Neodymium-iron-boron magnet manufacturing process
A manufacturing process, NdFeB technology, applied in the field of NdFeB magnet manufacturing process, can solve problems such as sieve clogging, affecting the effect of magnetic powder filtration, affecting the service life of the vibrating screen, etc., and achieve the effect of improving the filtering effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
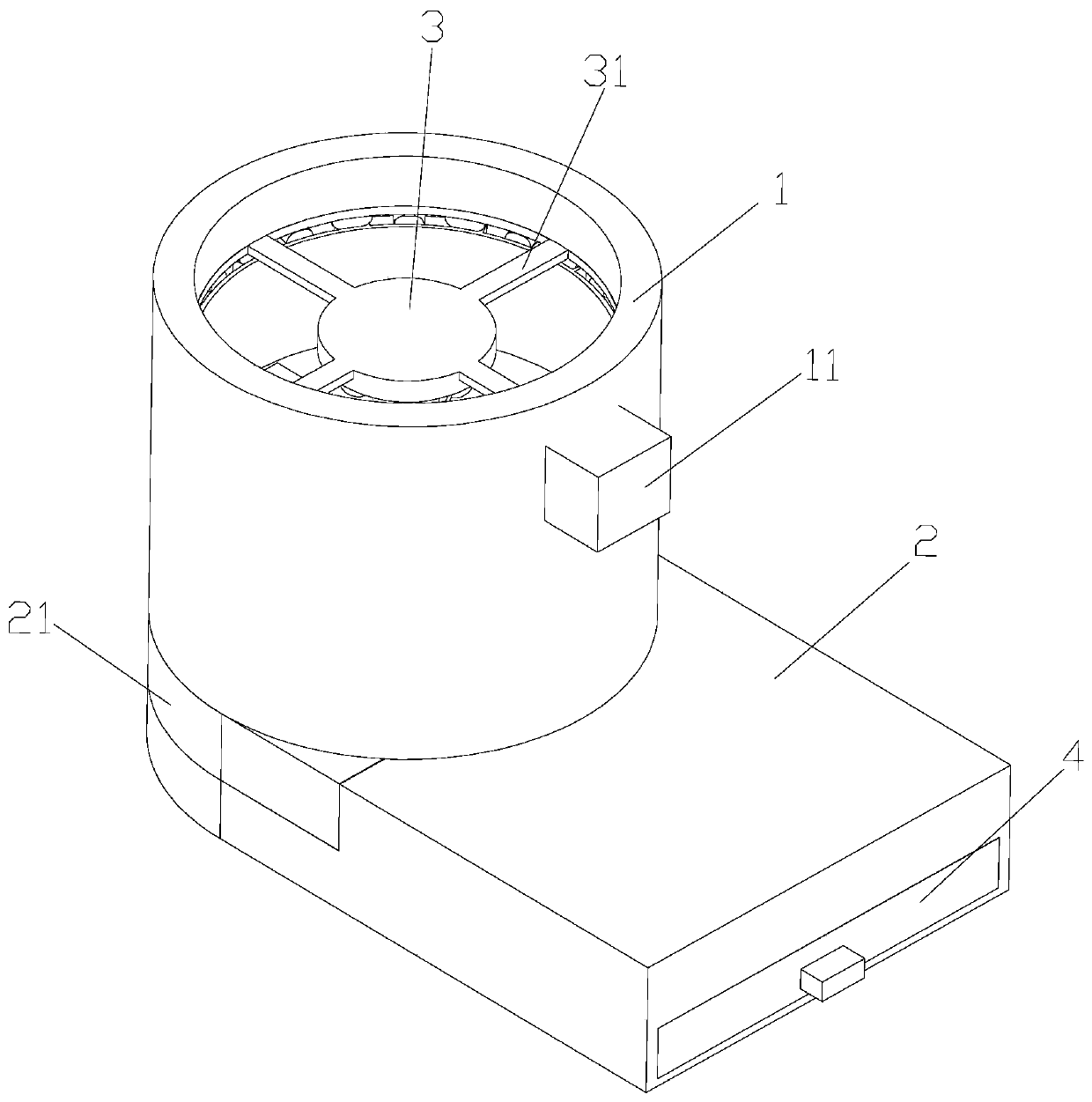
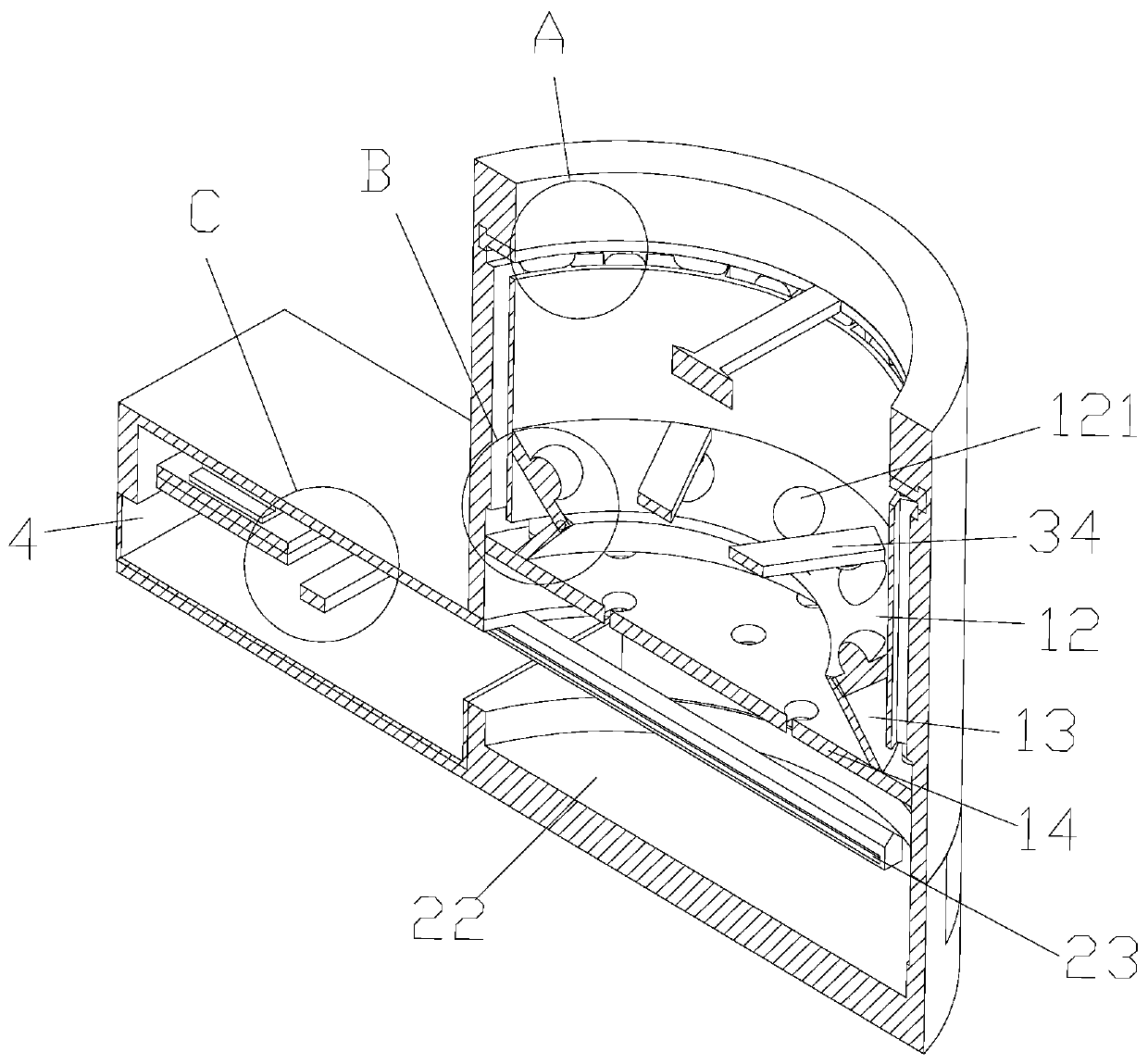
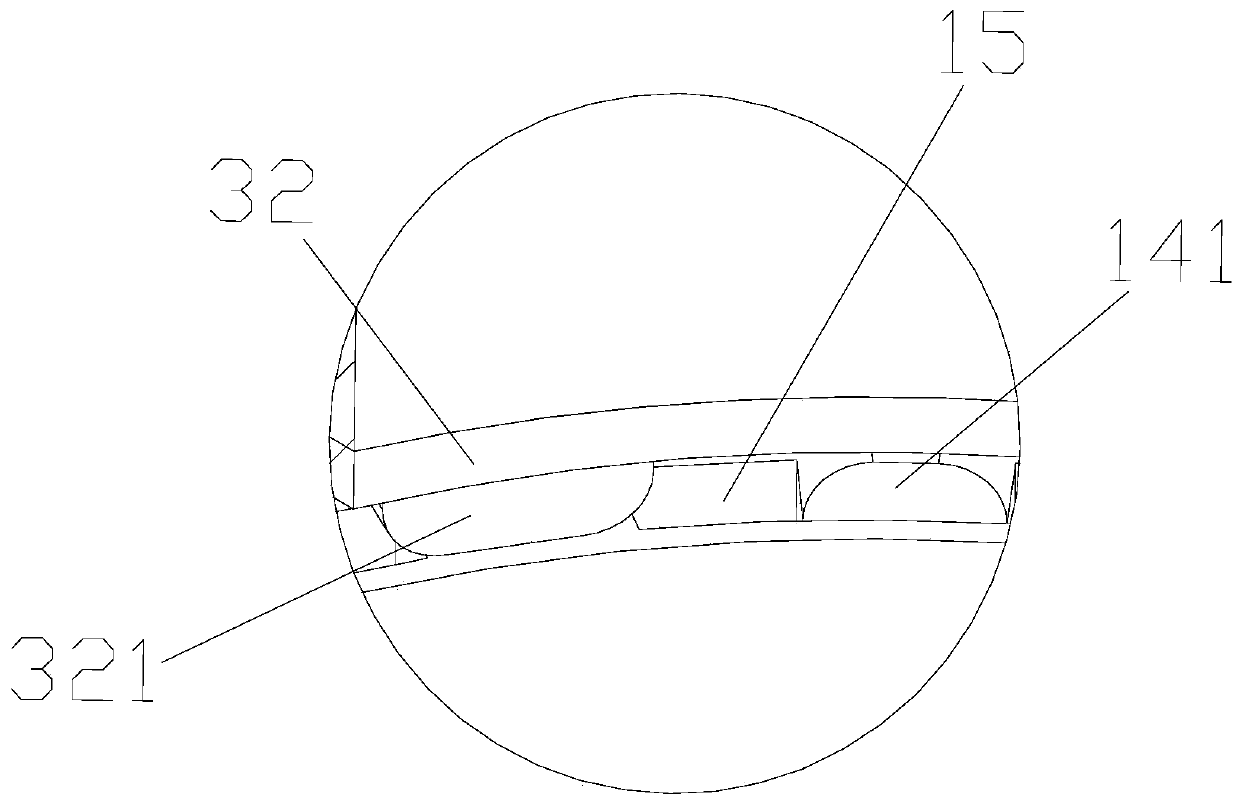
[0037] A manufacturing process of NdFeB magnets, including: a. Smelting: first charge the material and then evacuate to below 1Pa, start heating with low power, continue to pump while heating, and absorb the gas and water in the state as the temperature rises Gradually desorb and be drawn out until the charge is generally dark red, close the valve and fill with argon, increase the power to heat up to the complete melting of the charge, and carry out refining for 5 minutes, after refining, reduce the power and pour, pouring is completed and cooled; b. Powder making: Put the NdFeB particles into the jet mill for high-speed collision, so that the particles form powder under the high-speed collision, collect the formed powder and put it into the internal parts of the sieving machine for screening, and remove the impurities in the magnetic powder; c. Forming: including orientation and pressing. The function of orientation is to turn the c-axis of the easy magnetization direction of ...
Embodiment 2
[0050] A manufacturing process of NdFeB magnets, including: a. Smelting: first charge the material and then evacuate to below 1Pa, start heating with low power, continue to pump while heating, and absorb the gas and water in the state as the temperature rises Gradually desorb and be drawn out until the charge is generally dark red, close the valve and fill with argon, increase the power to heat up to the complete melting of the charge, and carry out refining for 5 minutes, after refining, reduce the power and pour, pouring is completed and cooled; b. Powder making: Put the NdFeB particles into the jet mill for high-speed collision, so that the particles form powder under the high-speed collision, collect the formed powder and put it into the internal parts of the sieving machine for screening, and remove the impurities in the magnetic powder; c. Forming: including orientation and pressing. The function of orientation is to turn the c-axis of the easy magnetization direction of ...
Embodiment 3
[0052] A manufacturing process of NdFeB magnets, including: a. Smelting: first charge the material and then evacuate to below 1Pa, start heating with low power, continue to pump while heating, and absorb the gas and water in the state as the temperature rises Gradually desorb and be drawn out until the charge is generally dark red, close the valve and fill with argon, increase the power to heat up to the complete melting of the charge, and carry out refining for 5 minutes, after refining, reduce the power and pour, pouring is completed and cooled; b. Powder making: Put the NdFeB particles into the jet mill for high-speed collision, so that the particles form powder under the high-speed collision, collect the formed powder and put it into the internal parts of the sieving machine for screening, and remove the impurities in the magnetic powder; c. Forming: including orientation and pressing. The function of orientation is to turn the c-axis of the easy magnetization direction of ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com