Ebullated bed reactor with internal circulation catalyst and hydrogenation method thereof
A fluidized bed reactor and catalyst technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, chemical/physical processes, etc., can solve the problems of few operation means, inability to form a circulation, and difficulty in forming a circulation, and achieve low energy consumption, complete fluidization, To achieve the effect of inner loop
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
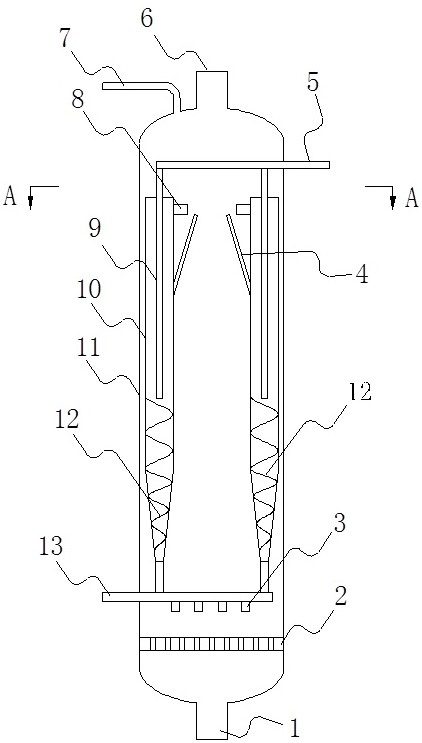
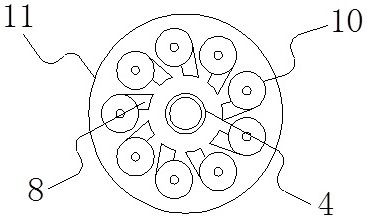
[0070] This embodiment adopts as figure 1 and figure 2 The ebullated bed reactor shown. The ebullated bed reactor is a laboratory reactor with an inner diameter of 3.6cm and a height of 2m. There are 10 cyclone separators inside, and the raw material is vacuum residue.
[0071] The hydrogenation reaction process is as follows:
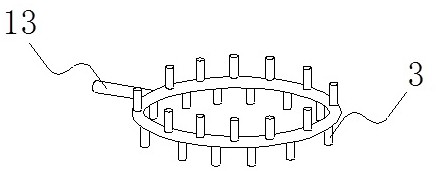
[0072] (1) First mix the vacuum residue with hydrogen, then enter the ebullated bed reactor, and distribute it evenly through the gas-liquid distributor 2 to form a gas-liquid mixture. The gas-liquid mixture drives the catalyst to flow upward and undergo hydrogenation catalytic reaction, decompression The impurity components in the residual oil are reacted and removed under the hydrogen atmosphere; the macromolecular hydrocarbons are continuously decomposed into small molecules.
[0073] (2) After the gas-liquid mixture flows upward and diverts through the conical tube 4, the liquid forms a horizontal separation velocity, and then the liquid drives...
Embodiment 2
[0077] This embodiment adopts as figure 1 and figure 2 The ebullated bed reactor shown. The ebullated bed reactor is an industrial ebullated bed vacuum residue reactor with an inner diameter of 3m and a height of 36.9m. There are 10 cyclone separators inside, and the raw material is vacuum residue.
[0078] The hydrogenation reaction process is as follows:
[0079] (1) The vacuum residue is heated and mixed with hydrogen, and then enters the ebullated bed reactor, and is evenly distributed through the gas-liquid distributor 2 to form a gas-liquid mixture. The gas-liquid mixture drives the catalyst to flow upward and undergo a hydrogenation catalytic reaction. The impurity components in the vacuum residue are reacted and removed in the hydrogen atmosphere; the macromolecular hydrocarbons are continuously decomposed into small molecules.
[0080] (2) After the gas-liquid mixture flows upward and diverts through the conical tube 4, the liquid forms a horizontal separation vel...
Embodiment 3
[0084] The ebullating bed reactor of this embodiment, the raw material is vacuum residual oil, and the difference with embodiment 2 ebullating bed reactor is: the inner diameter of ebullating bed reactor is 4.5m, height 16.4m, the liquid outlet 5 and cylinder 11 There is a circulating pipeline connected between the bottoms, and the circulating oil is pressurized by the circulating pump.
[0085] The hydrogenation reaction process is as follows:
[0086] (1) First mix the vacuum residue with hydrogen, then enter the ebullated bed reactor, and distribute it evenly through the gas-liquid distributor 2 to form a gas-liquid mixture. The gas-liquid mixture drives the catalyst to flow upward and undergo hydrogenation catalytic reaction, decompression The impurity components in the residual oil are reacted and removed under the hydrogen atmosphere; the macromolecular hydrocarbons are continuously decomposed into small molecules.
[0087] (2) After the gas-liquid mixture flows upward ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com