Application of hypocrellin A to preparation of medicines for photodynamic therapy of candida albicans infectious diseases of skin
A technology of Candida albicans and Hypocretin A, which is applied in the biological field to achieve the effect of enhancing the activity and increasing the level of ROS
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0054] Example 1: Antifungal Activity Test of Hypocretin A
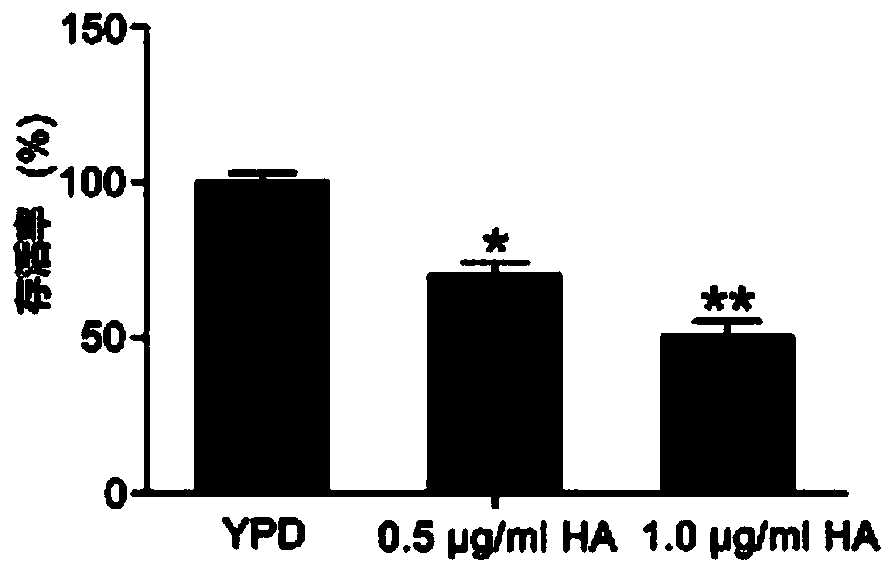
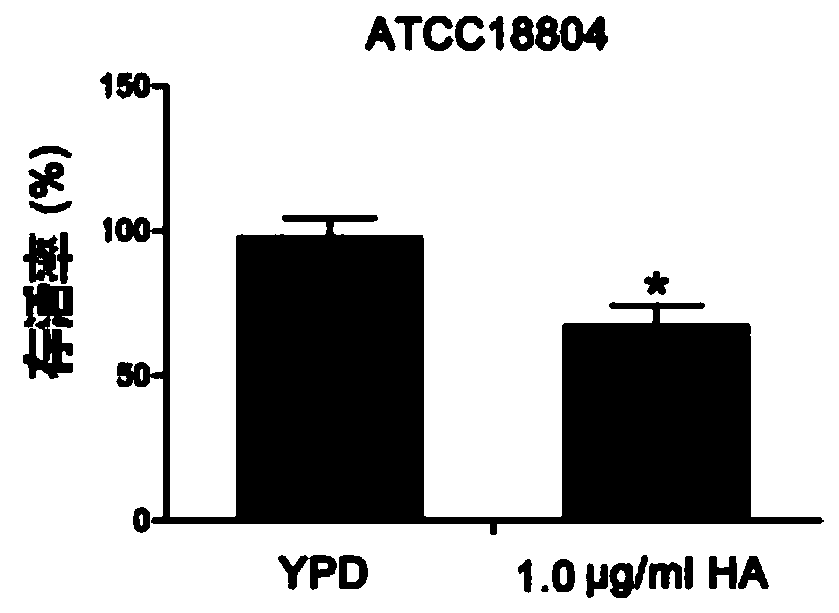
[0055] The overnight cultures of Candida albicans strains SC5314, ATCC18804 and 07318 were activated and cultured in YPD medium to the logarithmic phase, and then treated with 0.5 and 1.0 μg / ml hypocrellin A for 30 minutes under a 50W tungsten halogen lamp; The light intensity at the treatment site is 30mW / cm 2 . After continuing to culture the culture for 3 h in the dark, the cells were harvested and spread on a YPD agar plate, incubated at 30° C. for 24 h, and the number of colony forming units (CFU) was counted. The experiment was repeated three times independently.
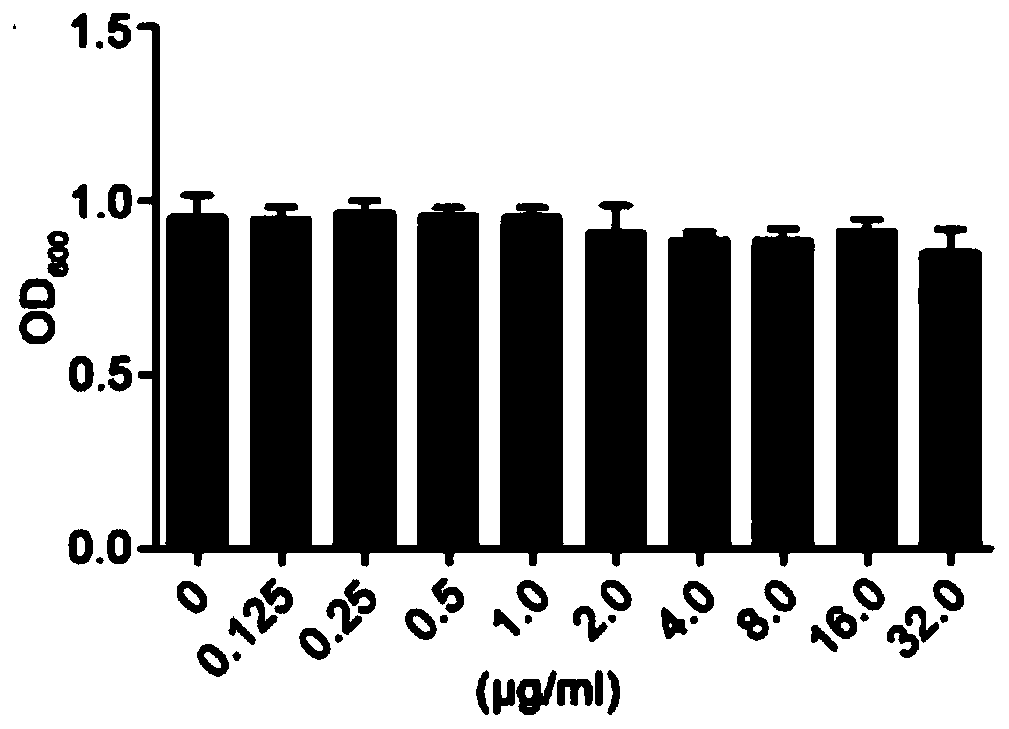
[0056] In order to observe the effect of hypocrellin A on the growth of Candida albicans, SC5314 strain was treated with hypocrellin A in the presence of light and without light. Such as figure 1 As shown by the results, Hypocretin A had no significant effect on the growth of Candida albicans cells without light. Such as figure 2 As shown in ...
Embodiment 2
[0057] Example 2: Intracellular ROS measurement after Hypocretin A treatment
[0058] ROS levels in C. albicans cells were determined using 2',7'-dichlorofluorescein diacetate (DCFH-DA). DCFH-DA can be converted to the membrane-impermeable reagent DCFH by intracellular esterase, which can then be rapidly oxidized by ROS to its fluorescent derivative DCF. The fluorescence intensity of DCF can indicate the level of ROS generation. Collect the overnight Candida albicans culture and dilute to 10 6 cells / ml. After incubation to the logarithmic phase, the cells were incubated with hypocretin A for 30 min in the light, and then incubated in the dark for 3 h. Then, Candida albicans cells were collected, washed once with YPD medium, and stained with 10 μM DCFH-DA for 30 min in the dark. Finally, the green fluorescence intensity of the resuspended cells was analyzed using a FACSCalibur flow cytometer (Becton Dickinson, USA).
[0059] Such as Figure 5 The results showed that hyp...
Embodiment 3
[0060] Example 3 : Plasma Membrane Potential Evaluation After Hypocretin A Treatment
[0061] The present invention uses DiBAC4(3) staining to evaluate the cell membrane potential of the Candida albicans strain. DiBAC4(3) is a plasma membrane potential-sensitive fluorescent probe that is only present in the outer region of the plasma membrane in normal cells. However, depolarization of the cell membrane can lead to its influx, the binding of the probe to lipid-rich compounds and resulting in increased fluorescence. As previously described, the membrane potential molecular probe DiBAC4 (3) was used to assess the change of plasma membrane potential. The treated Candida albicans were collected by centrifugation and washed three times with PBS, then resuspended, and 20 μg / ml membrane potential sensitive dye DiBAC4 was added to PBS ( 3), and incubate the sample at 37° C. in the dark for 30 min. The percentage of depolarized C. albicans cells in the suspension was determined by ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com