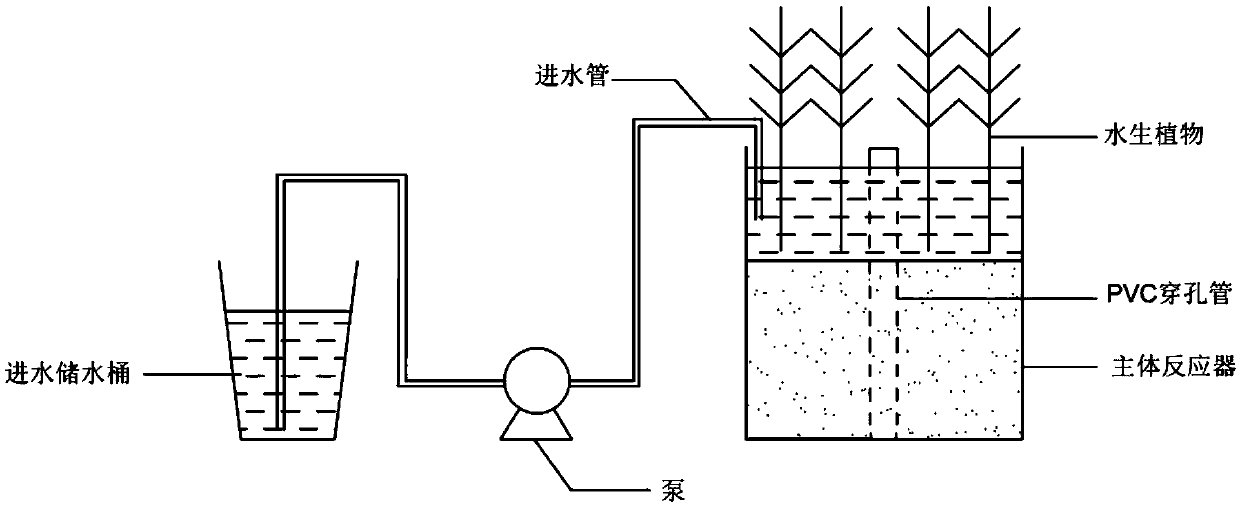
Technology for lakeside matrix to strengthen nitrogen and phosphorus removal
A technology for denitrification and phosphorus removal, lakeside belt, applied in chemical instruments and methods, water pollutants, water/sludge/sewage treatment, etc. The effect of strengthening hydraulic transmission and improving physical and chemical properties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
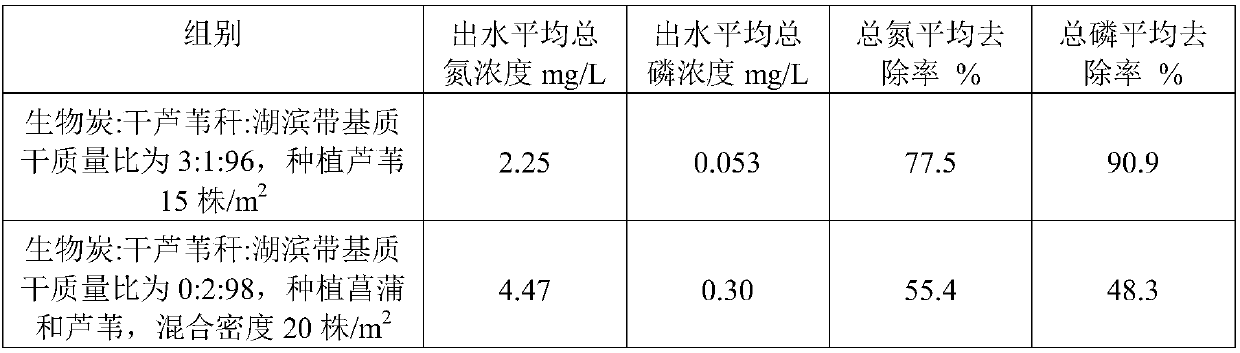
[0037] Embodiment 1: biochar: dry reed stalk: the dry mass ratio of the lakeside zone substrate is 3:1:96, planting 15 reeds / m 2 .
[0038] Wash the reed stalks, dry them at 80°C for 24 hours, and then crush them into reed powder to obtain reed powder with a particle size of 0.2-0.5mm. Under protection, after pyrolysis at high temperature for 1 hour, cool to room temperature, rinse with distilled water for 2-3 times to remove surface impurities, and dry at 80°C for 24 hours to obtain biochar; wash reed stalks and dry at 80°C for 24 hours, Cut into small sections of 5 cm; take the dry mass percentage of biochar:dried reed stalk:lakeside zone matrix as 3:1:96 after drying at 80°C for 24 hours, weigh the corresponding quality of biochar and dry reed stalk, and directly Add and mix on the substrate of the lakeside zone, the thickness of the conditioning substrate is 20cm of the substrate of the lakeside zone; then plant 15 reeds / m in the form of rhizomes on the mixed substrate 2...
Embodiment 2
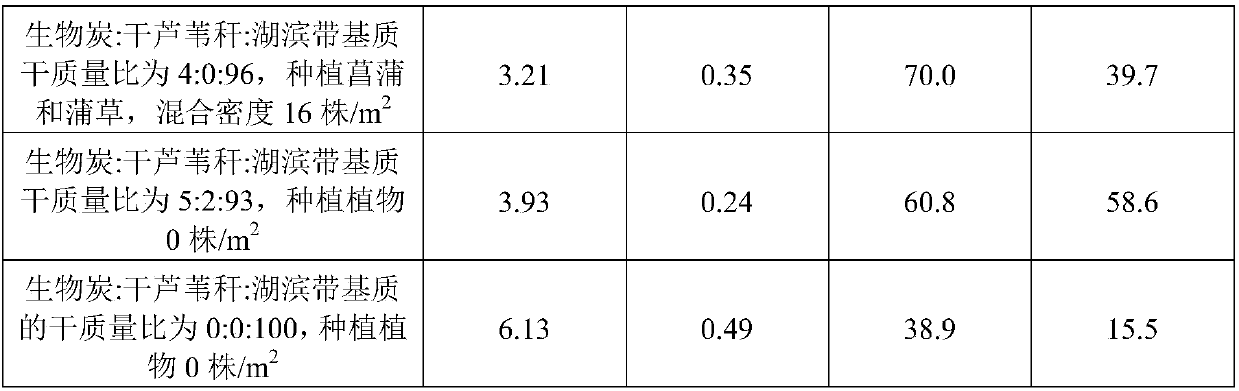
[0040] Embodiment 2: biochar: dry reed stalk: lakeside zone substrate dry mass ratio is 4:1:95, plant cattail and cattail grass, mixed planting density 18 plants / m 2 .
[0041] Wash the reed stalks, dry them at 80°C for 24 hours, and then crush them into reed powder to obtain reed powder with a particle size of 0.4-0.6mm. Under protection, after pyrolysis at high temperature for 1.5h, cool to room temperature, rinse with distilled water 2-3 times to remove surface impurities, dry at 83°C for 24h to obtain biochar; wash reed stalks, and dry at 85°C for 24h , cut into small sections of 10cm; take the mass of the corresponding biochar and dry reed stalks as the percentage of dry mass after drying at 85°C for 24h: biochar:dry reed stalks:lakeside zone matrix at 4:1:95, and directly Add and mix on the lakeside substrate, and adjust the substrate thickness to 30cm of the lakeside substrate; then plant cattails and cattails in the form of rhizomes on the mixed substrate, and the mix...
Embodiment 3
[0043] Embodiment 3: biochar: dry reed stalk: lakeside zone substrate dry mass ratio is 5:2:93, plant calamus and reed, mixed planting density 15 plants / m 2 .
[0044] Wash the reed stalks, dry them at 80°C for 24 hours, and then crush them into reed powder to obtain reed powder with a particle size of 0.3-0.7mm. Under protection, after pyrolysis at high temperature for 1.5 h, cool to room temperature, rinse with distilled water 2-3 times to remove surface impurities, and dry at 82° C. for 24 h to obtain biochar. Wash the reed stalks, dry them at 84°C for 24 hours, and cut them into 8cm pieces. Weigh the corresponding biochar and dry reed stalks based on the percentage of dry mass after drying at 83°C for 24 hours: biochar:dried reed stalks: lakeside substrate: 5:2:93, and add them directly to the lakeside substrate Mix, condition the substrate thickness to 30cm of lakeside substrate. Then plant calamus and reeds in the form of rhizomes on the mixed substrate, and the mixed...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com