Method for regenerating lithium iron phosphate waste
A technology of lithium iron phosphate and waste, applied in the field of regeneration of lithium iron phosphate waste, can solve the problems of increasing the recovery cost, loss of valuable components, and reducing the recovery rate, and achieves the effects of improving quality, inhibiting growth rate, and shortening the process.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
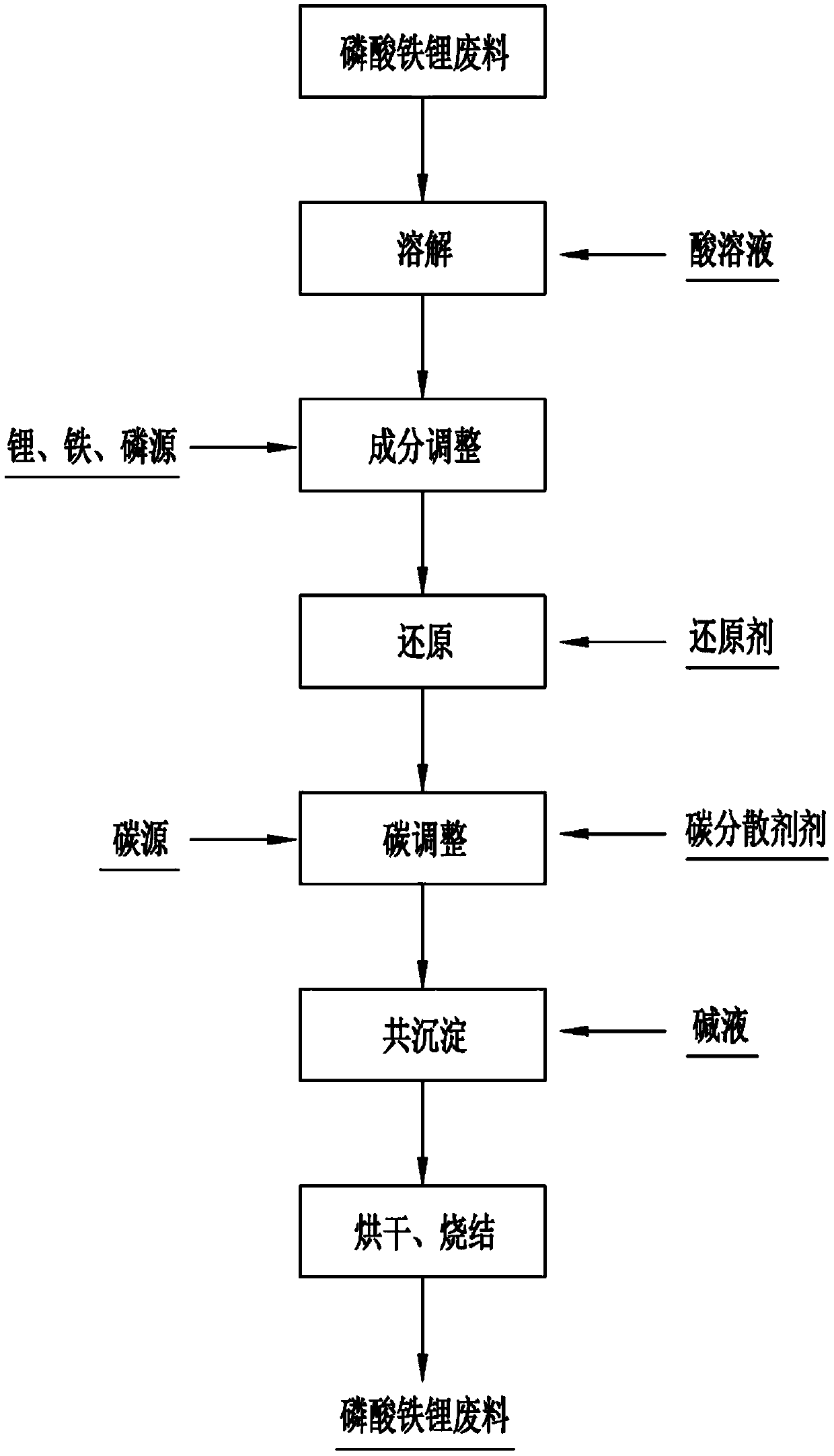
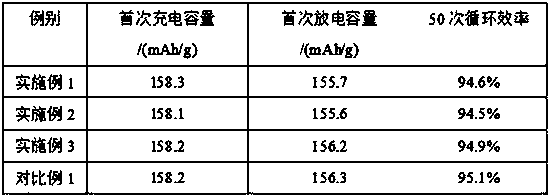
[0030] The lithium iron phosphate production material lacking lithium (unqualified ratio) was taken for component analysis. The test results showed that the main components of the waste were: lithium 3.91%wt, iron 33.46%wt, phosphate radical 58.5%wt, carbon 2.24%wt. And 2.09%wt other unavoidable trace elements. According to the composition, mix the waste material and hydrochloric acid in a molar ratio of 1:4, weigh 643.10 mass parts of waste material, 1600 mass parts of concentrated hydrochloric acid (analytical pure, hydrochloric acid content is 36.5%wt), 3416 mass parts of deionized water, and make hydrogen The acid solution with an ion concentration of 1.0 mol / L was stirred and dissolved at room temperature for 2 hours under the protection of nitrogen. The ferric iron content was measured to be 0.13%wt. The molar ratio of lithium:iron:phosphorus is 1:1.06:1.08, and the ratio needs to be adjusted. Add 10.46 parts by mass of lithium chloride (analytically pure, with a conten...
Embodiment 2
[0033] The carbon-deficient and carbon-rich (unqualified ratio) lithium iron phosphate production materials were taken for component analysis. The test results showed that the main components of the waste were: 4.32%wt of lithium in the carbon-deficient waste, 34.26%wt of iron, 60.07%wt of phosphate, carbon 0.66%wt. And 0.69%wt other unavoidable trace elements; carbon-rich waste 4.22%wt lithium, 33.86%wt iron, 58.11%wt phosphate, 3.26%wt carbon. And 0.55%wt other unavoidable trace elements. According to the composition, the carbon-deficient and carbon-rich waste materials can be designed into lithium iron phosphate with a carbon content of 1.96% in the final product. Therefore, take by weighing 645.30 mass parts of waste material (carbon-rich waste material, carbon-deficient waste material respectively claim 322.65 mass parts), waste material and sulfuric acid are 1:1.5 batching with molar weight, concentrated sulfuric acid 600 mass parts (analytical pure, sulfuric acid conte...
Embodiment 3
[0036] The raw material of lithium iron phosphate whose performance is not up to standard (abnormal sintering process) was taken for component analysis. The test results show that the main components of the waste are: 4.31%wt, iron 34.25%wt, phosphate radical 60.05%wt, carbon 1.21%wt. And 0.18% w other unavoidable trace elements. According to the composition, mix the waste material and hydrochloric acid in a molar ratio of 1:4, weigh 643.60 mass parts of waste material, 1600 mass parts of concentrated hydrochloric acid (analytical pure, hydrochloric acid content is 36.5%wt), 7847 mass parts of deionized water, and make hydrogen The acid solution with an ion concentration of 0.5 mol / L was stirred and dissolved at room temperature for 2 hours under the protection of nitrogen. The ferric iron content was measured to be 0.32%wt. The molar ratio of lithium:iron:phosphorus is 1:0.98:1.012, no need to adjust the ratio, just reduce the ferric iron, add 4.3 parts by mass of ascorbic a...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com