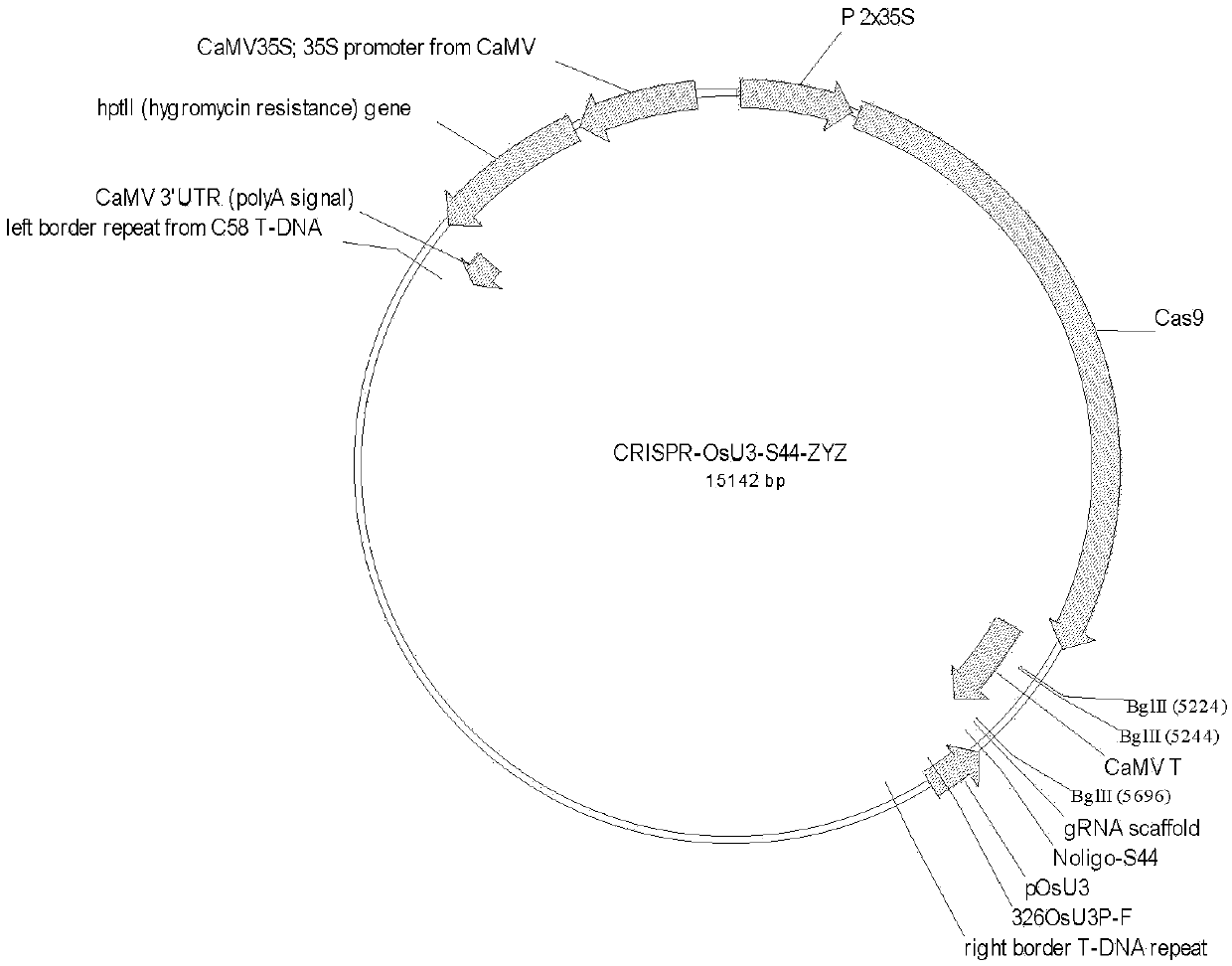
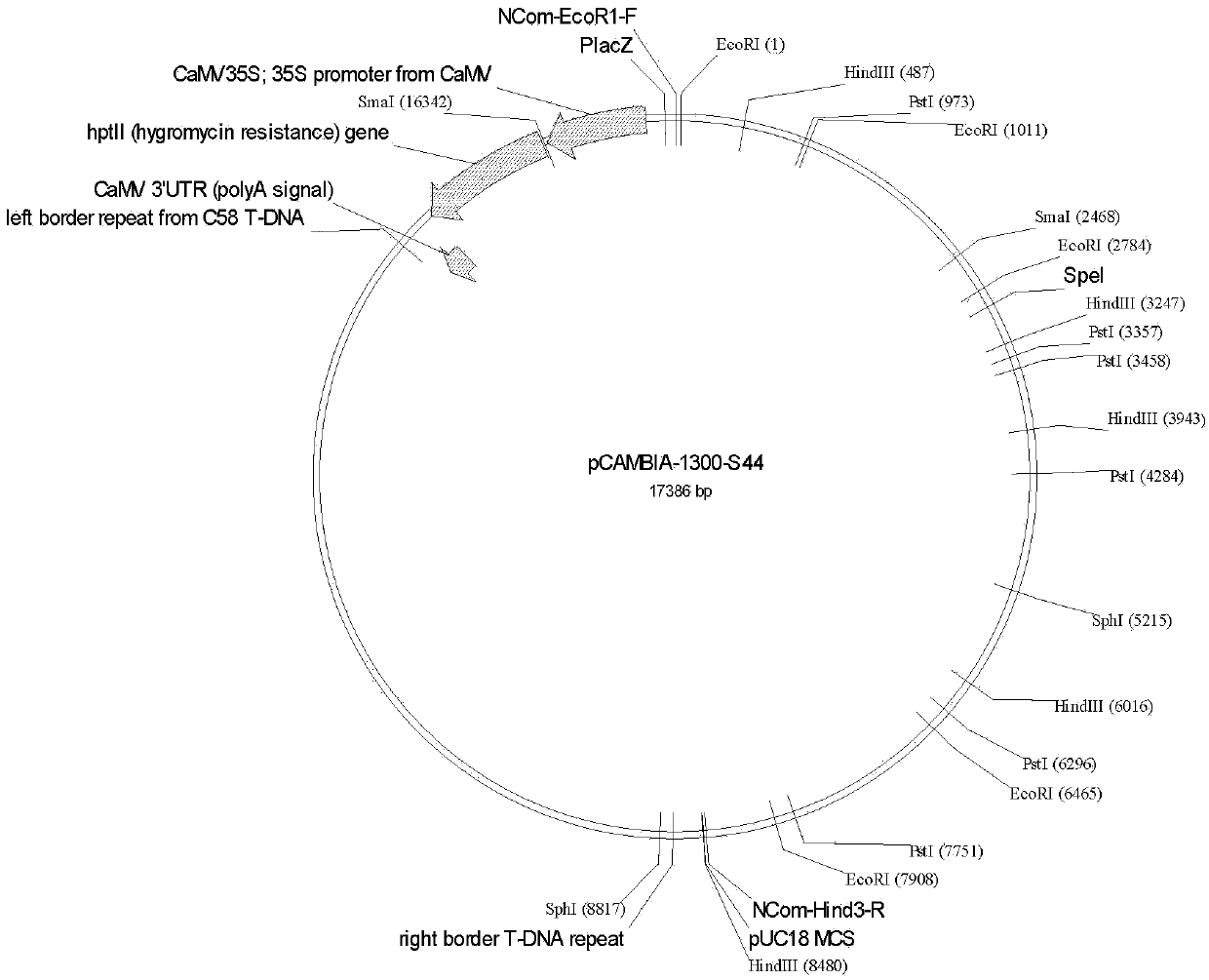
Method for obtaining male sterile lines of rice through fertility genes S44
A fertility gene and fertility technology, which is applied in plant hybrid breeding, fertility gene S44 and its mutants and its application in hybrid breeding, can solve the problem of limited resource utilization, substandard purity of hybrid seeds, and poor fertility. Vulnerable to external environmental factors
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0103] Embodiment 1, the screening of rice male sterile mutant s44
[0104] The mutant was obtained by mutagenizing the seeds of indica rice Huanghuazhan (M 0 ) method, wherein EMS mutagenesis concentration and mutagenesis time are 0.7% and 12 hours respectively, will come from M 0 The plants of the generation seeds were harvested after fruiting to obtain the mutant library (M 1 ). from M 1 The plants of the generation seeds are used for screening at the seed maturity stage, and the sterile plants are obtained through phenotype observation. Sterile plants are regenerated by cutting rice piles, and the regenerated plants are regenerated with I 2 -KI staining was used to detect pollen development and staining reaction, and one of the mutants was found to be sterile without pollen grains (lodine loss), and it was named s44 mutant.
Embodiment 2
[0105] Embodiment 2, genetic analysis of rice male sterile mutant s44
[0106] The F 1 The generation plants all appeared to be fertile. F again 1 F 2 The generation plants can be clearly divided into two groups of fertile plants and sterile plants, and the segregation ratio of fertile plants and sterile plants is close to 3:1 (see Table 1), indicating that the sterility mutation trait of the s44 mutant is caused by Single recessive nuclear gene control.
[0107] Table 1 Rice male sterile mutant s44 hybrid F 2 Generation Separation Ratio
[0108]
Embodiment 3
[0109] Example 3, Analysis of reproductive organ phenotype of rice male sterile mutant s44
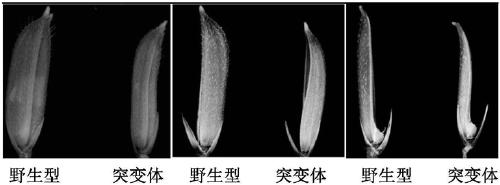
[0110] Compared with the wild-type Huanghuazhan, the s44 mutant grew normally, had a late heading, and the shape of the palea was significantly different from that of the wild type. The palea of the mutant was crescent-shaped, the entire width was narrowed, and the length did not change significantly ( See figure 1 ), and the anthers of the mutant are thin, white and slightly transparent (see figure 2 ). further use I 2 The pollen of the mutant was stained and detected by -KI solution, and it was found that the pollen of the wild type was normally stained, while the mutant showed no pollen grains, that is, it was in a state of failure (see image 3 ). It was further found that the female organs (including ovary, style and stigma) of the mutant were slightly larger than those of the wild type (see Figure 4 ), the stigma exposure rate was more than 85%, while the stigma of the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com