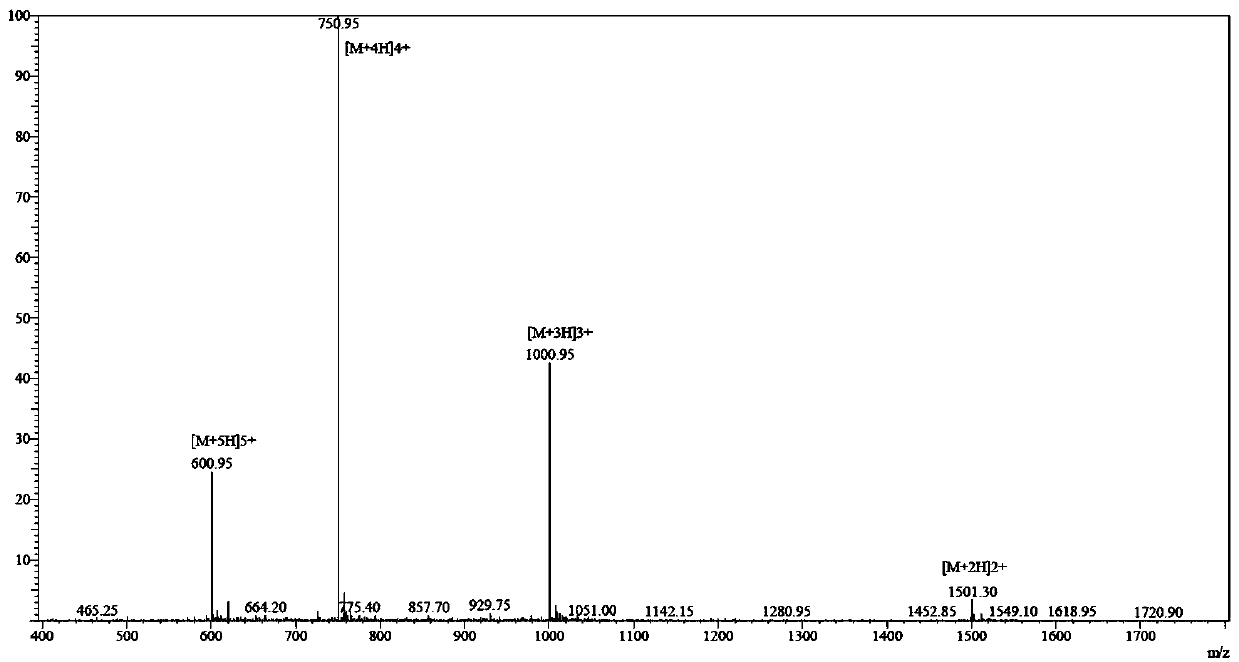
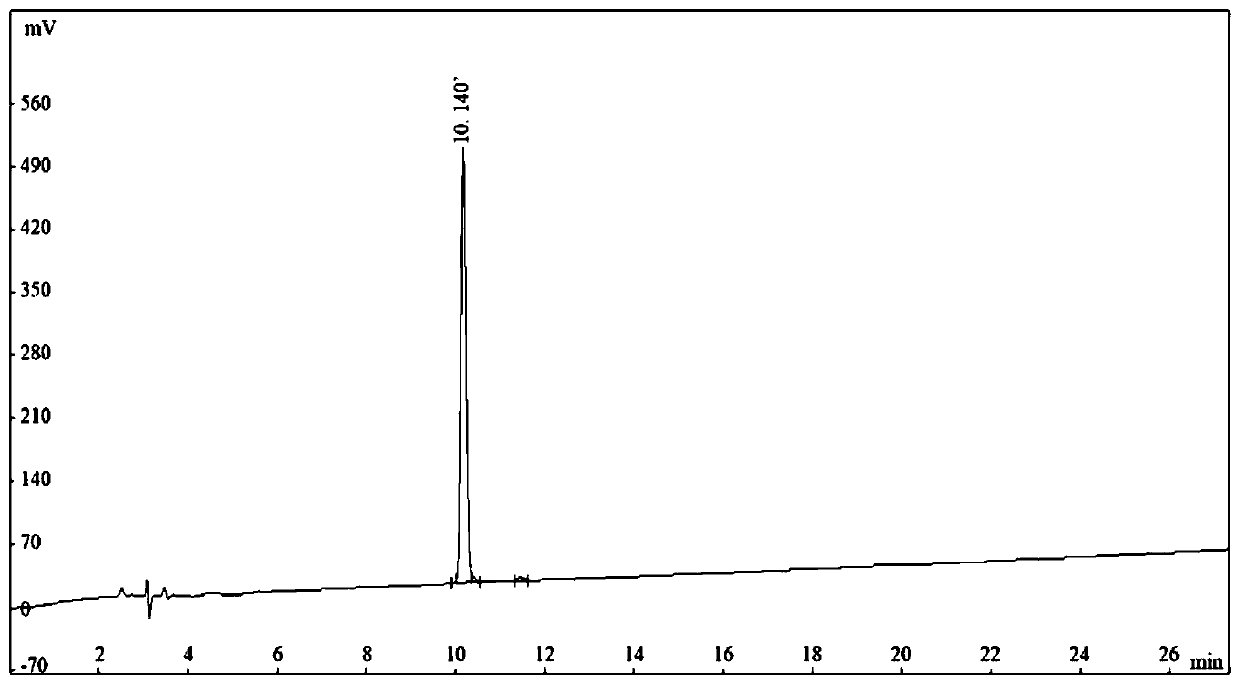
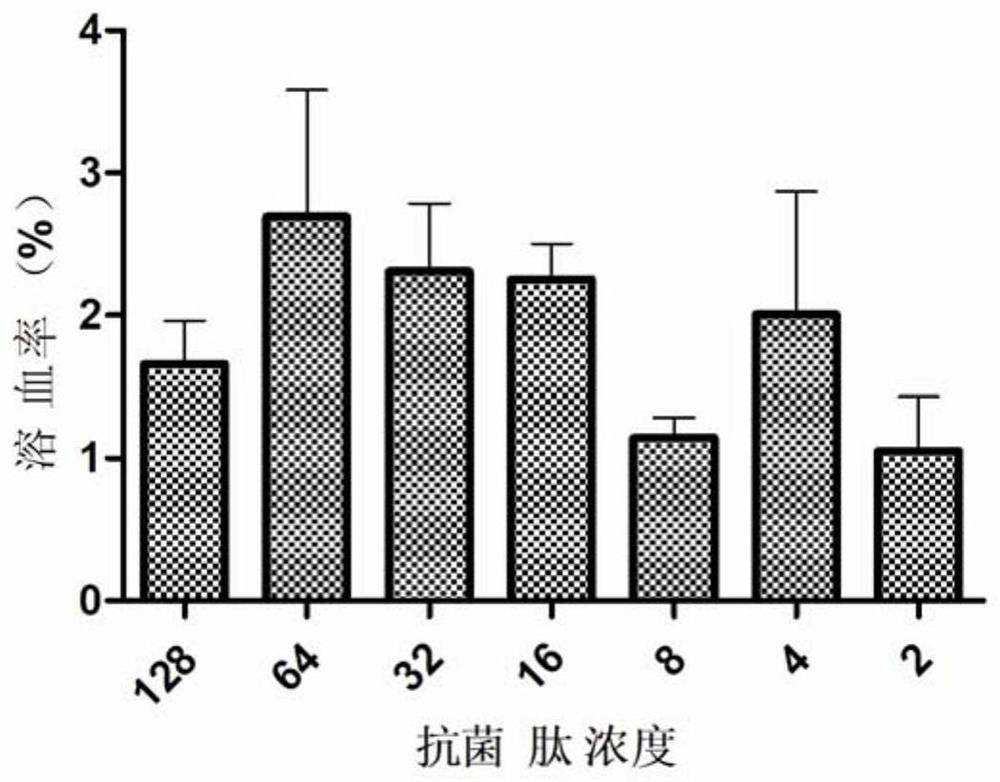
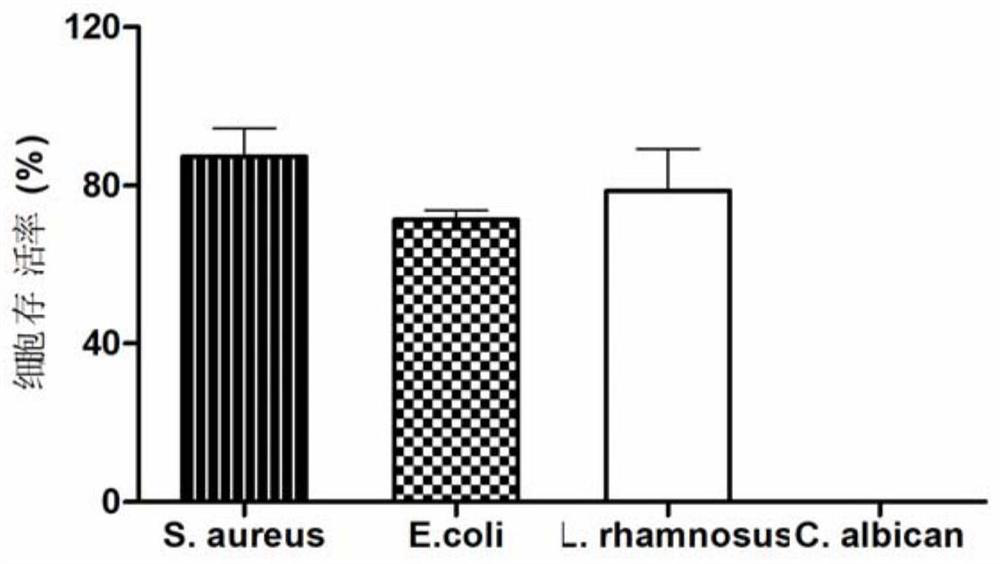
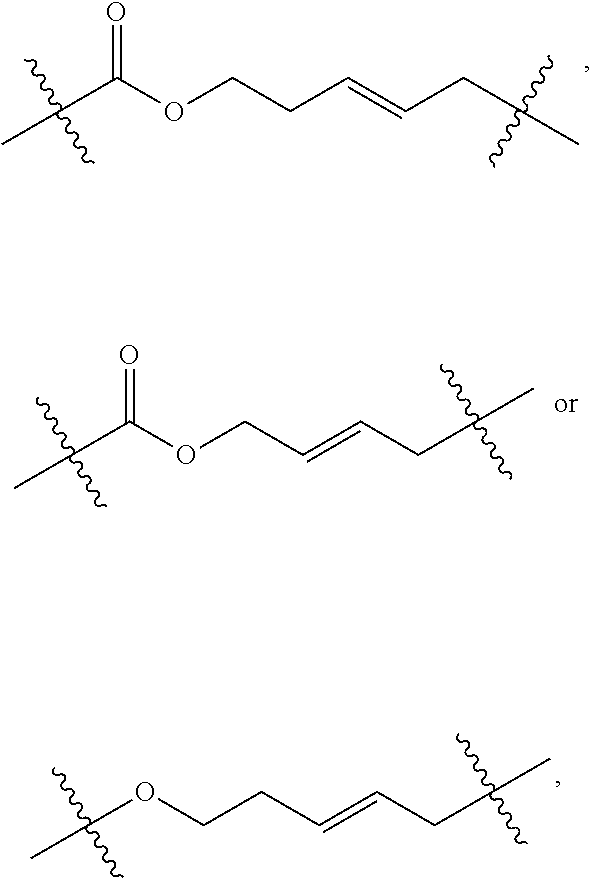
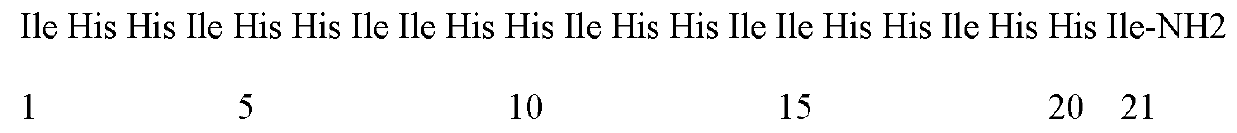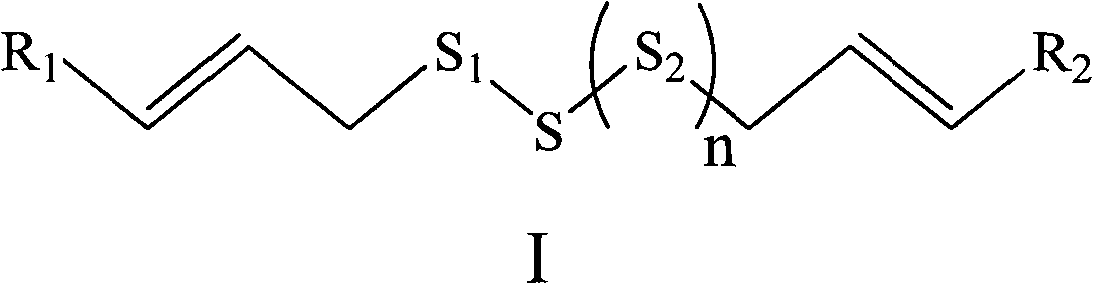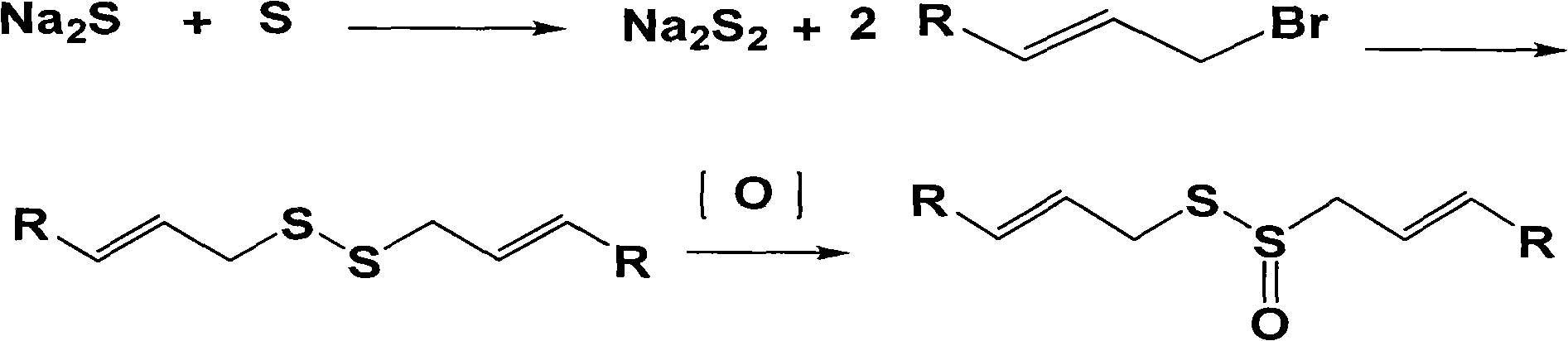Patents
Literature
34 results about "Fungal Infectious Disease" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Fungal Infectious Diseases Aspergillosis: infection with fungi of the genus Aspergillus leading to allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis, pulmonary aspergilloma, or invasive aspergillosis. Blastomycosis: inhalation of fungus called Blastomyces dermatitidis from the natural soil habitat.
Paeonia plant extract and preparation method and applications thereof
The invention provides a paeonia plant extract and a preparation method and applications thereof. The extract is prepared from paeonia seed cases, wherein the content of total polyphenol is 40%-90%, and the total polyphenol contains stilbene ingredient. Proved by experiment research, the extract or drug composition thereof can be used for preventing or treating fungus infection diseases, virus infection disease, cancer and other diseases.
Owner:INST OF MEDICINAL PLANT DEV CHINESE ACADEMY OF MEDICAL SCI
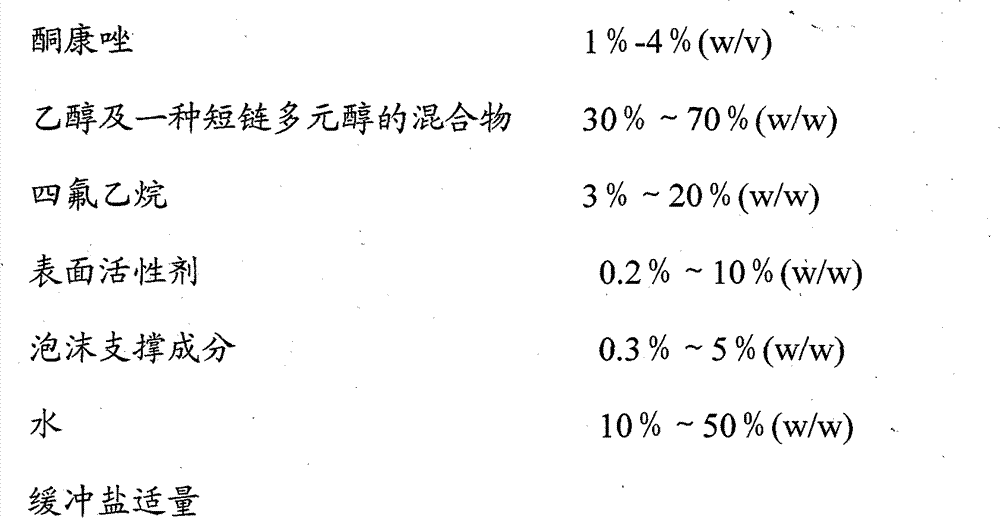
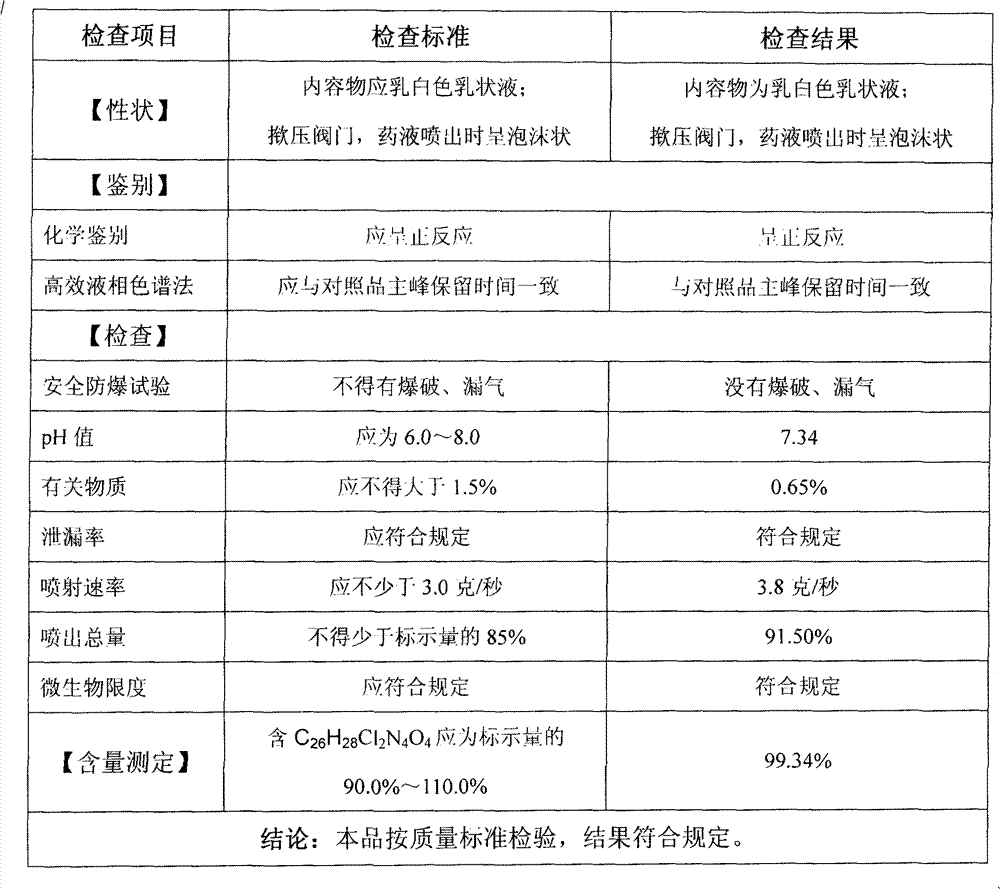
Ketoconazole foaming agent and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101856328AFine foamAvoid adverse situationsOrganic active ingredientsAntimycoticsDiseaseFoaming agent
The invention provides a ketoconazole foaming agent and a preparation method thereof, which are used for treating fungal infective diseases, such as seborrheic dermatitis and the like.
Owner:北京京卫燕康药物研究所有限公司
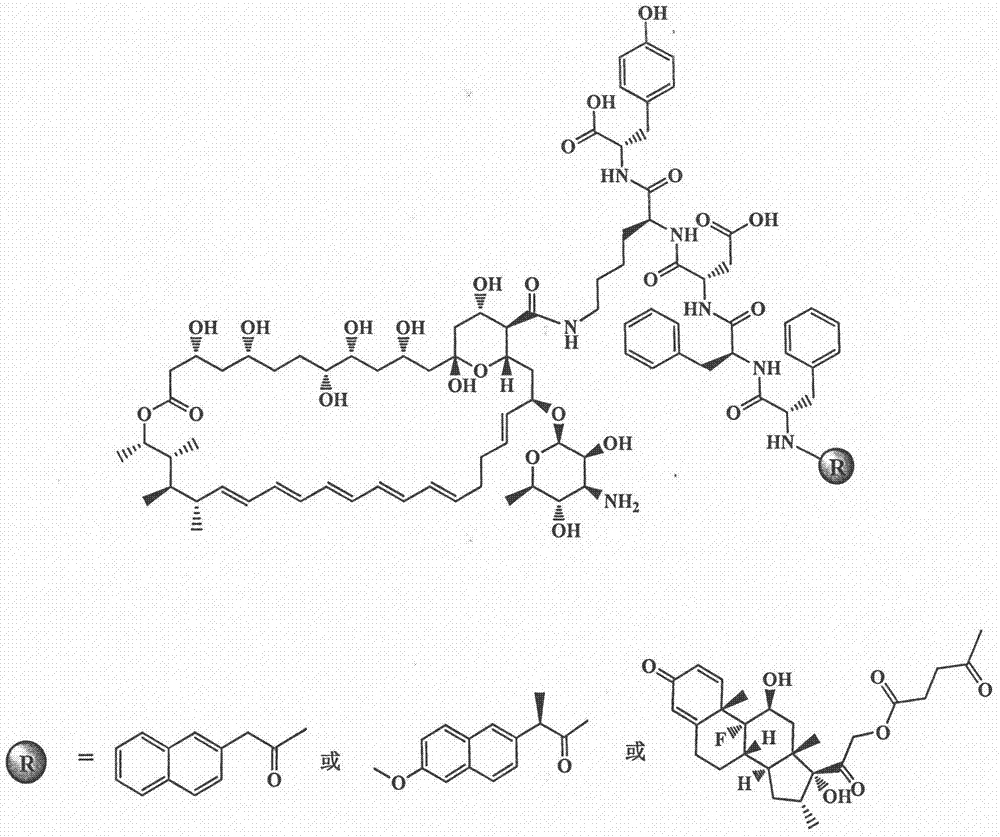
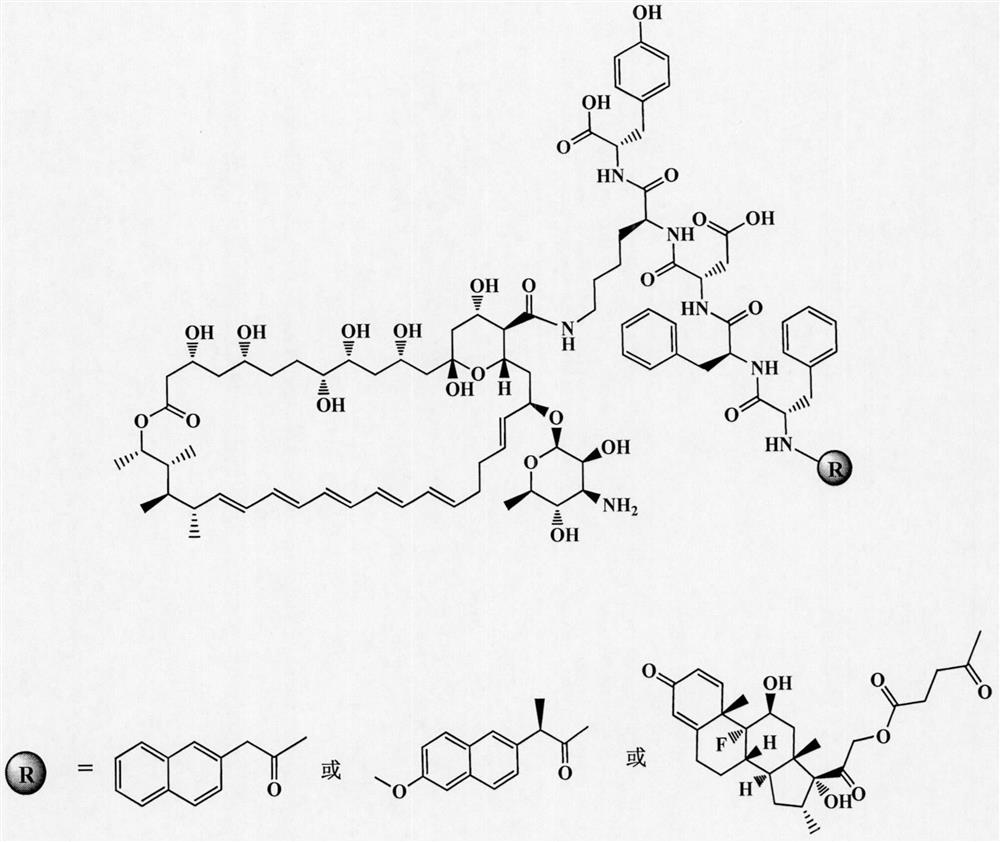
Amphotericin B polypeptide hydrogel drug carrier system for treatment of fungal infection
ActiveCN107375939AGood biocompatibilityImprove efficiencyOrganic active ingredientsAntimycoticsControlled releaseSide effect
Belonging to the field of biotechnology, the invention in particular relates to an amphotericin B polypeptide hydrogel drug carrier system for treatment of fungal infection. According to the invention, polypeptide hydrogel with great clinical application potential is employed for covalent binding of small molecule hydrophobic antibacterial drug amphotericin B to form the amphotericin B polypeptide hydrogel nano-drug carrier system. The prepared nano-drug carrier system has the characteristics of high drug loading capacity, high biocompatibility and high stability, at the same time has the advantages of sustained or controlled release of drugs, easy degradation of polypeptide carrier, reduced clinical toxic and side effects and obvious antifungal effect. The amphotericin B polypeptide hydrogel nano-drug carrier system can be stored and used in the form of amphotericin B polypeptide hydrogel nano-drug carrier system, also can be diluted with water for injection so as to be suitable for intravenous injection, or can be incorporated with other auxiliary materials to be prepared into tablets, pills, granules or capsules. The amphotericin B polypeptide hydrogel nano-drug carrier system provided by the invention is suitable for the antifungal and fungal infection disease treatment field, and has good application prospect.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
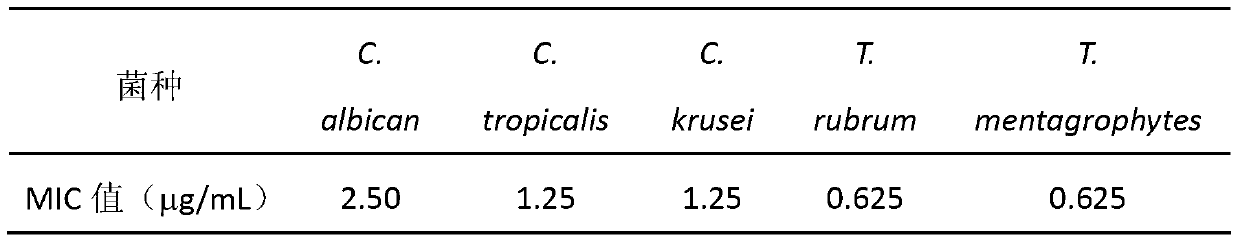
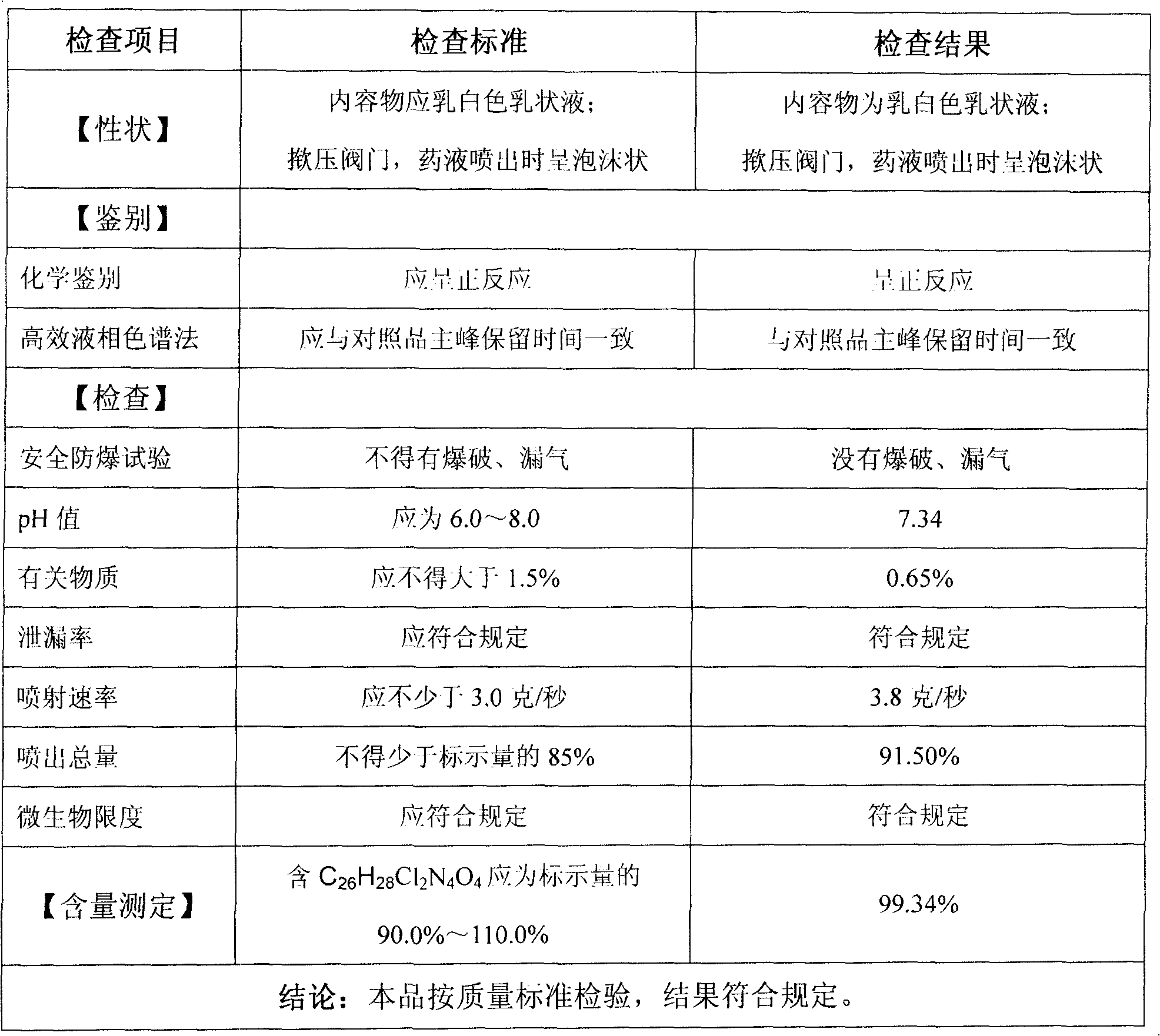
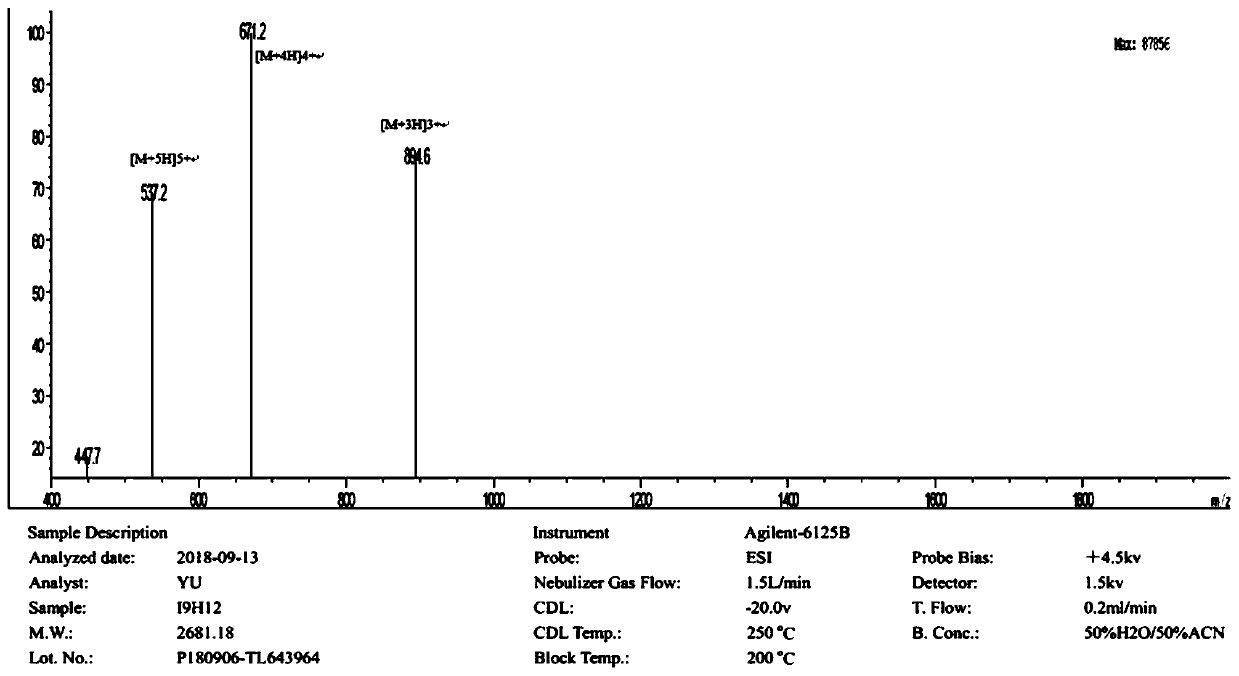
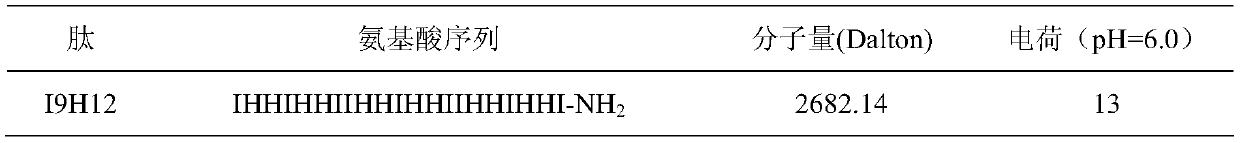
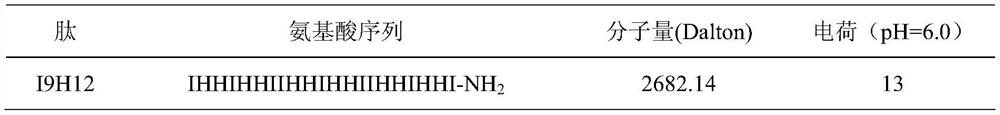
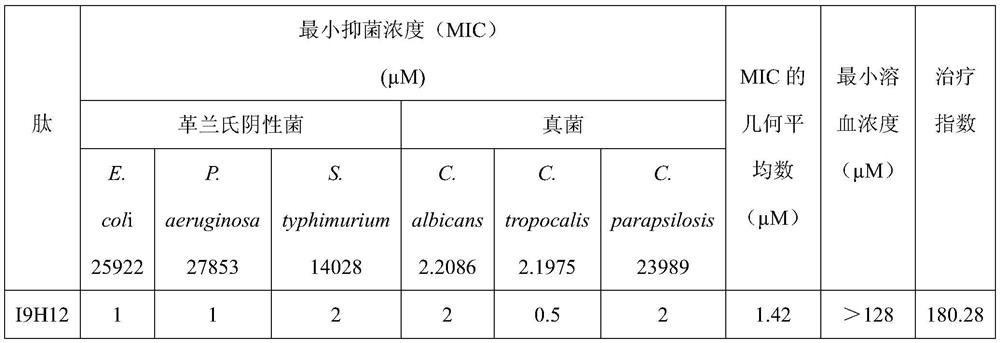
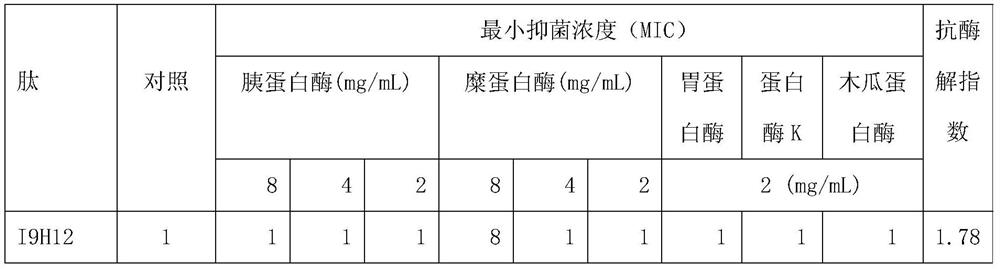
Enzymolysis-resisting antibacterial peptide I9H12 as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN109810178ASimple experimental techniqueHigh application potentialAntibacterial agentsAntimycoticsEnzyme digestionFungal Infectious Disease
The invention provides enzymolysis-resisting antibacterial peptide I9H12 as well as a preparation method and application thereof. A sequence of the antibacterial peptide I9H12 is shown as SEQ ID No. 1in a sequence table. The preparation method comprises the following steps: referring to the properties of amino acids; meanwhile, avoiding enzyme digestion sites of main proteinase in a body as muchas possible, and selecting hydrophobic amino acid isoleucine (Ile) and positive-charge amino acid histidine (His) as main amino acids to newly design the antibacterial peptide I9H12; carrying out amidation on a carboxyl terminal of the peptide to improve one positive charge and increase the stability of the peptide. The invention also provides the application of the antibacterial peptide to the preparation of targeting antibacterial medicines for treating gram-negative bacterium or fungus infectious diseases. According to the enzymolysis-resisting antibacterial peptide I9H12, the enzymolysis-resisting capability of the antibacterial peptide is effectively improved, and the application potential in actual production is improved.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Derived peptide W8 based on amphibious frog-source antibacterial peptides and preparation method and application of derived peptide W8
ActiveCN109553677ASimple experimental techniqueHigh clinical application valueAntibacterial agentsAntimycoticsDiseaseFungal Infectious Disease
The invention provides a derived peptide W8 based on amphibious frog-source antibacterial peptides and a preparation method and application of the derived peptide W8. The sequence of the derived peptide W8 is shown as SEQID No.1. The preparation method comprises the following steps of designing an antibacterial peptide P8 according to the amphibious frog-source antibacterial peptides, wherein thesequence of the designed antibacterial peptide P8 is showed as AARIILRPRFR, based on the sequence, enabling No. 8 proline to be assisted with an amino acid Trp, and designing the derived peptide W8 having the sequence shown as AARIILRWRFR. The invention provides an application of the derived peptide W8 to preparation of medicines for treating diseases infected with Gram-negative bacteria, gram-positive bacteria and fungi. The bacterium-restraining activity of the antibacterial peptide W8 is obviously higher than that of Kunitzin-RE, besides, the antibacterial peptide W8 has remarkable broad spectrum bacterium-restraining activity which is not possessed by the Kunitzin-RE, and the selectivity of the antibacterial peptide W8 between bacterium cells and lactation animal cells is improved.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Application of cyanoacrylate compound on treatment of human and animal fungal infectious diseases
The invention relates to application of a cyanoacrylate compound on the treatment of human and animal infectious diseases caused by fungus, particularly human and animal diseases such as skin diseases, keratitis, keratohelcosis, endophthalmitis, osteomyelitis, arthritis, sinus infection, onychomycosis, mycetoma and surgery or burning process infection caused by fusarium.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Application of formononetin in preparation of aspergillus fumigatus resistant medicament
InactiveCN103585143AGood antifungal activityBroad spectrum antifungalOrganic active ingredientsAntimycoticsAntifungal drugsAspergillus fumigatus
The invention relates to application of formononetin in aspergillus fumigatus prevention. The technical scheme of the invention provides application of the formononetin in preparation of a fungus infectious disease medicament. The fungus is aspergillus fumigatus. The compound in the invention is high in antifungal activity to various funguses on both the superficial part and the deep part. Compared with the conventional clinically applied antifungal medicament, the formononetin has the advantages of high efficiency, low toxicity, large antifungal spectrum and the like and can be used for preparing antifungal medicaments.
Owner:苏州市马尔泰新材料有限公司
Compounds having antifungal activity
InactiveUS20020160946A1Useful in therapyBiocideAntimycoticsChemical structureFungal Infectious Disease
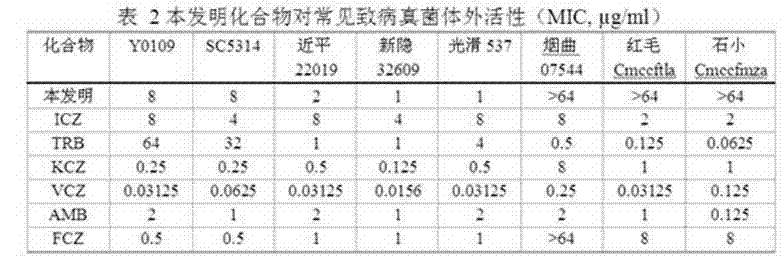
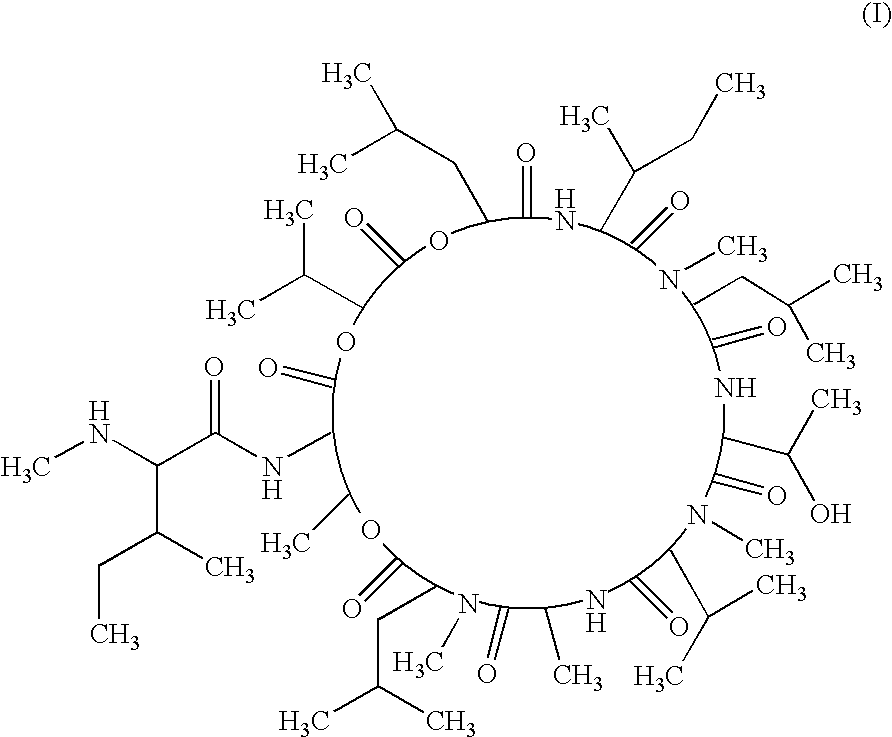
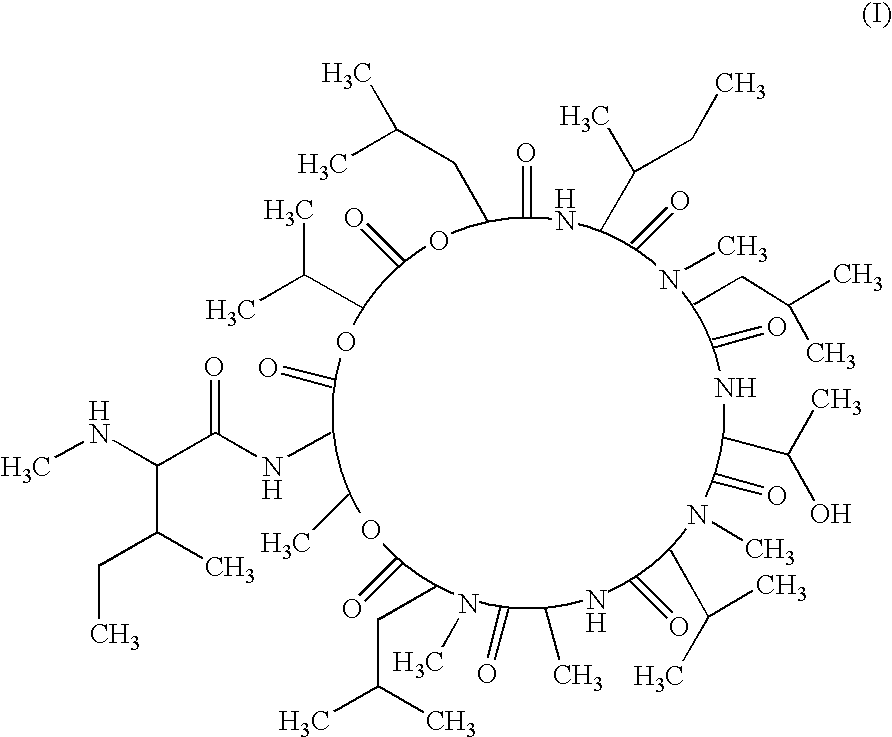
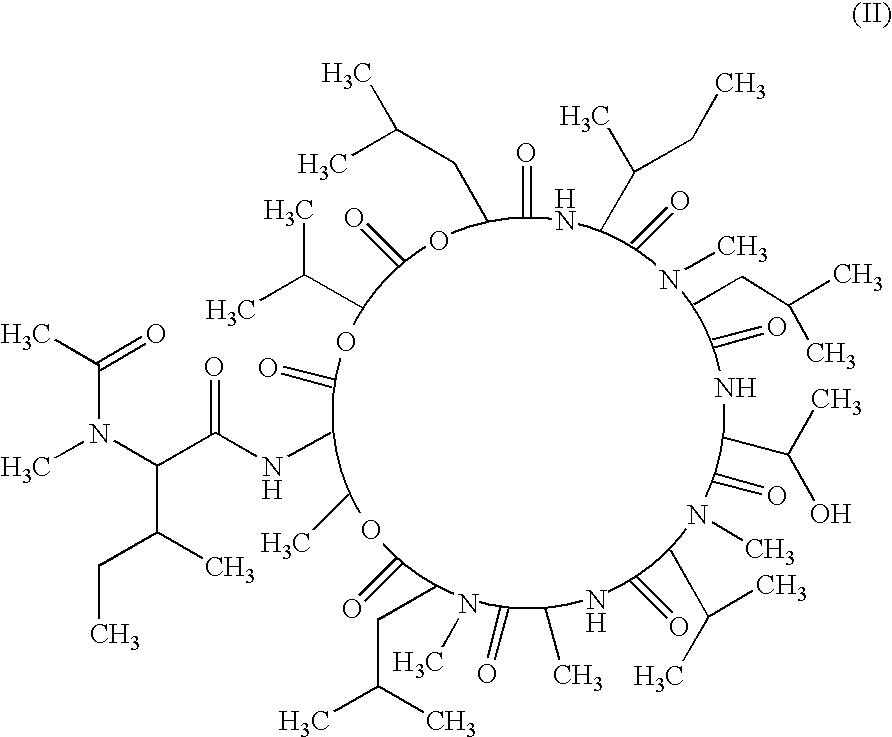
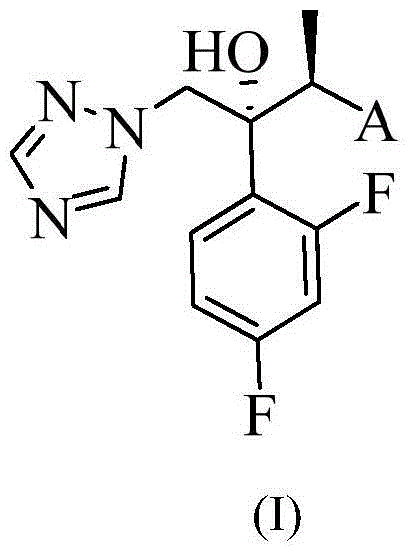
A compound of the following chemical structure (I) which exhibits antifungal activity and is useful in treating and preventing fungal infectious diseases: 1
Owner:SANKYO CO LTD
Application of formononetin in trichophyton rubrum
InactiveCN103565791AGood antifungal activityBroad spectrum antifungalOrganic active ingredientsAntimycoticsAntifungal drugsMedicine
The invention relates to application of formononetin in trichophyton rubrum. The technical scheme of the invention is the application of formononetin in preparing medicaments for treating antifungal infected diseases, wherein the fungus is trichophyton rubrum. The compound has an excellent antifungal activity on various superficial and deep funguses, has the advantages of high activity, low toxicity, broad antifungal spectrum and the like when being compared with an antifungal medicament in existing clinical application, and can be used for preparing antifungal medicaments.
Owner:苏州市马尔泰新材料有限公司
Application of 7-hydroxy-4'-methoxyisoflavone in antifungal medicament
InactiveCN103565794AGood antifungal activityBroad spectrum antifungalOrganic active ingredientsAntimycoticsAntifungalDisease
The invention relates to application of 7-hydroxy-4'-methoxyisoflavone in an antifungal medicament. The technical scheme is the application of 7-hydroxy-4'-methoxyisoflavone in preparing medicaments for treating fungus infected diseases, wherein the fungus is candida albicans. The compound has an excellent antifungal activity on various superficial and deep funguses, has the advantages of high activity, low toxicity, broad antifungal spectrum and the like when being compared with an antifungal medicament in existing clinical application, and can be used for preparing antifungal medicaments.
Owner:苏州市马尔泰新材料有限公司
Non-specific receptor binding type fungus targeting antibacterial peptide, and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN111533781AHigh application potentialImprove permeabilityAntimycoticsPeptide/protein ingredientsAntifungalDisease
The invention discloses a non-specific receptor binding type fungus targeting antibacterial peptide, and a preparation method and application thereof. The sequence of the antibacterial peptide P19 isshown as SEQ ID No. 1. The preparation method comprises the following steps: statistically analyzing related structure function parameters of the antibacterial peptide with activity to bacteria or fungi in a natural antibacterial peptide library by using R language; comparing the related parameters; screening by using the high-frequency amino acid composition, the high-frequency charge number, thehydrophobicity and the structure characteristics of the antifungal antibacterial peptide to obtain the optimal amino acid composition; and comparing the antibacterial activity and strain selectivityof each peptide chain to obtain the antibacterial peptide P19 controlled by hydrophobicity and amphipathicity of the adjusted amino acid sequence. The antibacterial peptide is applied to the preparation of drugs for treating fungal infectious diseases. The antibacterial peptide only has a relatively strong killing effect on fungal strains, especially candida albicans, has no influence on other bacterial strains, and shows relatively accurate targeting specificity.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Application of formononetin in cryptococcus neoformans
InactiveCN103565790AGood antifungal activityBroad spectrum antifungalOrganic active ingredientsAntimycoticsAntifungalDisease
The invention relates to application of formononetin in cryptococcus neoformans. The technical scheme of the invention is the application of formononetin in preparing medicaments for treating antifungal infected diseases, wherein the fungus is cryptococcus neoformans. The compound has an excellent antifungal activity on various superficial and deep funguses, has the advantages of high activity, low toxicity, broad antifungal spectrum and the like when being compared with an antifungal medicament in existing clinical application, and can be used for preparing antifungal medicaments.
Owner:苏州市马尔泰新材料有限公司
Application of formononetin in antifungal medicaments
InactiveCN103565793AGood antifungal activityBroad spectrum antifungalOrganic active ingredientsAntimycoticsAntifungal drugsMedicine
The invention relates to application of formononetin in antifungal medicaments. The technical scheme of the invention is the application of formononetin in preparing medicaments for treating antifungal infected diseases, wherein the fungus is candida glabrada. The compound has an excellent antifungal activity on various superficial and deep funguses, has the advantages of high activity, low toxicity, broad antifungal spectrum and the like when being compared with an antifungal medicament in existing clinical application, and can be used for preparing antifungal medicaments.
Owner:苏州市马尔泰新材料有限公司
Antioxidant polypeptide and a process for isolation and purification of the same
ActiveUS20110184146A1Reduce molecular weightEasily soluble in waterPeptide/protein ingredientsDepsipeptidesAntioxidative stressNeuro-degenerative disease
A polypeptide is isolated from Turmeric (Curcuma longa Linn) having molecular weight of about 8,000 Daltons. The polypeptide is highly water-soluble and absolutely non-toxic antioxidant, which is isolated using boiling water extraction. The polypeptide is an excellent antioxidant working at low concentration (of about 80 nM) to quench lipid peroxidation up to 90%. The polypeptide is highly effective against oxidative stress related diseases like arthritis, atherosclerosis, cardiovascular diseases, neurodegenerative diseases, cancer, cataract, malaria, bacterial and fungal infectious diseases.
Owner:ADICHUNCHANAGIRI BIOTECH & CANCER RES INST
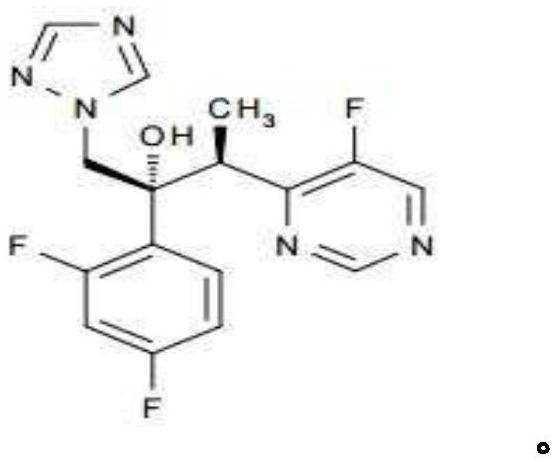
Triazole compound, pharmaceutical composition, preparation method and uses thereof
InactiveCN106032385AOrganic active ingredientsAntimycoticsFungal Infectious DiseaseInfective disorder
The present invention provides a novel triazole compound represented by a general formula (I), an optical isomer, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, a composition containing the novel triazole compound, and uses of the novel triazole compound. According to the present invention, the compound has excellent antifungal activity, such that the compound can be used for preparation of drugs for treatment of fungal infectious diseases, particularly deep infectious diseases caused by fungi. The general formula (I) is defined in the specification.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MATERIA MEDICA CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
A kind of ophthalmic composition, its preparation method and application
ActiveCN110812323BImprove stabilityLess irritatingOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderPreservative freeDrugs preparations
The invention belongs to the field of pharmaceutical preparations, and specifically relates to an ophthalmic composition, comprising the following components: 0.5-5 parts by weight of voriconazole and / or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, 8-35 parts by weight of a solubilizer, and 0.1-4 parts by weight of polyvinyl alcohol parts by weight. The present invention also relates to a method for preparing the ophthalmic composition and the use of the ophthalmic composition. The ophthalmic composition of the invention has high stability, low ocular irritation, no preservative, and good preventive or therapeutic effect on ocular fungal infectious diseases.
Owner:SHENYANG XINGQI PHARM CO LTD
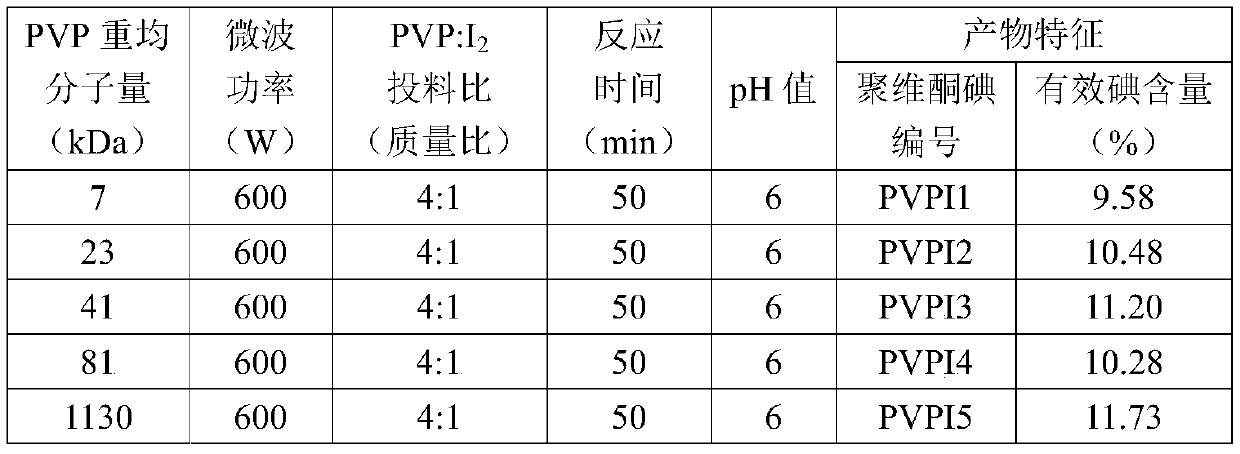
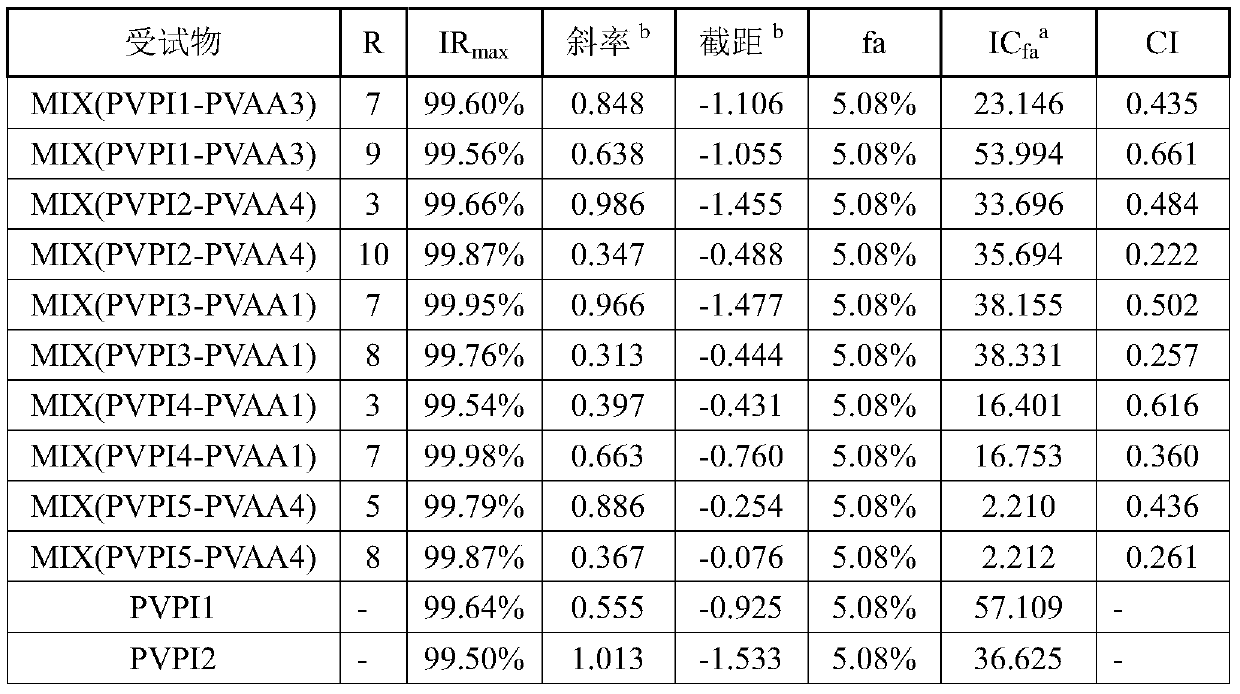
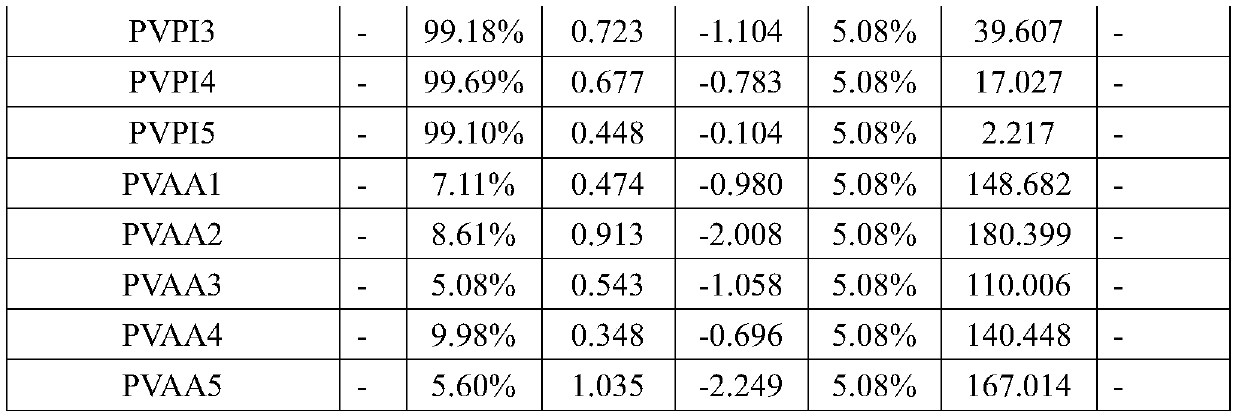
Antifungal composition as well as external preparation and application thereof
ActiveCN111494410AGood synergistic antibacterial effectAntimycoticsAerosol deliveryAntifungalDisease
The invention discloses an antifungal composition as well as an external preparation and application thereof, and relates to the technical field of medicines. The composition is prepared from povidoneiodine and polyvinyl alcohol acetate. The pharmaceutical preparation is an external preparation, wherein the composition and the pharmaceutical preparation can be used for preparing medicines for treating fungal infectious diseases. Povidone iodine and polyvinyl alcohol acetate in the composition disclosed by the invention can generate an excellent synergistic bacteriostatic effect on various pathogenic fungi; so that the external preparation prepared from the composition can be used for effectively treating fungal infectious diseases such as fungal vaginitis.
Owner:ZHONGSHAN WANHAN PHARM CO LTD
Ketoconazole foaming agent and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101856328BGood physical propertiesLong storage timeOrganic active ingredientsAntimycoticsDiseaseFoaming agent
The invention provides a ketoconazole foaming agent and a preparation method thereof, which are used for treating fungal infective diseases, such as seborrheic dermatitis and the like.
Owner:北京京卫燕康药物研究所有限公司
Agent for enhancing phagocytosis ability of neutrophils
PendingUS20210196787A1Improve abilitiesAntibacterial agentsAntimycoticsParasitic infectious diseaseViral infectious disease
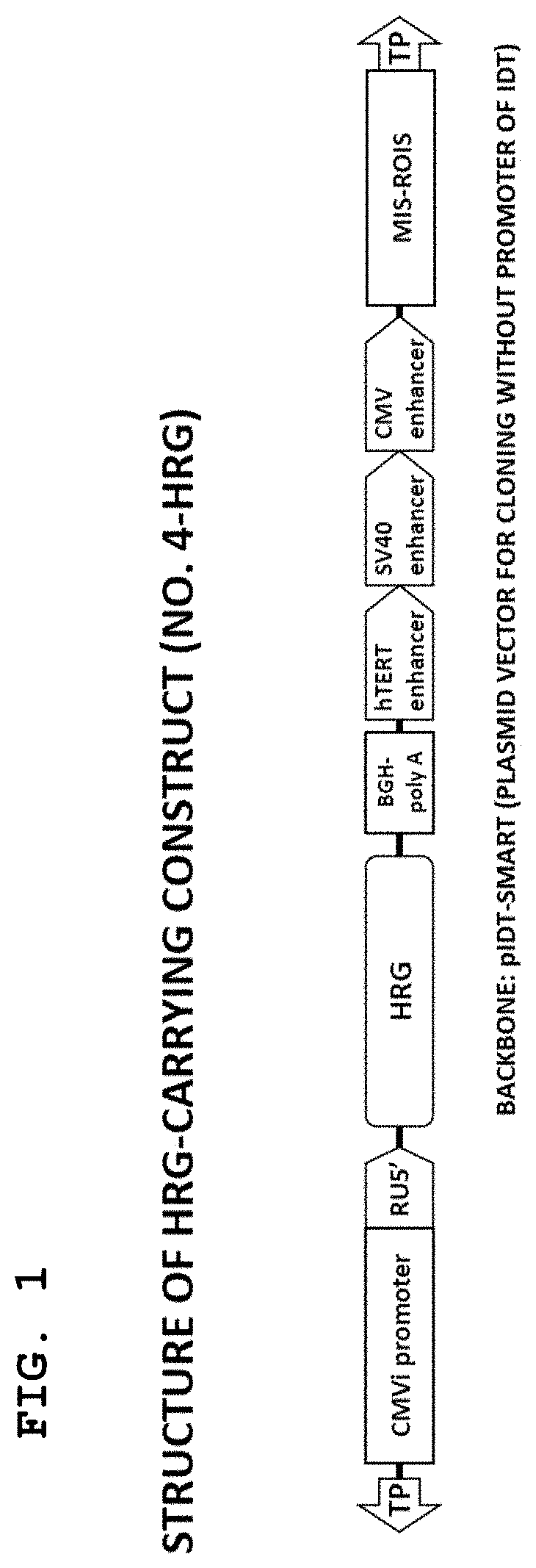
It is an object of the present invention to provide an agent for enhancing phagocytosis ability, specifically an agent for enhancing phagocytosis ability that functions as a therapeutic agent or therapeutic adjunct for various bacterial infectious diseases, viral infectious diseases, fungal infectious diseases, parasitic infectious diseases, and mixed infectious diseases thereof by enhancing phagocytosis ability of neutrophils. The above-mentioned object is achieved by an agent for enhancing phagocytosis ability including HRG as an active ingredient. The inventors of the present invention have focused attention on the function of HRG on regulation of neutrophil activities, and as the result of extensive investigations, have newly found that HRG effectively enhances phagocytosis ability against a pathogen or foreign matter derived from bacteria, viruses, fungi, parasites, and the like among the neutrophil activities.
Owner:UNIV OKAYAMA
Application of formononetin in antifungal medicaments
InactiveCN103565795AGood antifungal activityBroad spectrum antifungalOrganic active ingredientsAntimycoticsAntifungalDisease
The invention relates to application of formononetin in antifungal medicaments. The technical scheme of the invention is the application of formononetin in preparing medicaments for treating antifungal infected diseases, wherein the fungus is candida parapsilosis. The compound has an excellent antifungal activity on various superficial and deep funguses, has the advantages of high activity, low toxicity, broad antifungal spectrum and the like when being compared with an antifungal medicament in existing clinical application, and can be used for preparing antifungal medicaments.
Owner:苏州市马尔泰新材料有限公司
Antioxidant polypeptide and a process for isolation and purification of the same
ActiveUS8389677B2Reduce molecular weightEasily soluble in waterPeptide/protein ingredientsDepsipeptidesAntioxidative stressNeuro-degenerative disease
A polypeptide is isolated from Turmeric (Curcuma longa Linn) having molecular weight of about 8,000 Daltons. The polypeptide is highly water-soluble and absolutely non-toxic antioxidant, which is isolated using boiling water extraction. The polypeptide is an excellent antioxidant working at low concentration (of about 80 nM) to quench lipid peroxidation up to 90%. The polypeptide is highly effective against oxidative stress related diseases like arthritis, atherosclerosis, cardiovascular diseases, neurodegenerative diseases, cancer, cataract, malaria, bacterial and fungal infectious diseases.
Owner:ADICHUNCHANAGIRI BIOTECH & CANCER RES INST
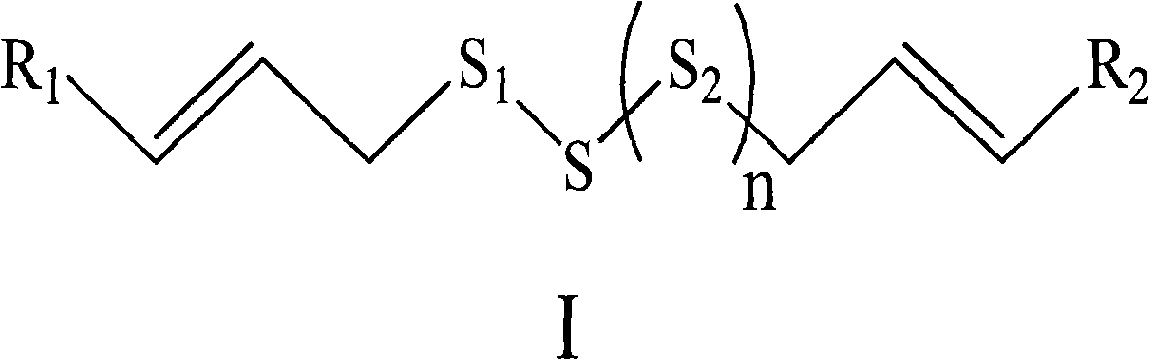
Substituted organic sulfur compound and application thereof
ActiveCN101624360AGood water solubilityEnhance anti-tumorOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryDiseaseSulphur compound
The invention relates to an organic sulfur compound substituted by a general formula (I), medicinal addition salt or ester or hydrate of the organic sulfur compound and a medical composition containing the compound, wherein R1, R2, S1, S2 and n are described as a specification. The invention also discloses a synthetic method and an application for preparing medicines which are used for treating bacterium and fungal infection diseases, neoplastic diseases and platelet aggregation diseases. The substituted organic sulfur compound has better functions for resisting tumors, infections and platelet aggregation and has higher application value in a medical field.
Owner:CUREGEN JIANGSU PHARMA
A kind of enzymolysis-resistant antimicrobial peptide i9h12 and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN109810178BSimple experimental techniqueHigh application potentialAntibacterial agentsAntimycoticsDiseaseCarboxyl radical
The invention provides an anti-enzymatic antibacterial peptide I9H12 and a preparation method and application thereof. The sequence of antimicrobial peptide I9H12 is shown in SEQ ID No. 1 of the sequence listing. Preparation method: Referring to the properties of amino acids, while avoiding the cleavage sites of major proteases in the body as much as possible, the hydrophobic amino acid isoleucine (Ile) and the positively charged amino acid histidine (His) were selected as the main amino acids to design a new I9H12 antimicrobial peptide , and amidation of the carboxy terminus of the peptide to increase a positive charge and increase the stability of the peptide. Application of the antibacterial peptide in the preparation of targeted antibacterial drugs for treating Gram-negative bacteria or fungal infectious diseases. The invention effectively improves the anti-enzymatic hydrolysis ability of the antibacterial peptide and improves its application potential in actual production.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Derivative peptide w8 based on amphibian frog-derived antimicrobial peptide and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN109553677BSimple experimental techniqueHigh clinical application valueAntibacterial agentsAntimycoticsDiseaseAntimicrobial peptides
The present invention provides a derivative peptide W8 based on amphibian frog-derived antimicrobial peptide and its preparation method and application. The sequence of the derivative peptide W8 is shown in SEQ ID No.1. The preparation method is as follows: According to the amphibian frog-derived antimicrobial peptide, the antimicrobial peptide P8 was designed. Its sequence is as follows: AARILRPRFR. As follows: AARIILRWRFR. The application of the derived peptide W8 in the preparation of medicines for treating Gram-negative bacteria, Gram-positive bacteria and fungal infectious diseases. The antibacterial activity of antibacterial peptide W8 is significantly stronger than that of Kunitzin‑RE, and it has a significant broad-spectrum antibacterial activity that Kunitzin‑RE does not possess. W8 improves the selectivity of antimicrobial peptides between bacterial cells and mammalian cells.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Amphotericin b polypeptide hydrogel drug-loading system for the treatment of fungal infections
ActiveCN107375939BGood water solubilityGood dilution resistanceOrganic active ingredientsAntimycoticsAntifungalFungal Infectious Disease
The invention belongs to the field of biological technology, and in particular relates to three amphotericin B polypeptide hydrogel nano drug-carrying systems for treating fungal infections. The invention uses the polypeptide hydrogel with great potential for clinical application, and covalently binds amphotericin B, a small-molecule hydrophobic antibacterial drug, to form an amphotericin B polypeptide hydrogel nanometer drug-loading system. The prepared nano drug loading system has high drug loading capacity, high biocompatibility and high stability, and at the same time has slow and controlled drug release behavior, easy degradation of polypeptide carrier, reduced clinical toxic and side effects and obvious antifungal effect. Amphotericin B polypeptide hydrogel nano-drug delivery system can be stored and used in the form of lyophilized powder, or diluted with water for injection for intravenous injection, or mixed with other excipients to make tablets, pills, and granules or capsules. The amphotericin B polypeptide hydrogel nano drug-loading system is suitable for the field of antifungal and fungal infectious disease treatment, and has a good application prospect.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
Antibacterial polypeptide Pb2-1 or PCL-1 and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN110386972AImprove the bactericidal effectGood broad-spectrum antibacterial activityAntibacterial agentsAntimycoticsAlpha helixFungal Infectious Disease
The invention discloses an antibacterial polypeptide Pb2-1 or PCL-1 and preparation method and application thereof.The amino acid sequences of the antibacterial polypeptides Pb2-1 and PCL-1 are as shown in SEQ ID NO:1 and SEQ ID NO:2 respectively. According to the antibacterial polypeptide Pb2-1 or PCL-1 and the preparation method and application thereof, based on polypeptide CATHPb2 from Python-bivittatu, through structure-fuction relationship studies, polypeptide Pb2-1 withhigh alpha-helix degree is obtained, the N-end is in covalent linkage withasection of eleven cyclopeptidehaving trypsininhibitory activity to obtain thenovel structure polypeptidePCL-1 consisting 24 amino acids. The prepared polypeptide Pb2-1 and PCL-1, the alpha-helix degree and hydrophobicityofan efficacy moduleareincreased; also, the PCL-1 is connected withthe eleven cyclopeptide sequence so that while good in vitro antibacterial activity is realized, the stability to trypsin is also significantly improved, and the polypeptide Pb2-1 and PCL-1 can be applied to the treatment of bacterial and fungal infectious diseases.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
Non-specific receptor-binding fungal targeting antimicrobial peptide and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN111533781BHigh application potentialImprove permeabilityAntimycoticsPeptide/protein ingredientsAntifungalDisease
The invention discloses a non-specific receptor-binding fungal targeting antimicrobial peptide, a preparation method and application thereof. The sequence of the antimicrobial peptide P19 is shown in SEQ ID No.1. Preparation method: use R language to statistically analyze the relevant structural and functional parameters of antibacterial peptides active against bacteria or fungi in the natural antibacterial peptide library, compare the relevant parameters, and use the high-frequency amino acid composition and high-frequency charge number of antifungal antibacterial peptides, hydrophobicity, The optimal amino acid composition was obtained by screening the structural properties, and the antibacterial activity and strain selectivity of each peptide chain were compared, and the antimicrobial peptide P19 was obtained by adjusting the sequence hydrophobicity and amphiphilicity through amino acid adjustment. The antibacterial peptide is used in the preparation of medicines for treating fungal infectious diseases. The antimicrobial peptide only has a strong killing effect on fungal strains, especially Candida albicans, and has no effect on other bacterial strains, showing more precise targeting specificity.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
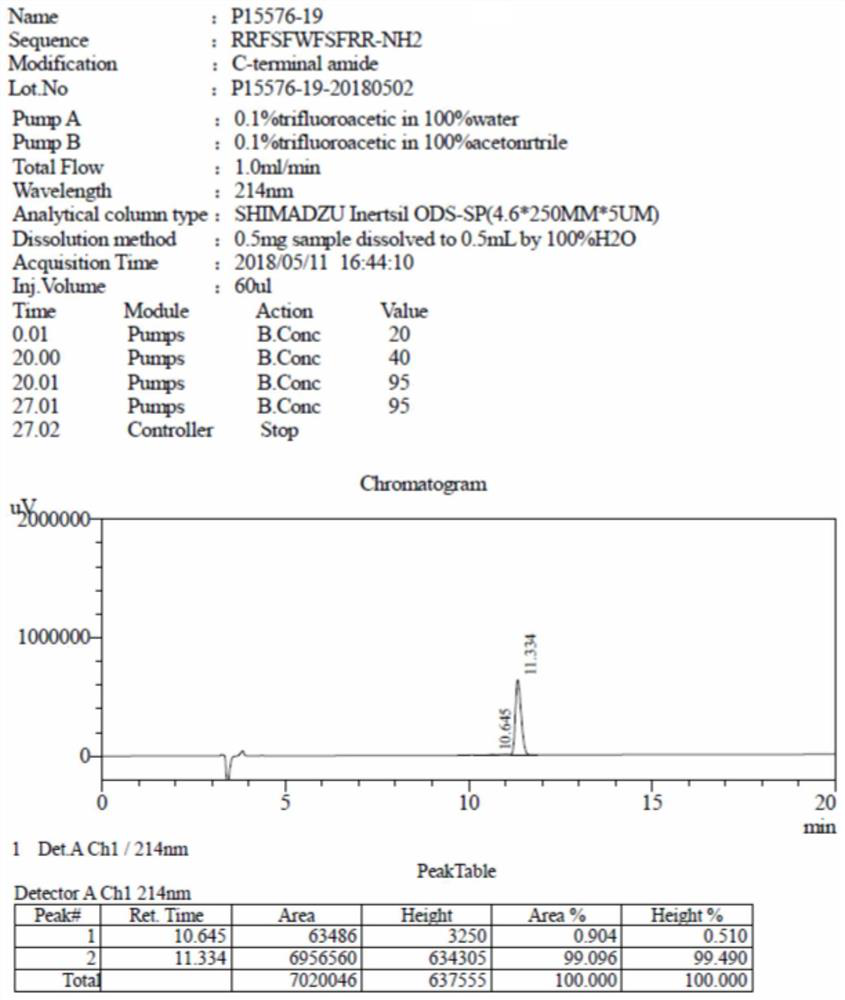
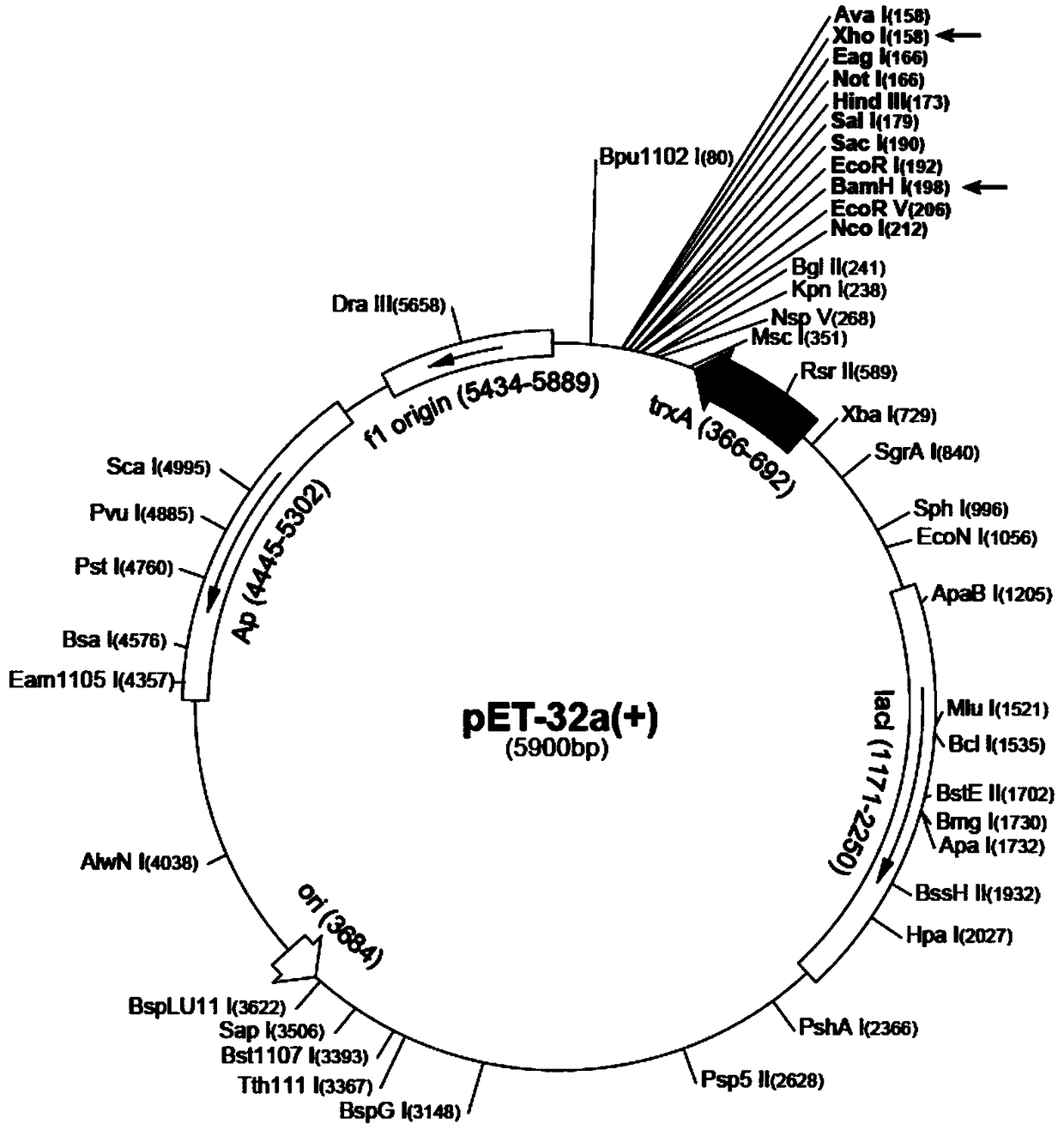
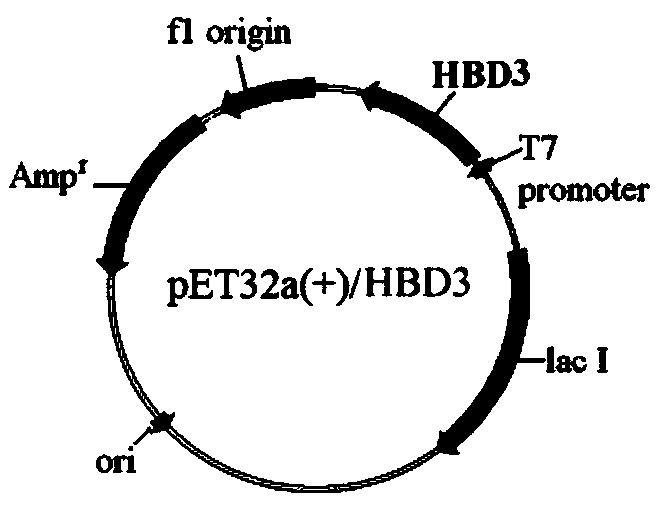
Novel use and preparation method of human beta-defensin 3
InactiveCN108837146ALow costAbundant productionAntimycoticsPeptide/protein ingredientsEscherichia coliEukaryotic plasmids
The invention discloses a novel use and a preparation method of human beta-defensin 3, and provides application of the human beta-defensin 3 in preparation of medicines for treating fungal, especiallyfilamentous fungal infectious diseases. The invention provides a preparation method of a recombinant human beta-defensin 3 polypeptide, wherein the preparation method comprises the following steps: inserting an HBD3 mature peptide gene into a pET32a(+) plasmid; transferring the correctly constructed recombinant plasmid into Escherichia coli to obtain expression engineering bacteria; inducing andculturing the expression engineering bacteria to express an HBD3 fusion protein; and finally obtaining the recombinant human beta-defensin 3 polypeptide by nickel affinity chromatography, thrombin digestion, purification and concentration. The invention proposes the novel use of the human beta-defensin 3. The preparation method provided by the invention has characteristics of low production cost,high yield and easy assurance of biological activity of the polypeptide.
Owner:GUIZHOU MEDICAL UNIV
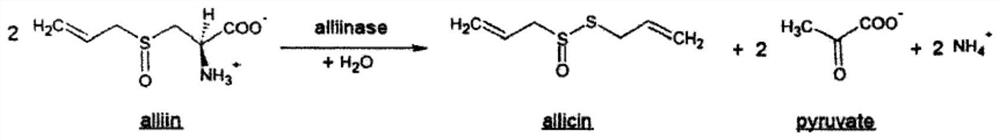
Application of allicin in preparation of anti-saccharomycetes drugs
ActiveCN113101284AEnhanced inhibitory effectImproved symptoms in infected miceOrganic active ingredientsAntimycoticsAntifungal drugCell membrane
The invention provides application of allicin in preparation of anti-saccharomycetes drugs, and relates to the technical field of medicines. Experiments show that the allicin has a good antibacterial effect on cryptococcus and candida, and the allicin combined with the antifungal drug also has good antibacterial activity on cryptococcus and candida. Experiments also show that allicin achieves a bacteriostatic or bactericidal effect by destroying capsules or cell walls or cell membranes of cryptococcus. The allicin has better activity against cryptococcus in vivo and in vitro. The allicin preparation can be used as a medicine which is safe, effective, small in toxic and side effects and low in price and is used for clinically treating fungal infectious diseases.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF GUANGZHOU MEDICAL UNIV (GUANGZHOU RESPIRATORY CENT) +2
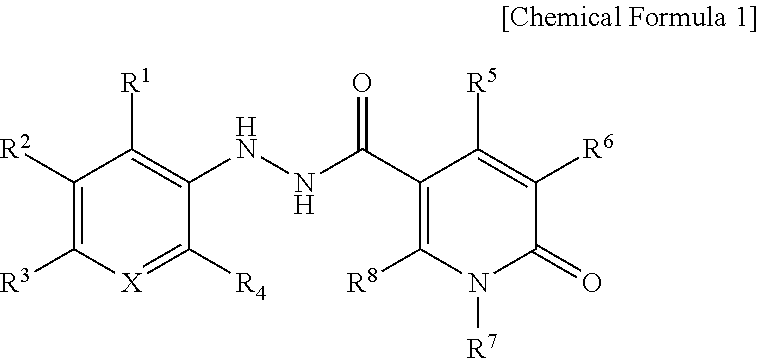
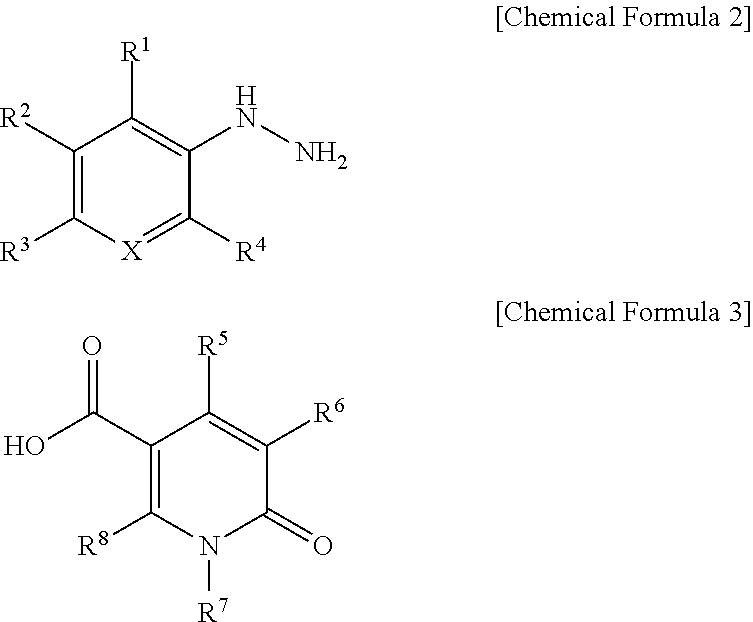
Antifungal oxodihydropyridinecarbohydrazide derivative
ActiveUS9617216B2High activityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsAspergillusCandida famata
The present invention relates to novel oxodihydropyridinecarbohydrazide derivatives with excellent antifungal activities, an antifungal composition containing the same, and its use for the prevention and treatment of fungal infectious diseases. The oxodihydropyridinecarbohydrazide derivatives of the present invention have excellent antifungal and fungicidal activities, and thus will be useful for the prevention and treatment of various fungal infections by Candida spp., Aspergillus spp., Cryptococcus neoformans and Trichophyton spp., etc. Additionally, the oxodihydropyridinecarbohydrazide derivatives of the present invention, unlike other fungicidal preparations, can be orally administered.
Owner:DAEWOONG PHARM CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com