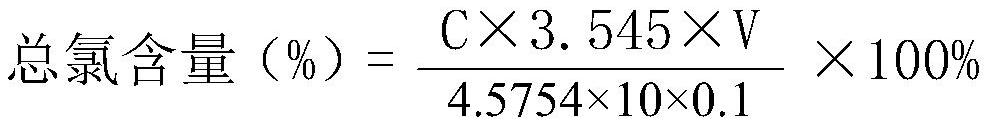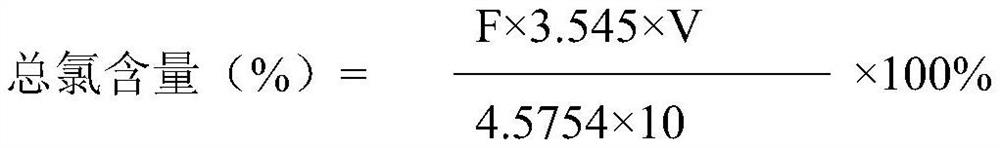Patents
Literature
32 results about "Dichlorofluorescein" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
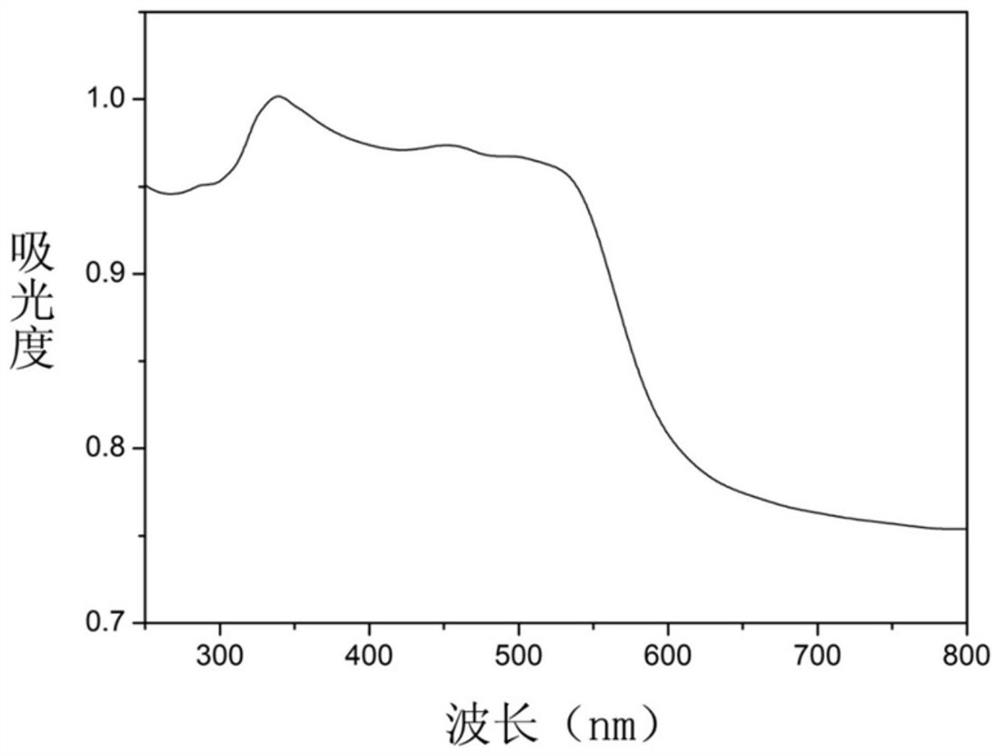
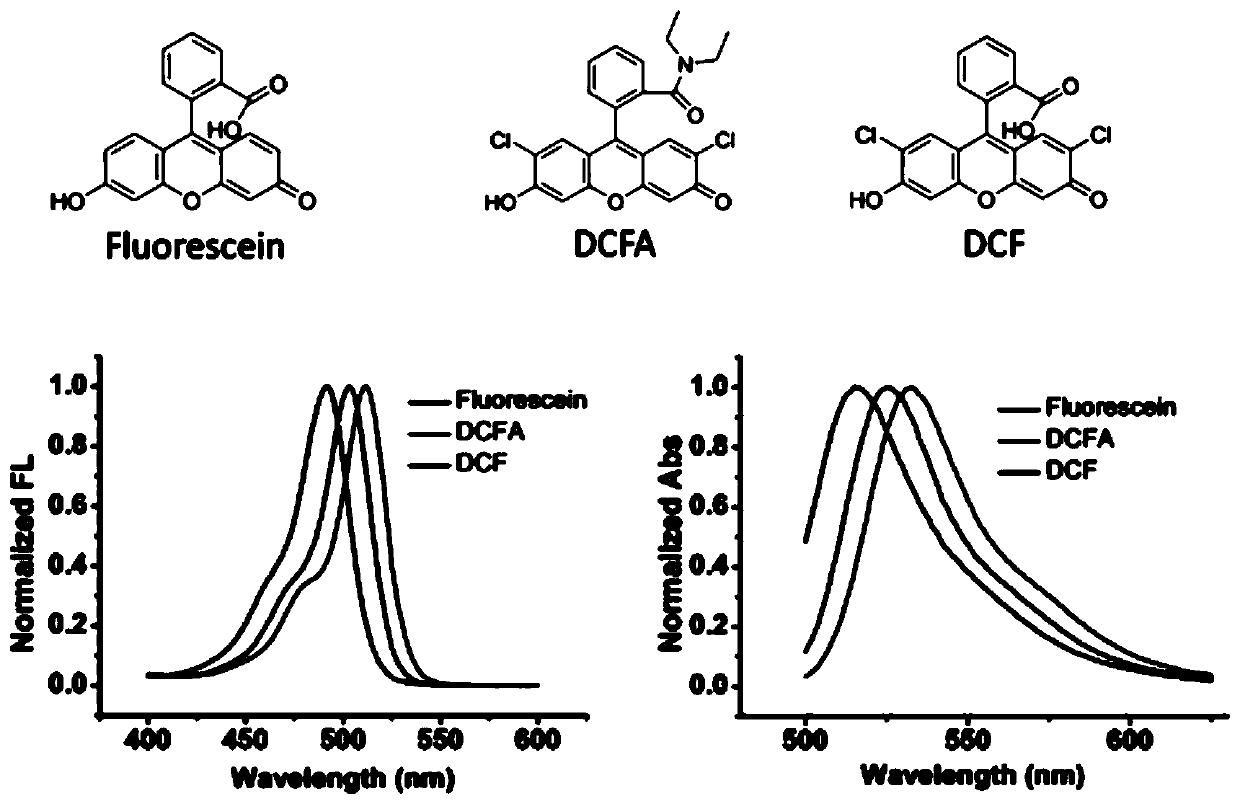
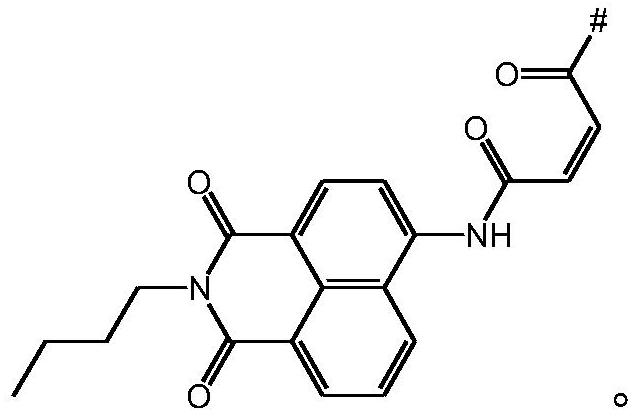
Dichlorofluorescein (DCF) is an organic dye of the fluorescein family, being substituted at the 2 and 7 positions by chloride. It is used as an indicator for argentometry by Fajans method. It is also used in the cellular antioxidant activity (CAA) assay. Dichlorofluorescin (DCFH) is a probe that is trapped within cells and is easily oxidized to fluorescent dichlorofluorescein (DCF). The method measures the ability of compounds to prevent the formation of DCF by 2,2'-Azobis(2-amidinopropane) dihydrochloride (ABAP)-generated peroxyl radicals in human hepatocarcinoma HepG2 cells. By itself, dichlorofluorescin (DCFH) also quantifies intracellular hydrogen peroxide as well as cellular oxidative stress.
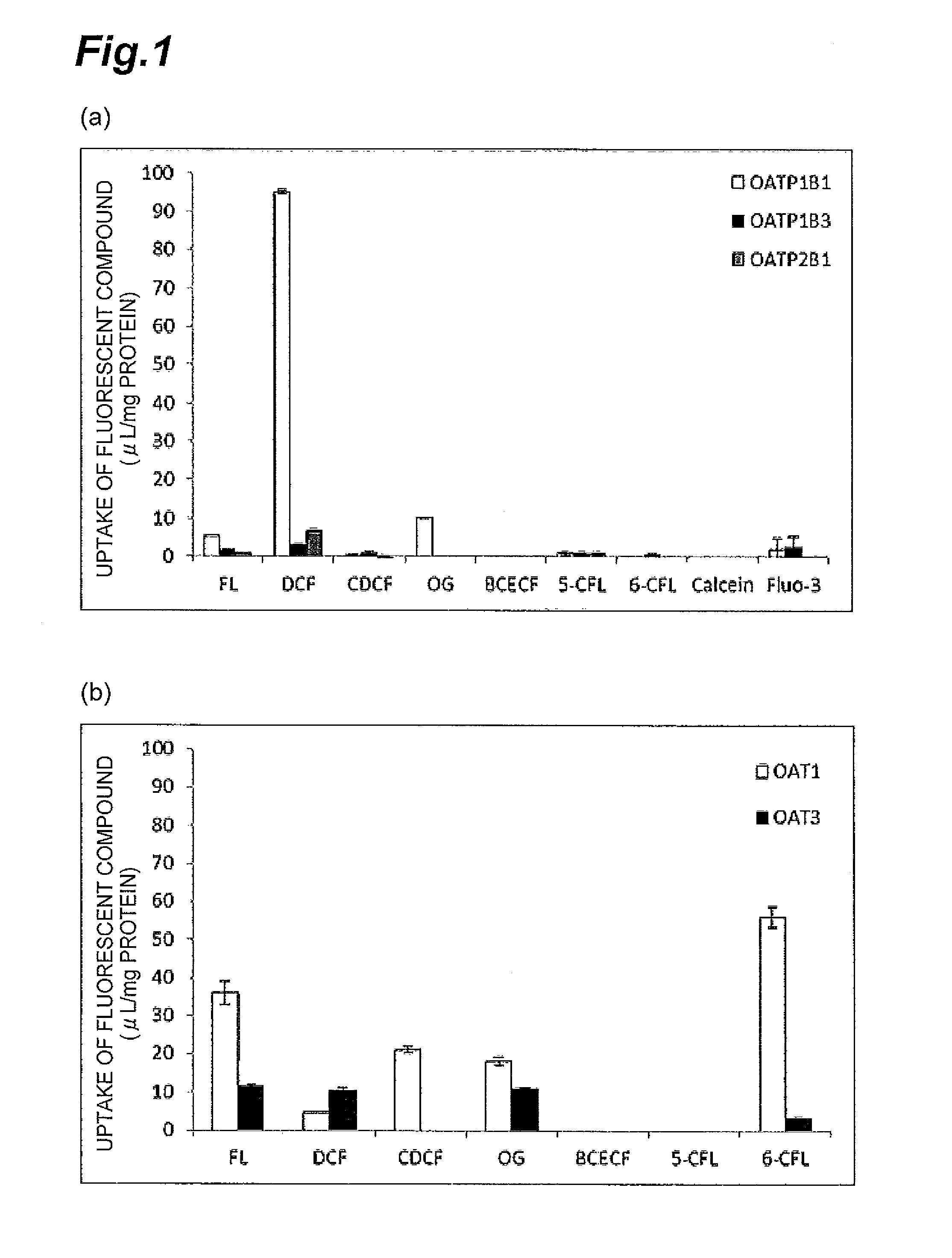
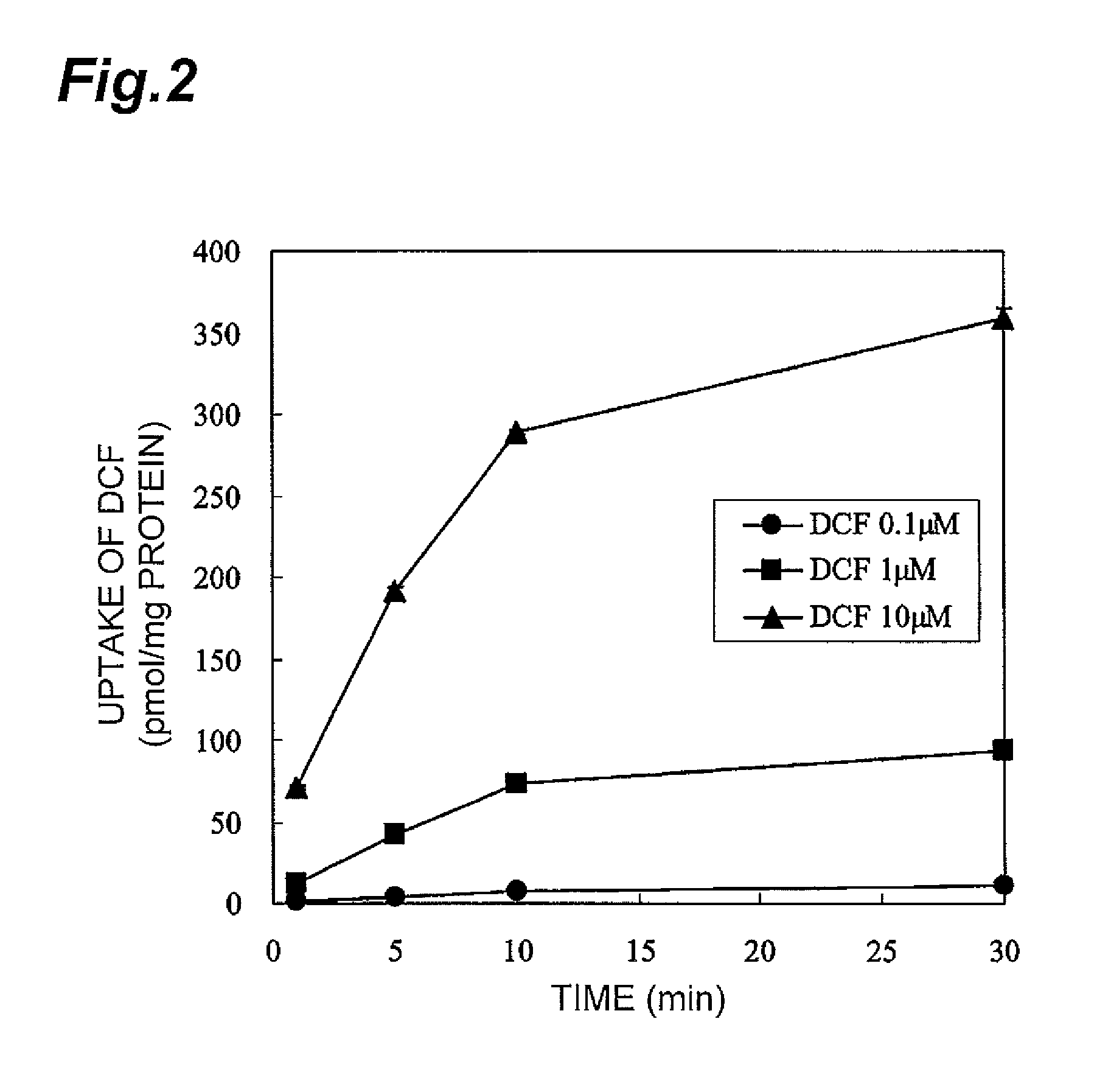
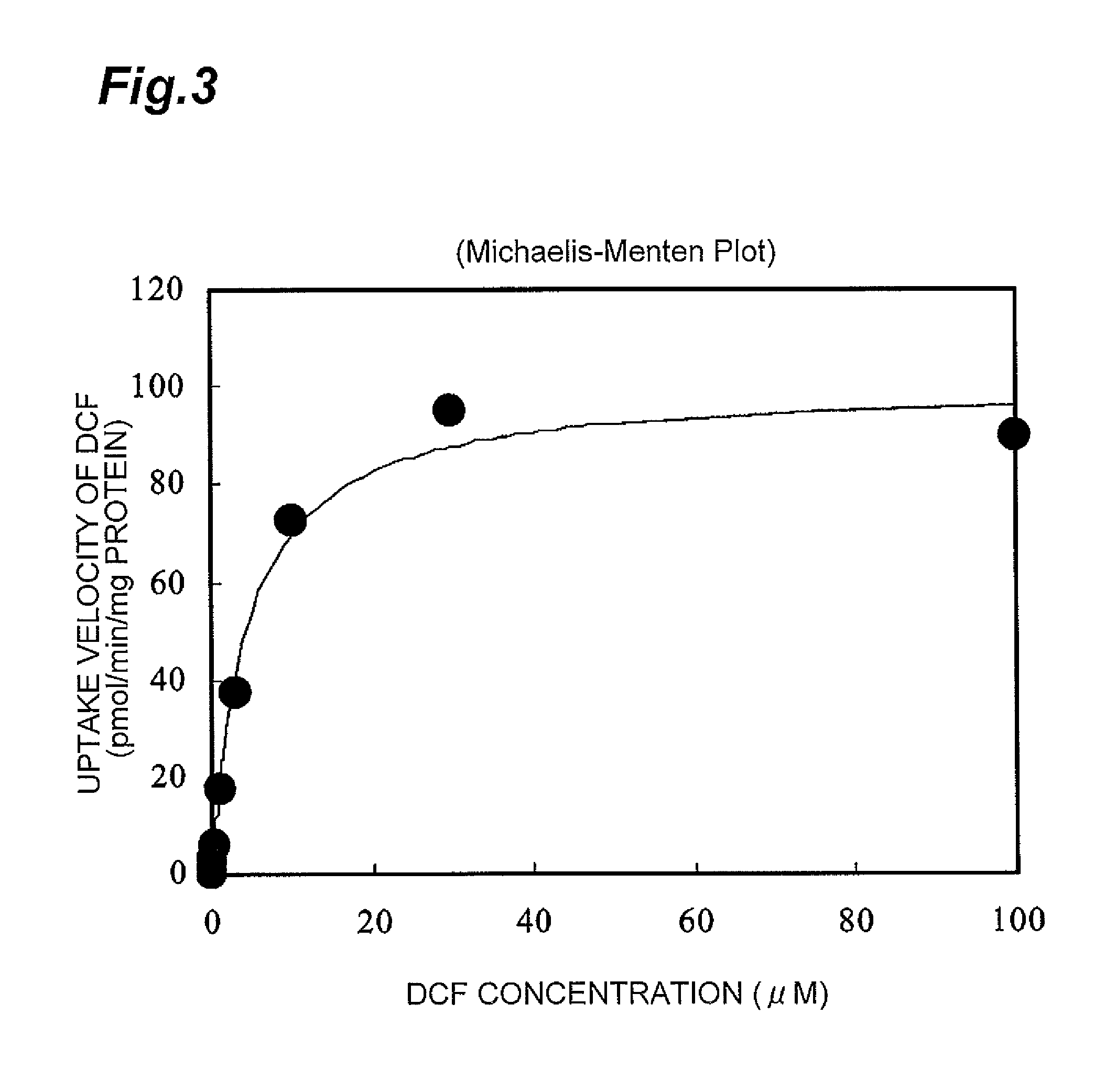
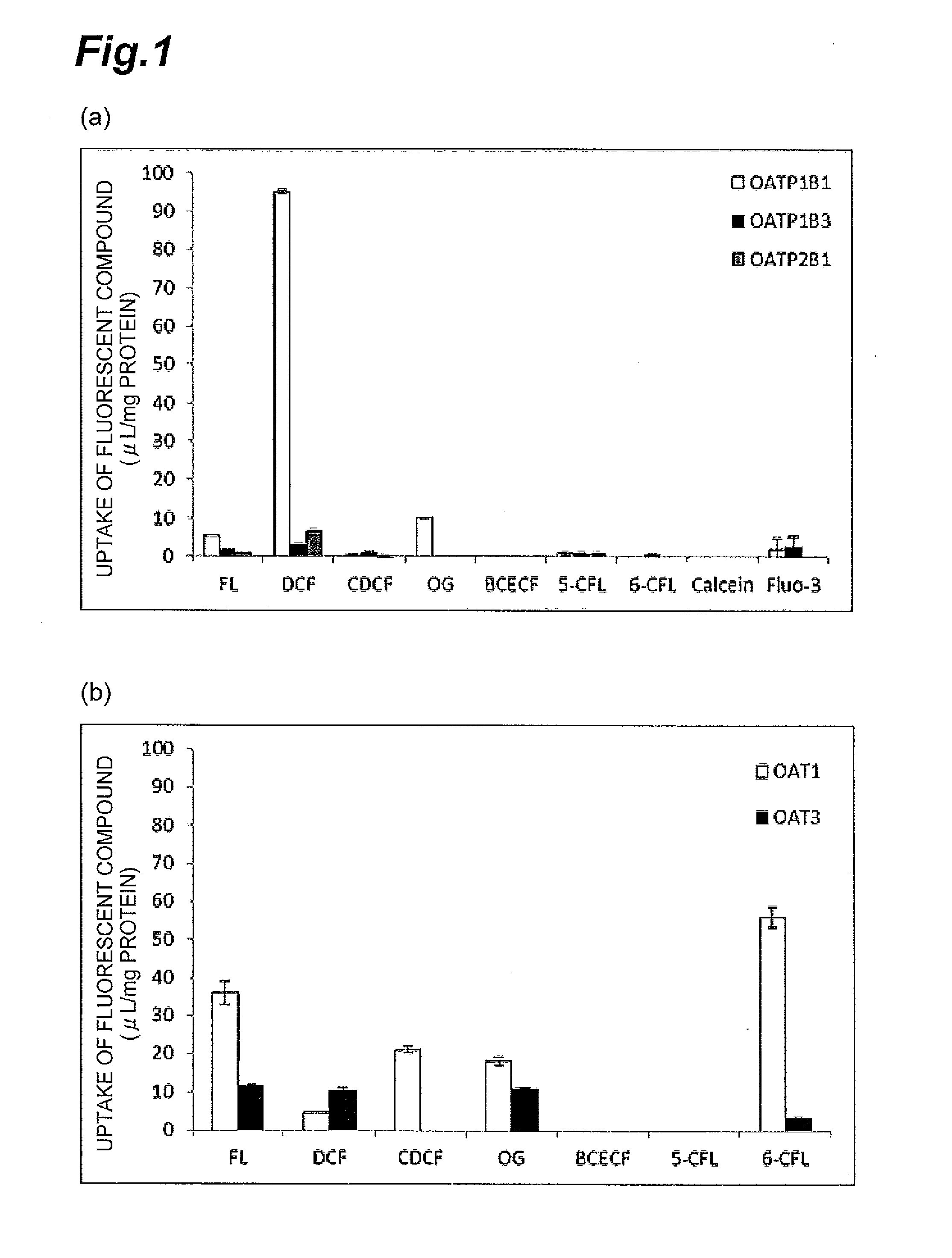
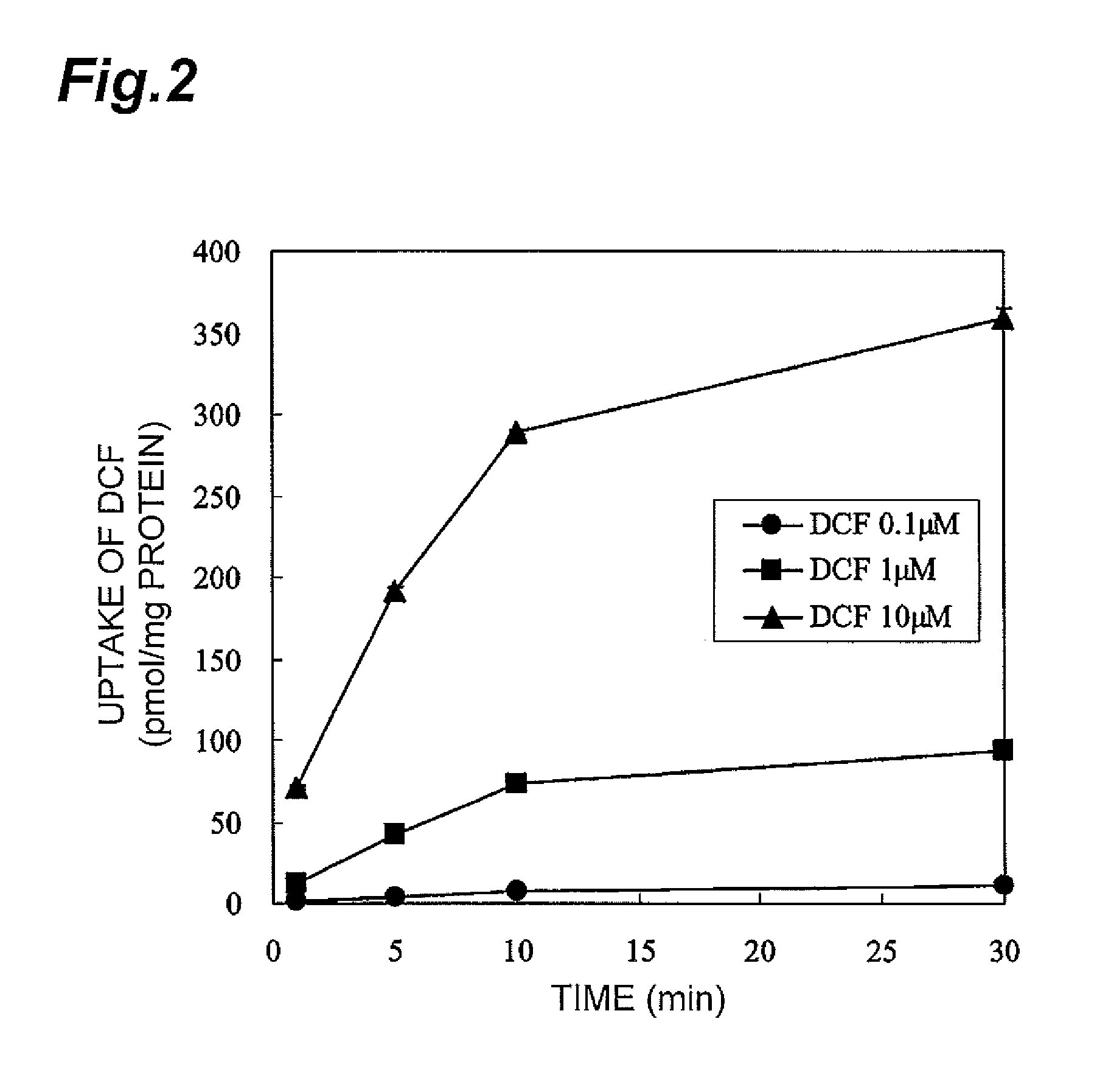
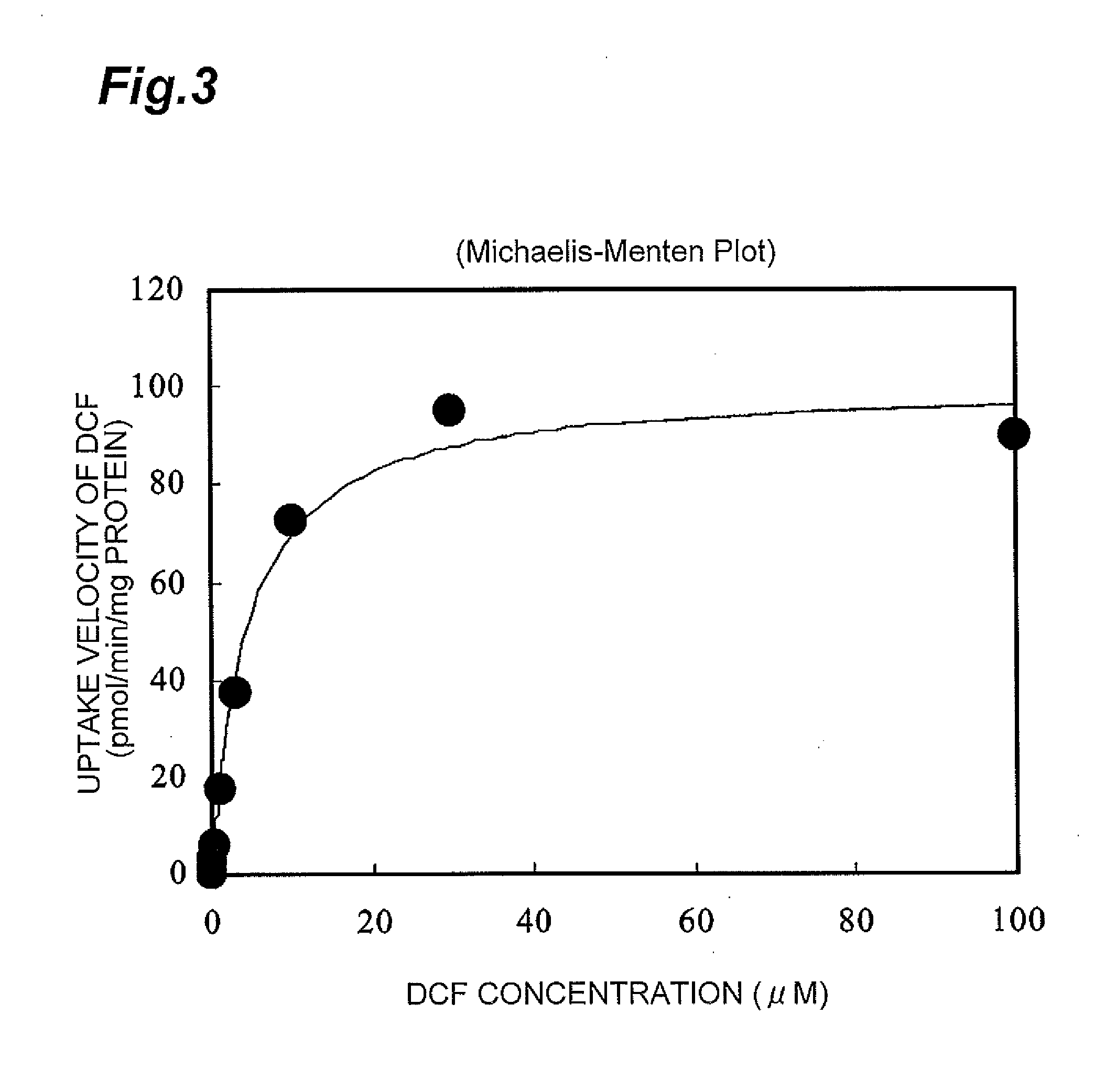
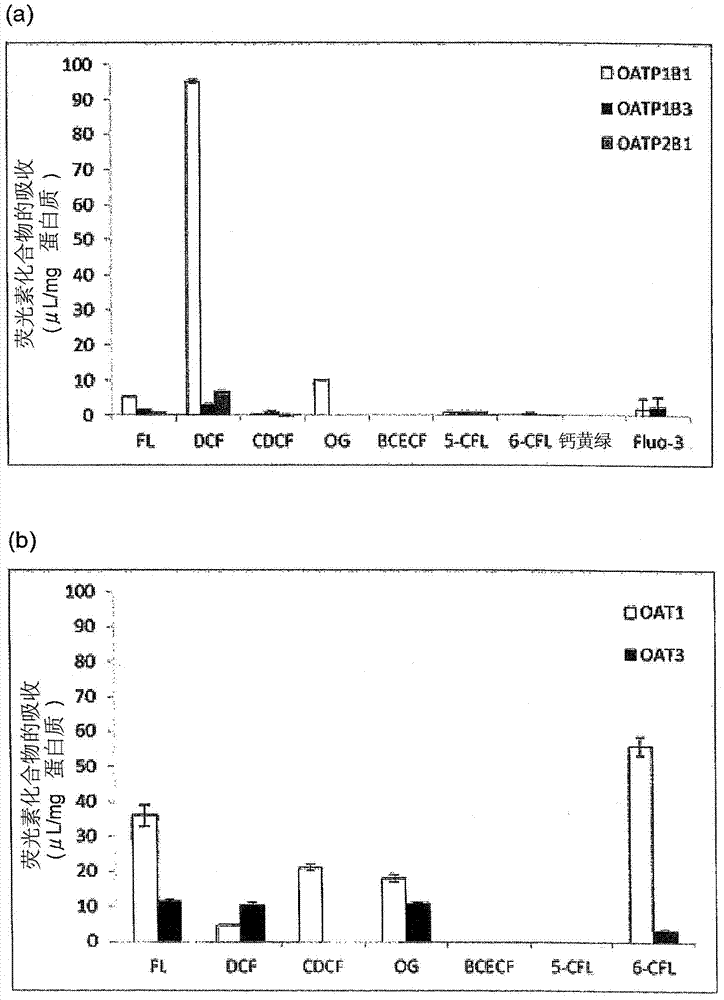
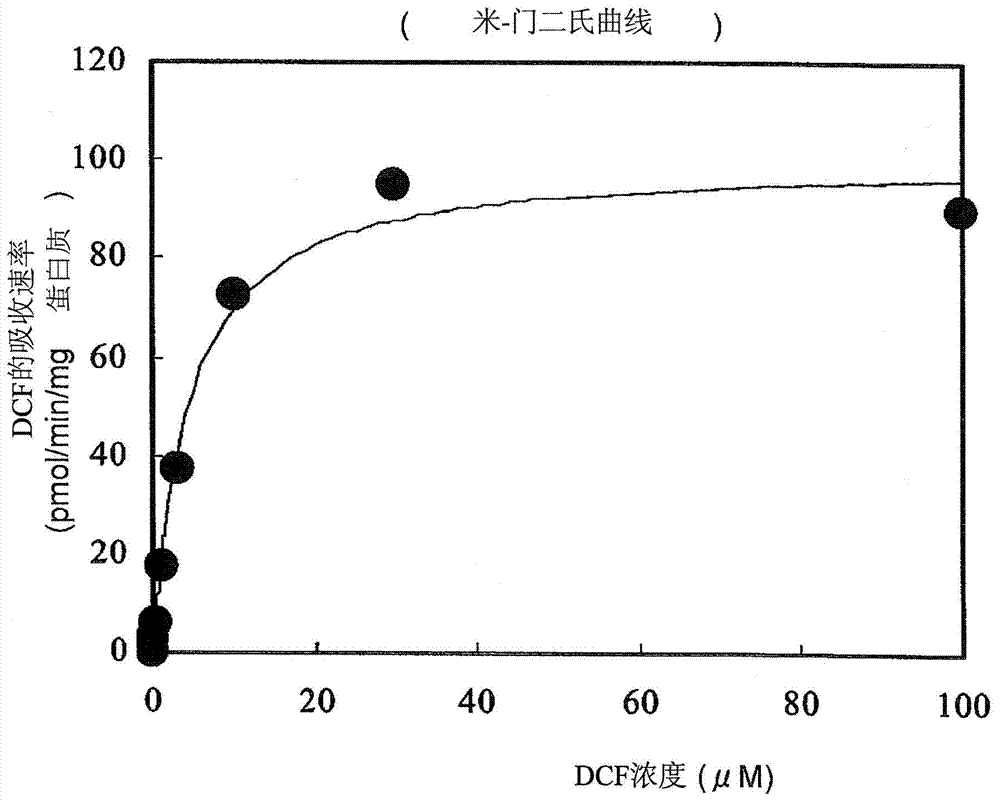
Method for screening for compound capable of enhancing or inhibiting OATP1B1 transport activity, and method for determining expression level of OATP1B1
ActiveUS8945865B2Enhances and inhibits transport activityEasy to operateCompound screeningApoptosis detectionMeasurement testDichlorofluorescein
The present invention provides a method of screening for a compound that enhances or inhibits the transport activity of OATP1B1, using dichlorofluorescein. The present invention also provides a use of dichlorofluorescein in measurement of the expression level of OATP1B1. The present invention further provides a method for measuring the expression level of OATP1B1 in test cells, using dichlorofluorescein. The present invention further provides a use of a kit including dichlorofluorescein and positive cells expressing OATP1B1 in measurement of the expression level of OATP1B1 in test cells.
Owner:EISIA R&D MANAGEMENT CO LTD
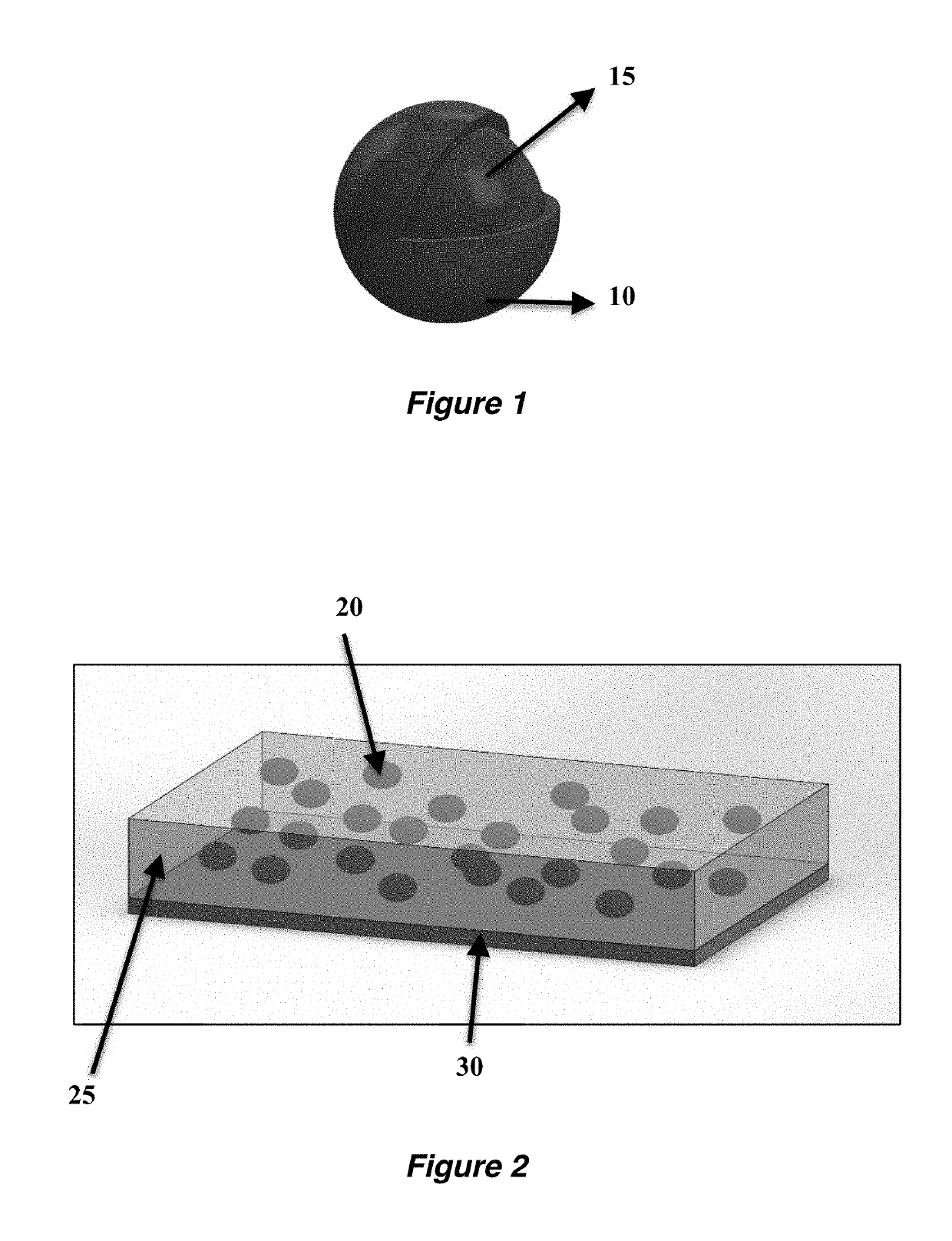
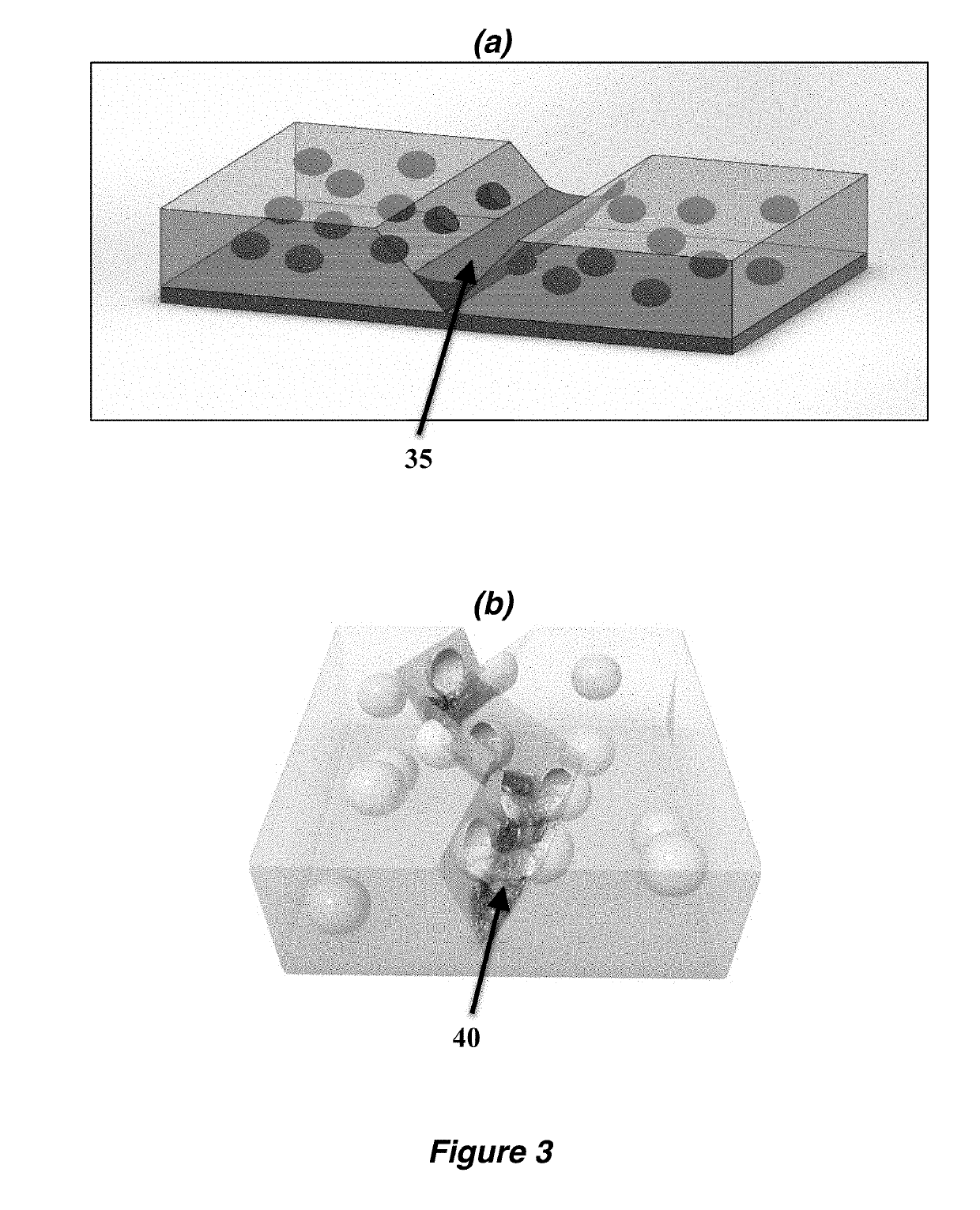
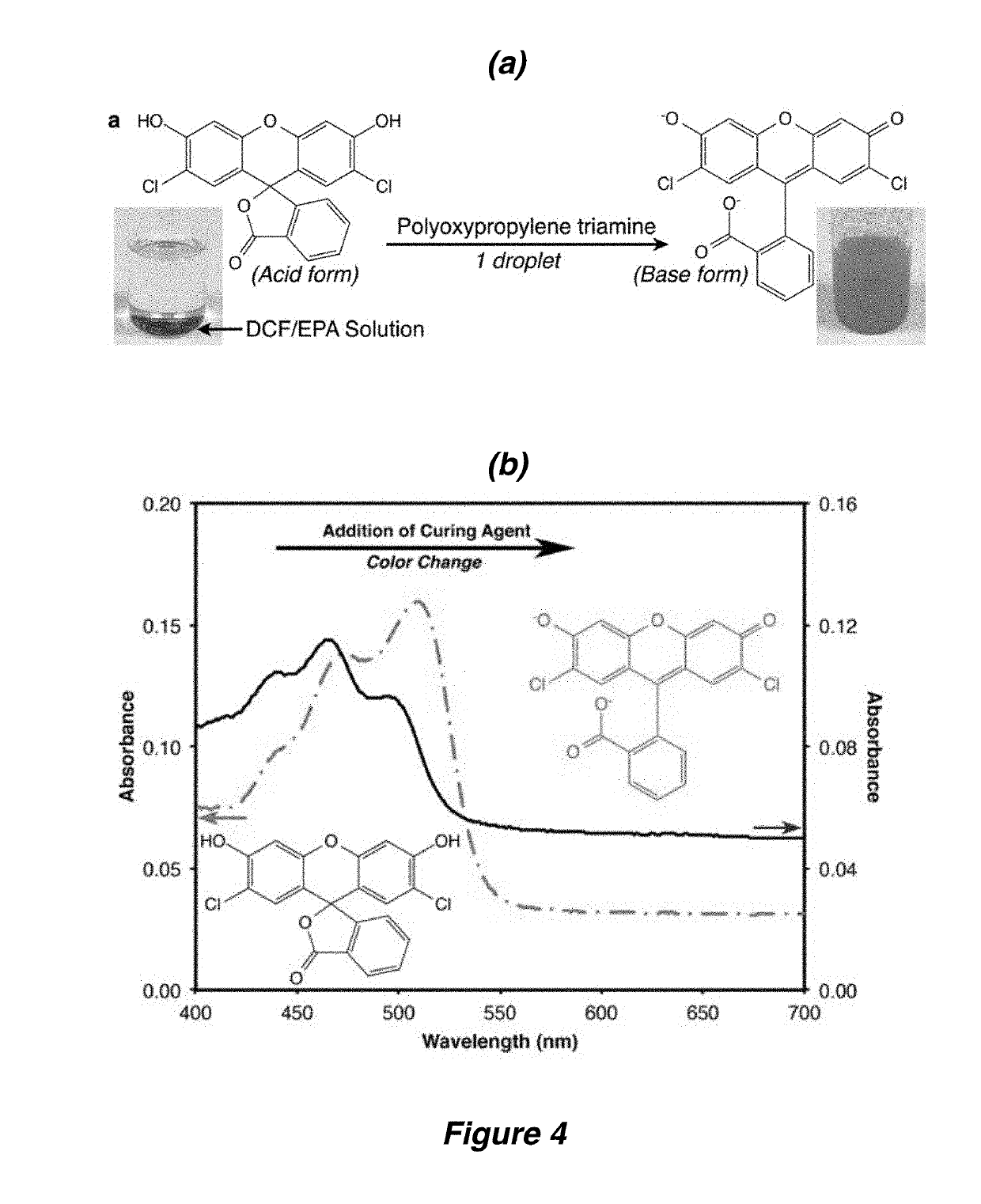
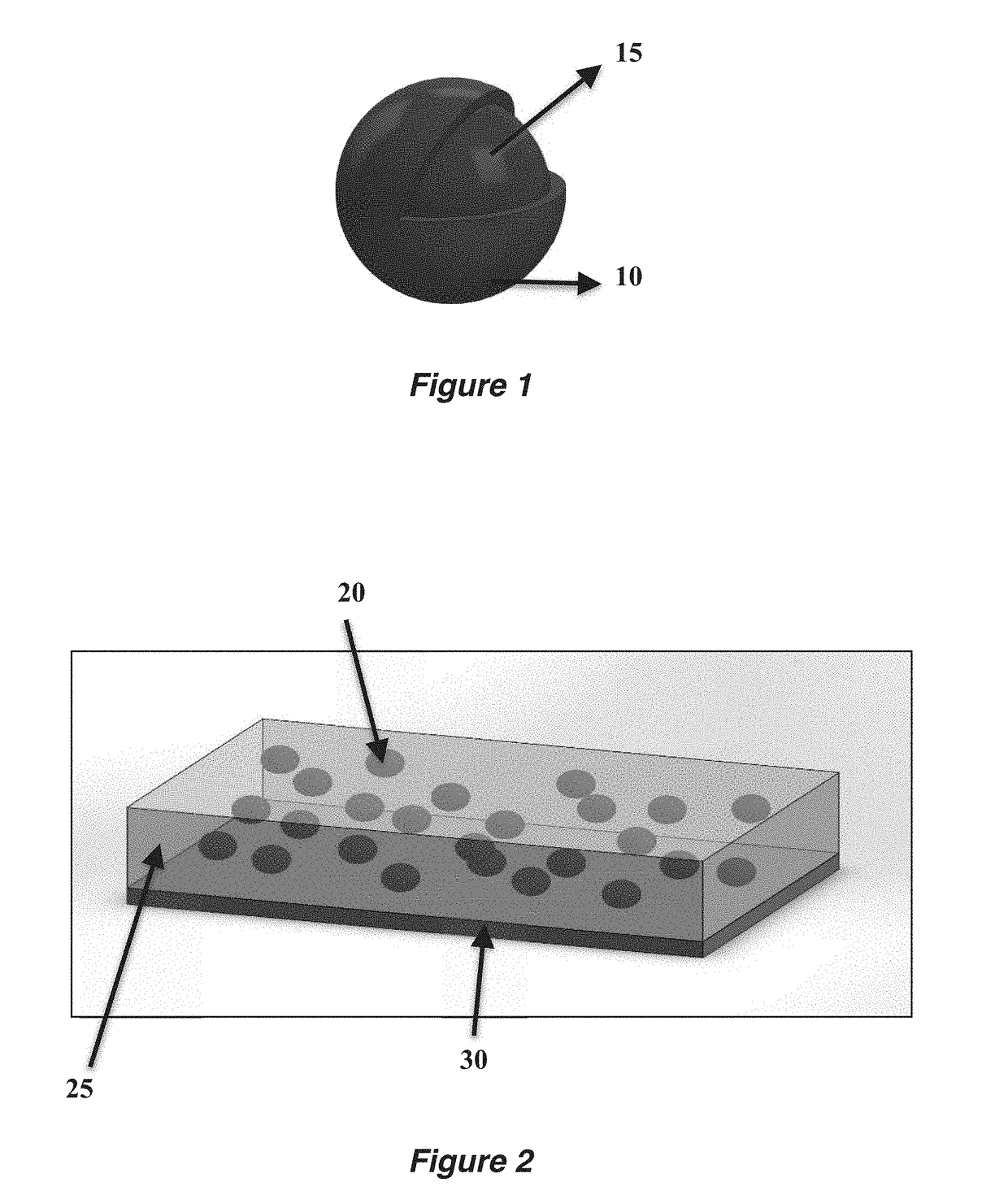
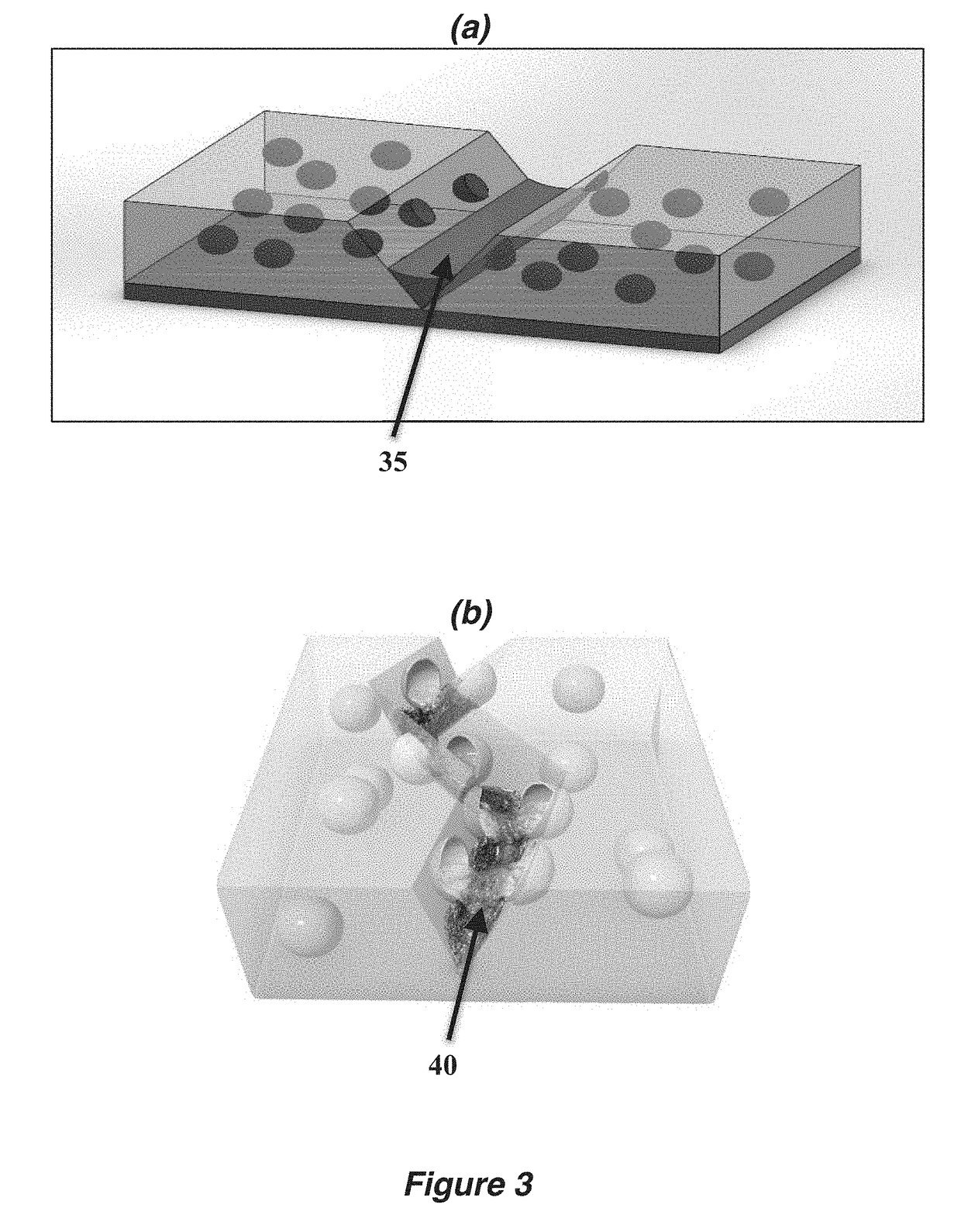
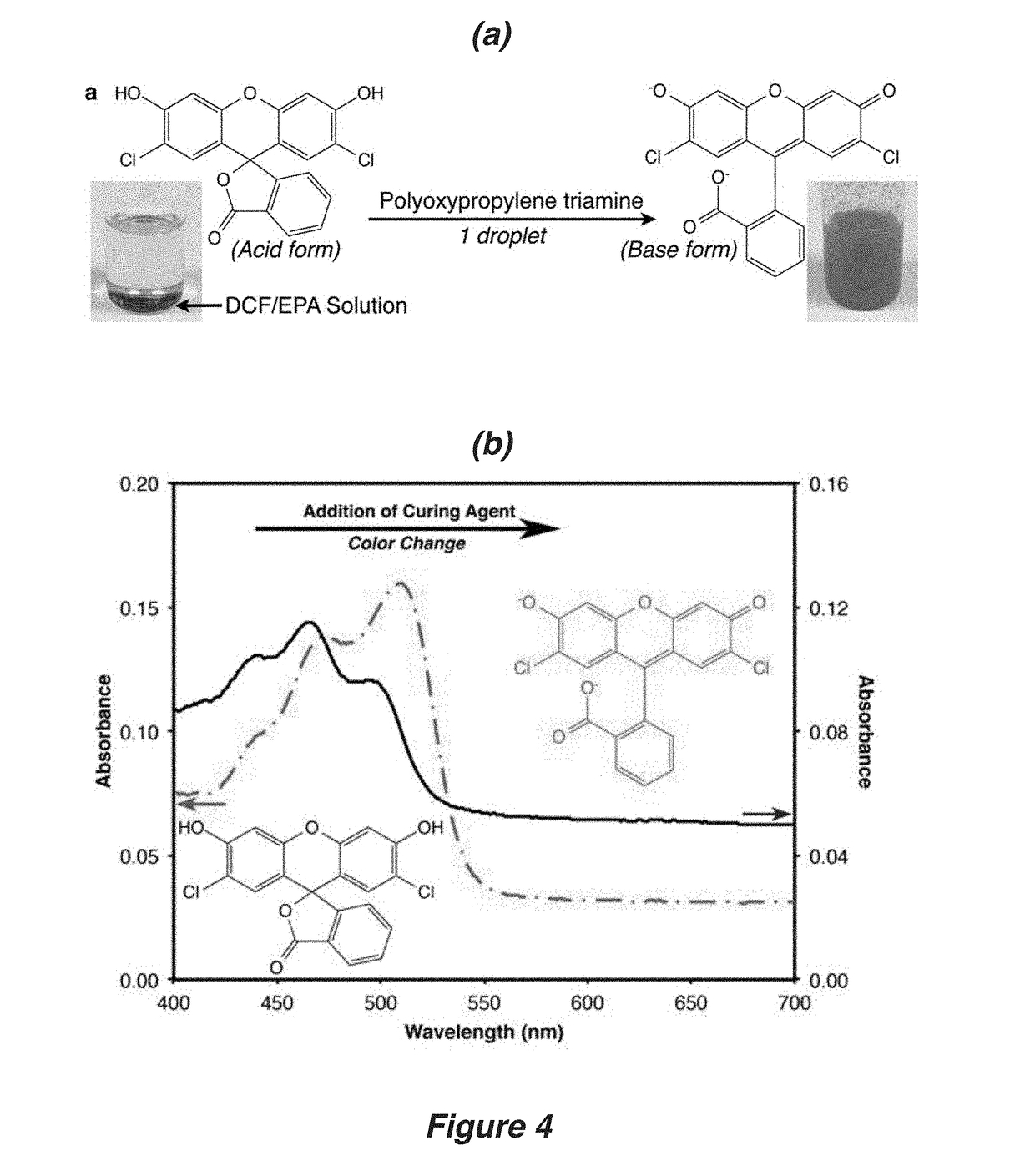
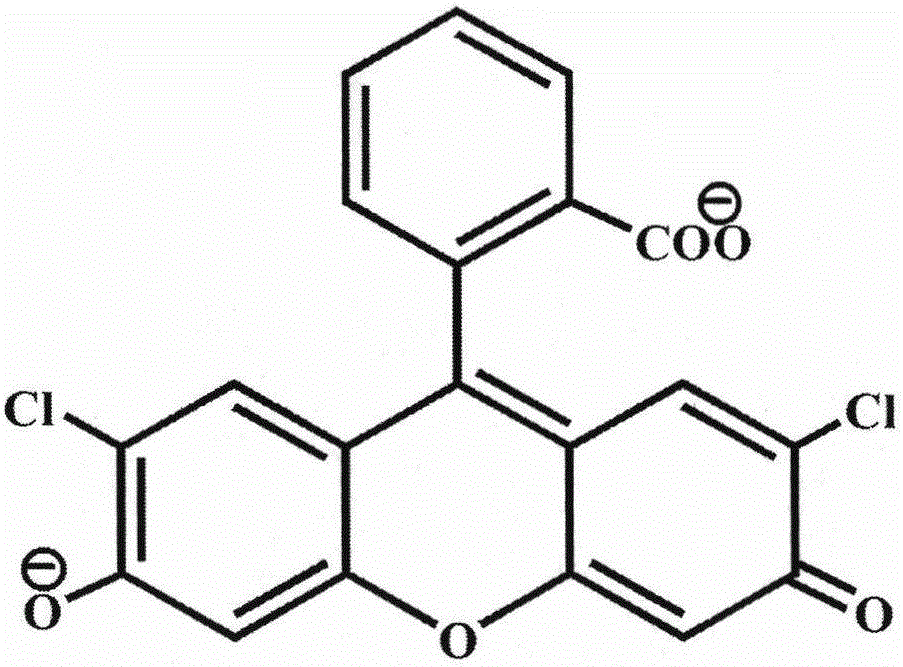
Autonomic damage indication in coatings
ActiveUS20170158883A1Improve safety and sustainabilityGuaranteed uptimeEpoxy resin coatingsFluorescaminePolymer science
Autonomous detection of damage in a polymer coating is described by utilizing microcapsules in a polymer coating having free and / or residual amines. The microcapsules contain a color indicator, such as 2′,7′-dichlorofluorescein (DCF), bromophenol blue (BPB) or fluorescamine, which is reactive with the free and / or residual amines present in the polymer coating. For coatings without the presence of free and / or residual amines, a color indicator microcapsule can be combined with a second type of microcapsule filled with a base. When sufficient damage is inflicted to the coating, the microcapsules in and / or around an area of the damage will rupture, and the color indicator will react with the free and / or residual amines or the base to autonomically indicate the area in which the coating has been damaged.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Method for detecting content of active oxygen in cells
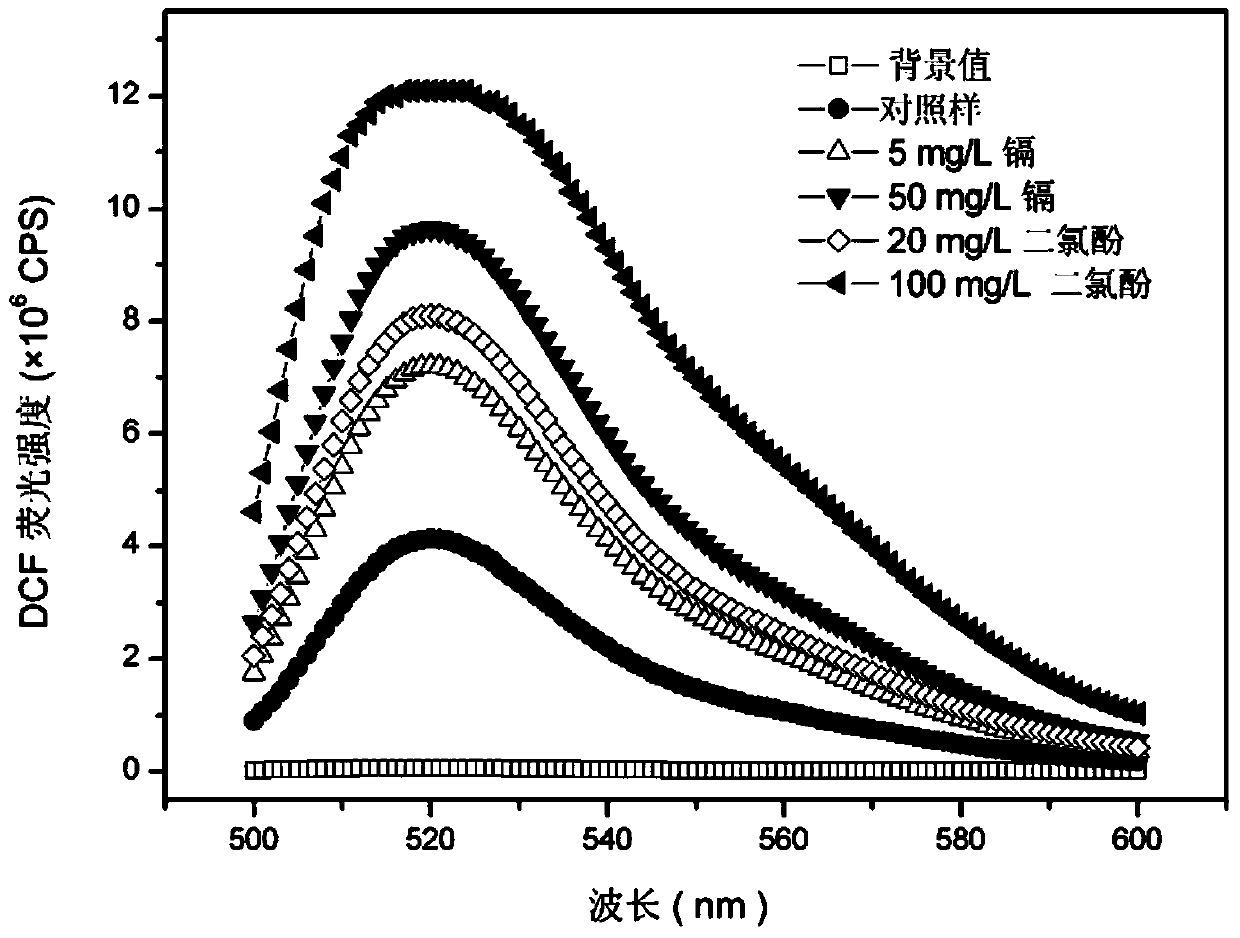
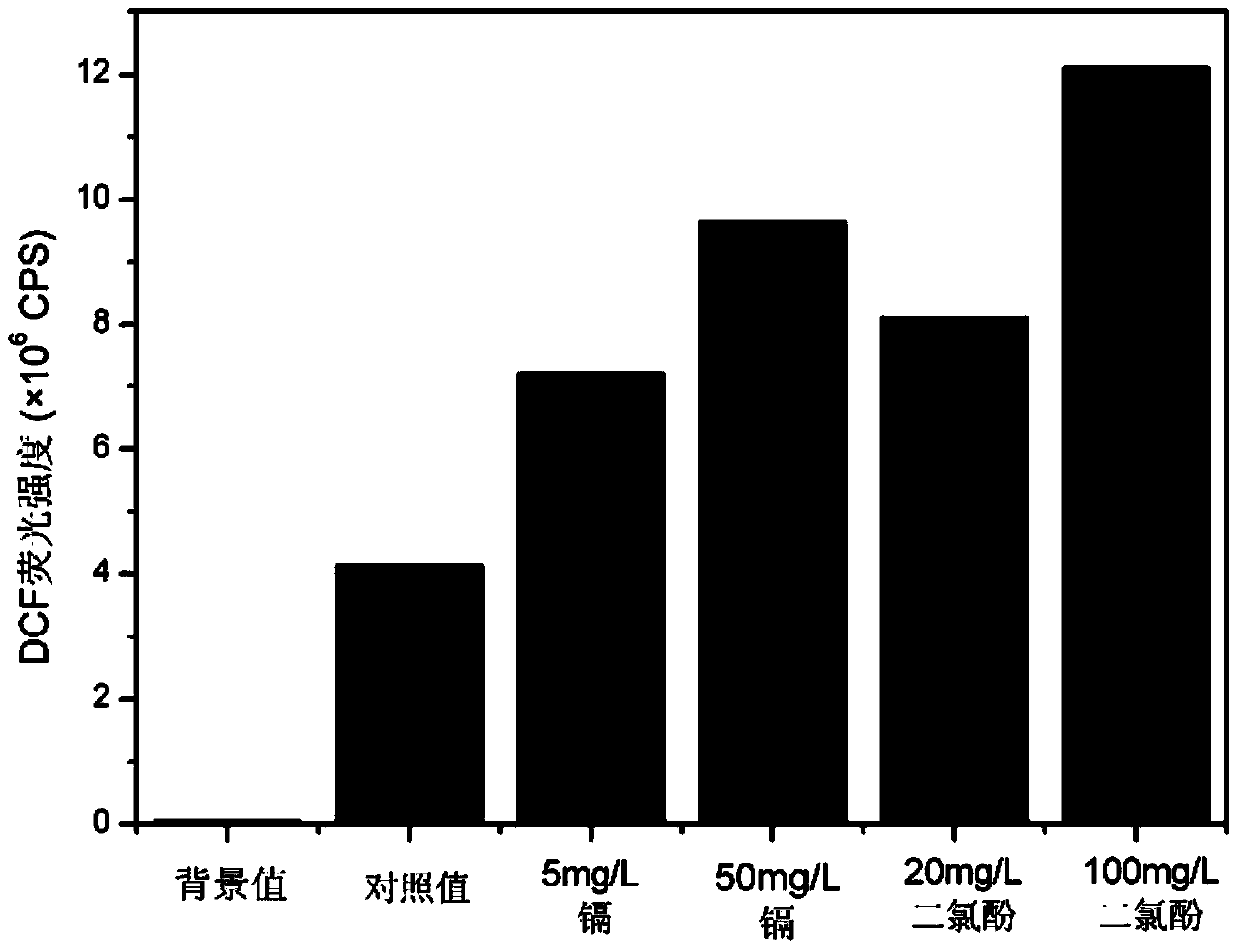
InactiveCN106191194ATrue reflection of damageThe test result is accurateMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceDichlorofluoresceinOxygen
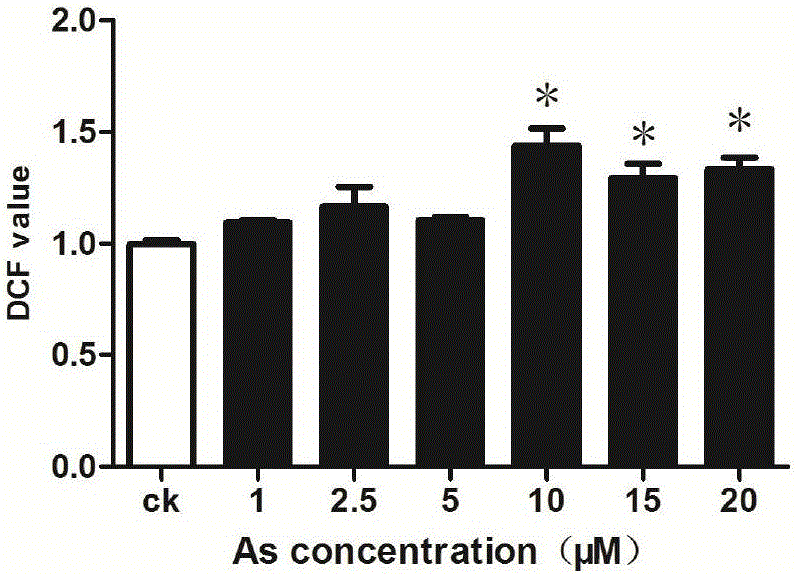
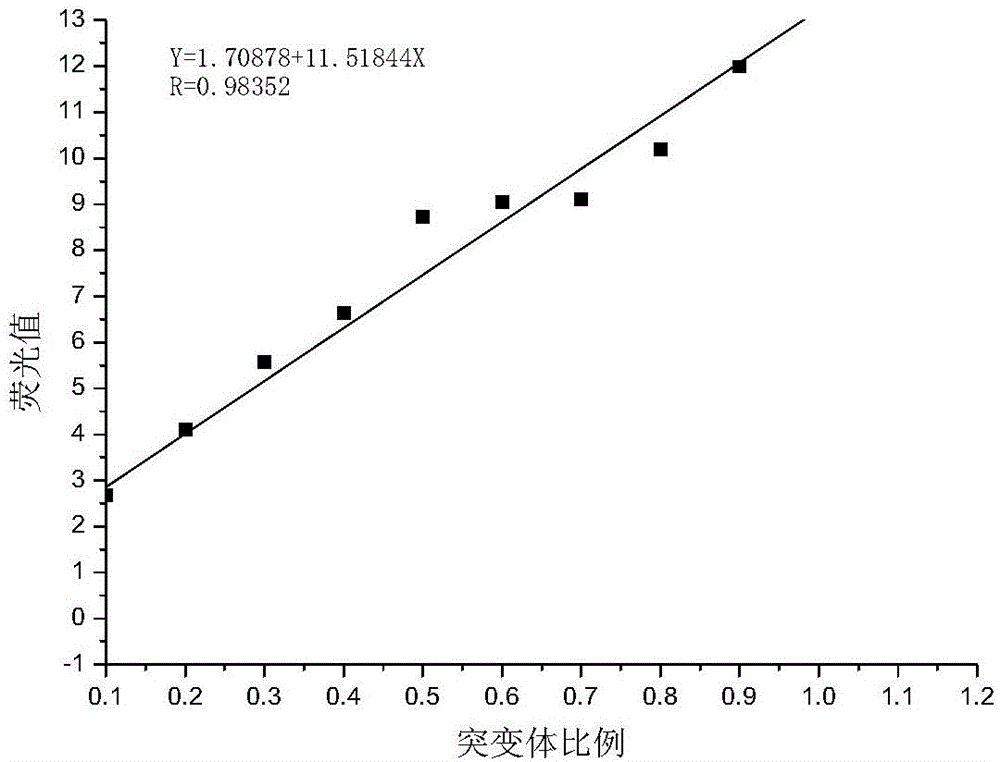
The invention discloses a method for detecting content of active oxygen in cells. The method has the advantage that a DCF (dichlorofluorescein) fluorescence signal value of a single live cell corresponding to pollutants exposed under different concentrations can be obtained; a detection result is accurate, and the problem of inaccurate measuring of final fluorescence intensity due to change of cell number caused by exposing of the pollutants is solved; the corresponding fluorescence signal value of single cell under a certain concentration can be truly reflected, and the injury to cells by pollutant exposing can be truly and accurately reflected, so as to lay a solid foundation for the application of an in-vitro cell model into the toxicity evaluation of the pollutants.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Reagent for determining sodium chloride content in urine, test paper strip thereof, preparation method thereof and purpose thereof
InactiveCN104849270AEasy to measureRapid determinationMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorDichlorofluoresceinSulfosalicylic acid
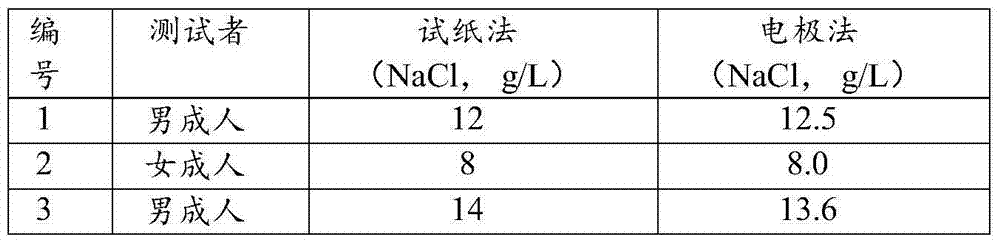
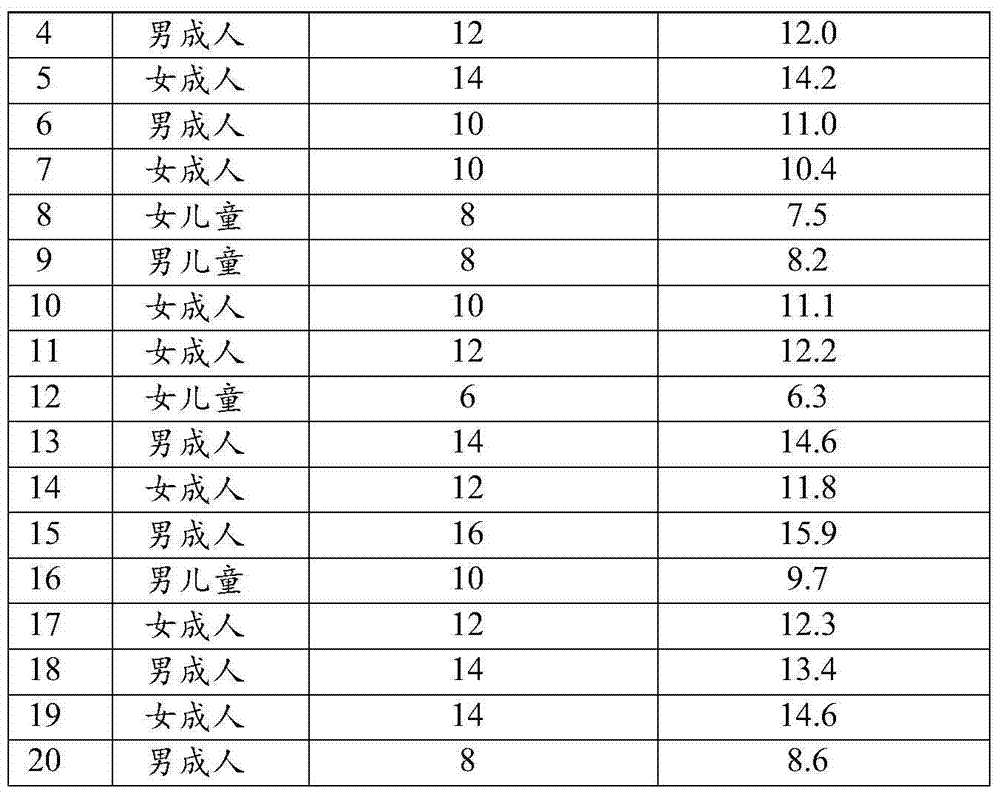
The invention belongs to the field of analytical chemistry and particularly relates to a reagent for determining sodium chloride content in urine, a test paper strip thereof, a preparation method thereof and a purpose thereof. The reagent is composed of a reagent A and a reagent B; the reagent A is composed of 1-60 weight parts of silver nitrate and 1 volume part of water; the reagent B contains 0.5-20 weight parts of 2,7-dichlorofluorescein and 1 volume part of organic solvent selected from at least one of alcohol, phenol, ether, acid, amide and ketone of C1-C10. The reagent B further contains 0.5-50 weight parts of surface active agents and 1-70 weight parts of sulfosalicylic acid, and the relation between the weight part and the volume part is g / L. The test paper strip for determining sodium chloride content in urine is simple and convenient to operate, low in cost, favorable for industrial production and capable of quickly and conveniently determining sodium chloride content in urine, and thus can judge whether the salt intake is excessive.
Owner:汇征联合(北京)医疗器械有限公司
Method for measuring active oxygen level in phanerochaete chrysosporium in treated wastewater
InactiveCN103808703ASimplified representationAccurate representationPreparing sample for investigationFluorescence/phosphorescenceFiltrationDichlorofluorescein
The invention discloses a method for measuring the active oxygen level in phanerochaete chrysosporium in treated wastewater. The method comprises the following steps: washing a phanerochaete chrysosporium bacterium ball in the treated wastewater, adding a liquid culture medium for further culture, further adding 2',7'-dichloro dihydro fluorescein sodium diacetate into the liquid culture medium after culture to obtain a mixture solution, carrying out incubation on the mixture solution, filtering, then performing ultrasonic crushing and centrifuging on the bacterium ball obtained through filtration, extracting a supernate, and finally measuring the fluorescence intensity of the oxidized dichlorofluorescein in the supernate. The method has the advantages that the operation condition is simple, the application is easy and the active oxygen level in the phanerochaete chrysosporium in the treated wastewater can be accurately and visibly measured.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Novel high-performance water-based fluorescent ink
The invention relates to fluorescent ink. The fluorescent ink contains a fluorescent agent and can produce a fluorescent effect when encountering ultraviolet rays (sunlight, fluorescent lamps and mercury lamps are more frequent) and emit white light, so that the color looks like the color has a glare fluorescent feeling. The formula comprises the following components: 5-12% of dichlorofluorescein, 5-7% of sodium hydroxide, 3-5% of sodium carbonate, 2% of phosphoric acid, 2% of balance modifier, 5-8% of ethanol, 3% of fluorescent effect, not less than 70% of distilled water and 1% of additives.
Owner:SHANGHAI RONGJING CHEM TECH
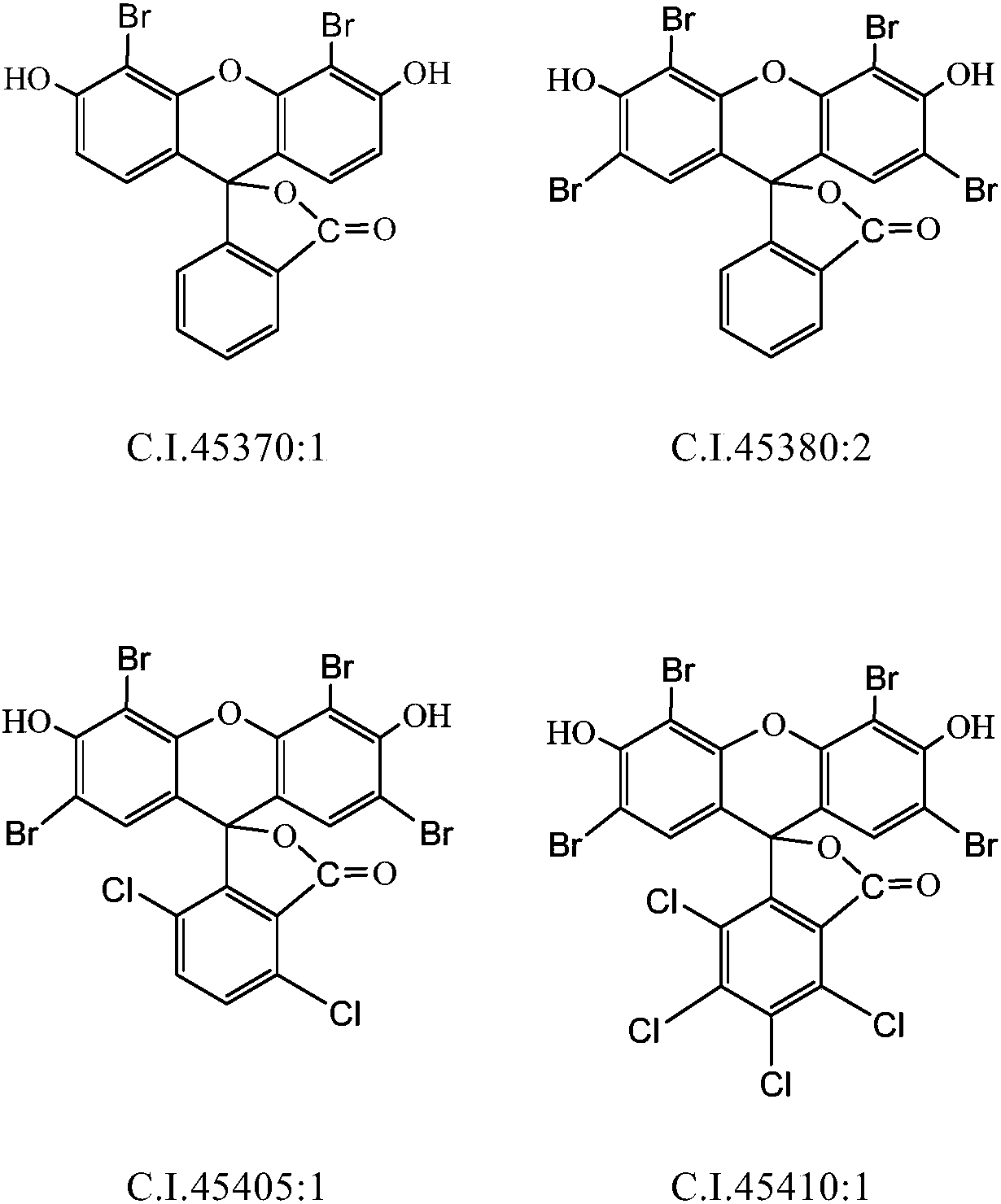
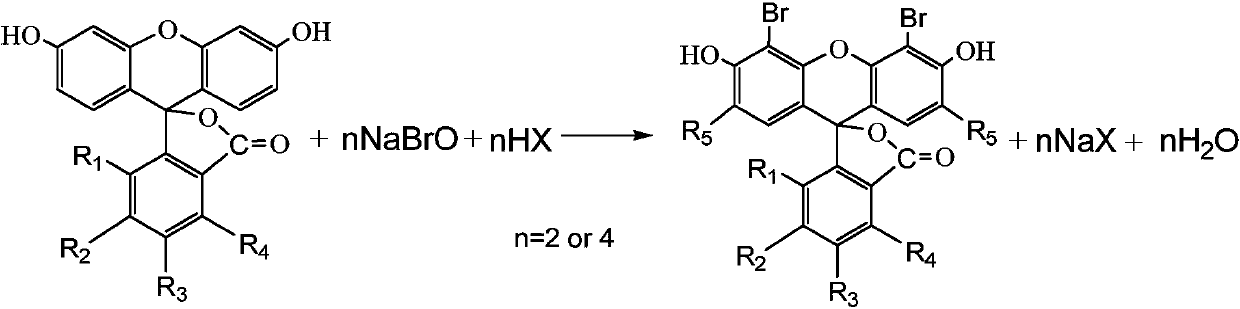
Preparation method of bromofluorescein type cosmetic dyestuff
The invention discloses a preparation method of a bromofluorescein type cosmetic dyestuff. Specifically, the dyestuff disclosed by the invention is prepared from 4',5'-dibromofluorescein (C.I.45370: 1) , 2',4',5',7'-tetrabromofluorescein (C.I.45380: 2), 2',4',5',7'-tetrabromo-4,7-dichlorofluorescein (C.I.45405: 1) and 2',4',5',7'-tetrabromo-4,5,6,7-tetrabromofluorescein (C.I.45410: 1). The preparation method comprises the following steps: (I) putting bromine into liquid alkali and a water solution of sodium hypochlorite at low temperature to prepare a sodium hypobromite solution; (II) dissolving fluorescein or corresponding chlorofluorescein or partially dissolving the fluorescein or the corresponding chlorofluorescein into an acid-containing solvent; dropwise adding the sodium hypobromitesolution at room temperature and carrying out bromination; (III) after reaching a bromination finishing point, adding a proper amount of a reducing agent to eliminate hypobromous acid if residual hypobromous acid exists; after removing a solvent, washing an obtained crude product with diluted hydrochloric acid and desalting; drying to obtain a target product.
Owner:上海染料研究所有限公司 +1
Preparation technology of allochroic silica gel and allochroic silica gel utensils
The invention provides preparation technology of allochroic silica gel and allochroic silica gel utensils. The allochroic silica gel comprises following raw materials: silica gel raw gel with a hardness of 40 DEG, coloring agents, and an allochroic powder; the allochroic powder comprises polyoxymethylene melamine, styrene maleic anhydride polymer, a surface active thickening agent, and dichloro fluorescein; and the ratio of the coloring agents to the allochroic powder is controlled to be 1:0.5-1. The allochroic silicagel is capable of displaying the color of doped coloring agents of different colors at different temperatures through the fluorescence effect of the allochroic powder with heat sensitivity; especially, color change can be realized in a very short time period at critical temperature values.
Owner:东莞市虎添翼塑胶制品有限公司
Method for screening for compound capable of enhancing or inhibiting oatp1b1 transport activity, and method for determining expression level of oatp1b1
ActiveUS20140024070A1Enhances and inhibits transport activityDetected safely and inexpensivelyCompound screeningApoptosis detectionScreening methodDichlorofluorescein
The present invention provides a method of screening for a compound that enhances or inhibits the transport activity of OATP1B1, using dichlorofluorescein. The present invention also provides a use of dichlorofluorescein in measurement of the expression level of OATP1B1. The present invention further provides a method for measuring the expression level of OATP1B1 in test cells, using dichlorofluorescein. The present invention further provides a use of a kit including dichlorofluorescein and positive cells expressing OATP1B1 in measurement of the expression level of OATP1B1 in test cells.
Owner:EISIA R&D MANAGEMENT CO LTD
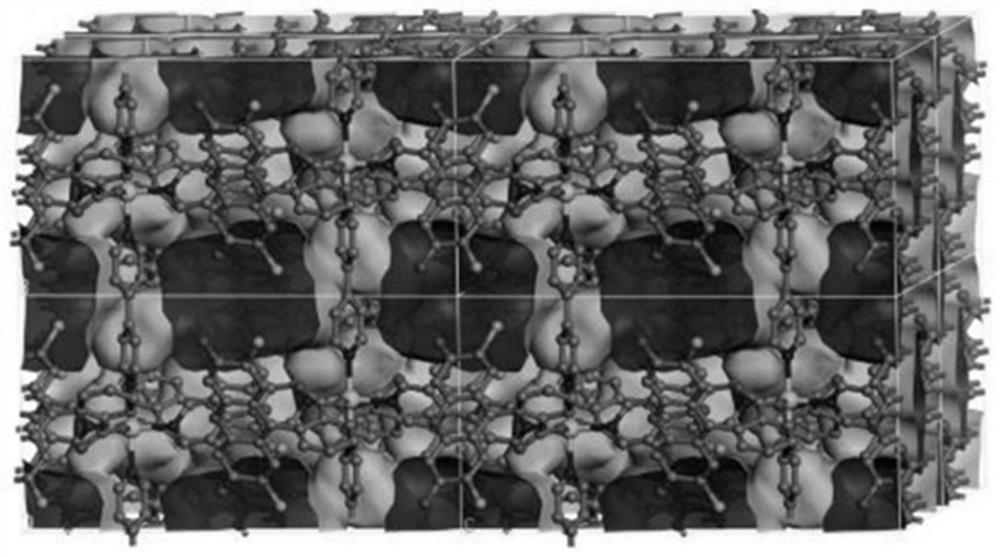
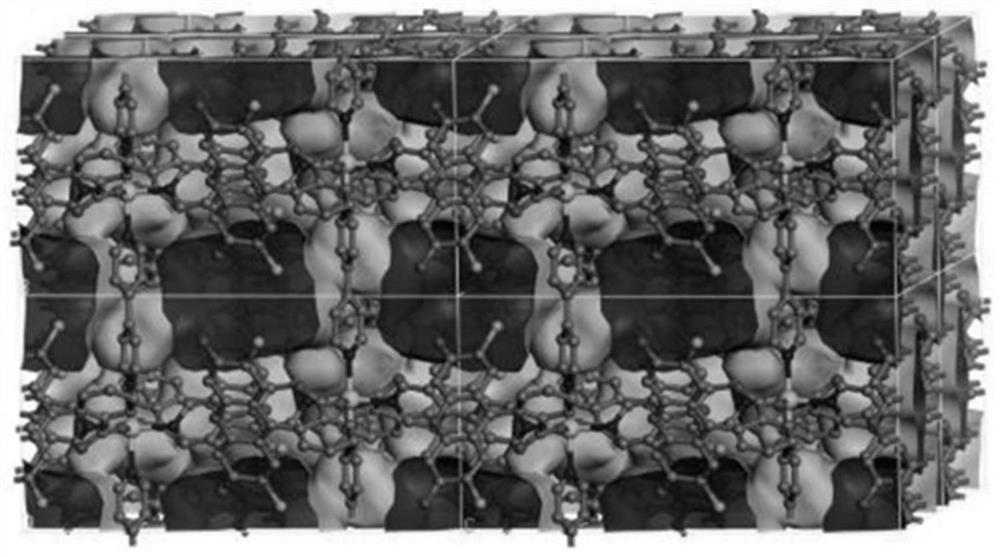
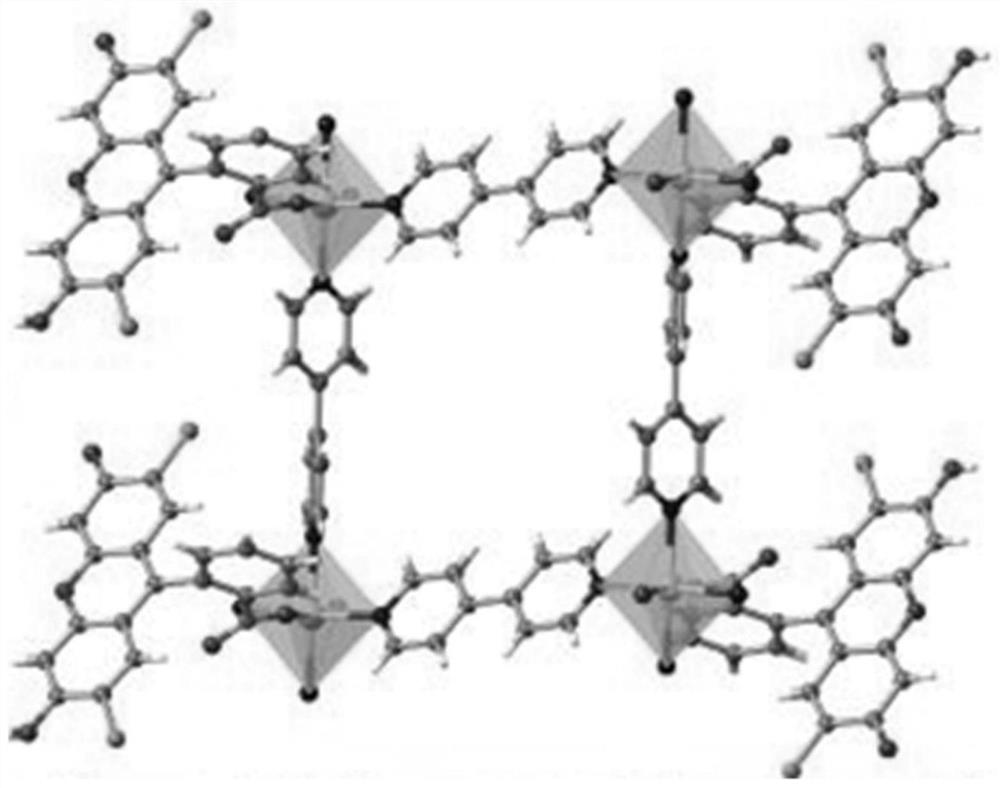
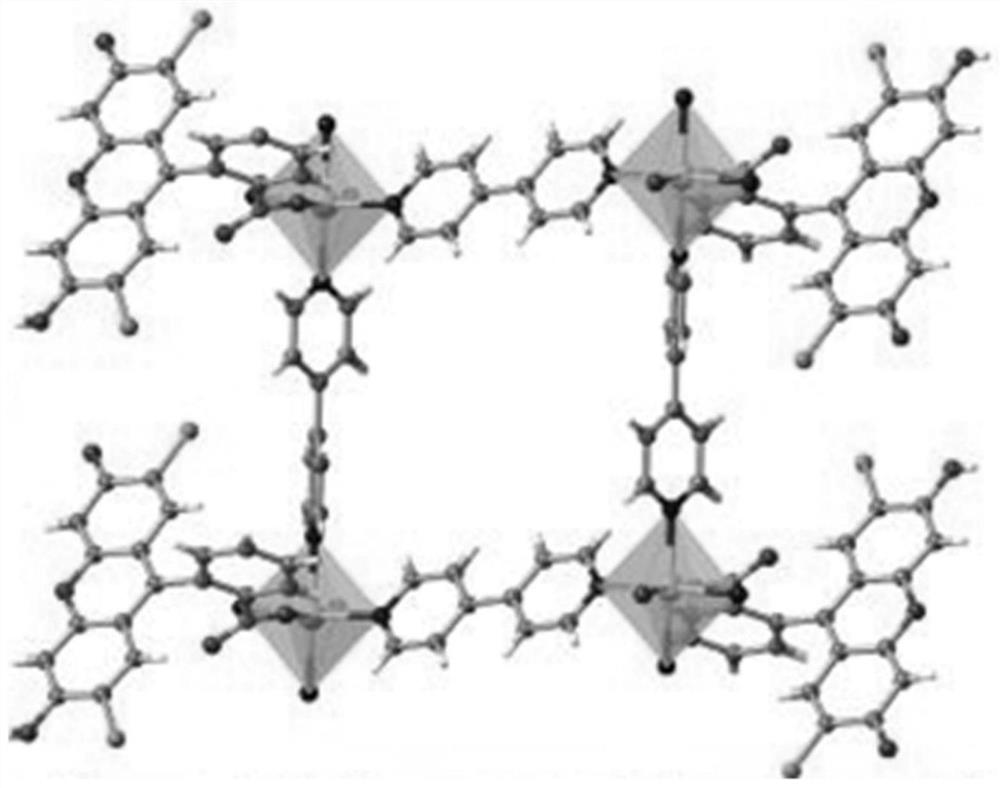
Visible light catalyzed styrene bifunctionalization reaction metal-organic framework material as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN111909221AIncrease profitImprove efficiencyOrganic chemistry methodsOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCrystal systemFluorescence
The invention discloses a visible light catalyzed styrene bifunctionalization reaction metal organic framework material as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The molecular formula of the material is C30H17Cl2N2O5.5Co0.5, the crystal system is monoclinic, the space group is C2 / c, and the cell parameters are as follows: alpha = 90.00 degrees, beta = 104.889 (2) degrees, gamma = 90.00 degrees and the number of molecules in cells is 8. The general chemical formula of the material is Co0.5(DCF)(bpy)(H2O)0.5, wherein the DCF is 2',7'-dichlorofluorescein, and the bpy is 4,4'-dipyridyl. The material provided by the invention has high-efficiency performance of catalyzing styrene bifunctionalization reaction to synthesize 1,3-oxa-thiacyclopentane-2-imino under the condition of visible light, and is simple in preparation process, high in catalytic efficiency, good in cycling stability and easy for large-scale preparation.
Owner:XUZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
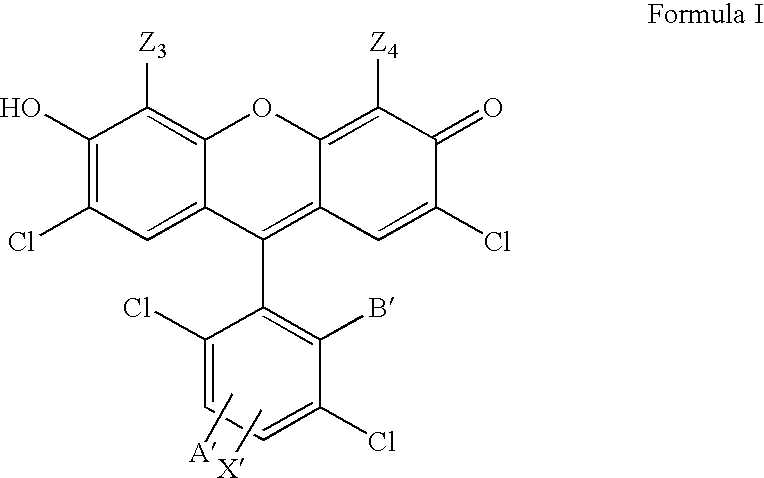
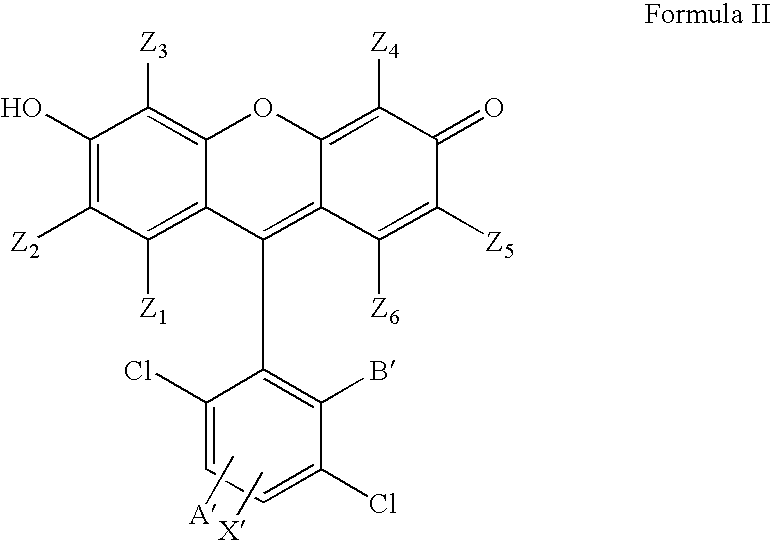
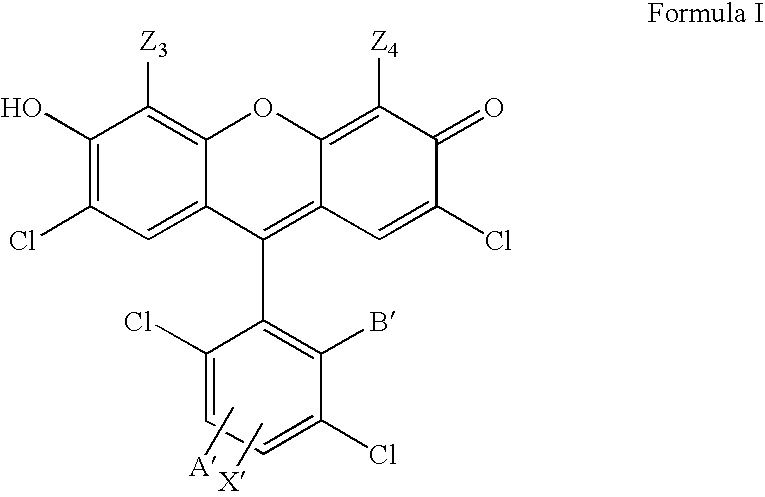
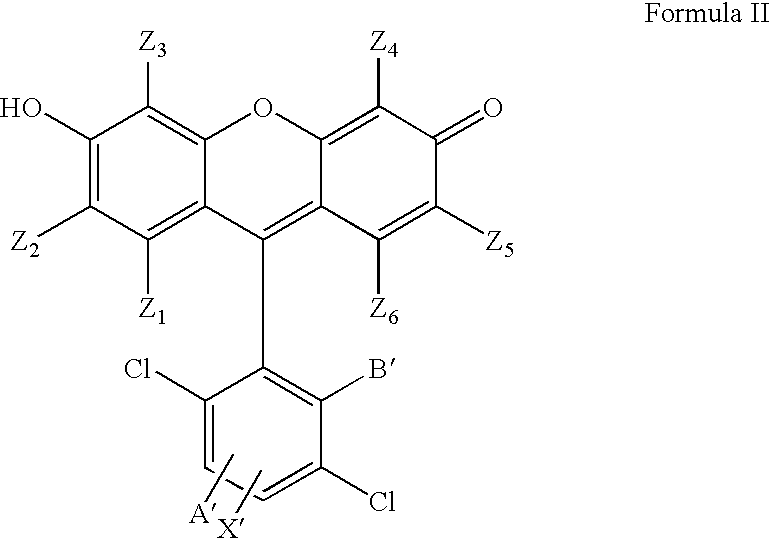
4,7-dichlorofluorescein dyes as molecular probes
InactiveUS20060063734A1Improve efficiencySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementFluoresceinDichlorofluorescein
Long wavelength, narrow emission bandwidth fluorecein dyes are provided for detecting spacially overlapping target substances. The dyes comprise 4,7-dichlorofluoresceins, and particularly 2′,4′,5′,7′-tetrachloro-4,7-dichloro-5- (and 6-)carboxyfluoresceins. Methods and kits for using the dyes in DNA analysis are provided.
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC
An antitumor medicine screening kit and a using method thereof
ActiveCN105738329AEnables high-throughput screeningEasy to operateFluorescence/phosphorescenceEscherichia coliNematode
The invention discloses an antitumor medicine screening kit and a using method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of biomedicine. The kit comprises caenorhabditis elegans, a nematode culture medium, escherichia coli and dye. An objective of screening effective antitumor medicines rapidly, efficiently and accurately with simple operation and a high throughout is achieved by utilizing different dyeing effects of the dye that is 2',7'-dichlorofluorescein diacetate on mutants and wild type caenorhabditis elegans, thus saving time and the cost for personnel researching and developing antitumor medicines.
Owner:甘肃药业集团科技创新研究院有限公司
Autonomic damage indication in coatings
ActiveUS20190144705A1Improve safety and sustainabilityGuaranteed uptimeEpoxy resin coatingsFluorescaminePolymer science
Autonomous detection of damage in a polymer coating is described by utilizing microcapsules in a polymer coating having free and / or residual amines. The microcapsules contain a color indicator, such as 2′,7′-dichlorofluorescein (DCF), bromophenol blue (BPB) or fluorescamine, which is reactive with the free and / or residual amines present in the polymer coating. For coatings without the presence of free and / or residual amines, a color indicator microcapsule can be combined with a second type of microcapsule filled with a base. When sufficient damage is inflicted to the coating, the microcapsules in and / or around an area of the damage will rupture, and the color indicator will react with the free and / or residual amines or the base to autonomically indicate the area in which the coating has been damaged.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
4,7-dichlorofluorescein dyes as molecular probes
InactiveUS20050084870A1Improve efficiencySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementFluoresceinDichlorofluorescein
Long wavelength, narrow emission bandwidth fluorescein dyes are provided for detecting specially overlapping target substances. The dyes comprise 4,7-dichlorofluorescein, and particularly 2′, 4′,5′,7′-tetrachloro-4,7-dichloro-5-(and 5-) carboxyfluoresceins. Methods and kits for using the dyes in DNA analysis are provided.
Owner:APPLERA
Polymer fluorescent probe and application thereof
ActiveCN111849464AHigh detection sensitivityFluorescence/phosphorescenceIn-vivo testing preparationsFluoProbesImide
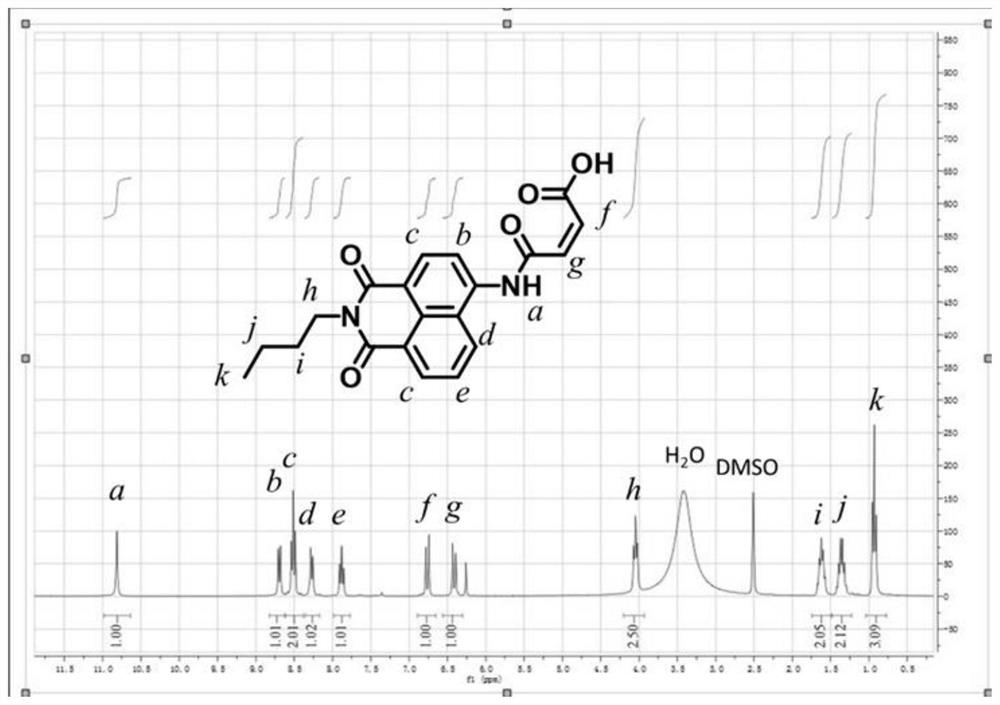
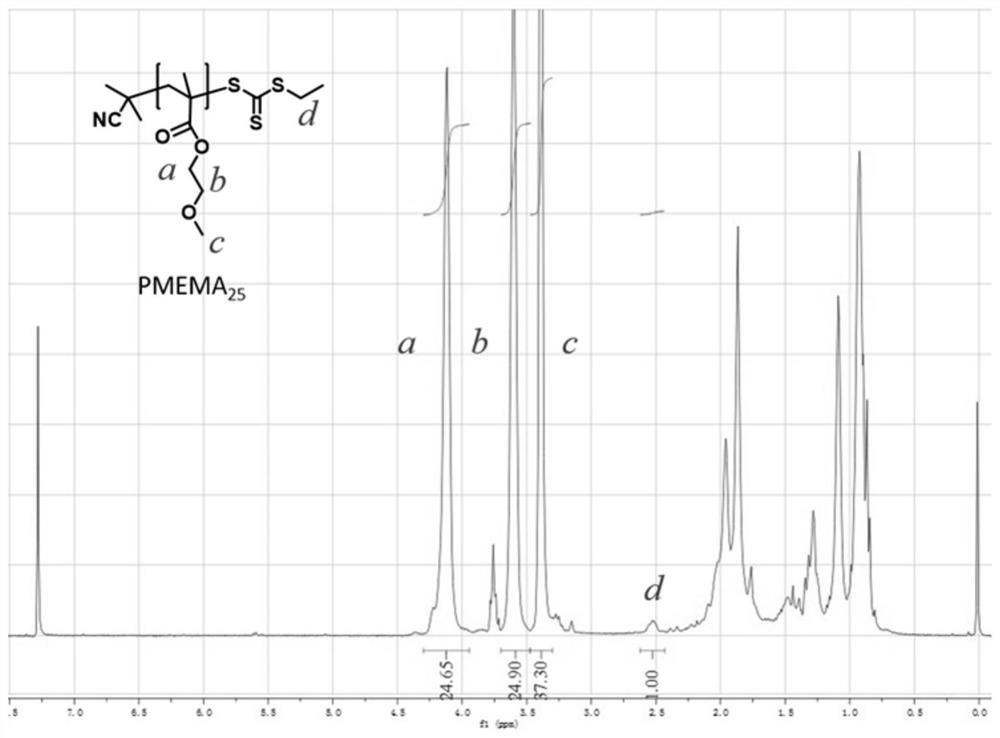
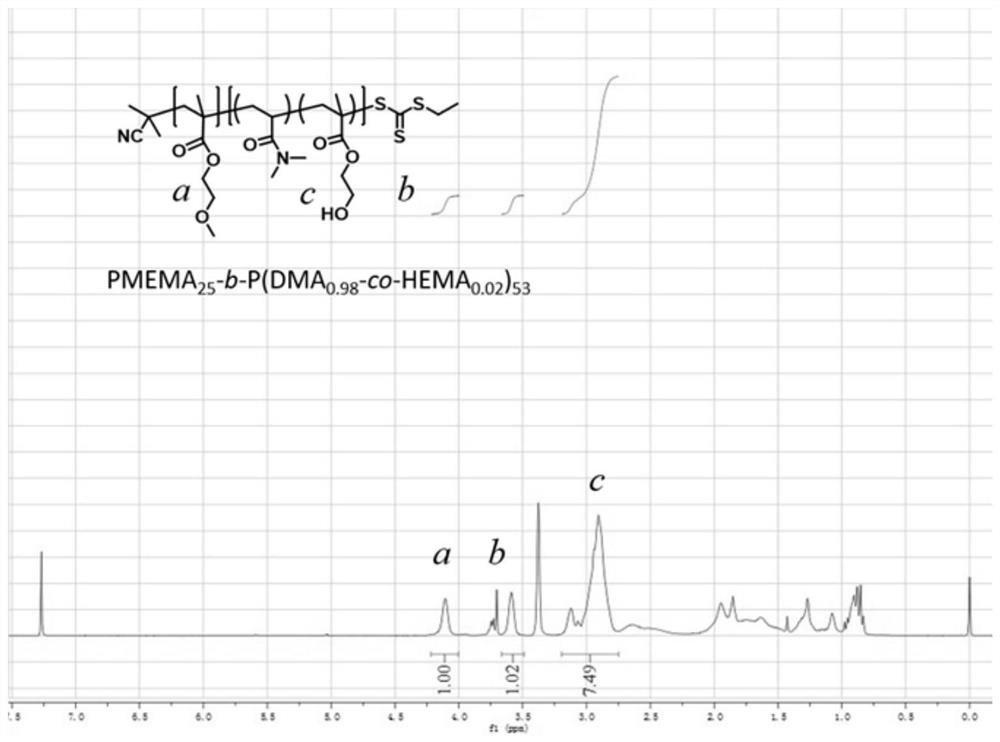
The invention provides a polymer-based fluorescent probe. The polymer-based fluorescent probe comprises an amphiphilic block copolymer and a sulfydryl responsive group and / or a dichlorofluorescein group grafted on the amphiphilic block copolymer. Compared with the prior art, the naphthalimides are taken as sulfydryl responsive fluorescent molecules, the naphthalimides have a relatively large rigidcoplanar structure and a conjugated system, a light-induced electron transfer mechanism exists in the structure, and when Michael addition occurs between the naphthalimides and sulfydryl, fluorescence is generated due to blocking of PET; thioether esterified dichlorofluorescein molecules are used as acid responsive fluorescent molecules, and ester bonds in the structures of the thioether esterified dichlorofluorescein molecules can be hydrolyzed by H<+> to endow the thioether esterified dichlorofluorescein molecules with conjugated structures, so that fluorescence is generated; in addition, the fluorescent molecules are grafted on the amphiphilic block copolymer to serve as a polymer-based fluorescent probe, and the polymer-based fluorescent probe has a high-sensitivity sulfydryl and / or acidity detection function, so that fluorescence tracking of a path of micelle entering a living body is realized.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Autonomic damage indication in coatings
ActiveUS10174221B2Improve safety and sustainabilityGuaranteed uptimeEpoxy resin coatingsFluorescaminePolymer science
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
2',7'-dichlorofluorescein and application of derivative thereof in protein detection
ActiveCN106289921AEasy to operateReduce stepsPreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansProtein detectionDichlorofluorescein
The invention relates to a protein negative staining detection technology, in particular to 2',7'-dichlorofluorescein and application of a derivative thereof in protein negative staining detection. The invention further provides a method for performing protein negative staining detection by applying the 2',7'-dichlorofluorescein. The method comprises the steps that direct dyeing is performed after protein gel electrophoresis is finished; then, developing is performed. The 2',7'-dichlorofluorescein has the advantages of being high in sensitivity, easy and rapid to operate, good in reproducibility, good in linear relation, good in mass spectrum compatibility, safe to use, low in cost and the like, an can be well applicable to research on high-throughput proteomics.
Owner:WENZHOU MEDICAL UNIV
Method for Determination of Active Oxygen Level in Phanerochaete chrysosporium After Treating Wastewater
InactiveCN103808703BSimplified representationAccurate representationPreparing sample for investigationFluorescence/phosphorescenceFiltrationDichlorofluorescein
The invention discloses a method for measuring the active oxygen level in phanerochaete chrysosporium in treated wastewater. The method comprises the following steps: washing a phanerochaete chrysosporium bacterium ball in the treated wastewater, adding a liquid culture medium for further culture, further adding 2',7'-dichloro dihydro fluorescein sodium diacetate into the liquid culture medium after culture to obtain a mixture solution, carrying out incubation on the mixture solution, filtering, then performing ultrasonic crushing and centrifuging on the bacterium ball obtained through filtration, extracting a supernate, and finally measuring the fluorescence intensity of the oxidized dichlorofluorescein in the supernate. The method has the advantages that the operation condition is simple, the application is easy and the active oxygen level in the phanerochaete chrysosporium in the treated wastewater can be accurately and visibly measured.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Hydrogenated dichlorofluorescein diacetamide derivative as well as preparation method and application thereof
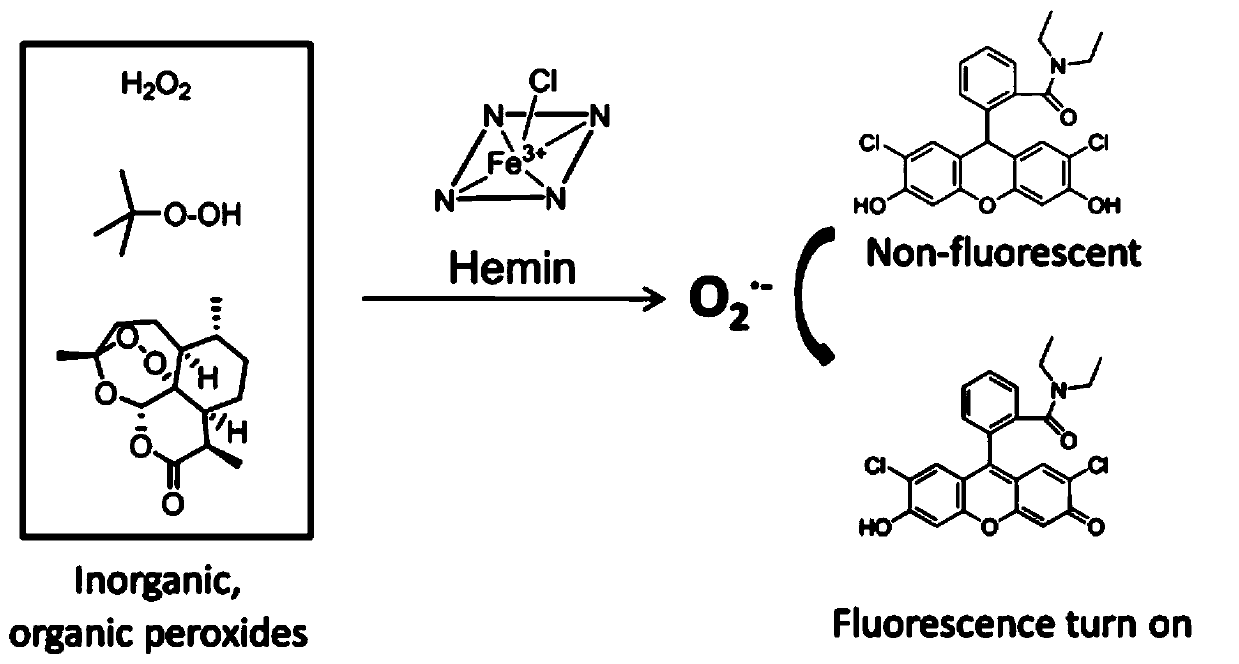
PendingCN111004200AEasy to detectGood effectOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescenceDichlorofluorescein
The invention relates to a hydrogenated dichlorofluorescein diacetamide derivative as well as a preparation method and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of heme detection. The hydrogenated dichlorofluorescein diacetamide derivative disclosed by the invention can be used as a fluorescence reporter molecule for heme detection, and the detection method disclosed by the inventioncan be used for conveniently and quickly detecting heme; according to the invention, three peroxides H2O2, TBHP and ART are respectively mixed with DCFHA to prepare a detection reagent; the three systems can be used for rapid detection of heme, the detection limit can reach the picomole level, the DCFHA / H2O2 detection method can successfully distinguish bloodstains and coffee stains, and fluorescence can be seen with naked eyes under ultraviolet light; the DCFHA / ART is doped into the filter paper to prepare the detection test paper, and the detection test paper has good effects in heme detection and blood determination, can be used as a portable device, and is used in criminal investigation and other practical applications.
Owner:GUANGZHOU UNIVERSITY OF CHINESE MEDICINE
A kind of polymer fluorescent probe and its application
ActiveCN111849464BLarge structureIncreased sensitivityFluorescence/phosphorescenceIn-vivo testing preparationsFluoProbesPhotoinduced electron transfer
The invention provides a polymer-based fluorescent probe, which comprises an amphiphilic block copolymer and a thiol-responsive group and / or a dichlorofluorescein group grafted on the amphiphilic block copolymer. Compared with the prior art, the present invention uses naphthalimides as sulfhydryl-responsive fluorescent molecules, which have a relatively large rigid coplanar structure and a conjugated system. There is a photoinduced electron transfer mechanism in this structure. When naphthalimides After Michael addition with sulfhydryl groups, fluorescence is produced due to the obstruction of PET; thioether-esterified dichlorofluorescein molecules are used as acid-responsive fluorescent molecules, which can be induced by H + The ester bond in its structure is hydrolyzed to make it have a conjugated structure, thereby generating fluorescence; and the present invention grafts the above-mentioned fluorescent molecules on the amphiphilic block copolymer as a polymer-based fluorescent probe with a highly sensitive mercapto group And / or the detection function of acidity, so as to realize the fluorescent tracking of the path of micelles entering the living body.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Method for screening for compound capable of enhancing or inhibiting OATP1B1 transport activity, and method for determining expression level of OATP1B1
ActiveCN103597090ACutting costsMeasure securityCompound screeningApoptosis detectionDichlorofluoresceinBiology
The present invention provides a method of screening for a compound that enhances or inhibits the transport activity of OATP1B1, using dichlorofluorescein. The present invention also provides a use of dichlorofluorescein in measurement of the expression level of OATP1B1. The present invention further provides a method for measuring the expression level of OATP1B1 in test cells, using dichlorofluorescein. The present invention further provides a use of a kit including dichlorofluorescein and positive cells expressing OATP1B1 in measurement of the expression level of OATP1B1 in test cells.
Owner:EISIA R&D MANAGEMENT CO LTD
Reagent, device and method for rapidly counting eukaryotic microorganisms
PendingCN114134198ASimple compositionGuaranteed accuracyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCarboxyl radicalFluorescence
The invention discloses a reagent, a device and a method for rapidly counting eukaryotic microorganisms. The reagent comprises an osmotic buffer solution, a fluorescent staining solution and a reconstitution fluid, wherein the osmotic buffer solution is prepared from the following components: epsilon-polylysine, dodecyl-beta-D-maltoside and glycine; a staining component in the fluorescent staining solution is selected from fluorescein diacetate, 5 (6)-carboxyl-2 ', 5'-dihydroxyl-2 ', 5'-dihydroxyl-2 ', 5'- the fluorescein diacetate is one or more of 5, 7 '-dichlorofluorescein diacetate, 5-chloromethyl fluorescein diacetate, 5 (6)-carboxyl fluorescein diacetate, 6-carboxyl fluorescein diacetate, 5-carboxyl fluorescein diacetate, 5-nitryl-fluorescein diacetate and 6-nitryl-fluorescein diacetate. According to the reagent disclosed by the invention, a broad-spectrum bacteriostatic agent epsilon-polylysine is used as a carrier to transport a fluorescent staining solution to penetrate through cell walls and enter bacterial cell plasm, fluorescence is generated through excitation of exciting light, bacterial colonies are identified and counted, and a culture medium capable of accelerating the growth rate of thalli is used in a matched manner, so that the microbial detection efficiency is greatly improved.
Owner:ACAD OF NAT FOOD & STRATEGIC RESERVES ADMINISTRATION
Antitumor drug screening kit and use method thereof
ActiveCN105738329BEnables high-throughput screeningEasy to operateFluorescence/phosphorescenceEscherichia coliNematode
The invention discloses an antitumor medicine screening kit and a using method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of biomedicine. The kit comprises caenorhabditis elegans, a nematode culture medium, escherichia coli and dye. An objective of screening effective antitumor medicines rapidly, efficiently and accurately with simple operation and a high throughout is achieved by utilizing different dyeing effects of the dye that is 2',7'-dichlorofluorescein diacetate on mutants and wild type caenorhabditis elegans, thus saving time and the cost for personnel researching and developing antitumor medicines.
Owner:甘肃药业集团科技创新研究院有限公司
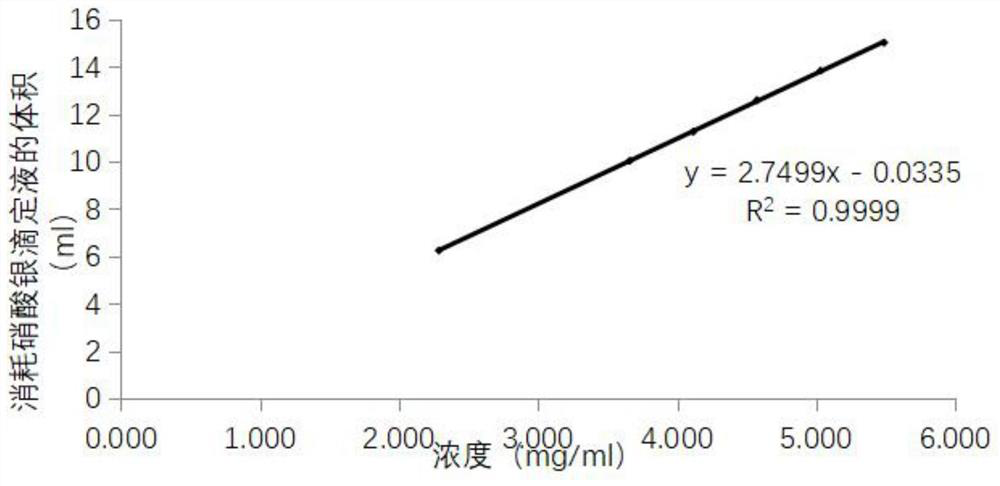
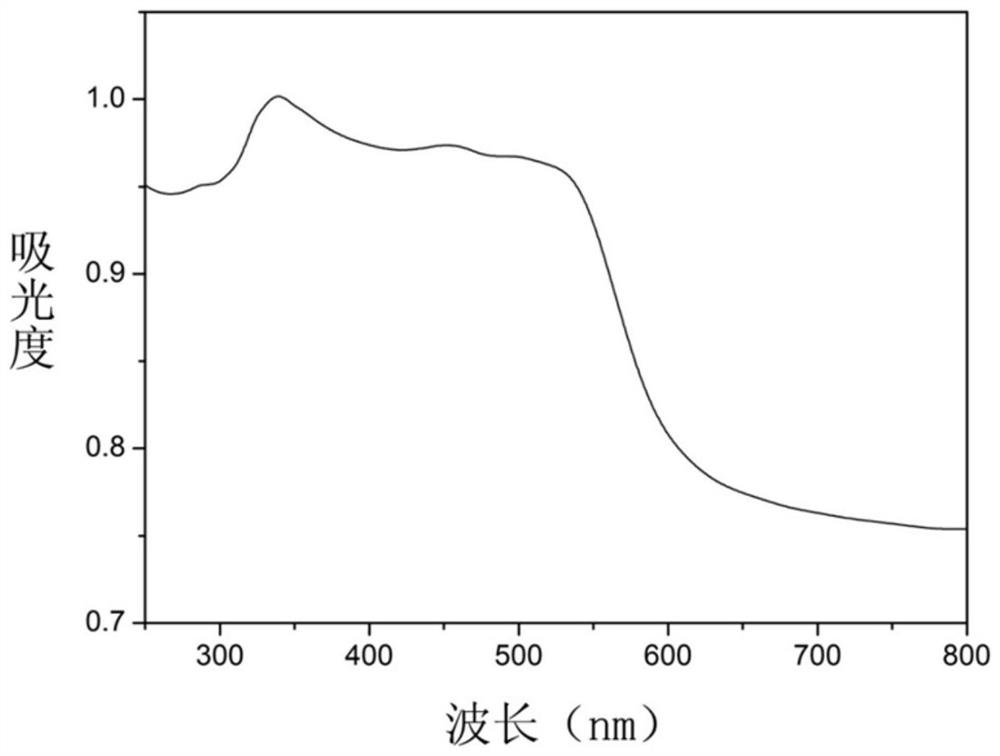
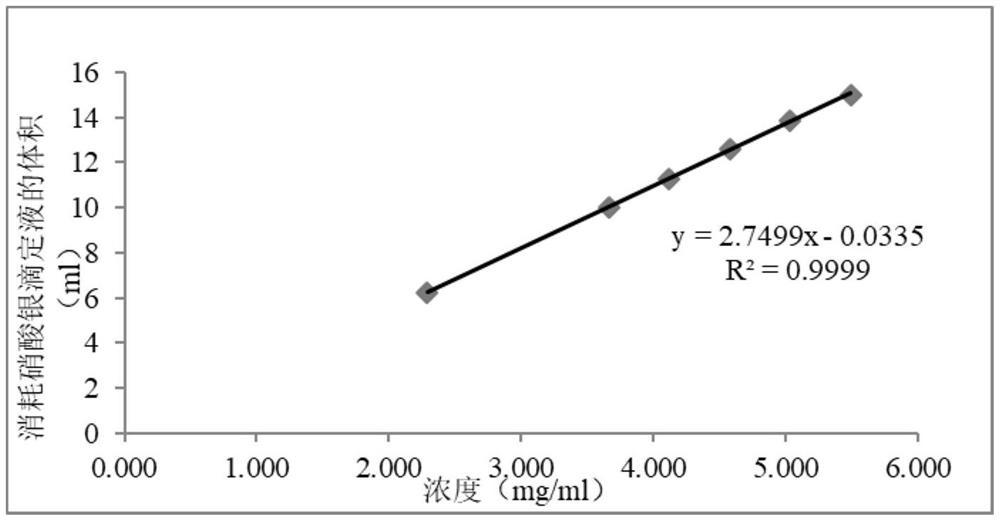
Method for determining total chlorine content in compound preparation containing sodium citrate
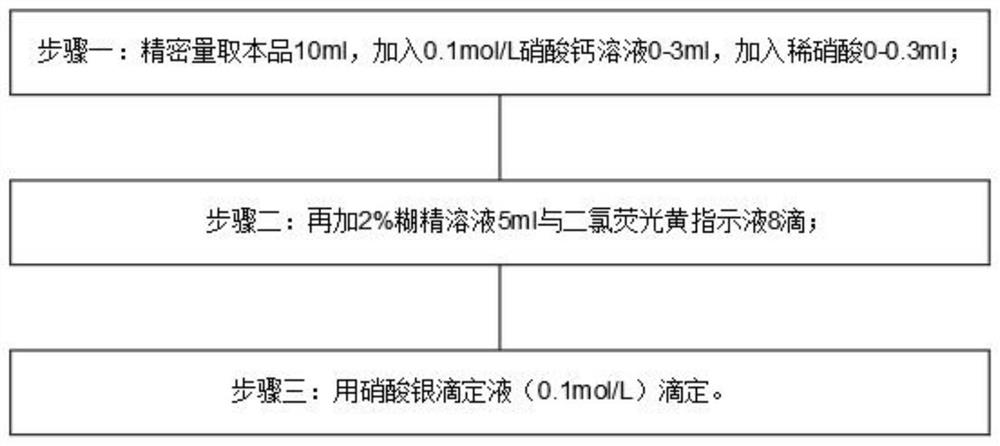
InactiveCN113514604AEliminate the effects ofGuaranteed accuracyChemical analysis using titrationPhysical chemistryDichlorofluorescein
The invention discloses a method for measuring the total chlorine content in a compound preparation containing sodium citrate, which comprises the following steps: 1, precisely measuring 10ml of the compound preparation, adding 0-3ml of 0.1 mol / L calcium nitrate solution, and adding 0-0.3 ml of dilute nitric acid; 2, adding 5ml of 2% dextrin solution and 8 drops of dichlorofluorescein indicating liquid; 3, titrating with a silver nitrate titration solution (0.1 mol / L); as a preferable technical scheme of the invention, each 1ml of silver nitrate titration solution (0.1 mol / L) is equivalent to 3.545 mg of chlorine; the method has the beneficial effects that 10 ml of the compound preparation is precisely measured, 5 ml of a 2% dextrin solution and 8 drops of the dichlorofluorescein indicator solution are added, titration is performed by using the silver nitrate titration solution (0.1 mol / L), and on the basis that 1 ml of the silver nitrate titration solution (0.1 mol / L) is equivalent to 3.545 mg of chlorine], 1 ml of the 0.1 mol / L calcium nitrate solution and 0.1 ml of dilute nitric acid are added, so that the influence of sodium citrate in the compound preparation containing sodium citrate on the total chlorine content determination can be eliminated, therefore, the accuracy of total chlorine content determination is ensured.
Owner:西安乐析医疗科技有限公司
Wheat tissue active oxygen fluorescence labeling method
InactiveCN102589942BInhibitory activityDetection sciencePreparing sample for investigationFluorescenceDichlorofluorescein
Owner:CROP RES INST SHANDONG ACAD OF AGRI SCI
A metal-organic framework material for visible light-catalyzed bifunctionalization of styrene and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN111909221BIncrease profitImprove efficiencyOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsOrganic chemistry methodsCrystal systemFluorescence
The invention discloses a metal-organic framework material for the difunctionalization reaction of styrene catalyzed by visible light, its preparation method and application. The molecular formula of the material is C 30 h 17 Cl 2 N 2 o 5.5 co 0.5 , the crystal system is monoclinic, the space group is C2 / c, and the unit cell parameters are: α=90.00°, β=104.889(2)°, γ=90.00°, and the number of molecules in the unit cell is 8; the material The general chemical formula is Co 0.5 (DCF)(bpy)(H 2 O) 0.5 , wherein, DCF is 2',7'-dichlorofluorescein, and bpy is 4,4'-bipyridine. The material provided by the invention has the high-efficiency performance of catalyzing the difunctionalization reaction of styrene under visible light conditions to synthesize 1,3-oxathiolane-2-imino. The preparation process of the invention is simple, the catalytic efficiency is high, and the cycle Good stability and easy large-scale preparation.
Owner:XUZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
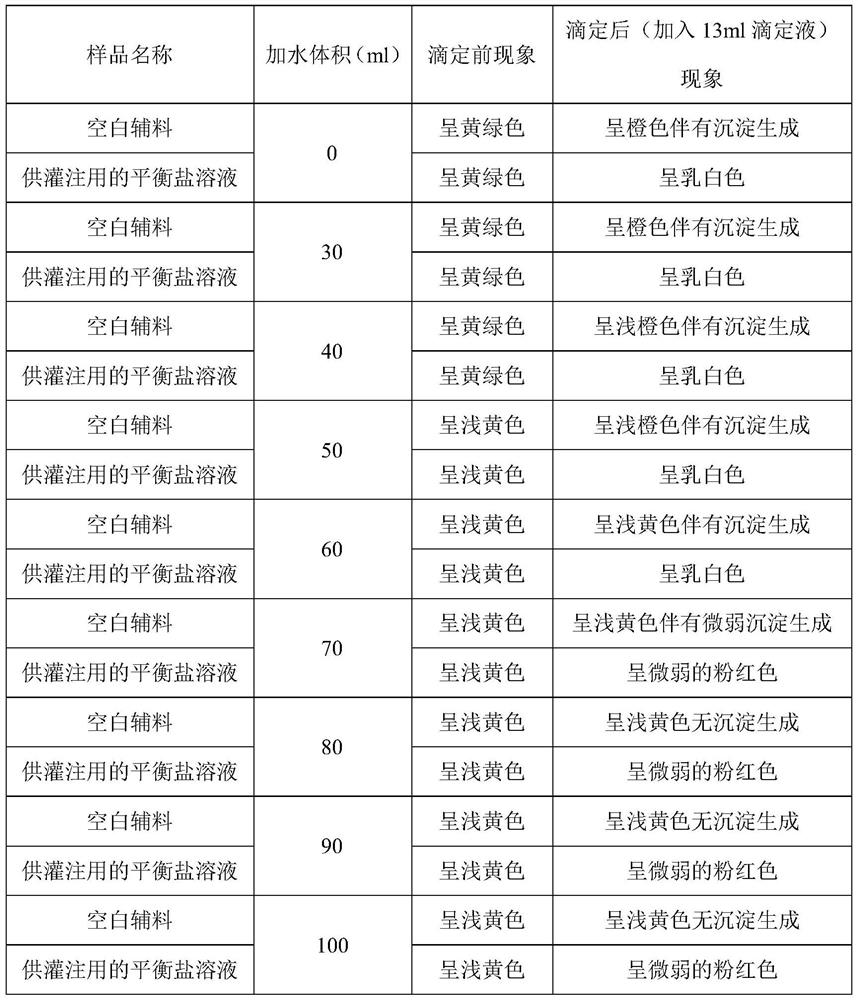
Method for determining total chlorine content in balanced salt solution for perfusion
PendingCN113533632AMeet the requirements of total chlorine content determinationAccurate quality controlMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorChemical analysis using titrationPharmaceutical industryDichlorofluorescein
Owner:西安乐析医疗科技有限公司
Antioxidant drug screening kit
ActiveCN106950202BImprove filtering effectEasy to useFluorescence/phosphorescenceEscherichia coliDichlorofluorescein
The invention belongs to the technical field of biomedicine, and in particular relates to an antioxidant drug screening kit and a use method thereof. The antioxidant drug screening kit provided by the present invention includes Caenorhabditis elegans, nematode culture medium, Escherichia coli OP50, 2', 7' dichlorofluorescein ethylene glycol, and can be used for high-throughput screening of antioxidant drugs. The invention is easy to operate and fast in detection, and is suitable for large-scale popularization in the field of screening antioxidant drugs.
Owner:甘肃药业集团科技创新研究院有限公司
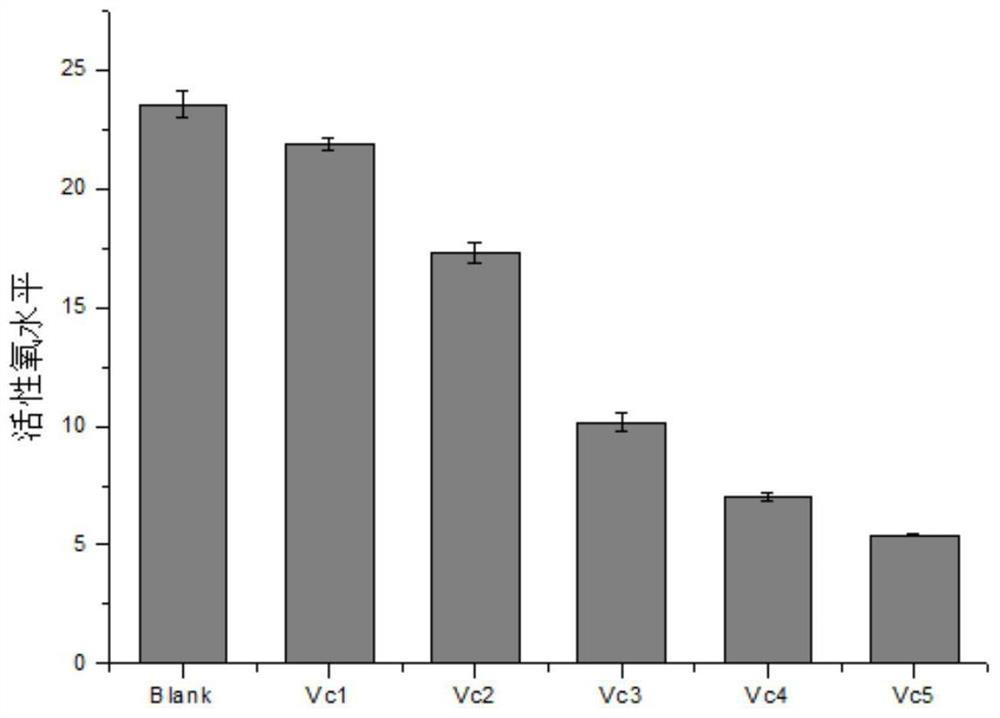
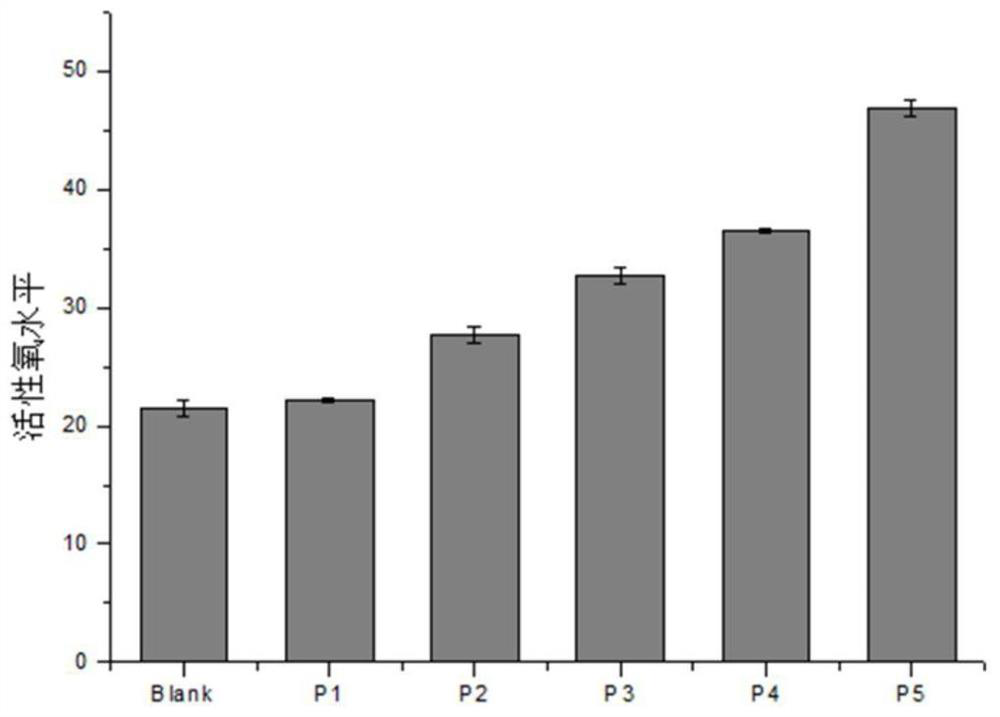
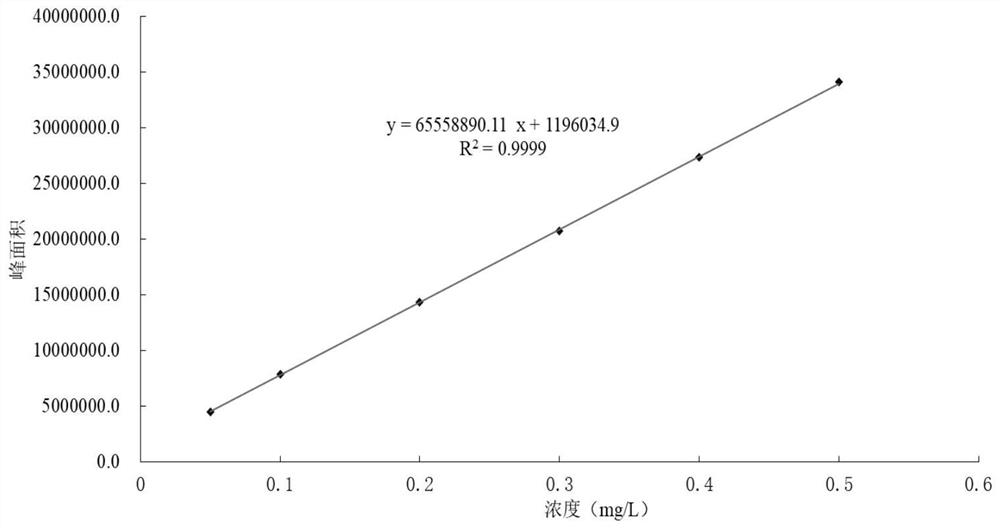
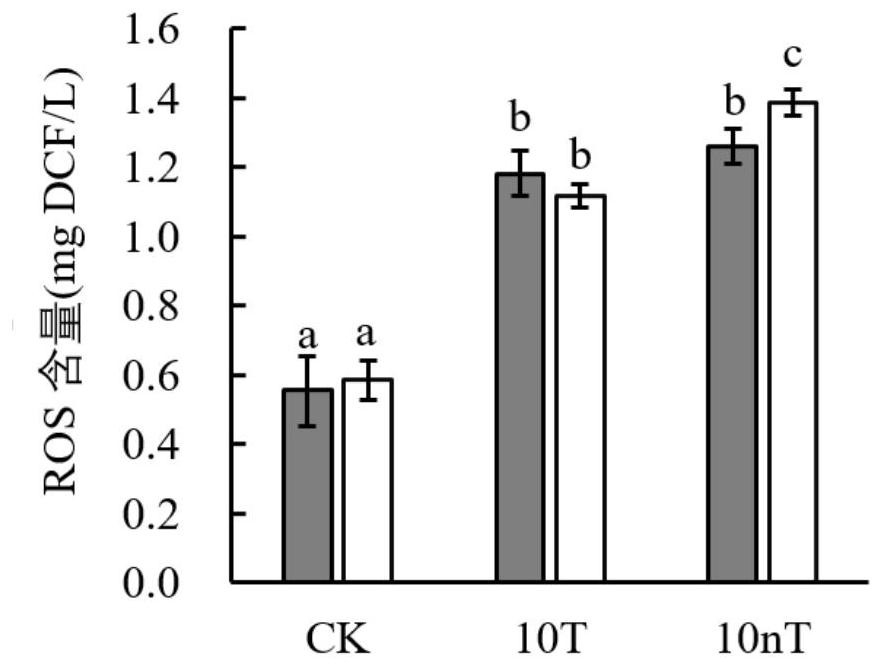
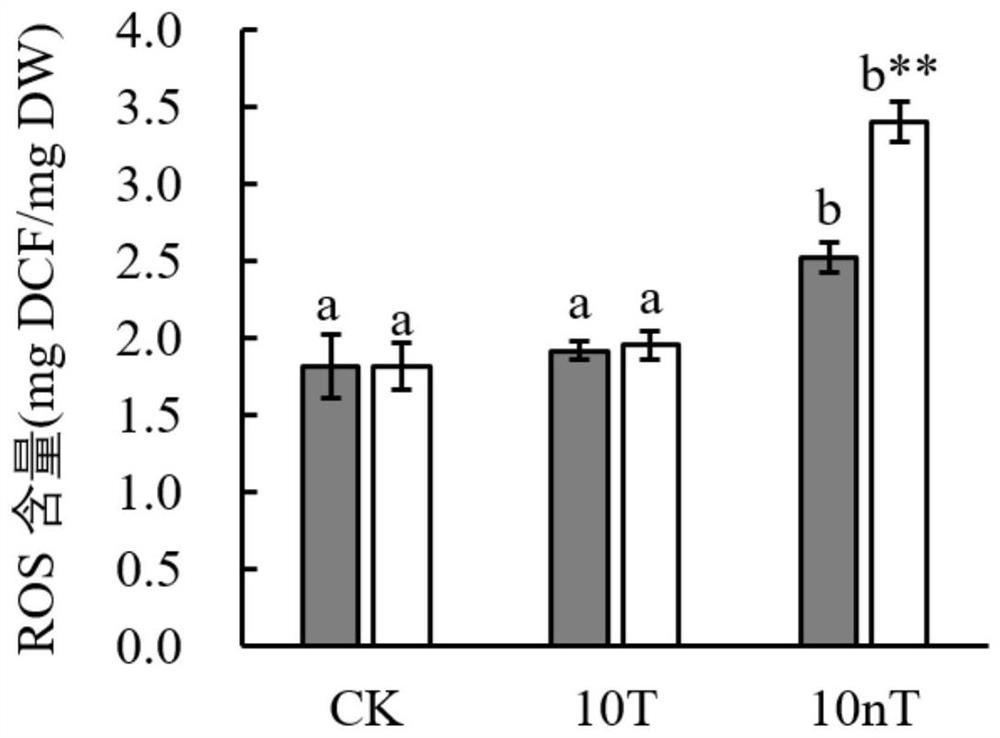
Method for Quantitative Determination of In Vitro/In Vitro Superoxide Radical Content Generated by Environmental Stress
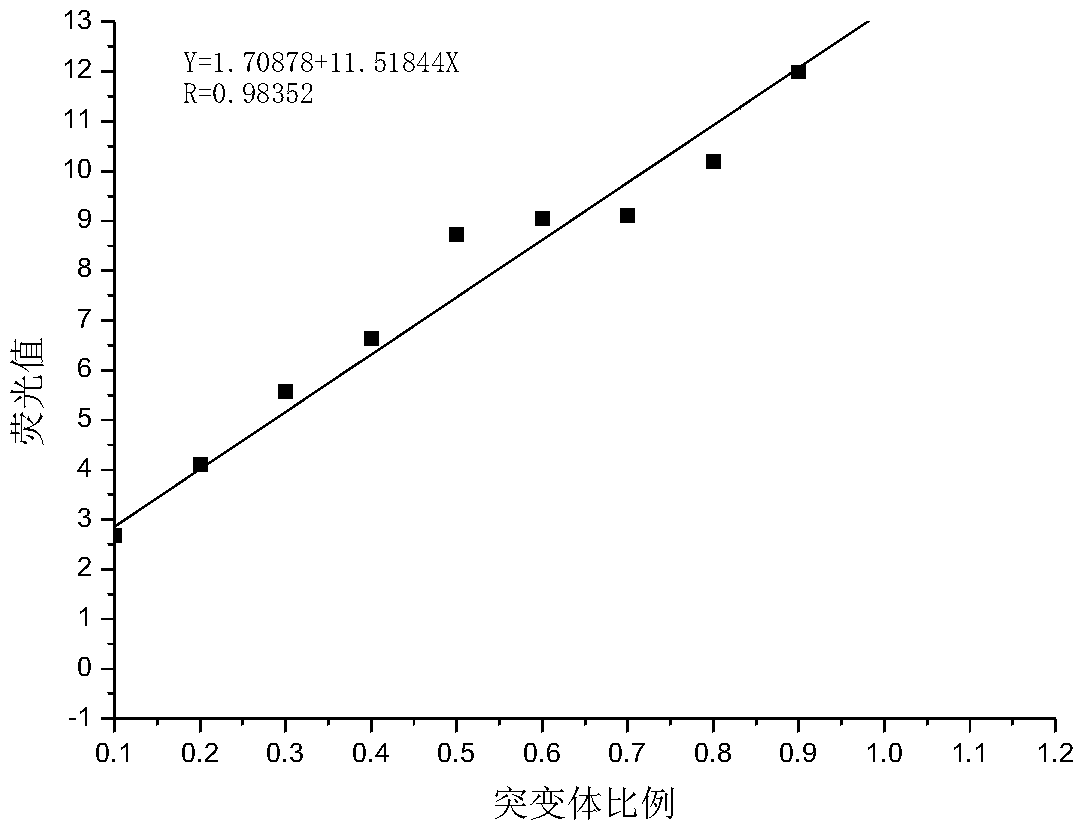
ActiveCN114200065BReduce distractionsComparableComponent separationQuantitative determinationDichlorofluorescein
The invention provides a method for quantitatively measuring the content of superoxide radicals in vivo / external generated by environmental stress, which comprises the following steps: step S1, preparing a test solution: taking a sample to be tested, and preparing a test solution; Step S2, prepare a reference substance solution: take the standard substance 2,7-dichlorofluorescein, dissolve it in water, and prepare a reference substance solution; Step S3, use a high performance liquid chromatograph-fluorescence detector to analyze the test solution and the reference substance solution. In step S4, take the peak area of the reference solution as the ordinate and the concentration of the reference solution as the abscissa, draw a standard curve, and calculate the 2,7-dichlorofluorescein in the test solution according to the standard curve the content of superoxide radicals. By adopting the technical scheme of the present invention, ROS can be quantitatively measured, the interference of external environmental factors is reduced, the comparability between different batches is made, and the method is simple and reliable.
Owner:维塔探索(广东)科技有限公司
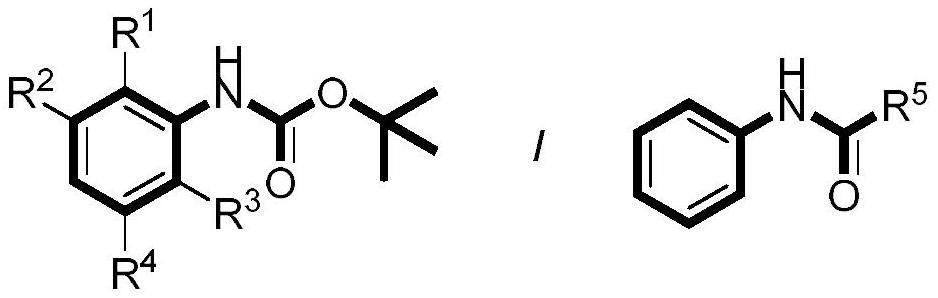
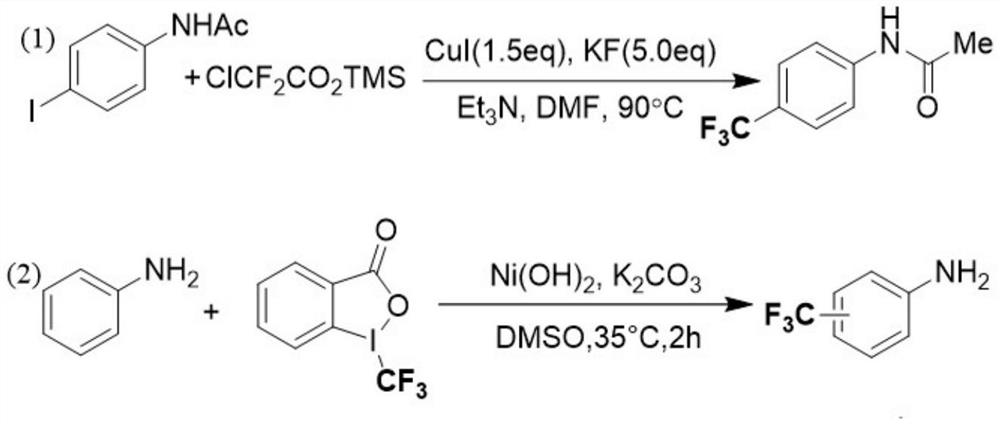
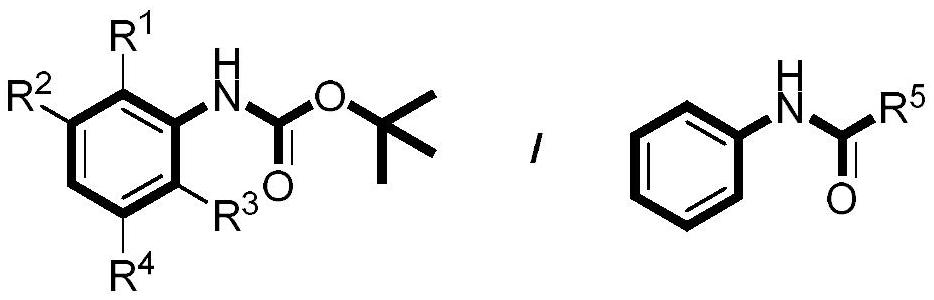
Preparation method of aniline para-trifluoromethylated derivative
ActiveCN113214113ARaw materials are easy to getRich varietyCarbamic acid derivatives preparationCarboxylic acid nitrile preparationPotassium persulfateFluorescence
The invention discloses a preparation method of an aniline para-trifluoromethylated derivative. The method comprises the following steps: sequentially adding an aniline derivative, 4, 5-dichlorofluorescein, potassium persulfate and sodium trifluoromethanesulfinate into a glass reaction tube, and reacting at room temperature (23-25 DEG C) under 40W blue LED (light-emitting diode) by taking dimethyl sulfoxide as a solvent to obtain the aniline para-trifluoromethylated derivative. According to the invention, the aniline derivative is used as an initiator, and the raw materials are easily available and various; products obtained by the method disclosed by the invention have various types and can be directly applied to modification of drug molecules; and meanwhile, the synthesis route is safe and easy to implement, the cost is low, the reaction operation and post-treatment process are simple, the selectivity is good, the side reaction is few, and the amplification reaction can be carried out.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com