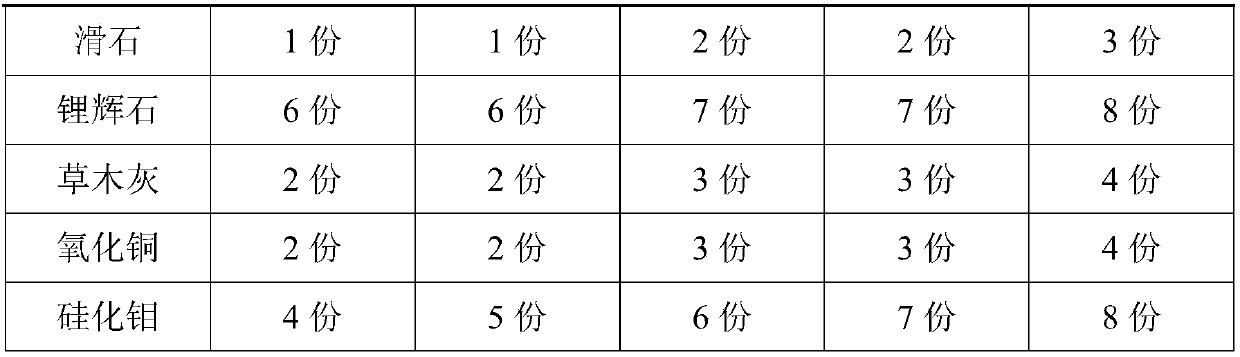
[0027] This embodiment provides a high-strength ancient building ceramics resistant to rapid cold and rapid heat, including a tire material and a glaze. The tire material includes the following raw materials by weight: 38 parts of kaolin, 18 parts of quartz, 25 parts of potash feldspar, and 10 parts of clay. Parts, 1 part of talc, 3 parts of spodumene; the glaze includes the following raw materials by weight: 24 parts of orthoclase, 20 parts of mullite, 20 parts of zinc oxide, 10 parts of calcium oxide, 6 parts of spodumene, 1 part of talc, 2 parts of plant ash, 2 parts of copper oxide, 4 parts of molybdenum silicide.
[0028] This embodiment also provides a method for making high-strength ancient ceramics resistant to rapid cold and rapid heat, including the following steps:
[0029] Step 1. The tire material is weighed and crushed according to the weight ratio and then put into a ball mill and added with water for wet grinding. The weight ratio of water added during wet grinding ...
Embodiment 2
[0036] This embodiment provides a high-strength ancient building ceramics resistant to rapid cold and rapid heat, including a tire material and a glaze. The tire material includes the following raw materials by weight: 39 parts of kaolin, 19 parts of quartz, 26 parts of potash feldspar, and 11 parts of clay. Parts, 1 part of talc, 4 parts of spodumene; the glaze includes the following raw materials by weight: 25 parts of orthoclase, 22 parts of mullite, 21 parts of zinc oxide, 10 parts of calcium oxide, 6 parts of spodumene, 1 part of talc, 3 parts of plant ash, 2 parts of copper oxide, 5 parts of molybdenum silicide.
[0037] This embodiment also provides a method for manufacturing high-strength ancient ceramics resistant to rapid cold and rapid heat, which includes the following steps:
[0038] Step 1. According to the weight ratio, the tire material is respectively weighed and crushed and put into a ball mill to add water for wet grinding. The weight ratio of water added during ...
Embodiment 3
[0045] This embodiment provides a high-strength ancient ceramics resistant to rapid cold and rapid heat, including a tire material and a glaze. The tire material includes the following raw materials by weight: 40 parts of kaolin, 20 parts of quartz, 28 parts of potash feldspar, and clay 12 parts, 2 parts of talc, 5 parts of spodumene; the glaze includes the following raw materials by weight: 26 parts of orthoclase, 23 parts of mullite, 22 parts of zinc oxide, 11 parts of calcium oxide, 7 parts of spodumene , 2 parts of talc, 3 parts of plant ash, 3 parts of copper oxide, 6 parts of molybdenum silicide.
[0046] This embodiment also provides a method for manufacturing high-strength ancient ceramics resistant to rapid cold and rapid heat, which includes the following steps:
[0047] Step 1. According to the weight ratio, the tire material is weighed and crushed and put into a ball mill to add water for wet grinding. The weight ratio of water added during wet grinding is material: bal...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com