Enzymolysis-resisting antibacterial peptide I9H12 as well as preparation method and application thereof
An I9H12, anti-enzyme technology, applied in the preparation method of peptides, antibacterial drugs, antifungal agents, etc., can solve the problem of less antibacterial peptides
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0012] Antimicrobial Peptide Design:
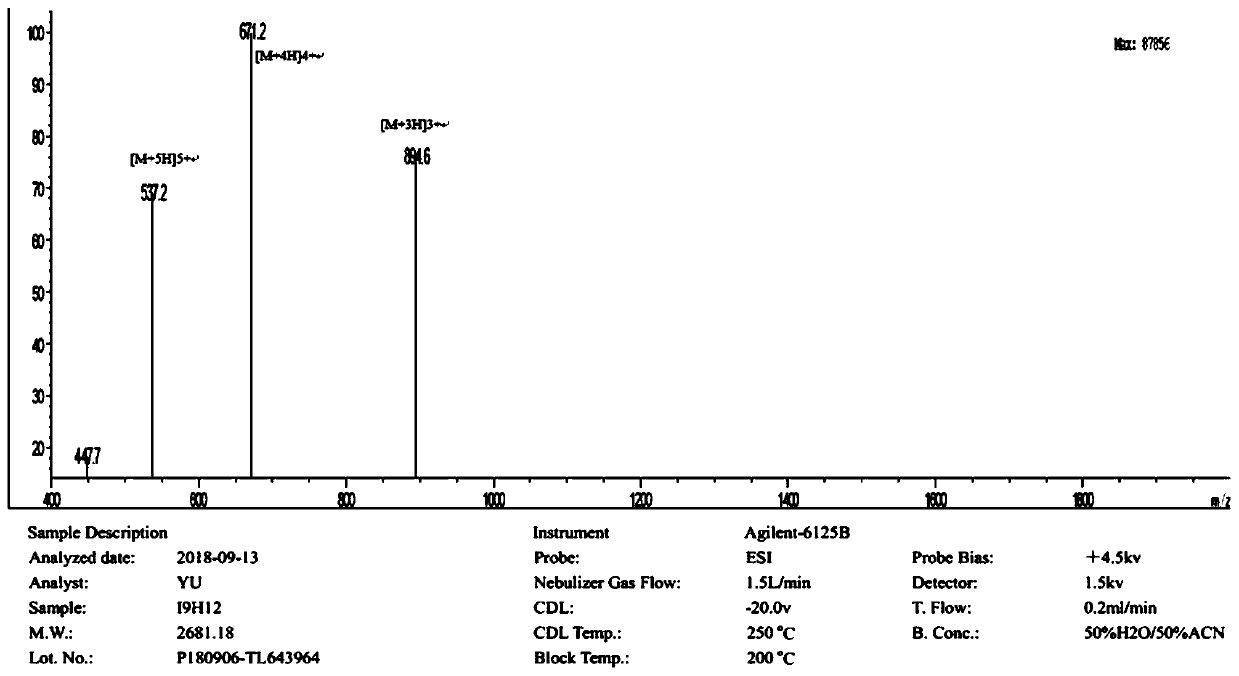
[0013] The amino acid sequence of the antimicrobial peptide I9H12 is:
[0014]
[0015] Referring to the properties of amino acids, while avoiding the cleavage sites of major proteases in the body as much as possible, the hydrophobic amino acid isoleucine (Ile) and the positively charged amino acid histidine (His) were selected as the main amino acids to newly design the I9H12 antimicrobial peptide. The carboxyl terminus of the peptide is amidated to add a positive charge and increase the stability of the peptide. The sequences of the antimicrobial peptides are shown in Table 1.
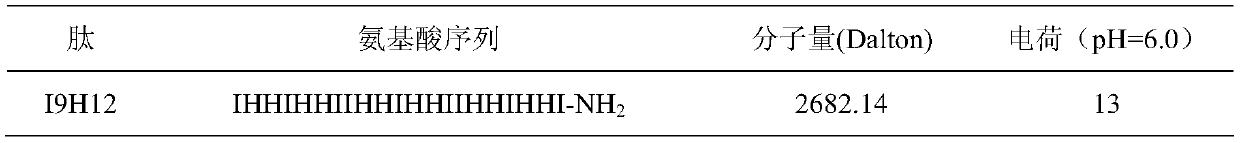
[0016] Table 1 Main parameters of newly designed peptides
[0017]
[0018] I9H12 is a small peptide with 21 amino acids, the charge number is +13 at pH 6.0, and the hydrophobic amino acid ratio is 0.4286.
Embodiment 2
[0020] The above-mentioned antimicrobial peptides were synthesized using a peptide synthesizer. The method was solid-phase chemical synthesis, and the specific steps were:
[0021] 1. The preparation of antimicrobial peptides is carried out one by one from the C-terminal to the N-terminal, and is completed by a peptide synthesizer. First, Fmoc-X (X is the first amino acid at the C-terminal of each antimicrobial peptide) is inserted into Wang resin, and then the Fmoc group is removed to obtain X-Wang resin; then Fmoc-Y-Trt-OH (9 -Fmoxy-trimethyl-Y, Y is the second amino acid at the C-terminus of each antimicrobial peptide); according to this procedure, it is synthesized from the C-terminus to the N-terminus until the synthesis is completed, and the side of the Fmoc group is removed chain protection resin;
[0022] 2. Add a cleavage reagent to the peptide resin obtained above, react at 20°C for 2 hours in the dark, filter; precipitate with TFA (trifluoroacetic acid) and wash, m...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0025] Detect the antibacterial activity, hemolytic activity and protease hydrolysis ability of the designed and synthesized antimicrobial peptide in vitro;
[0026] 1. Determination of antibacterial activity: The minimum inhibitory concentration of several antibacterial peptides was determined by the micro broth dilution method. Bacterial single colonies were picked and cultured overnight in MHB medium, and transferred to new MHB to grow to mid-logarithmic phase. Then the above bacterial solution was centrifuged and resuspended in MHB adjusted to pH 6.0 to a final concentration of 1 × 10 5 CFUml -1 , and transferred to a 96-well plate, 50 μl per well, and the fungi were diluted in RPMI 1640 (pH=6.0) medium containing morpholine propanesulfonic acid (MOPS). 50 μl of BSA (pH=6.0) containing different concentrations of peptides were added to the above-mentioned 96-well plate, and the final peptide concentration in the 96-well plate ranged from 0.125 to 64 μM. After incubating...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com