A kind of polymer fluorescent probe and its application
A fluorescent probe and polymer technology, applied in the field of fluorescent probes, can solve the problems of easy shedding, application limitations, and difficulty in achieving long-term tracking of organisms.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
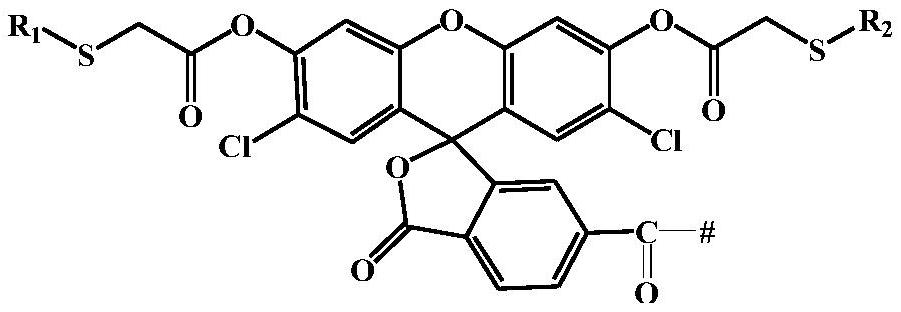
[0059] The present invention also provides a preparation method for the above-mentioned polymer-based fluorescent probe, comprising: carrying out a copolymerization reaction of a hydrophobic monomer and a hydrophilic monomer to obtain an amphiphilic block copolymer; Reacting with the thiol-responsive monomer represented by formula (I) and / or the dichlorofluorescein monomer represented by formula (II) to obtain a polymer-based fluorescent probe;
[0060]
[0061] Wherein, R is the alkyl group of C1~C10; R 1 with R 2 Each independently is an alkyl group of C1~C5; said R, R 1 with R 2 All are the same as above, and will not be repeated here;
[0062] The hydrophobic monomer is preferably one or more of alkoxy acrylate, alkoxy methacrylate, hydroxyalkyl acrylate and hydroxyalkyl methacrylate; the alkoxy acrylate, The number of carbon atoms in the alkyl group in the alkoxy methacrylate, hydroxyalkyl acrylate and hydroxyalkyl methacrylate is independently preferably 1-10, mor...
preparation example 1
[0072] Preparation Example 1: Preparation method of dichlorofluorescein molecule (DSF-COOH) protected with (ethylthio)acetic acid
[0073]
[0074] Weigh mercaptoacetic acid (5g, 54.4mmol), then add bromoethane (6.45g, 59.8mmol) in batches to sodium hydroxide (3mol / L) in methanol solution (100mL), reflux the mixture for 8h, after cooling Spin to dry to obtain ethylthioacetic acid (5.9g, yield: 90%); Oxalyl chloride (6.8g, 53.9mmol) was added to ethylthioacetic acid (5.9g, 49.2mmol) at 0°C under stirring In dichloromethane solution (100 mL), the reaction mixture was heated to 40° C. until no more hydrogen chloride was evolved (approximately two hours). After the reaction was finished, dichloromethane was removed by rotary evaporation under vacuum conditions to obtain ethylthioacetyl chloride (6.5g, 46.7mmol, yield: 95%); then ethylthioacetyl chloride (6.5g, 46.7mmol) and 5-carboxy-2',7'-dichlorofluorescein (9.4g, 21.2mmol) were dissolved in anhydrous N,N-dimethylformamide (...
preparation example 2
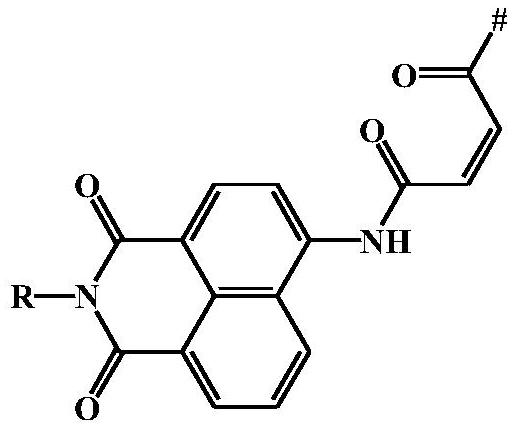
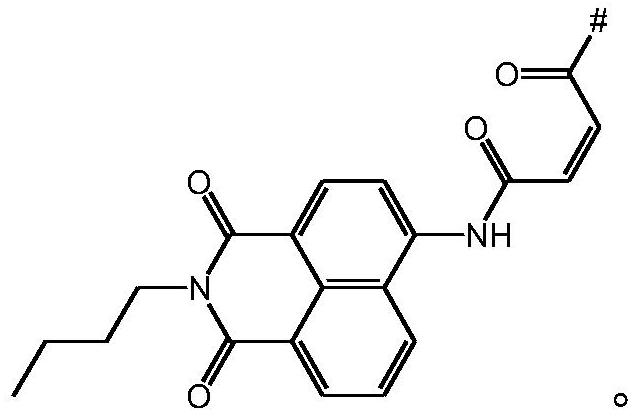
[0075] Preparation Example 2: Preparation of NAM-COOH by Amidation Reaction of Aminonaphthalene Diimide and Maleic Anhydride
[0076]
[0077] 4-Amino-N-butylnaphthalene diimide (5g, 18.6mmol) and maleic anhydride (2.8g, 28.0mmol) were dissolved in chloroform (80mL), refluxed for 12h, cooled to room temperature after the reaction, and After the solvent was removed by rotary evaporation under vacuum conditions, column chromatography separation was carried out with pure ethyl acetate as eluent to obtain the fluorescent moiety 4-maleimido-1,8-naphthoimide NAM- COOH (6.7 g, yield: 80%).
[0078] The 4-maleimido-1,8-naphthalimide NAM-COOH obtained in Preparation Example 2 is analyzed by nuclear magnetic resonance, and its hydrogen nuclear magnetic resonance spectrum is obtained as figure 1 shown.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com