High temperature resistant valve-controlled lead-acid storage battery and manufacturing method of positive plate
The technology of a lead-acid battery and its manufacturing method is applied in the direction of lead-acid battery electrodes, lead-acid batteries, lead-acid battery construction, etc., which can solve the problems of easy deformation of the battery, short service life, poor heat dissipation performance of the shell, and improve the heat dissipation effect , improve the service life, the effect of fast heat dissipation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0045] S100. Preparation of lead paste: specifically include: automatically add 400 to 500 parts of lead powder and the corresponding proportion of red lead, colloidal graphite, short fiber, 4BS crystal seeds, stannous sulfate and three layers in the paste machine while stirring Graphite, and then add the remaining lead powder, and the time of adding and stirring is 10 minutes; then quickly add water to mix, and clean the plaster adhered to the surface of the stirring rod and the wall of the pot, add water and mix for about 5 minutes, and then pour acid , acid leaching time is 8 to 14 minutes, continue to stir, and control the temperature of the high temperature section to be 80 to 85 ° C, the high temperature duration is 11 to 15 minutes, continue to stir after the high temperature, the acid leaching and stirring time is 25 minutes, and then adjust the visual Specific gravity, continue to stir for 10 minutes to produce paste, the whole process is about 50 minutes, and the past...
Embodiment 1
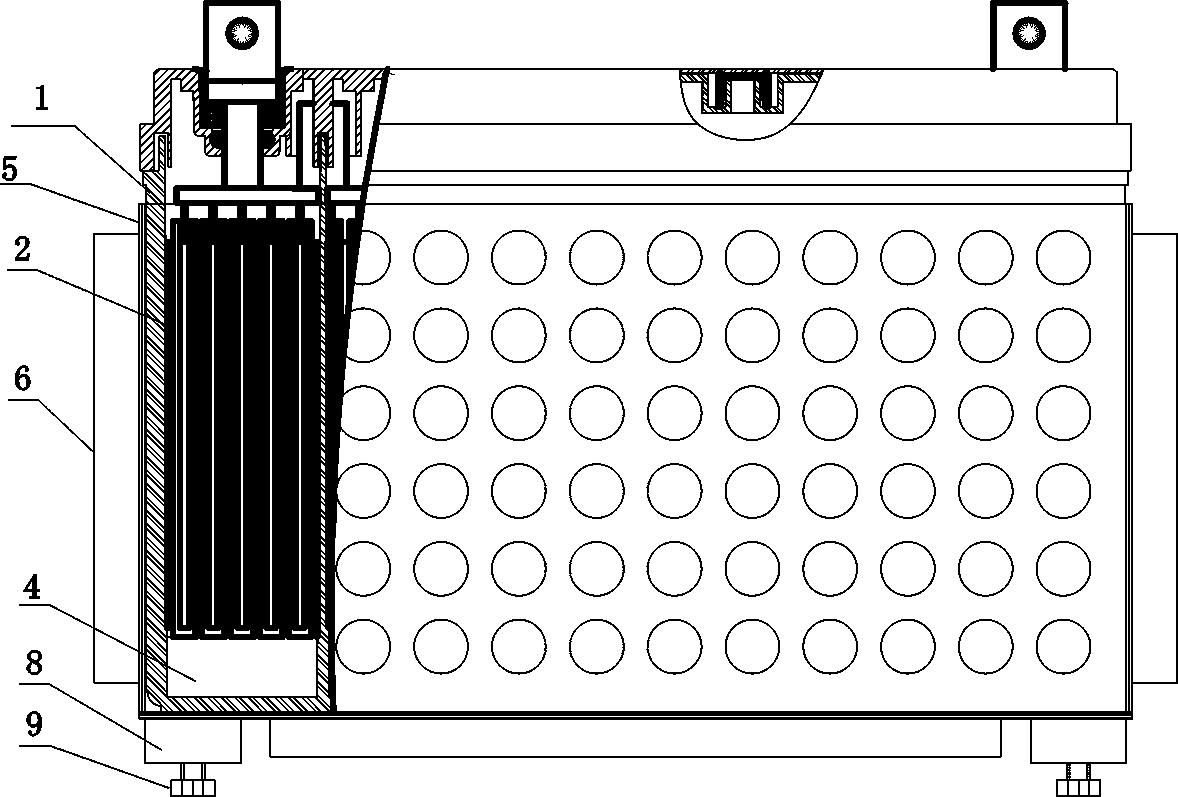
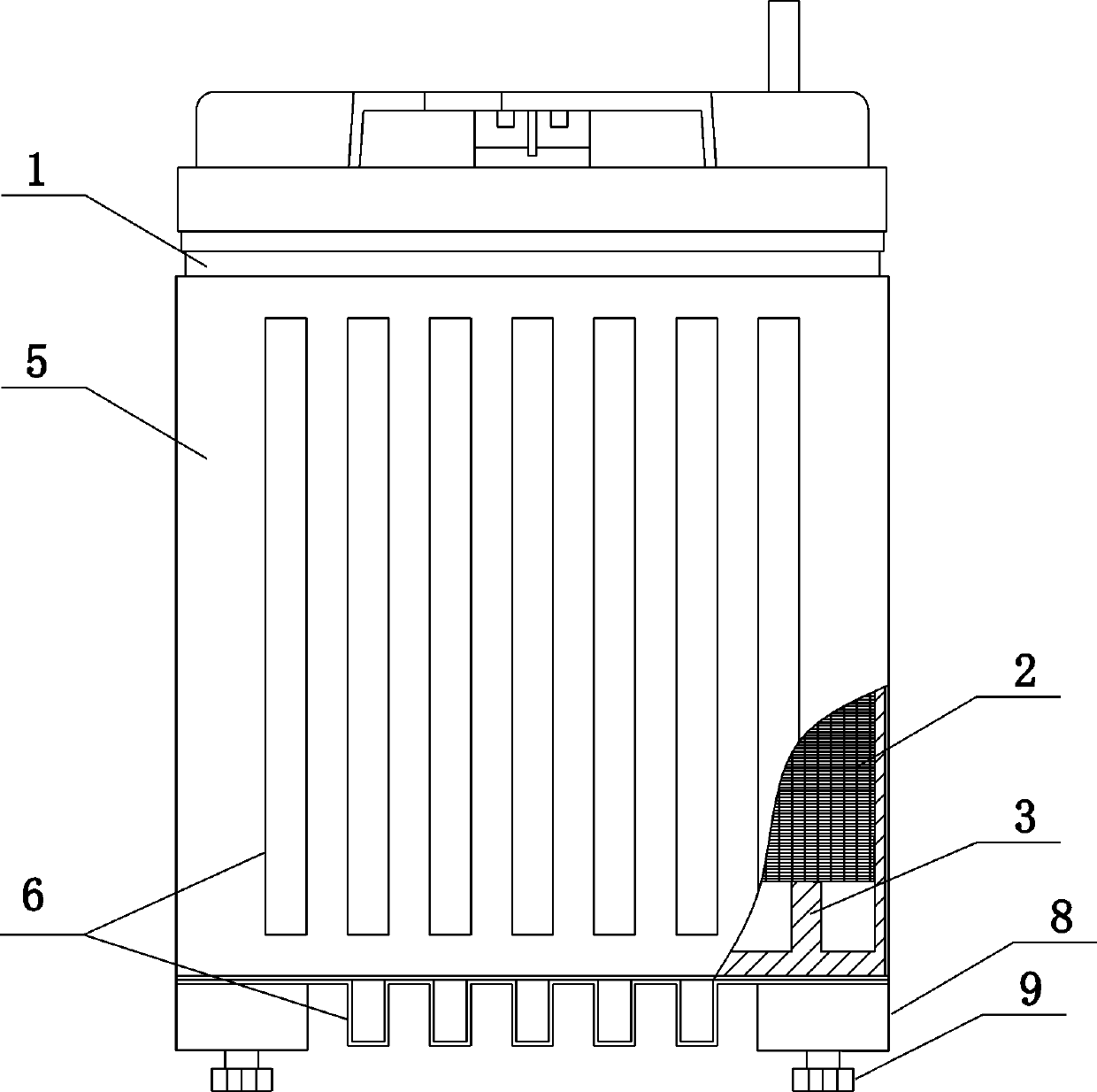
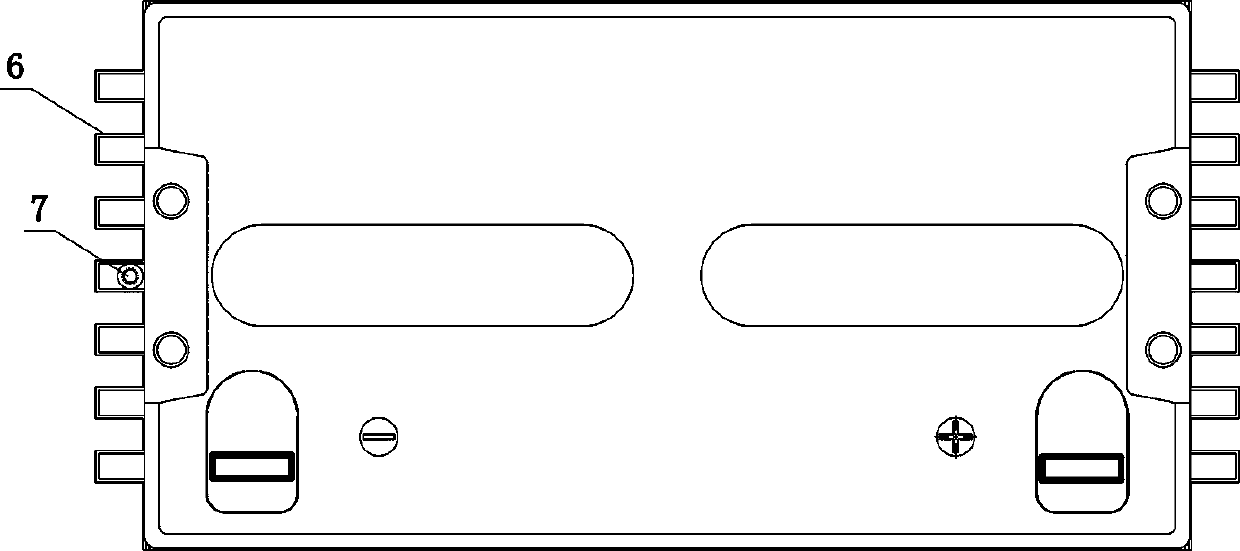
[0054] see figure 1 , figure 2 , image 3 , Figure 4, a high-temperature-resistant valve-regulated lead-acid battery, the battery includes a shell 1 and a positive plate and a negative plate arranged in the battery shell, and the positive plate and the negative plate are assembled into electrode groups 2 at intervals through separators and then installed inside the battery case. The housing 1 is made of ABS plastic material, the bottom of the housing 1 is thicker than the side wall of the housing, and the inner surface of the bottom of the housing 1 is provided with two parallel protrusions 3, and the direction of the protrusions 3 is perpendicular to the pole plate. The height of the bump 3 is about 13% of the height of the pole plate, and a groove 4 is formed between the bumps for storing colloid. A metal groove 5 is also provided outside the housing 1 , and the bottom of the metal groove 5 is glued to the bottom of the housing 1 . The size of the bottom surface of th...
Embodiment 2
[0064] The battery structure and positive electrode active material manufacturing method in this example are the same as those in Example 1. For details, refer to Example 1, which will not be described in detail here, but only the technologies that are different from Example 1 are listed, as follows:
[0065] (1) Positive active material, in parts by weight, including the following components: 9,00 parts of lead powder, 100 parts of red lead, 0.5 parts of colloidal graphite, 0.5 parts of short fiber, 10 parts of 4BS crystal seeds, 50% dilute sulfuric acid 85 parts, 0.5 parts of stannous sulfate, 0.5 parts of three-layer graphene, and 115 parts of pure water.
[0066] (2) In step S100, the acid leaching time is about 14 minutes, the temperature of the high temperature section is controlled to be 80° C., and the high temperature duration is 11 minutes.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com