Hi-C high-throughput sequencing library building method suitable for watermifoil
A high-throughput, foxtail algae technology, applied in the field of molecular biology, can solve the problems of poor inactivation effect of endogenous enzymes, affecting the validity of library data, affecting the effect of enzyme digestion reaction, etc., to achieve reduced losses, reduced Interference from background noise, the effect of expanding the applicable range
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
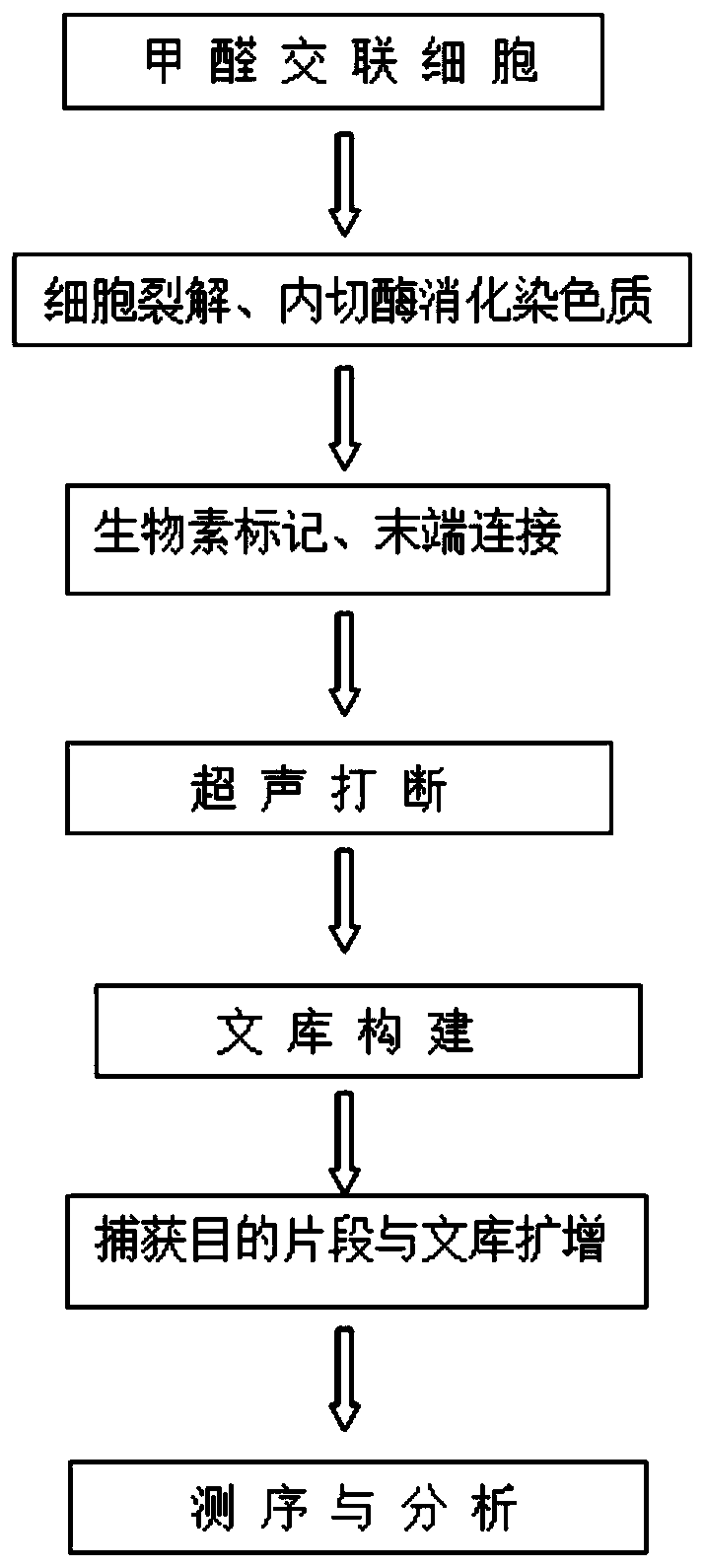
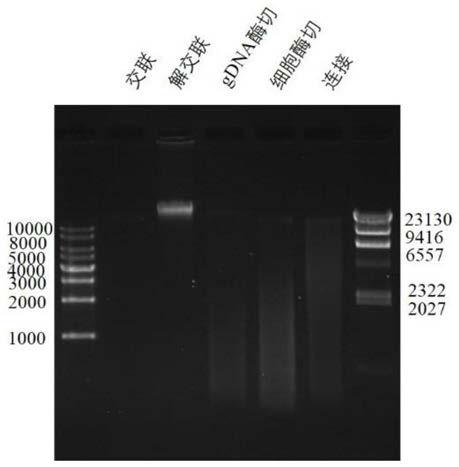
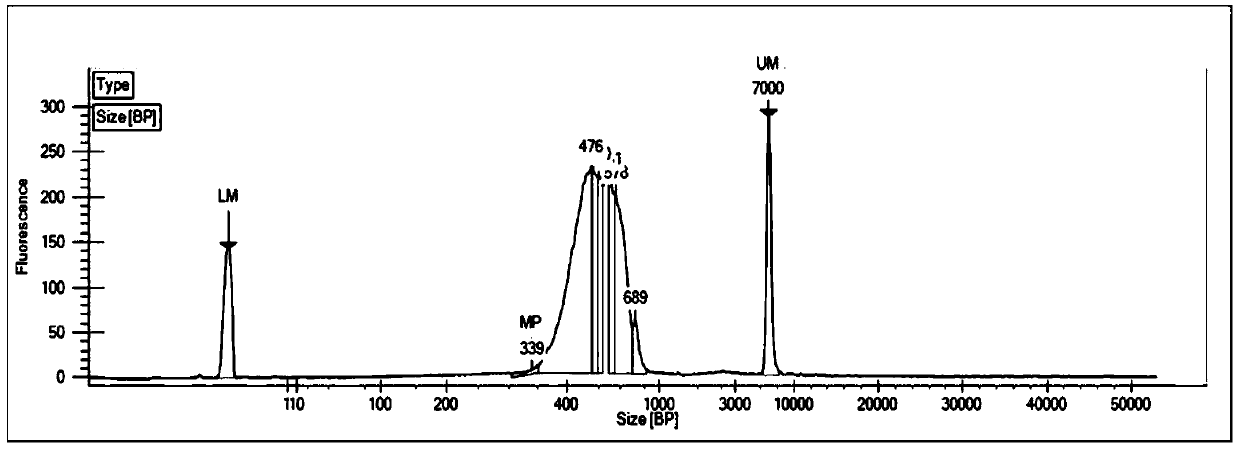
[0036] In this example, taking Trichomina as the research object, formaldehyde cross-linking was carried out on the tissue of Juvenilia nigrum, the cells were lysed to release chromatin, and then the chromatin was digested, biotin-labeled, intramolecularly linked, and ultrasonically interrupted, and finally the library was carried out. Build (eg figure 1 shown), the specific experimental process is as follows:
[0037] 1. Formaldehyde crosslinking of cells
[0038] (1) Take 2g of the young Trichosanthes tissue, cut into pieces about 0.5cm in size and put them into a 50mL centrifuge tube, and add 35mL of pre-cooled NIB lysate to the centrifuge tube (add 35μL of mercaptoethanol and 35μL of 100mM PMSF before the reaction ) and 2mL of about 37% formaldehyde solution (final concentration 2%), vacuum for 40min, it is recommended to operate on ice.
[0039] (2) Add 5 mL of 2.0 M glycine and treat under vacuum for 5 min to terminate cross-linking.
[0041] (...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com