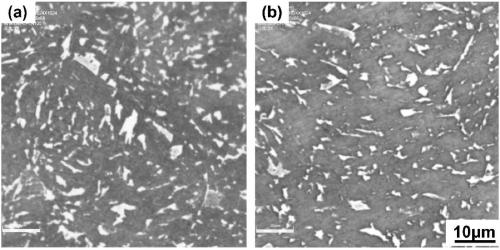
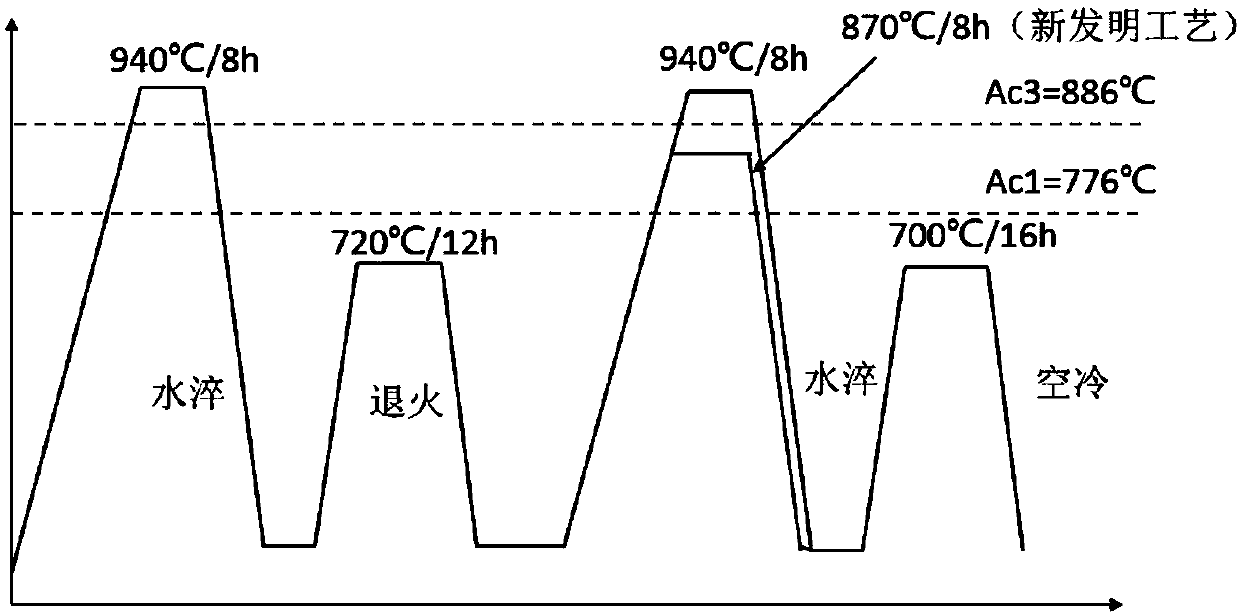
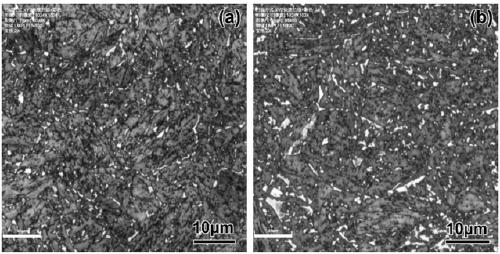
Heat treatment process for refining M-A island in granular bainite structure of low-carbon low alloy steel
A granular bainite and low-alloy steel technology, applied in the field of heat treatment of iron and steel materials, can solve problems such as difficulty in uniform dispersion and precipitation of carbides, reduction in strength, mismatch of strength and toughness of components, etc., to eliminate tissue heredity and inhibit growth speed Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] This implementation is to manufacture a Ni-Cr-Mo series low-alloy steel thick slab for racks on an offshore platform. First, the steel plate is sampled for chemical composition analysis. The test results are: 0.15C (weight percentage, the same below), 0.20Si, 1.5Ni, 1.20Cr, 0.45Mo, 0.005V, 0.005P, 0.002S, Fe balance. The Ac3 and Ac1 of this steel measured by thermal expansion are 857°C and 752°C respectively. According to the test results of the critical phase transition point of steel, the new / old heat treatment process is specifically formulated as follows:
[0033] (1) For the conventional treatment process, the rolled slab is subjected to austenitic treatment at 900°C x 8h, and then directly air-cooled and normalized;
[0034] (2) For the new heat treatment process, that is, on the basis of normalizing, the slab is tempered at 650°C, and the tempering holding time is about 2h, and it is cooled to room temperature by air cooling; then the steel plate is 830°C. Heat...
Embodiment 2
[0037] This implementation is to manufacture low-carbon and low-alloy -2.25Cr1Mo0.25V steel thick plates for a large-scale hydrogenation reactor. The specific implementation process is as follows:
[0038] (1) First, analyze the chemical composition of the thick plate samples. The test results are: 0.15C (weight percentage, the same below), 0.05Si, 2.46Cr, 1.01Mo, 0.28V, 0.15Ni, 0.006P, 0.002S, Fe amount, the result meets the requirements of relevant standards for the chemical composition of 2.25Cr-1Mo-0.25V steel, and belongs to the scope of application of the present invention. Take a φ3x10mm round bar on a rolled thick plate, and use the thermal expansion method to measure the Ac3 and Ac1 of the material to be 886°C and 776°C, respectively.
[0039] (2) After the slab is forged, the post-forging heat treatment (that is, normalizing treatment + tempering treatment) that needs to be carried out after forging. Therefore, in the subsequent performance heat treatment process, t...
Embodiment 3
[0042] In this embodiment, the heat treatment of complex thick-walled castings of G18CrMo2-6 steel low-pressure cylinders for nuclear power is taken as an example. The specific process is as follows:
[0043] (1) This embodiment is a large thick-walled casting made of G18CrMo2-6 steel with a maximum wall thickness of 400 mm. Firstly, the main chemical composition of the steel piece in this embodiment is detected to be 0.18C (weight percentage, the same below), 0.67Cr, 0.69Mo, 0.48Ni, 0.73Mn, and Fe balance, which is in line with the scope of low-carbon low-alloy steel applicable to the present invention. The phase transition critical points Ac1 and Ac3 of the material measured by thermal expansion are: 762°C and 883°C respectively;
[0044] (2) Similar to Example 1, this example also first carries out normalizing treatment to the casting, but the difference from Example 2 is that the normalizing austenitization temperature of this example is 960°C, the heat preservation is 20 ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Impact energy | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Yield strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com