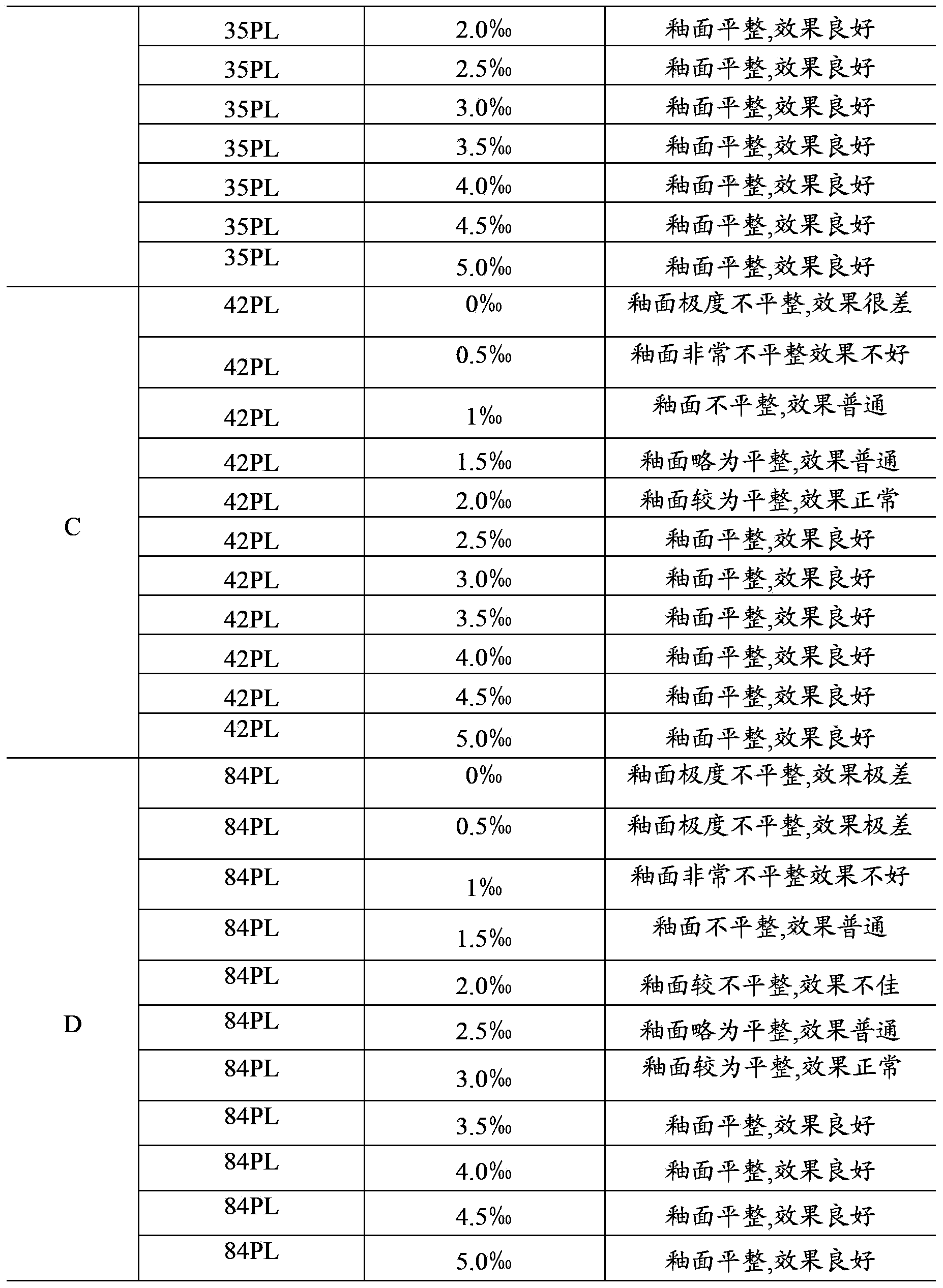
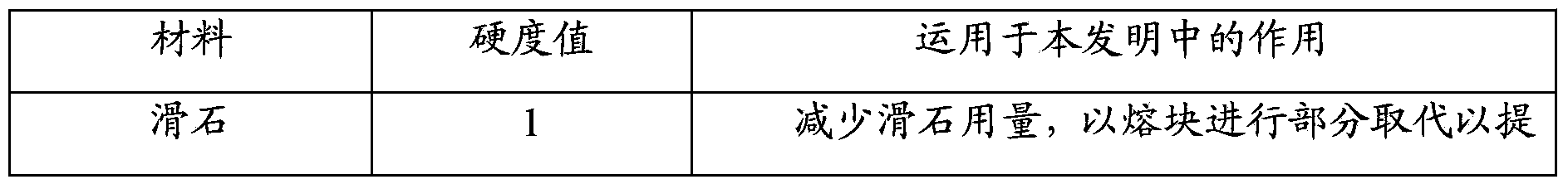
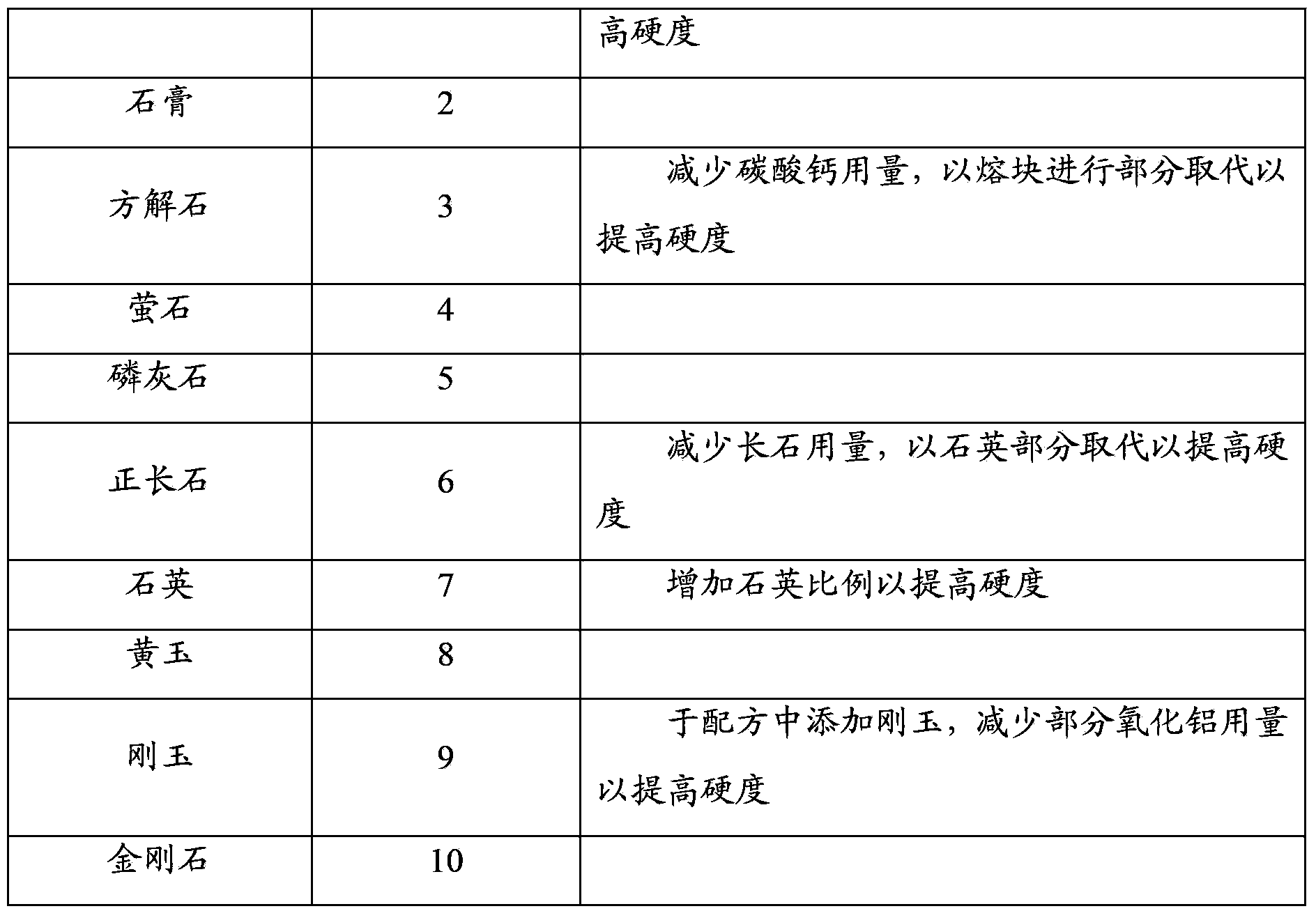
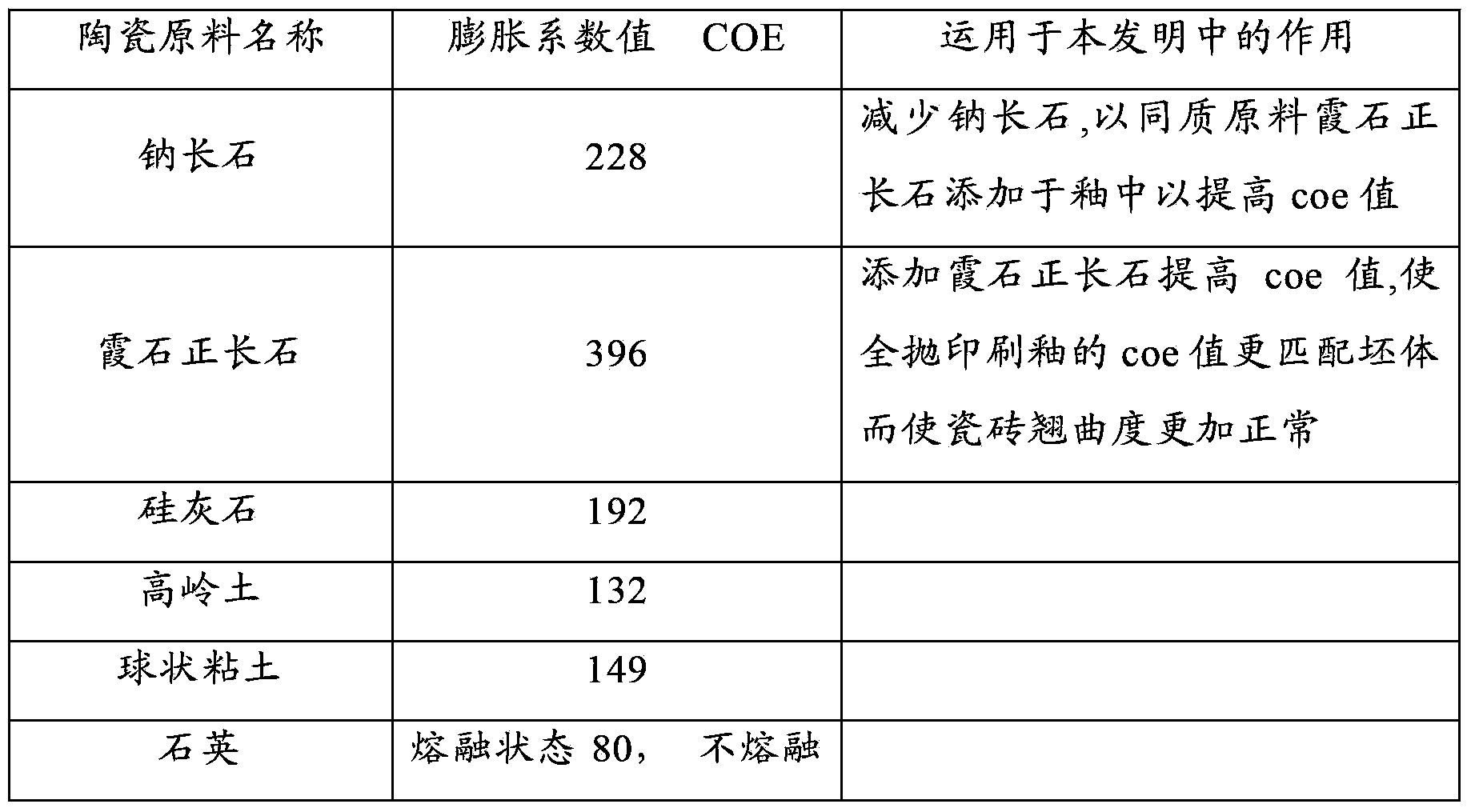
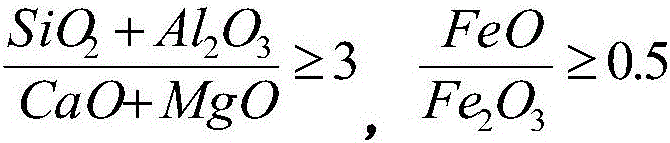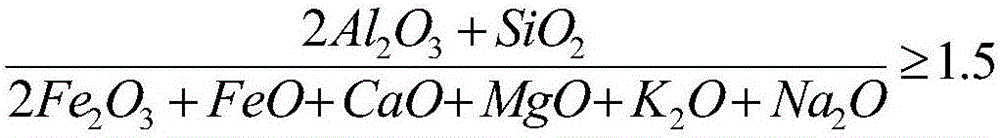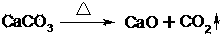Patents
Literature
51 results about "Orthoclase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Orthoclase, or orthoclase feldspar (endmember formula KAlSi₃O₈), is an important tectosilicate mineral which forms igneous rock. The name is from the Ancient Greek for "straight fracture," because its two cleavage planes are at right angles to each other. It is a type of potassium feldspar, also known as K-feldspar. The gem known as moonstone (see below) is largely composed of orthoclase.
Wear-resistant carbon fiber modified polyether-ether-ketone composite material and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a wear-resistant carbon fiber modified polyether-ether-ketone composite material, which is prepared from the following ingredients in parts by weight: 40 to 60 parts of polyether-ether-ketone resin, 10 to 30 parts of polyfluortetraethylene resin, 8 to 20 parts of polyimide resin, 2 to 5 parts of carbon fiber, 5 to 10 parts of vermiculite, 5 to 15 parts of parithenolide, 4 to 8 parts of orthoclase powder and 1 to 2 parts of compatilizers. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the composite material. The composite material has the advantages that the wear-resistant performance is good; the high-temperature-resistant performance is excellent; the processing is easy; the anti-impact performance is good; the intensity is high; the composite material can be widely applied to the field of mechanical part preparation; in addition, the preparation method is simple; the cost is low.
Owner:SUZHOU ZHENZHAN TECHCAL MATERIAL CO LTD
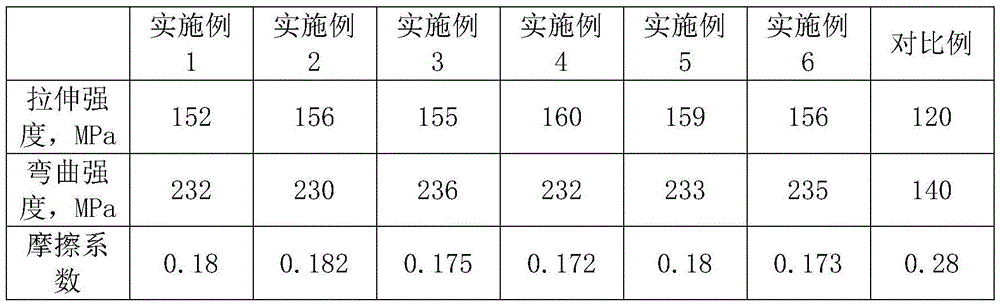
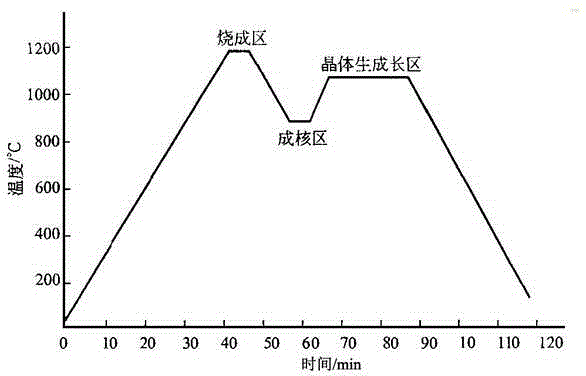
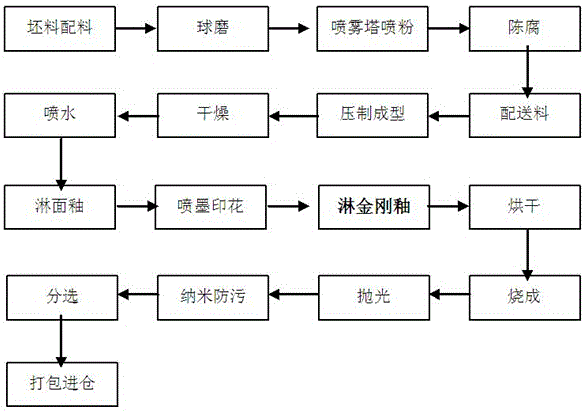
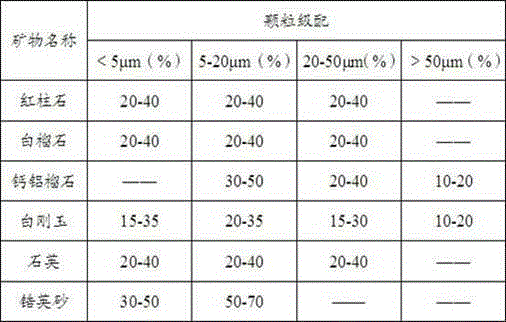
Wear resistant and high-hardness diamond glaze, preparation method and application
The invention discloses a wear resistant and high-hardness diamond glaze, a preparation method and application. The wear resistant and high-hardness diamond glaze is prepared from the following raw materials according to mass percent: 5 to 15% of kaolin, 5 to 10% of andalusite, 5 to 10% of orthoclase, 5 to 12% of leucite, 1 to 3% of essonite, 10 to 18% of nepheline, 5 to 15% of spodumene, 2 to 8% of wollastonite, 3 to 7% of quartz, 5 to 10% of zircon sand, 5 to 10% of white corundum, 1 to 3% of dolomite, 1 to 3% of calcined white talc, 0.1 to 0.5% of zinc oxide and 0.5 to 3% of additive. According to the wear resistant and high-hardness diamond glaze, the preparation method and the application, the selection of mineral raw materials of the glaze is optimized, firstly, the wear resistant and high-hardness mineral raw materials such as the andalusite (the hardness is 6.9 to 7.4), the white corundum (the hardness is 9.0), the leucite (the hardness is 5.5 to 6) and the essonite (the hardness is 7 to 7.5) are selected, the grain fineness and addition of the wear resistant and high-hardness mineral raw materials are controlled through reasonable grain composition, and by adopting the subsequent preparation process and application process, the wear resistance and hardness of the diamond glaze are greatly increased.
Owner:FOSHAN ZHONGCHENG SILICATE TECH CO LTD
Brilliant iron rust glaze, brilliant iron rust glaze ceramic product prepared from same and preparation method
The invention relates to a brilliant iron rust glaze, a brilliant iron rust glaze ceramic product prepared from the same and a preparation method, and belongs to the technical field of ceramics. The brilliant iron rust glaze comprises components in parts by mass as follows: 40-50 parts of nepheline-syenite, 10-20 parts of quartz, 2-8 parts of calcium carbonate, 18-22 parts of low-temperature frits, 2-6 parts of zinc oxide. 8-13 parts of calcium borate, 18-23 parts of manganese oxide and 1-4 parts of copper oxide, wherein the low-temperature frits comprise components in parts by mass as follows: 44-47 parts of borax, 28-32 parts of quartz, 18-22 parts of potash feldspar and 2-7 parts of kaolin. The brilliant iron rust glaze can imitate the iron rust appearance, so that the ceramic product can show the iron rust appearance on the surface and has brilliant silver bright points with three-dimensional sense; besides, with the adoption of the method, control is facilitated in a sintering process, energy saving is facilitated, and the yield of sintered products is higher.
Owner:FUJIAN DEHUA HUAMAO CERAMICS CO LTD
Production method of centrifugal glass cotton-like fiber
InactiveCN103130410ALow densityLow thermal conductivityGlass making apparatusChemical reactionCentrifugation
The invention discloses a production method of a centrifugal glass cotton-like fiber. According to the production method of the centrifugal glass cotton-like fiber, materials of quartz sands, orthoclases, limestones, glass cullet, soda ashes, borax and the like are adopted, the materials are mixed in a reasonable proportion, glass liquids can be obtained after physical and chemical reactions through kiln high-temperature melting, and short glass fiber cotton aggregates can be thrown out through high-speed centrifugal injection. Material produced through the production method of the centrifugal glass cotton-like fiber has the advantages of being small in density, low in heat conductivity, high in acoustic absorptivity, flame-resistant, frost-resistant, and not prone to decay. The material is ideal heat preservation and heat insulation material, and is mainly used in the heat insulation process of building rail structures, industrial equipment, and pipe networks, and fireproofing and the like of the buildings. The material can further used as a sound absorber which absorbs and eliminates sounds, sound-absorbing barriers, sound-absorbing wall faces and the like.
Owner:吴振华
Production method for continuous basalt fiber
ActiveCN106396421AImprove accuracyImprove rapid effectivenessGlass furnace apparatusTO-18Chemical composition
The invention discloses a production method for continuous basalt fiber. The production method is characterized by comprising the following steps: 1) material selection, i.e., comprehensive determination of raw basalt materials for production of the continuous basalt fiber based on the chemical components and mineral components of basalt: analyzing the content of SiO2 in the chemical components of basalt, selecting basalt with SiO2 content of 48 to 63% and with saturated or oversaturated SiO2, analyzing the mineral component of basalt, removing basalt containing olivine and selecting basalt with mineral components consisting of, by weight, 15 to 27% of quartz, 10 to 18% of orthoclase, 30 to 50% of plagioclase or 45 to 60% of plagioclase, and 15 to 30% of pyroxene; and 2) fusing and fiber molding of the selected raw basalt materials so as to obtain the continuous basalt fiber. The production method provided by the invention can substantially improve accuracy in basalt selection and optimize the fusing process and fiber molding process of a basalt melt, enables the basalt melt to be easy to homogenize and provides effective bases and criteria for production of the continuous basalt fiber.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Matte metal glaze, matte metal glaze ceramic product prepared from same and preparation method of matte metal glaze ceramic product
The invention relates to matte metal glaze, a matte metal glaze ceramic product prepared from the same and a preparation method of the matte metal glaze ceramic product, belonging to the technical field of ceramics. The matte metal glaze comprises the following components in parts by weight: 45-55 parts of nepheline orthoclase, 28-35 parts of clinkers, 4-7 parts of quartz, 2-8 parts of barium carbonate, 2-7 parts of disthene, 3-7 parts of kaolin, 22-27 parts of manganese oxide and 1-1.9 parts of copper oxide, wherein the clinkers comprise the following components in parts by weight: 38-42 parts of borax, 22-28 parts of quartz, 3-6 parts of kaolin, 12-17 parts of calcium carbonate, 8-13 parts of sodium nitrate and 2-7 parts of potassium carbonate. The matte metal glaze ceramic product is endowed with good texture and appearance by the matte metal glaze; and by integrating metal luster with low-pitched matte, the matte metal glaze ceramic product is low-pitched and luxurious.
Owner:FUJIAN DEHUA HUAMAO CERAMICS CO LTD
Novel printing glaze material and production method thereof
The invention provides a novel printing glaze material and a production method thereof. The novel printing glaze material consistent with standards is produced by putting the following components into a ball mill for grinding, wherein the components are as follows in percentage by weight: 32% to 42% of albite, 8% to 12% of nepheline orthoclase, 3% to 5% of wollastonite, 3% to 5% of kaolin, 1.5% to 2.5% of ball clay, 3% to 5% of quartz, 3% to 5% of aluminium oxide, 5% to 8% of corundum, 7% to 9% of calcium carbonate, 4% to 7% of zinc oxide, 1% to 2% of talc, 3% to 5% of dolomite, 1% to 2% of barium carbonate, 4% to 8% of clinker, and 6% to 15% of zirconium silicate. The produced novel printing glaze material has the advantages that color development of the ink is better, a problem of color system variation does not exist, the definition of ink figures and the flatness of glaze surfaces can be guaranteed, and a defect of printing ink gloss variation is overcome through controlling a molten softening point.
Owner:CARLOBBIA GLAZE KUNSHAN
Novel printing glaze material and production method thereof
The invention provides a novel printing glaze material and a production method thereof. The novel printing glaze material consistent with standards is produced by putting the following components into a ball mill for grinding, wherein the components are as follows in percentage by weight: 36% to 42% of albite, 8% to 10% of nepheline orthoclase, 6% to 8% of wollastonite, 4% to 8% of kaolin, 2% to 5% of ball clay, 4% to 7% of quartz, 3% to 5% of aluminium oxide, 5% to 8% of corundum, 8% to 10% of calcium carbonate, 1% to 2% of barium carbonate, 4% to 10% of clinker and 6% to 10% of fluxing agent. The produced novel printing glaze material solves the problems of needle hole, poor permeability, poor sewage suction performance, poor abrasive resistance and poor warping degree.
Owner:CARLOBBIA GLAZE KUNSHAN
Wear-resistant domestic ceramic product and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN110117184AHigh strengthHigh hardnessCeramic materials productionClaywaresWear resistantMullite
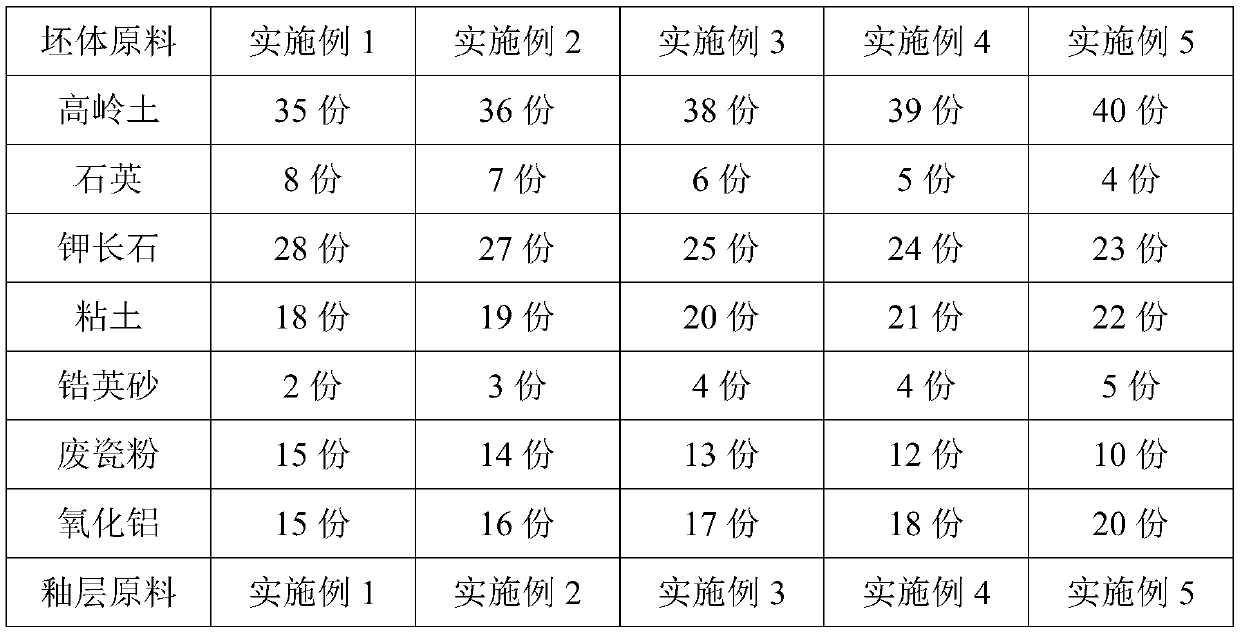
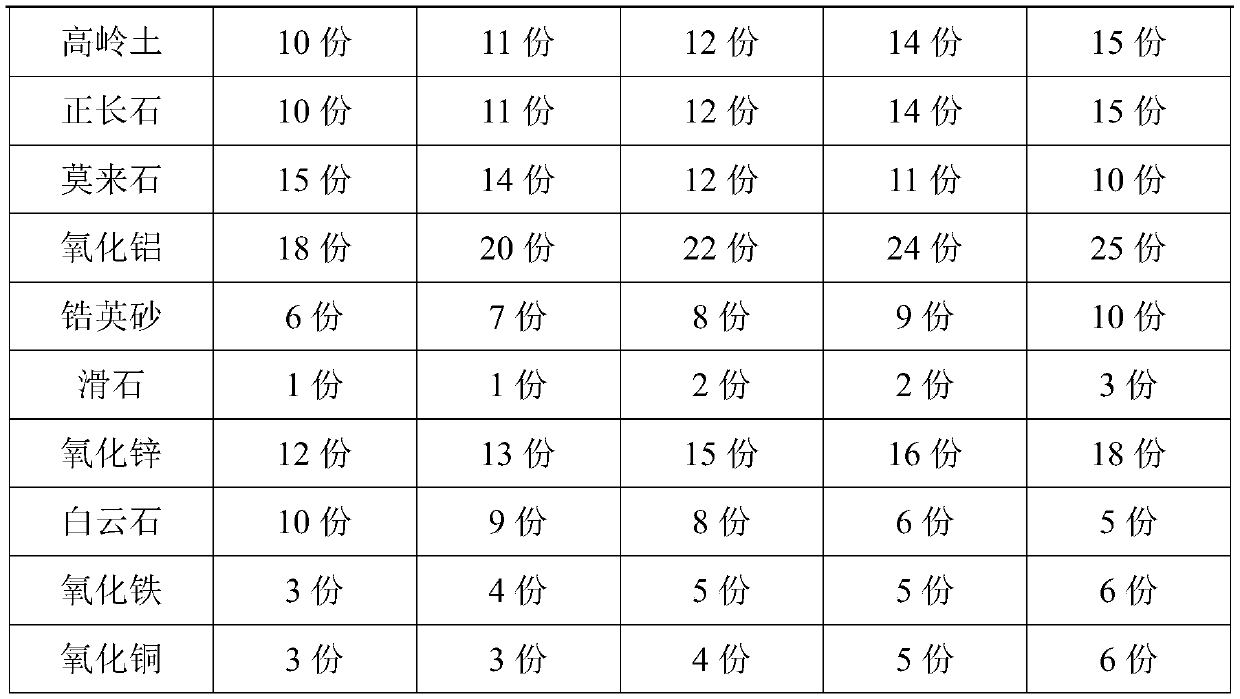
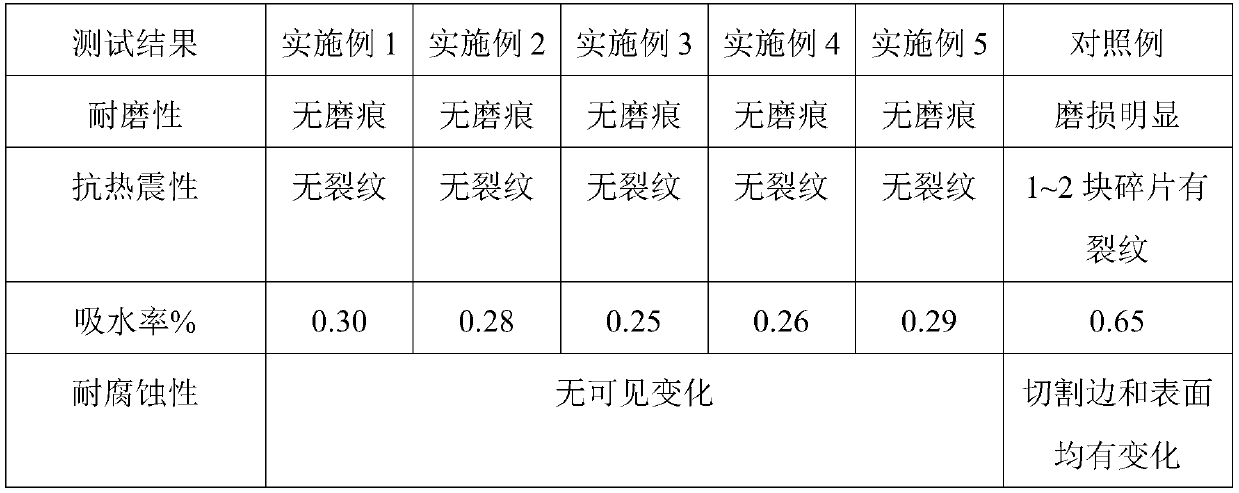
The invention provides a wear-resistant domestic ceramic product and belongs to the technical field of ceramics. The ceramic product comprises a matrix and glaze. The matrix is prepared from, by weight, 35-40 parts of kaolin, 4-8 parts of quartz, 23-28 parts of potash feldspar, 18-22 parts of clay, 2-5 parts of zircon sand, 10-15 parts of waste ceramic powder and 15-20 parts of alumina. The glazeis prepared from, by weight, 10-15 parts of kaolin, 10-15 parts of orthoclase, 10-15 parts of mullite, 18-25 parts of alumina, 12-18 parts of zinc oxide, 1-3 parts of talc, 6-10 parts of zircon sand,5-10 parts of dolomite, 3-6 parts of ferric oxide and 3-6 parts of copper oxide. A preparation method of the wear-resistant domestic ceramic product includes the following steps that matrix slurry isprepared, glaze slip is prepared, and green bodies are immersed in the glaze slip, then subjected to bisque firing and finally sintered at 1280-1380 DEG C. The domestic ceramic product obtained by theprovided raw materials and the process through sintering has the advantages of good wear resistance and high shock resistance.
Owner:福建省德化县合和陶瓷技术开发有限公司
Ancient green crackled glaze for ceramic decorations and preparation method of ancient green crackled glaze
The invention provides ancient green crackled glaze for ceramic decorations and a preparation method of the ancient green crackled glaze. The ancient green crackled glaze comprises the following components: 50-70 percent of nepheline orthoclase, 10-15 percent of talc, 10-15 percent of CaCO3, 3-8 percent of MgCO3, 4-8 percent of kaolin and 0.5-1.0 percent of CuCO3. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: weighing all the components, then sufficiently mixing the components, adding the mixture to a grinder, adding water which accounts for 50-60 percent of the dry powder, grinding for 5-12 hours, testing the granularity, and screening the ground mixture by using a 350-mesh screen, wherein residues are about 1-3g; and then blending the concentration of the ground glaze to true specific gravity at 42-45 DEG C, spraying or soaking the glaze onto a ceramic product, airing, then feeding the ceramic product into a kiln, carrying out glaze firing at 1185-1200 DEG C for 9-10 hours, finally naturally cooling and discharging the finished product from the kiln. The prepared ancient green crackled glaze is fine and soft in glaze surface, rich in texture and ancient in color and luster.
Owner:XIAMEN EDUNUS CERAMIC IND CO LTD
Lightweight thermal-insulation bricks and production method thereof
InactiveCN107253851AWide variety of sourcesLow costCeramic materials productionCeramicwareBrickThermal insulation
The invention discloses lightweight thermal-insulation bricks and a production method thereof and relates to the field of thermal-insulation bricks. The lightweight thermal-insulation bricks comprise mine tailings, modified laumontite, fly ash, silicon carbide fibers, attapulgite clay, orthoclase powder, hydrosol, a water reducing agent, water repellent, a foaming agent and a foam stabilizer. The production method includes: performing ball milling on the raw materials to obtain a powdered material; mixing all the raw materials, adding water, and evenly stirring to obtain slurry; performing compression moulding, natural maintaining, drying, high-temperature calcining and the like on the slurry to obtain the lightweight thermal-insulation bricks. The lightweight thermal-insulation bricks are low in dry density, lightweight, convenient and fast to transport, low in raw material cost, high in compressive strength, long in service life and promising in market prospect.
Owner:HEFEI SHANGHAN DECORATION ENG CO LTD
Film coating method for self-cleanness glass ceramics
The invention relates to a preparation method for glass ceramics, in particular to a film coating method for glass ceramics with self-cleanness function, namely a film coating method for self-cleanness glass ceramics. The method comprises the steps: taking blast furnace slag and orthoclase as raw materials to prepare glass ceramic blanks, preparing silica sol / polytetrafluoroethylene plating solution by utilizing sol-gel process, conducting film coating on the surface of the glass ceramic by utilizing a dip-coating method, and finally conducting thermal treatment to the obtain the glass ceramics with the surface having self-cleanness function. The principle crystalline phase of the prepared glass ceramics is akermanite, the polytetrafluoroethylene plays a good modification role on the silica sol, and the contact angle of the self-cleanness glass ceramics can achieve 120 degrees, thereby having strong hydrophobicity.
Owner:JIANGSU YITA NEW MATERIAL TECH
Method for predicting complexity of fracture network formed by shale fracturing
ActiveCN111275273ASolve problems that are not universally applicableForecastingResourcesPyriteCalcite
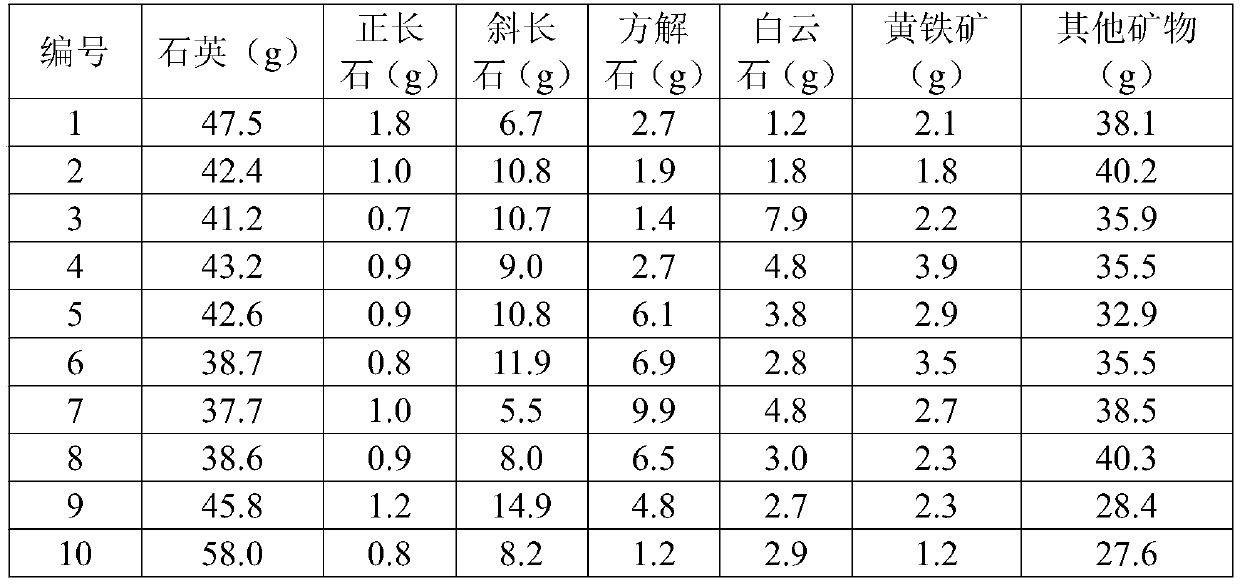
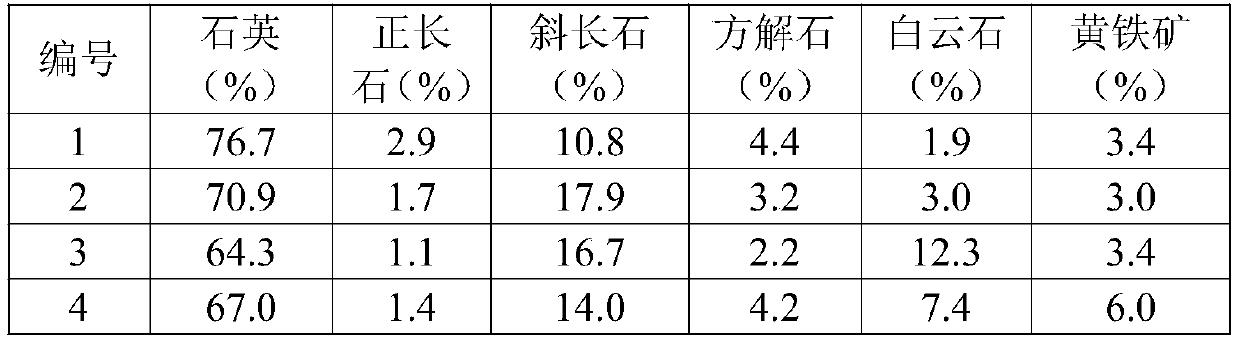
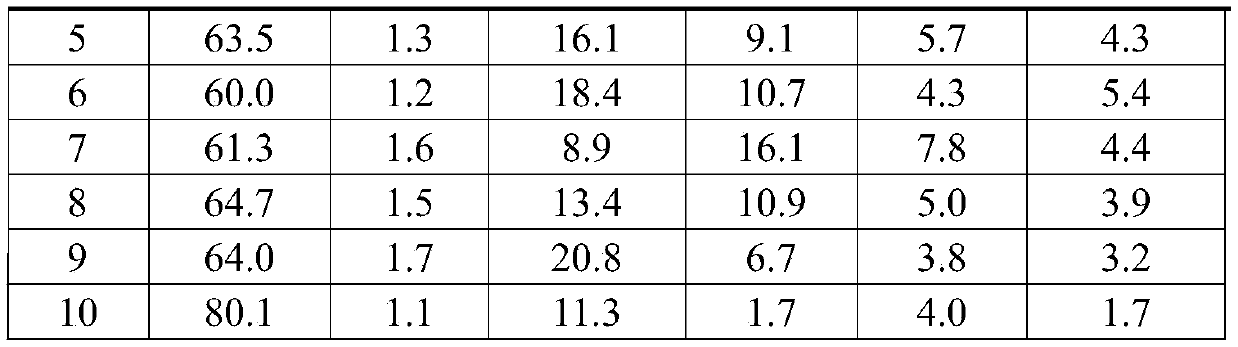
The invention discloses a method for predicting the complexity of a fracture network formed by shale fracturing, and the method comprises the steps: S1, determining the percentage contents of variousminerals, including quartz, orthoclase, plagioclase, pyrite, calcite, dolomite and other substances, of a shale core; s2, then determining the standard quantity to be 16.7% by utilizing the variety ofbrittle minerals; s3, recalculating the percentage contents of various brittle mineral components by only considering the brittle minerals; s4, determining a phase difference k by utilizing the standard quantity and the newly determined mineral percentage content; s5, calculating the brittleness B of the brittle mineral; and S6, finally, the brittleness index BI is determined by combining other minerals, and the larger the brittleness index BI value is, the larger the number of cracks is, and the more complex the fracture network formed through fracturing is. The invention provides a novel prediction method for the complexity of a fracture network formed by shale fracturing.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
Method for extracting soluble potassium sulfate by using orthoclase
InactiveCN103708505AImprove decomposition rateHigh yieldSulfate/bisulfate preparationResource utilizationDecomposition
The invention relates to a method for extracting soluble potassium sulfate by using orthoclase. The method comprises the following steps: smashing and uniformly mixing the orthoclase, limestone, ardealite and a roasting auxiliary, roasting at the high temperature of 500-1200 DEG C, smashing, leaching and evaporating to obtain crystals of the soluble potassium sulfate product, wherein the weight ratio of the limestone to the orthoclase to the ardealite is (0.5-4.9):1:(0.2-2.5); the weight of the roasting auxiliary accounts for 0.1-20% of the weight of the orthoclase; the roasting auxiliary is a mixture of one or more of potassium sulfate, sodium sulfate and fluorite. The method disclosed by the invention is relatively reasonable in process and strong in operability and has the advantages that the decomposition rate of the orthoclase can be effectively increased, thus the yield of potassium is increased; SiO2, Al2O3 and K2O components in the orthoclase are comprehensively utilized for producing high value-added products; the purposes of high resource utilization rate, low energy consumption and good environment compatibility are achieved.
Owner:BLUESTAR LEHIGH ENG INST CO LTD
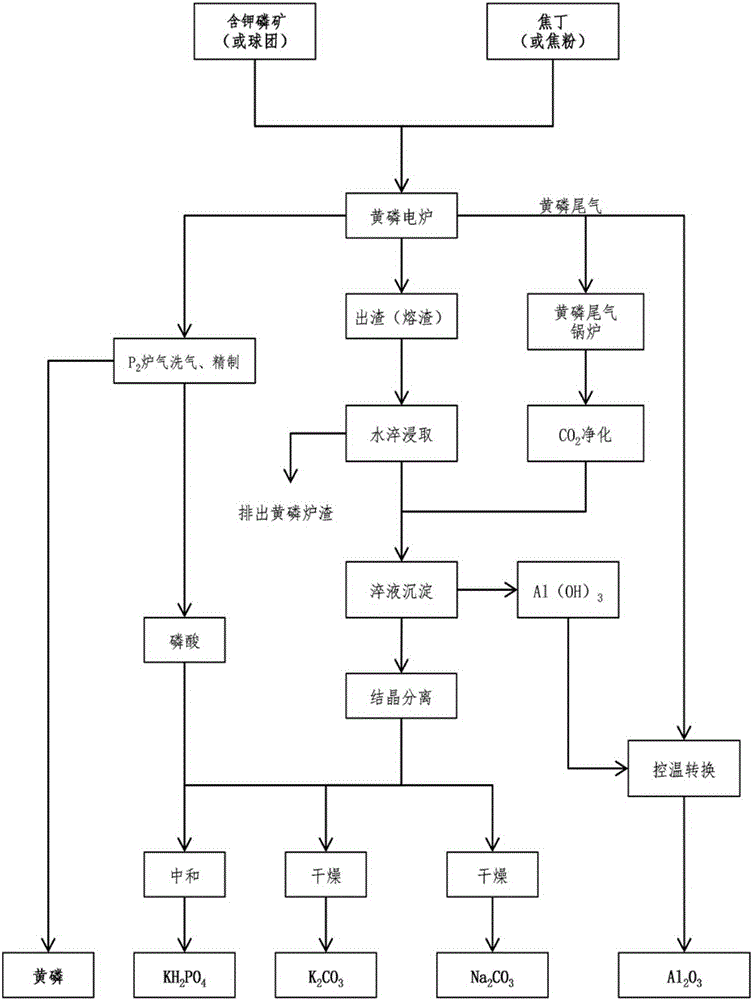
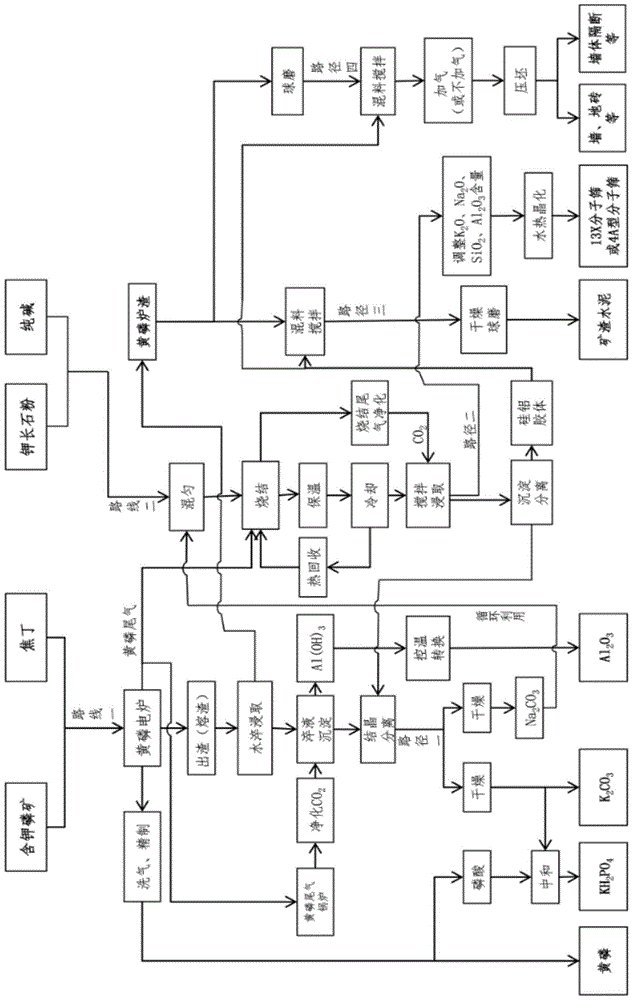
Energy-saving method for preparing yellow phosphorus, sylvite, sodium carbonate and aluminum oxide through potassium-bearing phosphorite
ActiveCN105197901AReduce manufacturing costTake advantage ofChemical industryAlkali metal carbonatesFiltrationQuenching
The invention relates to an energy-saving method for preparing yellow phosphorus, sylvite, sodium carbonate and aluminum oxide through potassium-bearing phosphorite. The method comprises the steps that the potassium-bearing phosphorite and coke nuts are added into a yellow phosphorus electric furnace to be reacted to obtain furnace gas containing P2; washing is conducted on the furnace gas, crude phosphorous is collected, refining is conducted, and high quality yellow phosphorus is obtained; water quenching is conducted on yellow phosphorus slags, the slags are removed, KAlO2 is dissolved out, filtration is conducted, Al(OH)3 is settled after CO2 is added, and water quench filtrate is obtained. The Al(OH)3 is converted through temperature control to obtain Al2O3, crystal separation and drying are conducted on the water quench filtrate, and K2CO3 and Na2CO3 are obtained. According to the energy-saving method for preparing the yellow phosphorus, the sylvite, the sodium carbonate and the aluminum oxide through the potassium-bearing phosphorite, series of problems that for a traditional electrothermal method that the potassium-bearing phosphorite is used for producing the yellow phosphorus through the yellow phosphorus electric furnace, the reaction is complex, the efficiency is low, furnace ore is unstable, and the benefit is poor are solved; compared with preparing K2CO3 through a traditional orthoclase sintering method, a high-temperature melting method, a hydrothermal method, a blast furnace smelting method and a low-temperature decomposition method, the energy consumption, material consumption and production cost can be greatly reduced, product profit margins are improved, and meanwhile environmental pollution is reduced.
Owner:黄钰雪
Method for manufacturing ceramic tile
The invention provides a method for preparing a ceramic tile, belonging to the clay ceramic product technical field characterized by compositions. The method for preparing the ceramic tile is characterized in that the basic formula mainly comprises the following raw materials by weight portion: 20 to 25 portions of watered mud, 20 to 30 portions of sodium ore, 20 to 30 portions of albite, 5 to 10 portions of orthoclase, 15 to 25 portions of feldspar and 2 to 5 portions of pencil stone. The product has clear layering effect on the surface and super infectant resistance and improves the surface finish by improving the formula and the powder size of the raw materials.
Owner:淄博东岳实业总公司建材厂
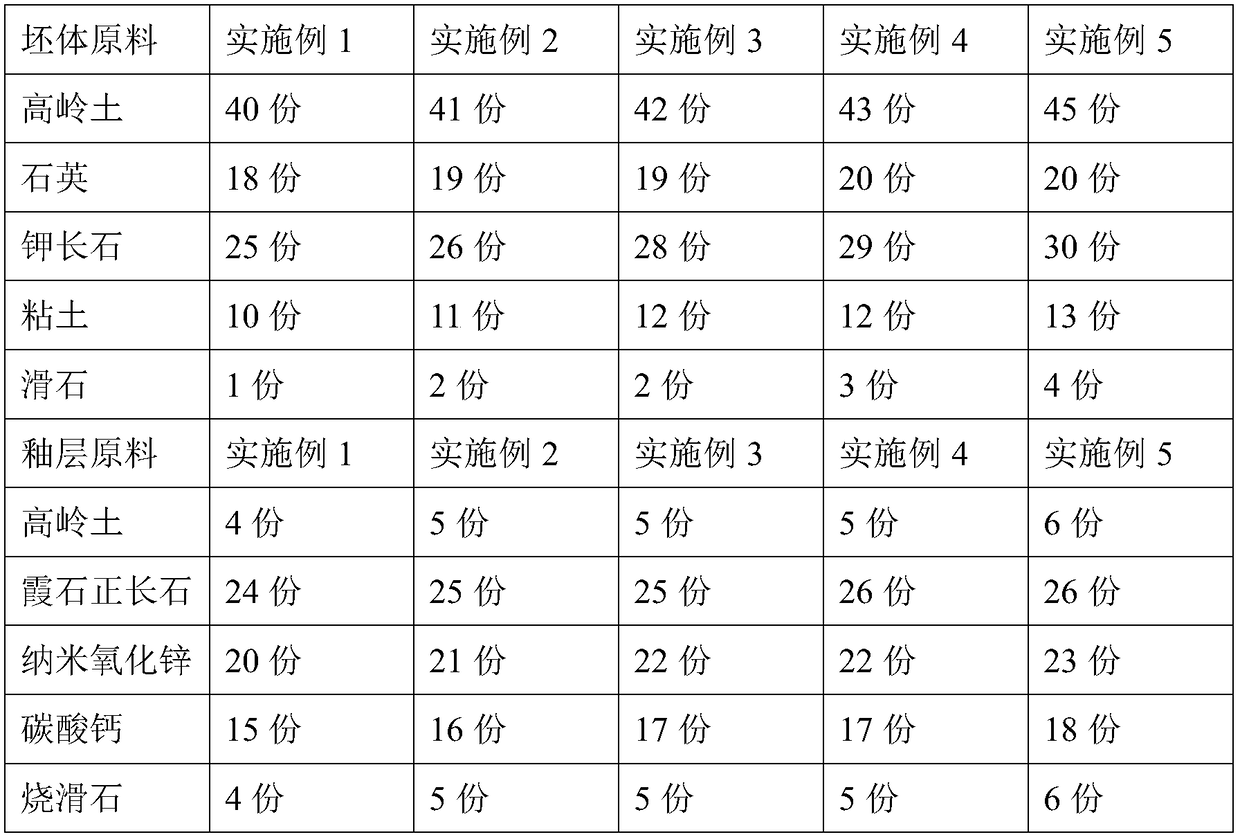
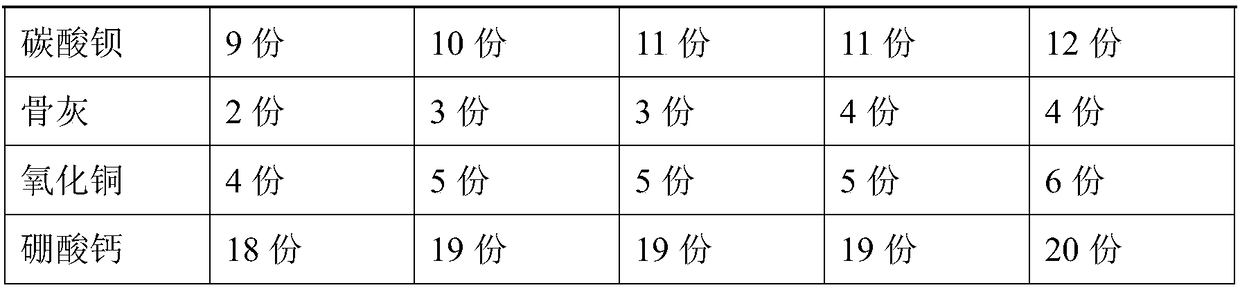
High-strength and crash-resistant sky blue glaze ceramic product and preparation method thereof
The invention provides a high-strength and crash-resistant sky blue glaze ceramic product which is prepared from an embryo material and a glaze material, wherein the embryo material is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 40-45 parts of kaolin, 18-20 parts of quartz, 25-30 parts of potassium feldspar, 10-13 parts of clay and 1-4 parts of talcum; the glaze material is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 24-26 parts of nepheline orthoclase, 20-23 parts of nano-zinc oxide, 15-18 parts of calcium carbonate, 4-6 parts of sintered talc, 4-6 parts ofkaolin, 9-12 parts of barium carbonate, 2-4 parts of bone ash, 4-6 parts of copper oxide and 18-20 parts of calcium borate. The preparation method of the high-strength and crash-resistant sky blue glaze ceramic product comprises the following steps: performing ball milling to obtain embryo material slurry and glaze slurry; making a green body from the embryo material slurry and performing biscuitfiring; glazing; and firing. The ceramic product prepared from the raw materials and by the technology provided by the invention shows a jade-like opalescent semi-transparent sky blue form and has asimple and elegant color as well as excellent crash resistance.
Owner:福建省德化业美陶瓷有限公司
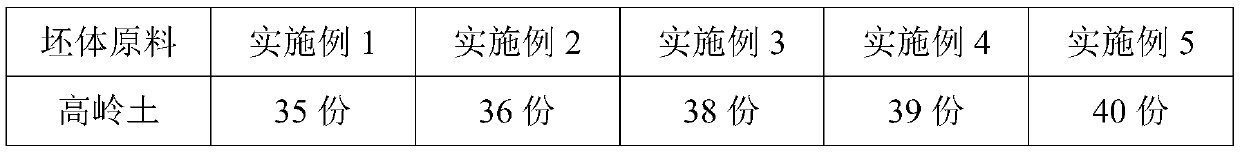
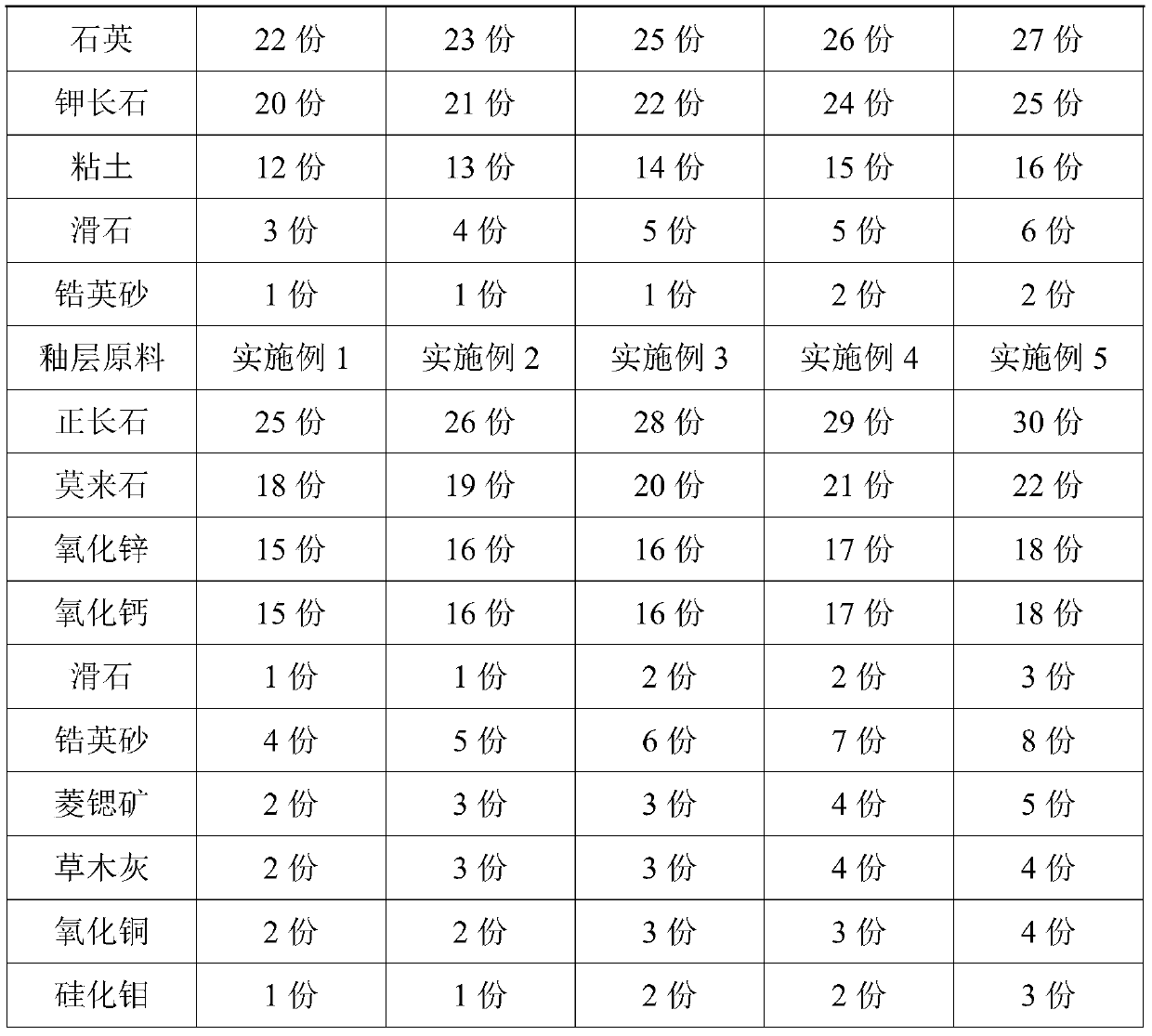
Thermal-insulation corrosion-resistant ancient building ceramic and preparation method thereof
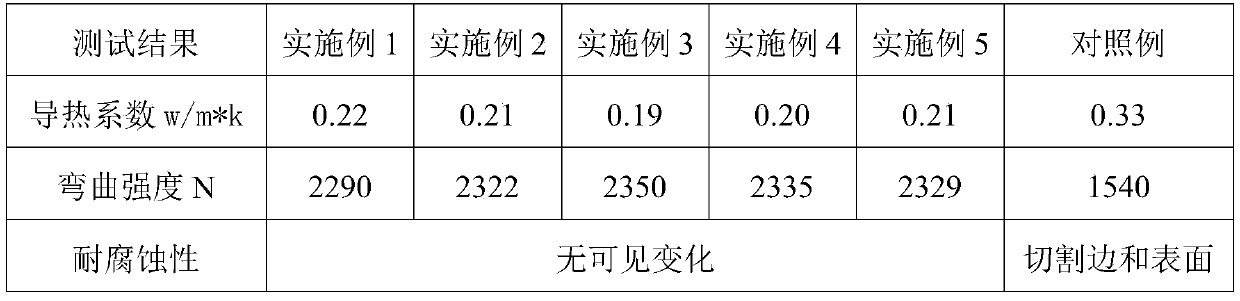
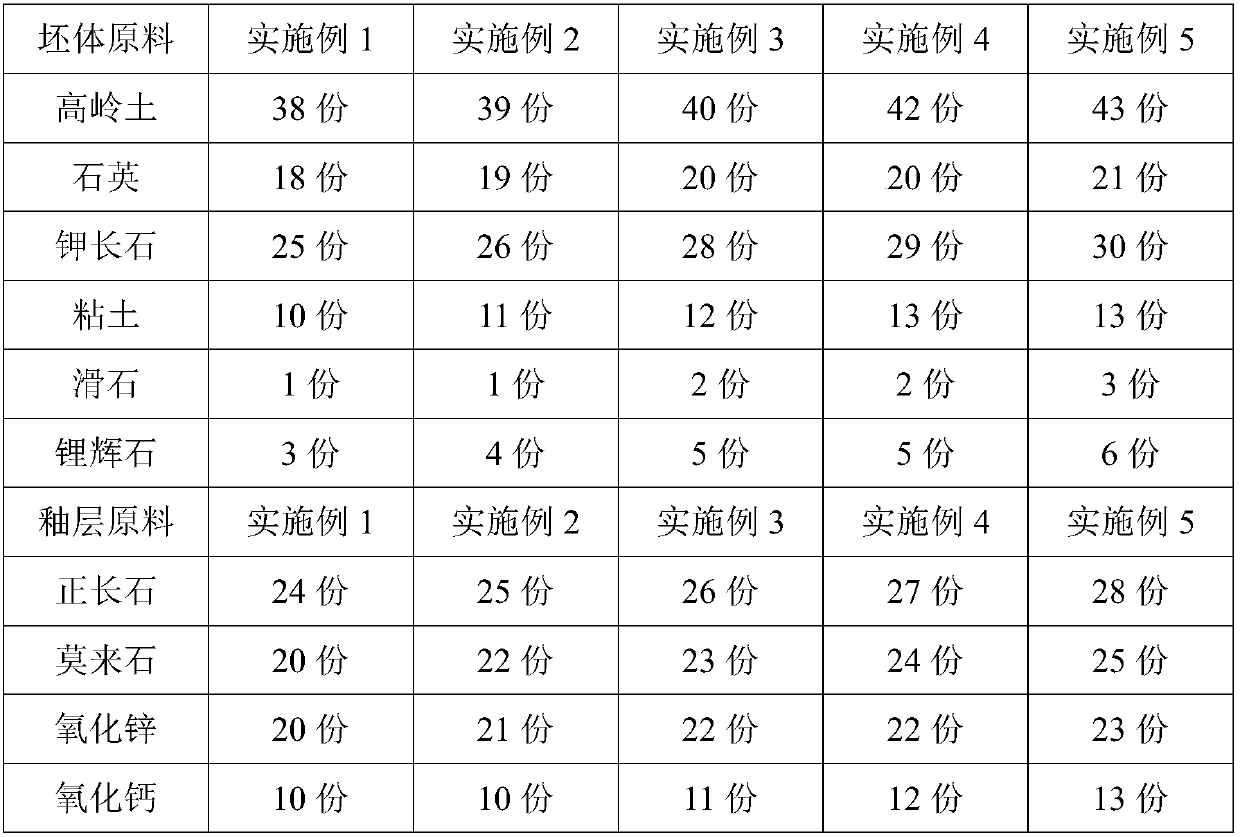
The invention provides thermal-insulation corrosion-resistant ancient building ceramic, and belongs to the technical field of ceramics. The thermal-insulation corrosion-resistant ancient building ceramic comprises a matrix material and a glaze material; the matrix material comprises the following raw materials in parts by weight: 35-40 parts of kaolin, 22-27 parts of quartz, 20-25 parts of potashfeldspar, 12-16 parts of clay, 3-6 parts of talc and 1-2 parts of zircon sand; and the glaze material comprises the following raw materials in parts by weight: 25-30 parts of orthoclase, 18-22 parts of mullite, 15-18 parts of zinc oxide, 15-18 parts of calcium oxide, 1-3 parts of talc, 4-8 parts of zircon sand, 2-5 parts of strontianite, 2-4 parts of plant ash, 2-4 parts of copper oxide and 1-3 parts of molybdenum silicide. The ancient building ceramic fired by using the raw materials and process provided by the invention has the characteristics of good heat insulation and corrosion resistance.
Owner:FUJIAN HUAXIA VAJRA TECH CO LTD
High-strength ancient building ceramic capable of resisting quick cooling and quick heating and preparation method thereof
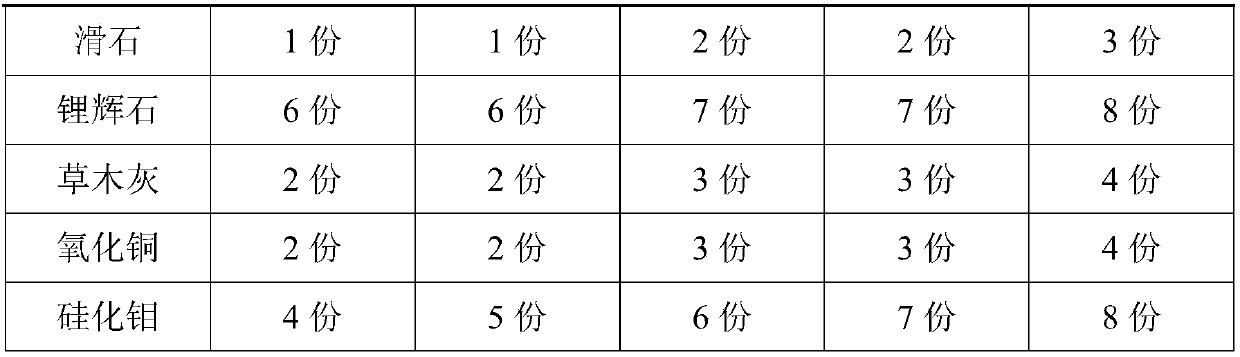
The invention provides a high-strength ancient building ceramic capable of resisting quick cooling and quick heating, and belongs to the technical field of ceramics. The high-strength ancient buildingceramic capable of resisting quick cooling and quick heating comprises a matrix material and a glaze material, wherein the matrix material comprises, by weight, 38-43 parts of kaolin, 18-21 parts ofquartz, 25-30 parts of potassium feldspar, 10-13 parts of clay, 1-3 parts of talc and 3-6 parts of spodumene; the glaze material comprises, by weight, 24-28 parts of orthoclase, 20-25 parts of mullite, 20-23 parts of zinc oxide, 10-13 parts of calcium oxide, 6-8 parts of spodumene, 1-3 parts of talc, 2-4 parts of plant ash, 2-4 parts of copper oxide and 4-8 parts of molybdenum silicide. The ancient building ceramic prepared from the raw materials through the technology has good heat insulation and corrosion resistance.
Owner:FUJIAN HUAXIA VAJRA TECH CO LTD
Low-temperature once-fired ceramic with opacified glaze and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN111960801AImprove liquidityAvoid lack of glazeCeramic materials productionClaywaresWood ashGlaze
The invention relates to the field of ceramic products and production methods thereof, and specifically relates to a low-temperature once-fired ceramic with opacified glaze and a preparation method. The bottom glaze layer is characterized by comprising the following raw materials in parts by weight: 5-6 parts of industrial iron oxide, 5-10 parts of wood ash, 3-5 parts of flint, 10-12 parts of quartz and 10-15 parts of orthoclase. The surface glaze layer is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 10 to 15 parts of fused powder, 15 to 18 parts of quartz, 10 to 15 parts of feldspar, 21 to 25 parts of albite, 2 to 3 parts of calcined talc, 8 to 10 parts of calcite, 2 to 3 parts of zircon and 1 to 2 parts of zinc oxide. According to the low-temperature once-fired ceramic with opacified glaze and the preparation method provided by the invention, the firing temperature is reduced, the opacified effect is good, the glaze form is rich, the fuel is effectively saved, the adaptability of the blank glaze is good, and the strength and hardness of the blank glaze are high.
Owner:FUJIAN QUANZHOU SHUNMEI GROUP
Recycling and clean production method for preparing yellow phosphorus, sylvite, aluminum oxide, molecular sieves, slag cement and architectural profiles through potassium-bearing phosphorite
ActiveCN105197902AReduce manufacturing costTake advantage ofSolid waste managementChemical industryFiltrationSlag
The invention relates to a recycling and clean production method for preparing yellow phosphorus, sylvite, aluminum oxide, molecular sieves, slag cement and architectural profiles through potassium-bearing phosphorite. The method utilizes two routes, for the first route, high quality yellow phosphorus is produced by the potassium-bearing phosphorite and coke nuts through an electrothermal method, water quenching is conducted on yellow phosphorus slags, KAlO2 is dissolved out, filtration is conducted, CO2 is introduced, Al(OH)3 is settled, first filtrate is obtained, and the Al(OH)3 is converted through temperature control to obtain Al2O3. For the second route, orthoclase power and Na2CO3 are evenly mixed, roasting is conducted through yellow phosphorus tail gas, water leaching is conducted through water, the CO2 is introduced to settle out silicon-aluminum colloid, and second filtrate is obtained. Crystallization and drying are conducted on the first filtrate and the second filtrate, and K2CO3 and Na2CO3 are obtained. The Na2CO3 returns to the second route to be recycled. The content of K2O, Na2O, SiO2 and Al2O3 is adjusted for partial silicon-aluminum colloid which is not subjected to sedimentation and the filtrate, hydrothermal crystallization reaction is conducted, and the molecular sieves are obtained; settled silicon-aluminum colloid is mixed with the yellow phosphorus slags to prepare the slag cement and / or the architectural profiles.
Owner:黄钰雪
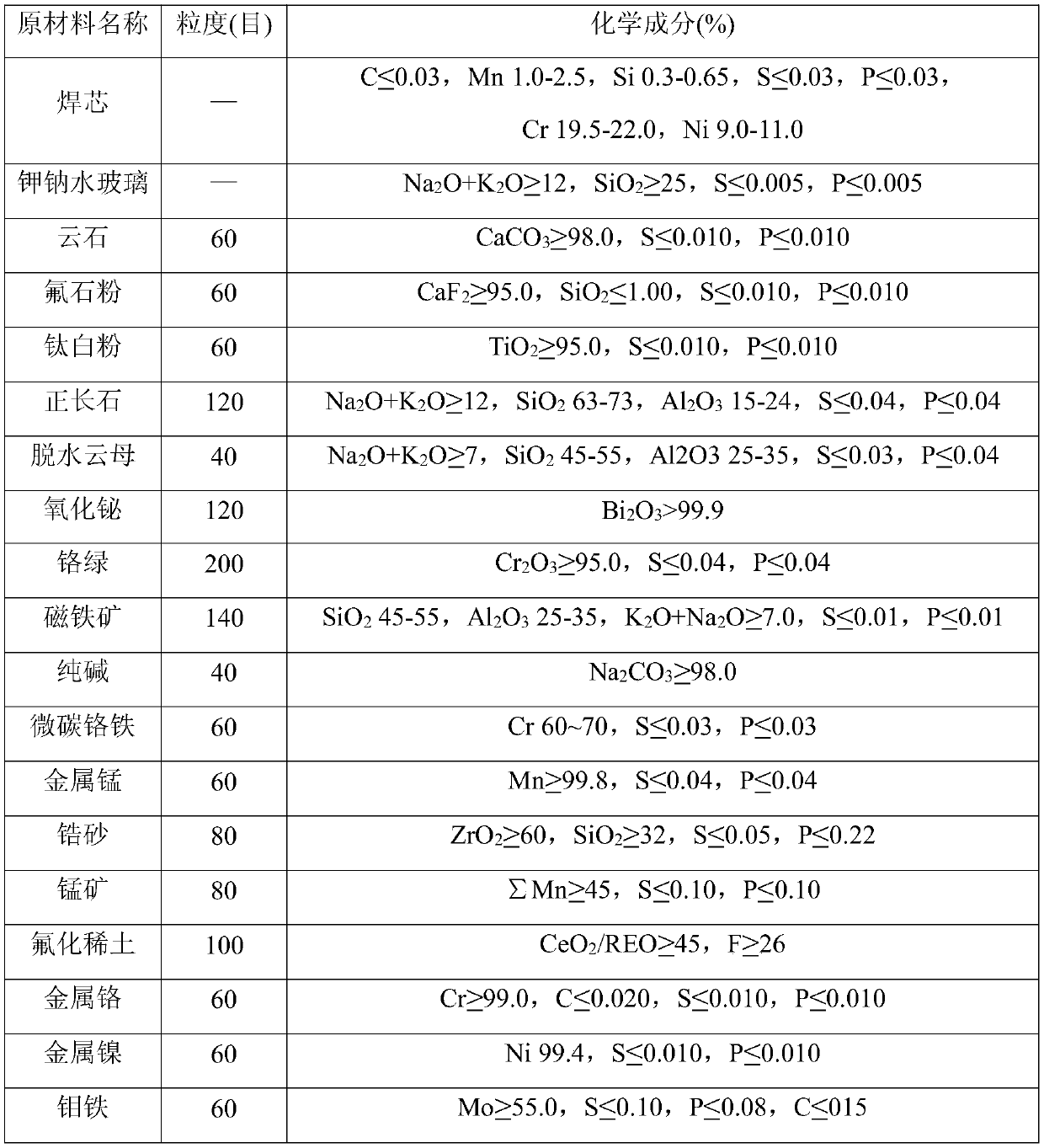
Welding rod for high current welding stainless steel pressure vessels
ActiveCN109759745AReduce dosageUniform melting rateWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaSlagAlloy
The invention discloses a welding rod for high current welding stainless steel pressure vessels, and belongs to the field of welding materials. The welding rod consists of two parts including a welding core and a coating coated on the surface of the welding core. The coating is prepared from the following components in percentage by weight: 25%-40% of titanium dioxide, 15%-30% of orthoclase, 11%-15% of fluorite powder, 8%-9% of marble, 0.1%-0.4% of bismuth oxide, 1.3%-2.5% of an arc stabilizer, 6.3%-8.5% of a deoxidant, 4%-10% of a slag forming constituent and 4.6%-15.3% of an alloy agent. When the stainless steel pressure vessels are welded, the welding rod can be used for being matched with 180A current to carry out welding, during the process of the welding, the coating is not red, thecoating is not cracked, and the welding seam is well formed.
Owner:725TH RES INST OF CHINA SHIPBUILDING INDAL CORP
Sea reef glaze for pottery ornaments and preparation method of sea reef glaze
The invention discloses sea reef glaze for pottery ornaments and a preparation method of the sea reef glaze. A technical formula of the sea reef glaze comprises the following components in percentage by mass: 3%-8% of nepheline orthoclase, 35%-55% of high alumina powder, 10%-30% of wollastonite, 3%-8% of dolomite, 10%-20% of calcium carbonate, 3%-8% of talc, 3%-8% of glaze clay and 0.5%-1.5% of CuCO3. The components are weighed according to the formula, fully mixed, and then added to a grinding tank; moisture accounting for 45%-50% the weight of dry powder is added for grinding for 10-15 hours, the concentration of the ground glaze slurry is adjusted until the true specific gravity is 45-50 when the residue rate is 0.1%-0.3% after the powder is screened with a 325-mesh screen, and the glaze slurry is applied to a pottery product through spraying or immersion, is aired and then fired in a kiln at the temperature of 1200-1235 DEG C for 8-11 hours; finally, the glaze is cooled naturally and taken out of the kiln. The prepared sea reef glaze has simple color and luster, is diversified, appears to be matte and rough and also has natural texture like clay glaze.
Owner:XIAMEN EDUNUS CERAMIC IND CO LTD
Resin precoated sand and preparation method thereof
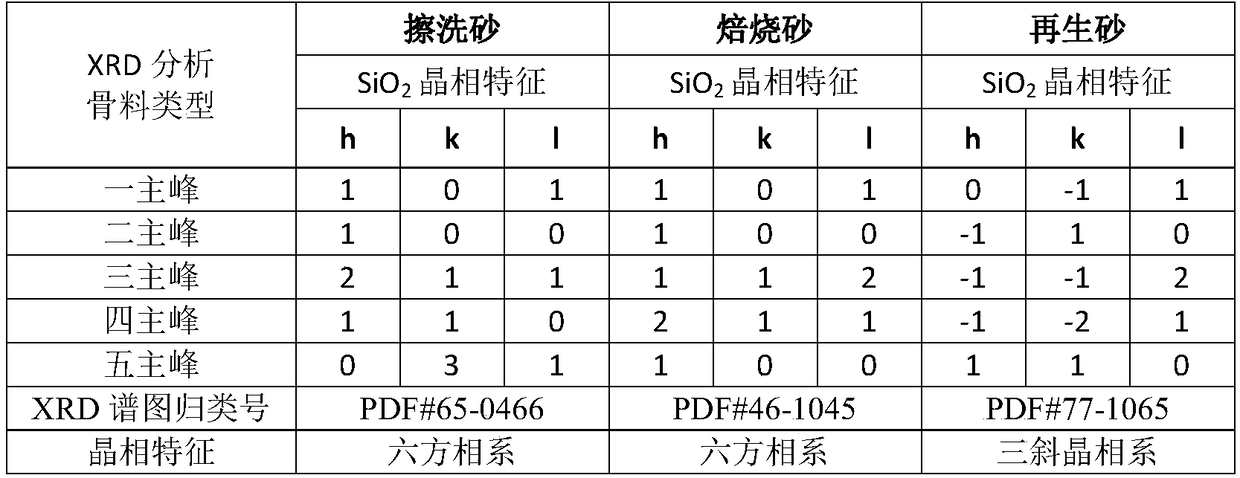
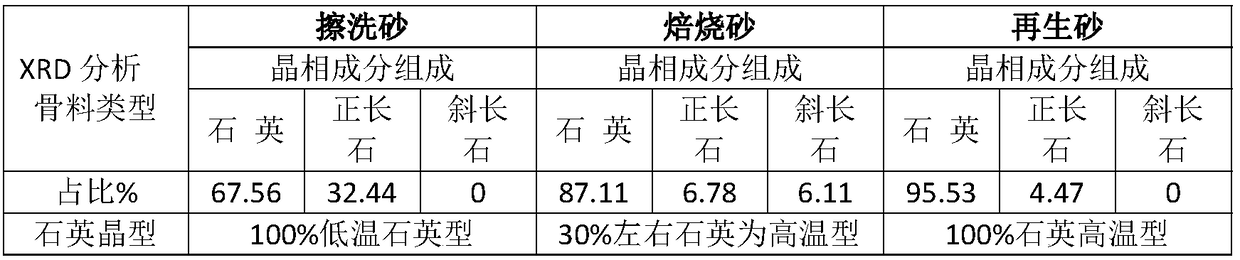
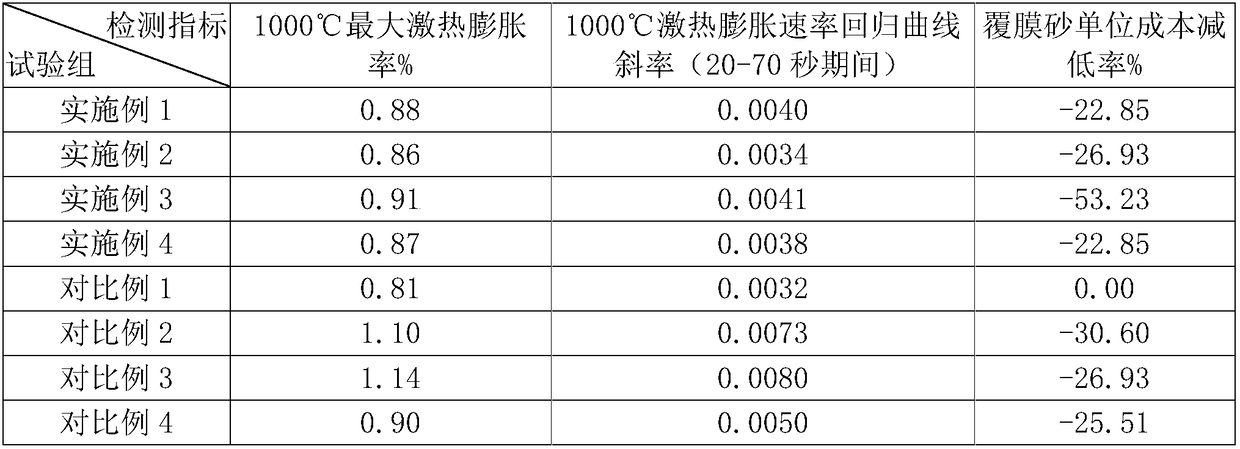
InactiveCN108746475AReduce veiningReduce the incidence of swelling defectsFoundry mouldsFoundry coresOrthoclaseMaterials science
The invention belongs to the technical field of casting modeling, and particularly discloses resin precoated sand and a preparation method thereof. The precoated sand comprises aggregate and thermoplastic resin. The content of a low-temperature phase beta in the aggregate is 0-51%, and the content of a high-temperature phase alpha is 35-100%. The content ratio of orthoclase in a total crystallinephase structure in the aggregate is not more than 16%, and the content ratio of anorthose in the total crystalline phase structure in the aggregate is not more than 5%. According to the technical method, the technical effect that coordinated expansion behavior is formed by adjusting the relation of the component ratio of high-temperature phase materials of the aggregate is achieved, so that a resin precoated sand product suitable for the thermal expansivity according to different pouring application needs is obtained, and the technical problem that various casting expansion type defects are caused by the fact that expansion behavior is not applicable is solved.
Owner:CHONGQING CHANGJIANG RIVER MOLDING MATERIAL GRP
Chemically temperable, corrosion-stable glasses
InactiveUS20200010353A1Improve acid resistanceIncreasing of the proportion of SiOGlass drawing apparatusGlass forming apparatusThermal dilatationSilicic acid
Owner:SCHOTT AG
Carbon-adsorption crackle glaze material for firewood fired pottery and preparation method thereof as well as ceramic prepared from carbon-adsorption crack glaze material and preparation method of ceramic
The invention relates to the field of pottery clay, a pottery clay preparation method, ceramic and a ceramic preparation method and in particular relates to a carbon-adsorption crack glaze material for firewood fired pottery and a preparation method thereof as well as ceramic prepared from the carbon-adsorption crack glaze material and the ceramic preparation method. The glaze material is preparedfrom the following components in parts by weight: 35 to 42 parts of kaolin, 16 to 22 parts of sodium carbonate, 10 to 13 parts of ball clay, 1 to 3 parts of salt, 7 to 10 parts of orthoclase, 5 to 7parts of zirconium silicate, 1 to 2 parts of cryolite and 1 to 2 parts of cellulose gum. Sodium carbonate in the glaze material adsorbs a lot of elemental carbon in a reduction atmosphere of a firewood firing kiln; a glaze surface is cracked through the salt and the kaolin; the ceramic glaze surface prepared from the carbon-adsorption crack glaze material forms carbon-adsorption and crack characteristics so that the ceramic has unique aesthetic value.
Owner:泉州市德化县艾慕陶瓷有限公司
Preparation and application method of high whiteness, high light transmittance and high plasticity ceramic green mud
The invention relates to a preparation and application method of high whiteness, high light transmittance and high plasticity ceramic blank mud, which uses Linchuan talc, phlogopite, orthoclase and American fairy water as raw materials, and undergoes raw material pretreatment, batching, ball milling, Aged, sieved, iron-removed, dehydrated, and smelted to obtain a ceramic body slime with a plasticity index greater than 20, and the ceramic body mud has a whiteness greater than 84 after molding, drying, biscuit firing, water replenishment, glazing, and high-temperature firing. Ceramic products with light transmittance greater than 7.5% / 2mm. The invention adopts common mineral raw materials and chemical raw materials for specific proportioning, and modifies the Linchuan talc, so that the green body has high whiteness, strong light transmittance, good plasticity and wide sintering range, and can also make The green body will not be deformed when it is fired at a high temperature of 1240-1310°C. It solves the shortcomings of high difficulty in production, complex molding process and narrow firing temperature range of high-whiteness and high-transparency ceramics, so it has broad market prospects.
Owner:JINGDEZHEN CERAMIC UNIV
Shatterproof ceramic product and preparation method thereof
The invention belongs to the field of ceramic products and particularly relates to a shatterproof ceramic product and a preparation method thereof. The shatterproof ceramic product is prepared from kaolin, gneiss, rhodochrosite, orthoclase, nano zirconium disilicide, red corundum, magnesite, mullite whiskers, yttria-stabilized zirconia, carbon fibers, wheat straw powder, sawdust, corn flour and nano antibacterial powder. Aggregate, auxiliary materials and other raw materials are utilized to prepare a ceramic blank, and the ceramic blank is dipped in a glaze and then sintered at the sintering temperature of 500-1300 DEG C. According to the provided shatterproof ceramic product and the preparation method thereof, the used materials improve the strength and reduce the total weight, the adhesion between particles is good, and the obtained ceramic product has certain seismic resistance and shatterproof performance.
Owner:杨史奋
High-temperature-resistant corrosion-resistant antifreeze ceramic product and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106116447AImprove performanceLow costCeramic materials productionClaywaresSodium BentoniteZirconate
The invention relates to a high-temperature-resistant corrosion-resistant antifreeze ceramic product and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of ceramics. The high-temperature-resistant corrosion-resistant antifreeze ceramic product comprises the following raw materials in parts by mass: 15-20 parts of nepheline orthoclase, 30-38 parts of Liling kaolin, 10-16 parts of Luochuan loess, 10-20 parts of a waste ceramic green body processing material, 5-9 parts of purple sand shale, 4-7 parts of flint clay, 2-4 parts of calcium zirconate, 5-10 parts of andalusite, 10-15 parts of a talc powder, and 9-14 parts of bentonite. Through the study of the ceramic product used raw materials, the ceramic raw material having excellent performance and relatively low cost is obtained; the ceramic product sintered by the preparation method has relatively good hardness and toughness, is not fragile, has relatively good weatherability, and is not easy to discolor; and in addition, a waste ceramic green body is retreatmented, so the matching performance of the waste ceramic green body with other raw materials in secondary recovery is effectively ensured.
Owner:德化县太阳鸟工艺品有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com