Method of making a flavoured sweetener and uses thereof
A flavor and sucrose technology, applied in the field of flavor sweeteners and the preparation and use of flavor sweeteners, can solve problems such as pollution, unstable CNS flavor, and inability to scale up industrially
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
[0126] The current market consists of a range of CNS and sweet sauces with different flavor profiles and chemical compositions that have been developed semi-independently over the years and are still being produced and used to meet local preferences.
[0127] To meet the demand for a range of different flavored sweetener and sweet sauce products, we have developed a common process that can be adapted for a wide variety of modifications to produce these products for consumers with different preferences.
[0128] Furthermore, the new process uses natural food-quality sugary raw materials that are available in large quantities, such as sugar cane juice from cultivated sugar cane species, which is produced on a much larger scale and with higher yields per hectare than coconut inflorescence sap. Therefore, flavor sweeteners and sweet sauces made from it can be obtained at significantly lower cost than traditional CNS and sweet sauces.
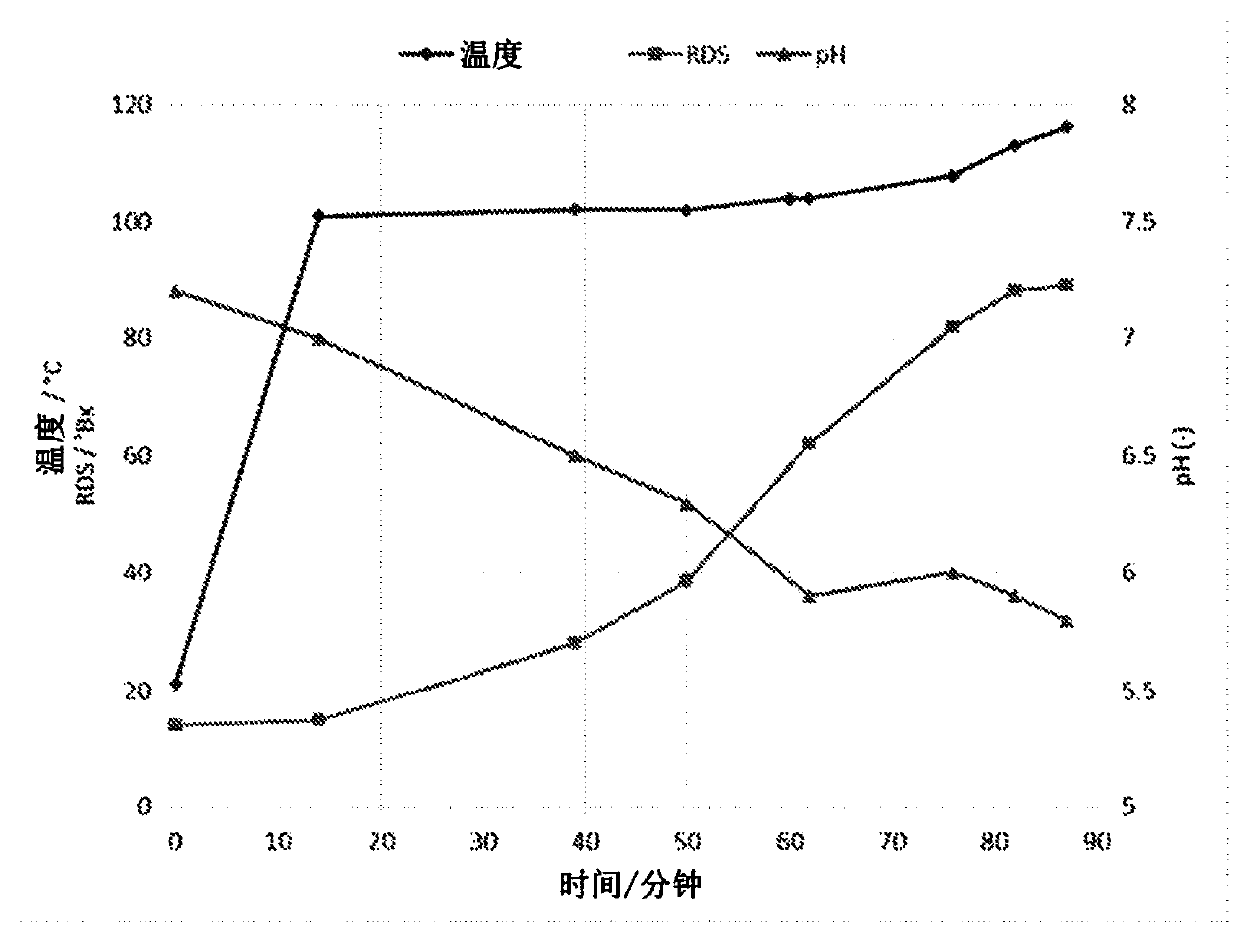
[0129]This general new process is based on th...
Embodiment 9
[0172] A sugar-like washing method using filtration to produce reduced sucrose flavor sweeteners is shown in Example 9, wherein sucrose crystals in semi-crystalline flavor sweeteners are removed from free sugars by washing with a mixture of ethanol and water. Separation from the shaped matrix. It is estimated that one-third of the sucrose is removed in this process, equivalent to about 15% by weight of the total flavor sweetener mass.
[0173] Low glycemic index sweeteners such as isomalt, isomaltulose, or tagatose can be added to these reduced sucrose flavored sweeteners to increase their sweetness without increasing their GI or cariogenic potential sex.
[0174] Natural Flavor Extracts
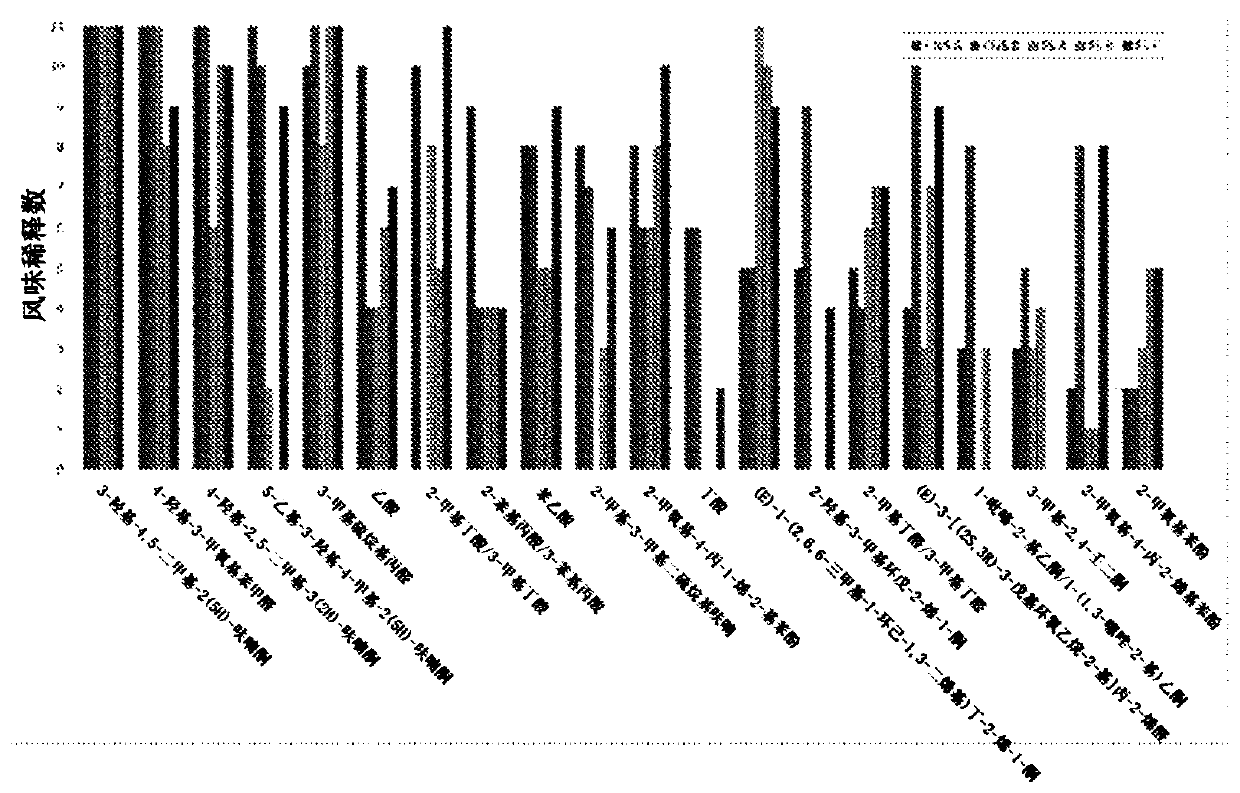
[0175] The methods outlined herein can also be used to prepare natural flavor extracts and / or natural flavor or aroma chemicals from modified unrefined plant extracts, flavored sweeteners, or sweet sauces made with flavored sweeteners, such as by solvent Extraction, supercritical CO2 extr...
Embodiment 10
[0176] A solvent extraction method using diethyl ether to prepare a natural flavor extract is shown in Example 10.
[0177] product
[0178] overview
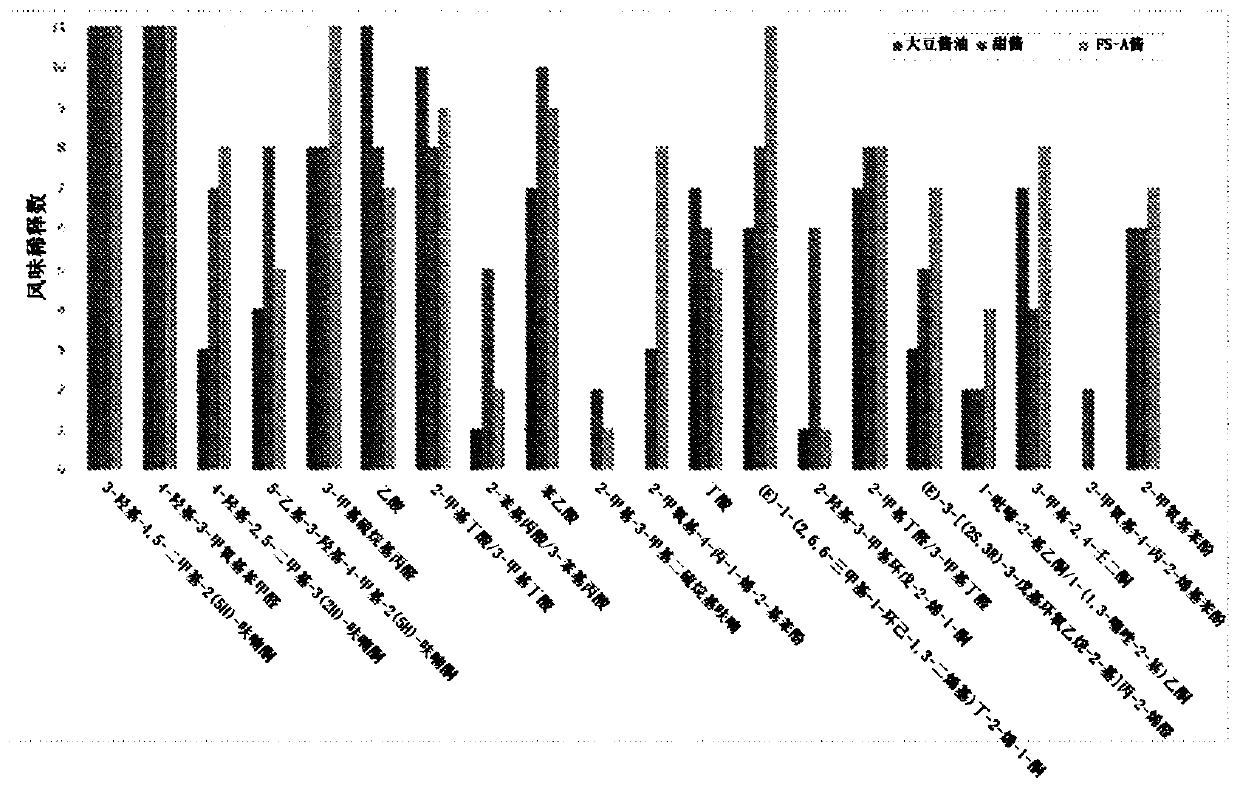
[0179] In Example 1, Flavor Sweetener A (FS-A) was prepared using microorganisms Stenotrophomonas maltophilia and Bacillus flexus incubated in sugarcane juice.
[0180] In Example 2, flavor sweetener B (FS-B) was prepared using microorganisms Bacillus subtilis and Bacillus flexus incubated in sugarcane juice.
[0181] In Example 3, Flavor Sweetener C (FS-C) was prepared using microorganisms Stenotrophomonas maltophilia and Bacillus flexus incubated in diluted raw sugar.
[0182] In Example 4, flavored sweeteners were prepared using the microorganisms Stenotrophomonas maltophilia and Bacillus flexus incubated in a 1:1 mixture of sugarcane juice and cane molasses.
[0183] In Example 5, flavor sweeteners were prepared using microorganisms Bacillus subtilis and Bacillus flexus incubated with diluted sugar cane syrup.
[0184...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| The inside diameter of | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com