Method for utilizing magnesium resource in wet zinc smelting process
A technology of hydrometallurgy and recycling of zinc, applied in the direction of process efficiency improvement, zinc halide, magnesium oxide, etc., can solve problems such as difficult to remove, affect the current efficiency of the electrowinning process, increase energy consumption of hydrometallurgy zinc, etc., to achieve Ensure the effect of the promotion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0028] The present invention will be described in further detail below in conjunction with specific examples.
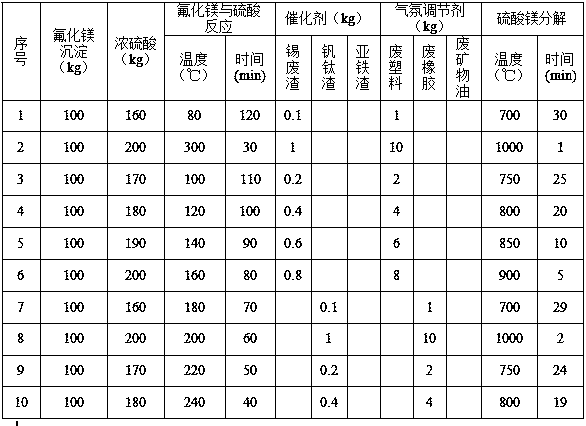
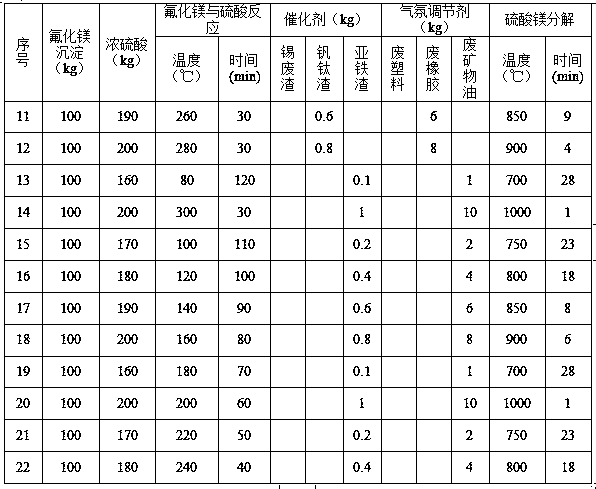
[0029] (1) Add magnesium fluoride seed crystals and zinc fluoride to the magnesium-containing zinc sulfate solution to obtain a coarse-grained magnesium fluoride precipitate, and liquid-solid separation; add concentrated sulfuric acid to the magnesium fluoride precipitate to heat and react to obtain hydrogen fluoride gas and magnesium sulfate; pass hydrogen fluoride into a container containing zinc oxide fumes to obtain zinc fluoride; add catalyst and atmosphere regulator to magnesium sulfate and heat and decompose to obtain magnesium oxide. The amount of concentrated sulfuric acid added in magnesium fluoride, the reaction temperature, the amount of catalyst and atmosphere regulator added in magnesium sulfate, and the decomposition temperature are shown in Table 1.
[0030]
[0031] Continuation from Table 1
[0032]
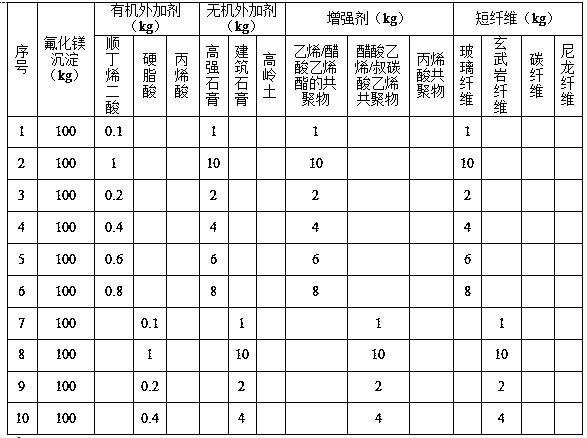
[0033] (2) Add magnesium sulfate with 60%...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| compressive strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com