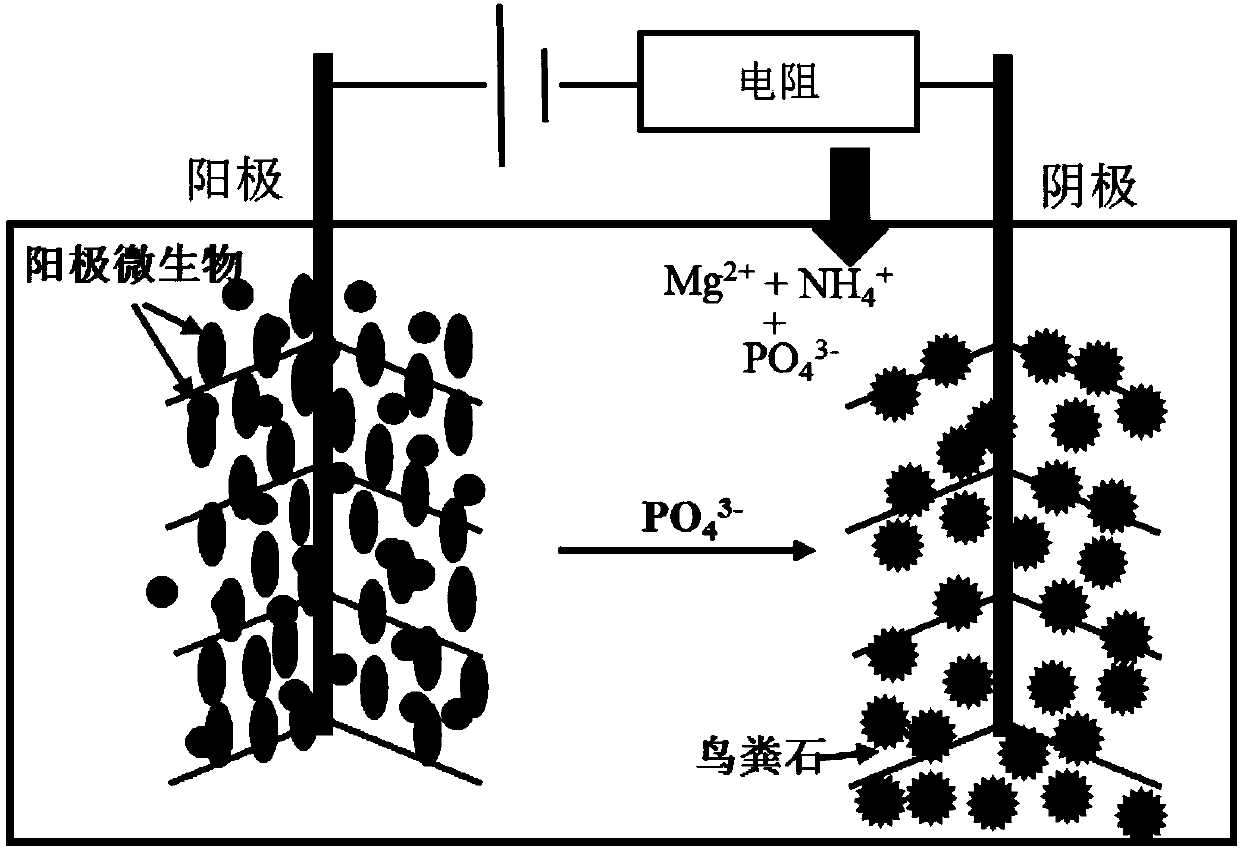
Method for in-situ recovery of high-purity struvite through microbial electrolytic cell
A microbial electrolysis cell and microbial electrolysis technology, applied in the direction of electrolysis components, electrolysis process, etc., can solve the problems of cumbersome operation of struvite, poor sedimentation and separation performance, reduce power consumption, etc., and achieve the effect of avoiding eutrophication of water body
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] (I) Construction of microbial electrolytic cell: a double-chamber H-type microbial electrolytic cell reactor is used, and high borosilicate glass (i.e. high borosilicate glass) is used for microbial electrolytic cell reaction; the effective volume of the reactor is 550mL, and the anode chamber and cathode chamber are 250mL respectively , the junction of the reactor is 50mL; assemble the microbial electrolytic cell reactor, fix the anode carbon brush and the cathode carbon brush, the diameter of the carbon brush bristles is 4cm, and ensure that the distance between the anode carbon brush and the cathode carbon brush is 9cm, and the reaction The top of the device is sealed with a blue silicone plug (or a rubber plug), and the gas is collected with a syringe, that is, the microbial electrolytic cell reactor is constructed;
[0033] (II) Microbial electrolytic cell acclimatization: take the effluent of the microbial fuel cell in stable operation as the inoculum, use 1.5g / L s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com