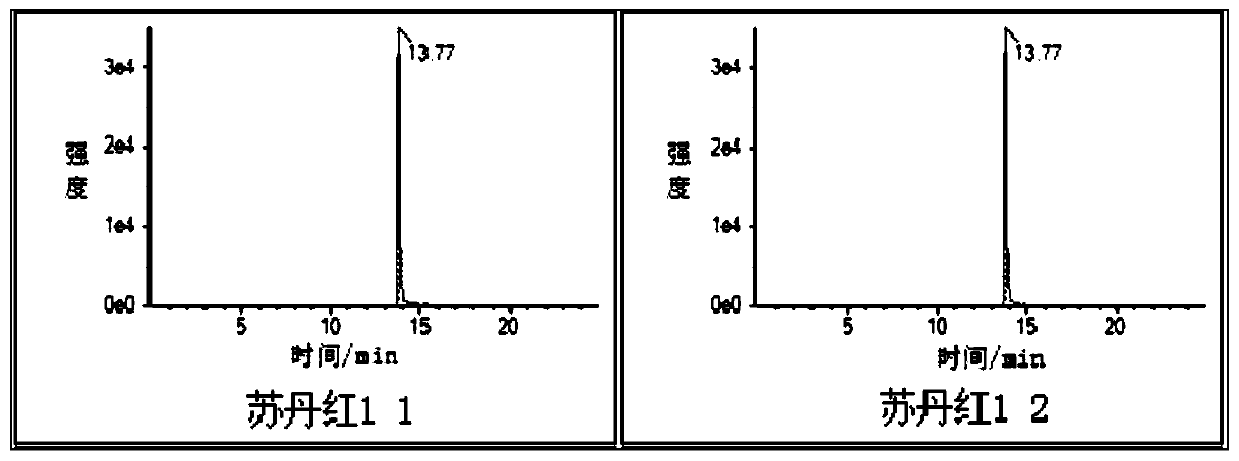
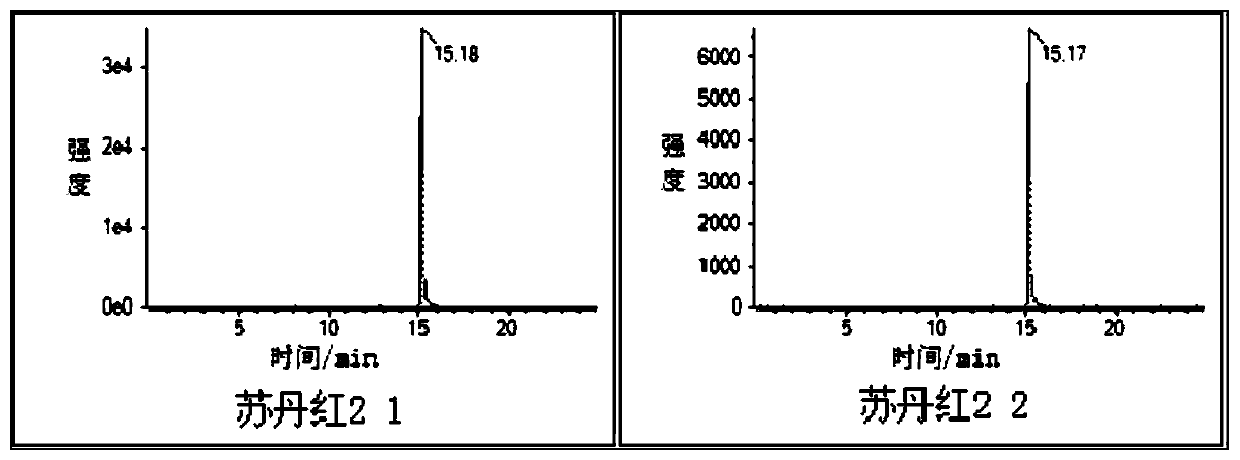
Method for measuring industrial dyes in food through GPC-LC-MS-MS method
A GPC-LC-MS-MS and food technology, which is applied in the field of GPC-LC-MS-MS determination of industrial dyes in food, can solve the problems of low detection efficiency of industrial dyes, save heating control and reduce detection costs , to ensure the effect of accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 2
[0140] The difference from Example 1 is that in step (1), the addition of the sample is 5 g, and the addition of ammonia water-acetonitrile solution is 20 mL; in step (3), the elution temperature of the liquid to be tested is 20°C.
Embodiment 3
[0142] The difference from Example 1 is that in step (1), the addition amount of the sample is 3 g, and the addition amount of ammonia water-acetonitrile solution is 10 mL; in step (3), the elution temperature of the liquid to be tested is 23 °C.
[0143] 2.4. Example 4
[0144] The difference from Example 1 is that in step ① in this example, the ammonia water volume fraction of the ammonia water-acetonitrile solution is 2%.
[0145] 2.5. Example 5
[0146] The difference from Example 1 is that in step ② in this example, the volume ratio of cyclohexane and ethyl acetate is 2:1.
[0147] 2.6. Example 6
[0148] The difference from Example 1 is that in step ③ in this example, the volume fraction of formic acid in the formic acid-water solution is 0.2%.
Embodiment 7
[0150] The difference from Example 1 is that in step ③ in this example, the elution temperature of the liquid to be tested is 30°C.
[0151] 2.8. Example 8
[0152] The difference from Example 1 is that in step ③, the liquid to be tested is eluted with methanol and formic acid-water solution with a volume fraction of formic acid of 0.1% as the mobile phase.
[0153] 2.9. Comparative Example 1
[0154] The difference with Example 1 is that in step 1., the ammonia water-acetonitrile solution is replaced with dehydrated alcohol in this comparative example.
[0155] 2.10. Comparative Example 1
[0156] The difference from Example 1 is that in this comparative example, in step ③, the formic acid-water solution is replaced with an acetone-n-hexane solution with an acetone volume fraction of 5%.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| ion source temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com