Method for efficiently synthesizing PHBs by knocking out rfaD gene
An efficient and genetic technology, applied in the field of efficient synthesis of PHB, can solve the problem that PHB cannot meet the needs of industrial production.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
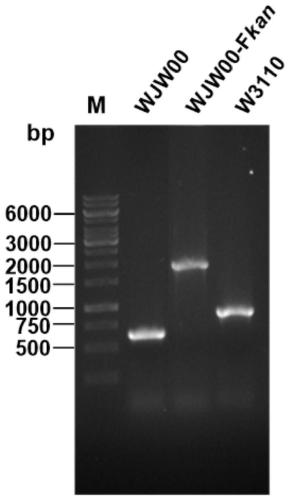
[0045] The construction of embodiment 1 engineering bacteria WJW00
[0046] The engineering bacteria WJW00 has been published in the SCI paper "Construction and Characterization of an Escherichia coli Mutant Producing Kdo 2 -Lipid A" (disclosure date: March 13, 2014). The specific construction process is as follows:
[0047] (1) Obtaining the rfaD gene knockout fragment
[0048] The knockout fragment of the rfaD gene was obtained by chemical total synthesis or step-by-step PCR amplification, and its two ends were the upstream and downstream homology arms of the rfaD gene, and the middle was a kan fragment with an FRT site. The nucleotide sequence of the rfaD gene knockout fragment is shown in SEQ ID NO.2. The rfaD gene knockout fragment was cloned into the plasmid pBlueScriptIISK(+) to obtain the recombinant plasmid pBlueScript IISK(+)-rfaDU-Fkan-rfaDD. Using the plasmid as a template, the knockout fragment rfaDU-Fkan-rfaDD can be amplified.
[0049] (2) Preparation and e...
Embodiment 2
[0055] Example 2 Construction of Engineering Strains W3110 / pDXW-8-phaCAB and WJW00 / pDXW-8-phaCAB
[0056] (1) Construction of plasmid
[0057] Plasmid pDXW-8-phaCAB has been co-produced with L-isoleucine in Corynebacterium glutamicum in the article "Ma, W., Wang, J., Li, Y., et.al. WM001[J].Microb Cell Fact,2018,17(1):93 10.1186 / s12934-018-0942-7" (publication date: 2018-12-31). The specific construction process is as follows:
[0058] The eutrophicum rosenbergii genome NC_008313.1 was used as a template, and the primers phaCAB-F / phaCAB-R were used to amplify the phaCAB gene cluster (see the accession number for the phaCAB gene cluster https: / / www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov / nuccore / MH558939.1), the PCR product was digested with restriction endonucleases EcoRI and XhoI, and the vector pDXW-8 (patent: a kind of E. 04-14) It was also digested with EcoRI and XhoI. After purification, the digested product was ligated overnight at 22°C with T4 ligase, transformed into E. coli DH5α, and th...
Embodiment 3
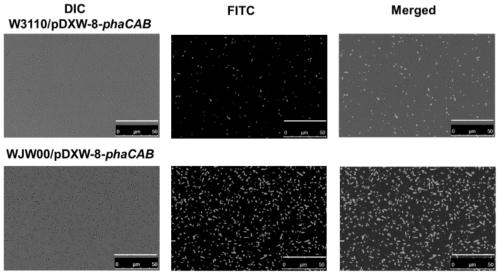
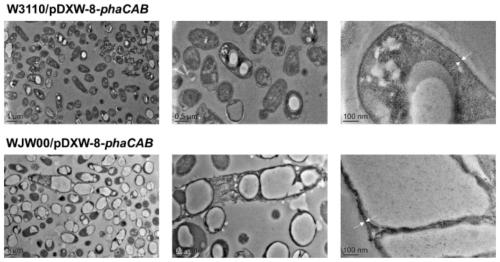
[0065] Qualitative observation of embodiment 3 engineering bacterium fermentation production PHB
[0066] LB medium composition: yeast powder 5g / L, tryptone 10g / L and NaCl 10g / L.
[0067]The composition of M9G medium: 20g / L glucose (Glucose), 17.1g / L disodium hydrogen phosphate dodecahydrate (Na 2 HPO 4 12H 2 O), 3g / L potassium dihydrogen phosphate (KH 2 PO 4 ), 0.5g / L sodium chloride (NaCl), add 1mM magnesium sulfate (M gSO 4 ), 0.1mM calcium chloride (CaCl 2 ), 10mg / mL vitamin B1 (VB 1 ).
[0068] (1) Seed liquid culture
[0069] Recombinant bacteria W3110 / pDXW-8-phaCAB and WJW00 / pDXW-8-phaCAB1 ring lawns were picked respectively and added to 25mL LB medium, and 30μg / mL kanamycin was added, and cultured at 37°C and 200rpm for 5h to mid-logarithmic phase.
[0070] (2) Synthesis of PHB by fermentation
[0071] Culture method: the seed solution (OD 600 = about 1.8) According to the initial OD 600 =0.25 was transferred to conventional PHB fermentation medium M9G, and...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Wall thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Dry cell weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com