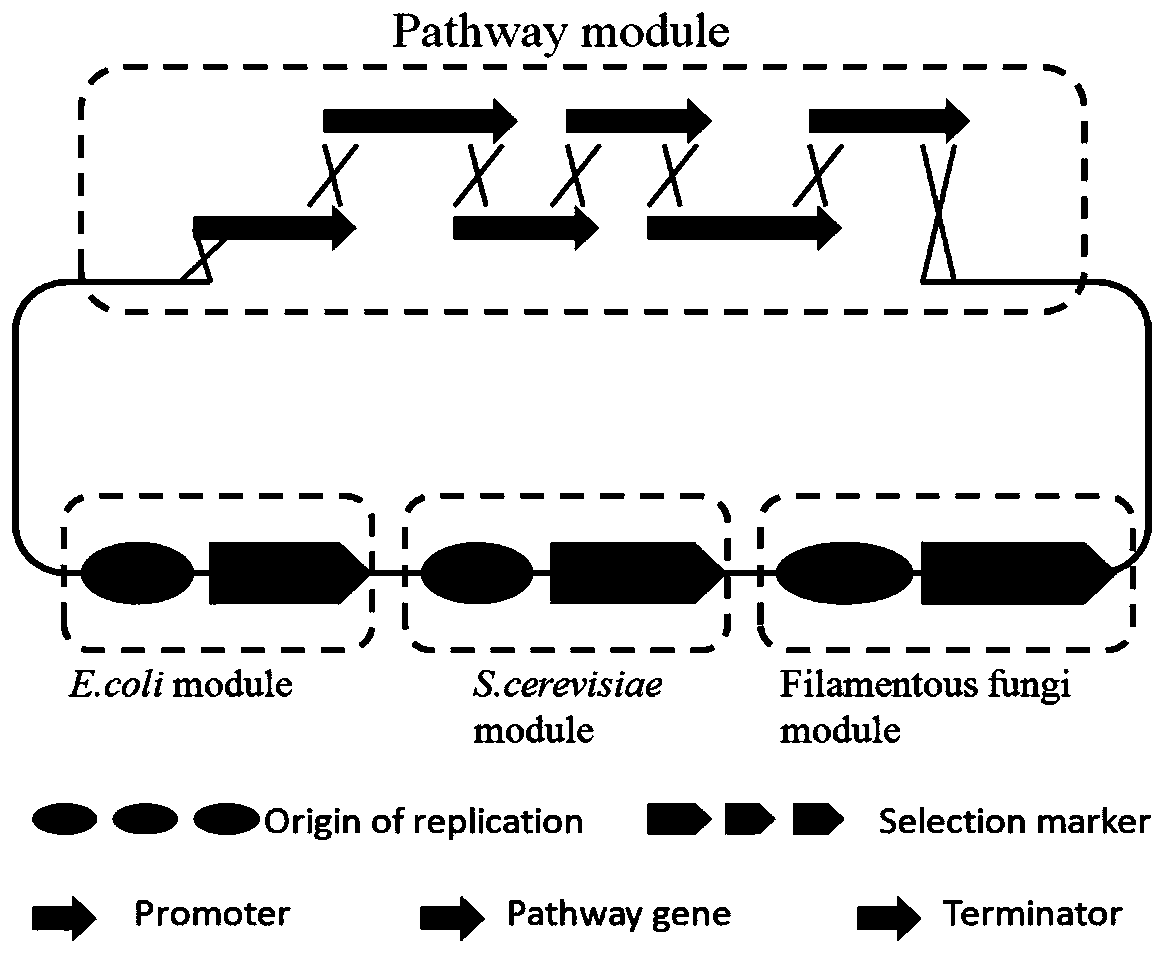
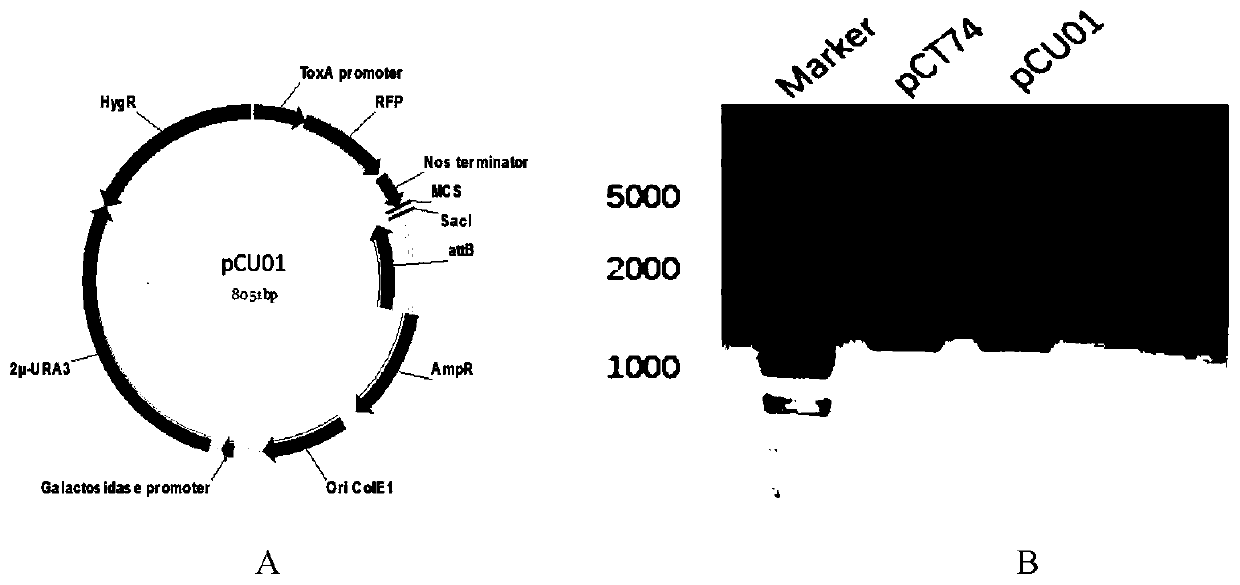
Method for rapidly constructing filamentous fungus expression vector
A filamentous fungus and expression vector technology, applied in the field of filamentous fungal vector construction, can solve the problems of high cost, many non-specific fusion fragments and high error rate, and achieve the effect of high accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] Example 1: Acquisition of Escherichia coli Replication Module, Yeast Replication Module and Filamentous Fungi Replication Module
[0023] The medium used is: LB medium (1L): 10g peptone, 5g yeast extract, 10g sodium chloride, and 20g agar should be added to the solid medium.
[0024] The plasmid pCT74 was hydrolyzed with restriction endonuclease SalI to obtain the skeleton structure of the expression vector of filamentous fungi, which contains the replication module of E. Mycin resistance gene and replication initiation element), and the part of HygR excised by SalI restriction endonuclease was cloned using pCT74 as template. The clones of yeast self-replicating sequence 2μOri and auxotrophic selection marker URA3 in the yeast plasmid replication module were amplified using the pCRCT plasmid as a template, and the promoter, target gene, and terminator sequences were amplified by PCR using pCT74 as a template. The sequence is shown in Table 3, and the assembled fragment...
Embodiment 2
[0031] Embodiment 2: Each fragment co-transforms yeast
[0032] The medium used is: SC-URA medium (600mL): 1g YNB, 3g ammonium sulfate, 0.414g CMS-URA, 550mL single distilled water, autoclaved (115°C, 30min); add 50mL 24% glucose solution (filter sterilized).
[0033] YPD medium (1L): 10g yeast extract, 20g peptone, 20g glucose, 20g agar should be added to the solid medium.
[0034] Production of competent yeast cells: (1) Pick a single yeast clone and culture it in 2mL YPD medium at 30°C and 250rpm overnight. (2) Determination of bacterial liquid OD 600nm , draw part of the bacterial solution into fresh YPD medium (make the solution OD 600nm =0.2) Cell OD after continuing to culture for 4-5h 600nm reach 0.8, centrifuge at 4000 rpm for 5 min at 4°C, and remove the supernatant. (3) The cells were resuspended and washed with 5 mL of cold sterile water, centrifuged at 4000 rpm for 10 min at 4°C, and the supernatant was discarded. (4) Add 1 mL of cold sterile water to resusp...
Embodiment 3
[0036] Example 3: Extraction and enrichment of yeast assembly plasmids
[0037] The reagents used are: yeast wall breaking buffer: 2% Triton X-100, 1% SDS, 100mmol / L NaCl, 10mmol / L Tris-Cl (pH 8.0), 1mmol / L Na2EDTA.
[0038] TE buffer: 10mmol / L Tris-HCl, 1mmol / L EDTA, pH 8.0.
[0039] Extraction of yeast transformant plasmids: (1) Randomly select 10 single clones on the SC-URA plate, insert each single clone into 10 mL of SC-URA liquid medium, and culture overnight at 30°C (500 μL of bacterial solution + 500 μL 50% glycerol, frozen at -80° refrigerator for preservation). (2) Centrifuge the remaining yeast liquid at 13,000 rpm for 1 min, discard the supernatant, and add 1.2 mL of yeast wall breaking buffer to suspend the yeast. (3) Dispense the suspension into 1.5mL EP tubes filled with glass beads (about 0.3g per tube), 200 μL per tube, vortex for 5 minutes, and then freeze the bacteria repeatedly in liquid nitrogen and in boiling water at 95°C Each time for 1 min (about 3 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com