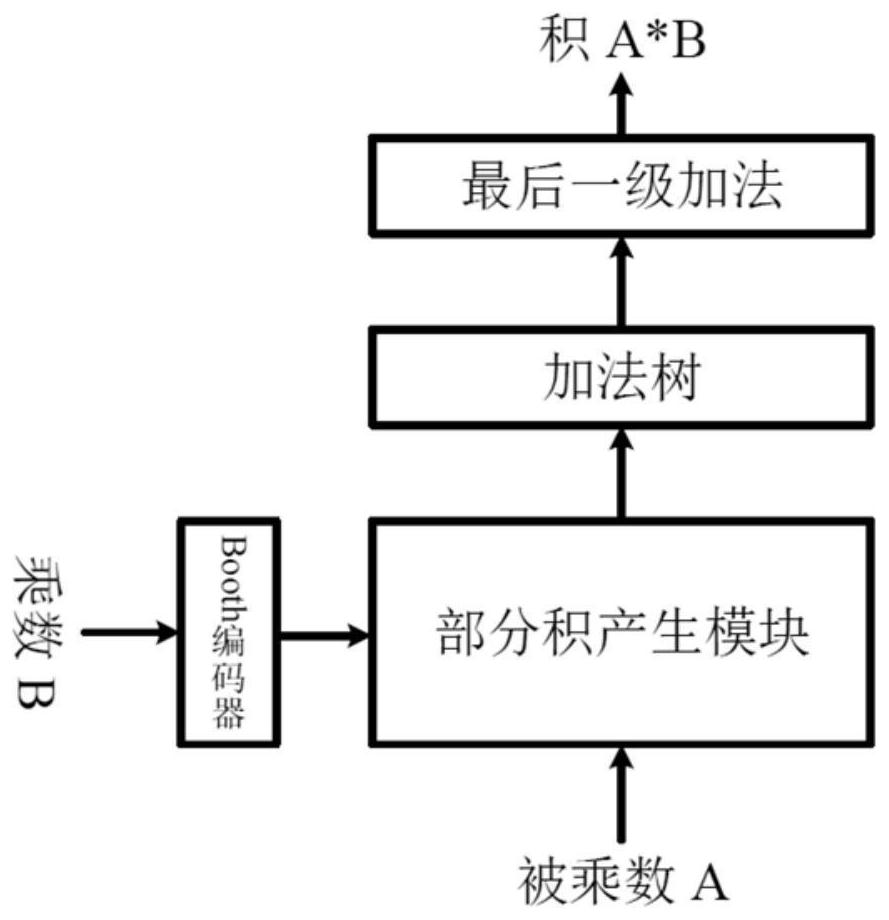
A non-volatile 8-bit booth multiplier based on rram
A non-volatile, multiplier technology, applied in the direction of instruments, static memory, digital memory information, etc., can solve the problem of lack of non-volatile multiplier design, to reduce read and write power consumption and leakage power consumption, The effect of fast power-on speed and high reliability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment
[0066] 1 Improvements to the traditional radix-4Booth algorithm
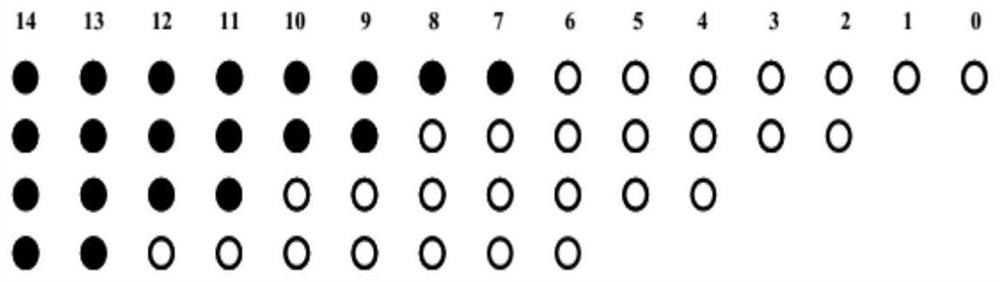
[0067] For an 8-bit Booth multiplier, each partial product generated by Booth encoding needs to extend the sign bit to 16 bits in the highest bit, which means that more memory needs to be used to store these redundant sign bits , a traditional extension such as figure 2 As shown, the black dots represent the sign bits, and the white dots represent the data bits.
[0068] In fact, these redundant sign bits can be reduced by:
[0069] A 15-bit partial product complement can be represented as follows:
[0070] S S S S S S S S Z 7 Z 6 Z 5 Z 4 Z 3 Z 2 Z 1
[0071] This redundant form can be rewritten as:
[0072] -S Z 7 Z 6 Z 5 Z 4 Z 3 Z 2 Z 1
[0073] because
[0074] -s*2 14 +(s*2 13 +s*2 12 +s*2 11 +s*2 10 +s*2 9 +s*2 8 )
[0075] =-s*2 14 +s*(2 14 -2 8 )=-s*2 8 (2-4)
[0076] Thus, for an 8-bit radix-4Booth multiplier, four partial products can represent image 3 . ...
Embodiment 1
[0116] Overall simulation and functional verification of the multiplier of the present invention
[0117] The design environment of the multiplier in the present embodiment is the Virtuoso Schematic tool of Cadence Company, and what emulation environment is to use is the 45nm process storehouse (GDPK045) of low threshold voltage, operating voltage V dd = 0.8V, working clock CLK = 357MHz. The RRAM model used can be found in P.Chen and S.Yu,"Compact Modeling of RRAMDevices and Its Applications in 1T1R and 1S1R Array Design,"in IEEETransactions on Electron Devices,vol.62,no.12,pp.4022-4028 , Dec. 2015.
[0118] In the RRAM model of this embodiment, we modified some parameters so that the R of RRAM HRS ≈100R LRS , to meet the design requirements of our multiplier.
[0119] Transient simulation results:
[0120] The transient simulation results are as Figure 23 shown. The multiplicand A is input from the external register as "01101101", and the multiplier B is configured in...
Embodiment 2
[0123] 1 Single multiplier performance comparison
[0124] In order to comprehensively evaluate the performance of the 8-bit new non-volatile Booth multiplier, Table 3 shows the speed, area, power consumption, and non-volatility of the 1-row multiplier and the 2-row multiplier, and compares them with [1 ] (See S. Kuang, J. Wang, and C. Guo, "Modified booth multipliers with a regular partial product array," IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, vol.56, no.5, pp.404–408 , May 2009.) and [2] (see W.Liu, L. Qian, C. Wang, H. Jiang, J. Han, and F. Lombardi, “Design of approximate radix-4 booth multipliers for error-tolerant computing, "IEEE Transactions on Computers, vol.66, no.8, pp.1435–1441, Aug 2017.) The proposed 8-bit multiplier was compared. At the same time, we used the same process library GDPK045 to design a traditional Booth multiplier, and evaluated its speed, area, and power consumption, so as to compare the difference between the new multiplie...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com