Melt-processed material with high cellulose fiber content
A technology of cellulose fiber and melt processing, applied in the direction of biological packaging, etc., can solve the problems of materials with high cellulose content that are not disclosed
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0069] fiber
[0070] Dried bleached kraft fiber (K46) by SCA AB ( pulp mill, Sweden). Before use, the fibers were soaked in water and disintegrated, then mechanically beaten in a Voith mill to an energy input of 160 Wh / kg (approximately 30SR).
[0071] Chemicals
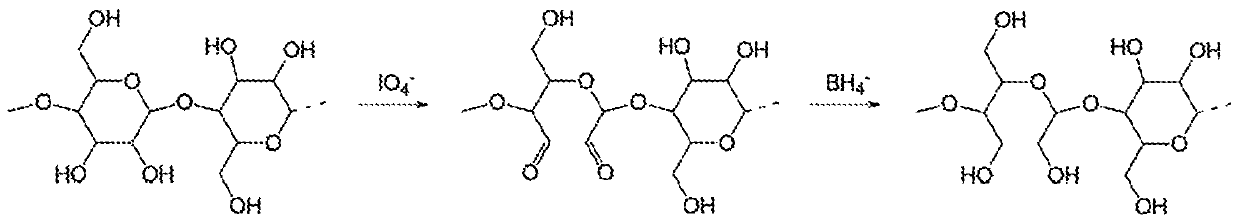
[0072] Sodium (meta) periodate was used to oxidize cellulose, isopropanol (purity ≥ 99.8%) was used as radical scavenger and hydroxylamine hydrochloride was used to determine the degree of oxidation. Sodium borohydride was used to reduce dialdehyde cellulose to diol cellulose. These and all other chemicals, such as hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide, are of analytical grade.
[0073] Oxidation of Cellulose
[0074] Under stirring, 5.4 g sodium periodate / g fiber was added to a 4 g / L fiber suspension containing 6.3% isopropanol (by volume) as a radical scavenger to prevent side reactions and chain scission. To further prevent chain scission, the oxidation reaction was performed in the dark for 16 h, 24 h, o...
Embodiment 2
[0080] To test the effect of the modified scale-up and to provide sufficient material for a longer test series, the following experimental setup was used:
[0081] Modifications were carried out as described in Example 1, but instead of a dry content of 0.4%, it was increased to 4%, and the amount of oxidant was reduced to 1.4g (NaIO 4 ) / g fiber, the temperature was raised to 50°C to shorten the reaction time to 3-4 hours. The degree of oxidation was determined to be 38% by carbonyl content analysis (these fibers are hereinafter referred to as fibers 38).
[0082] During the reduction step, the amount of reducing agent was reduced from 0.5 g / g fiber to 0.2 g / g fiber (complete reduction of aldehyde as measured by carbonyl content assay).
Embodiment 3
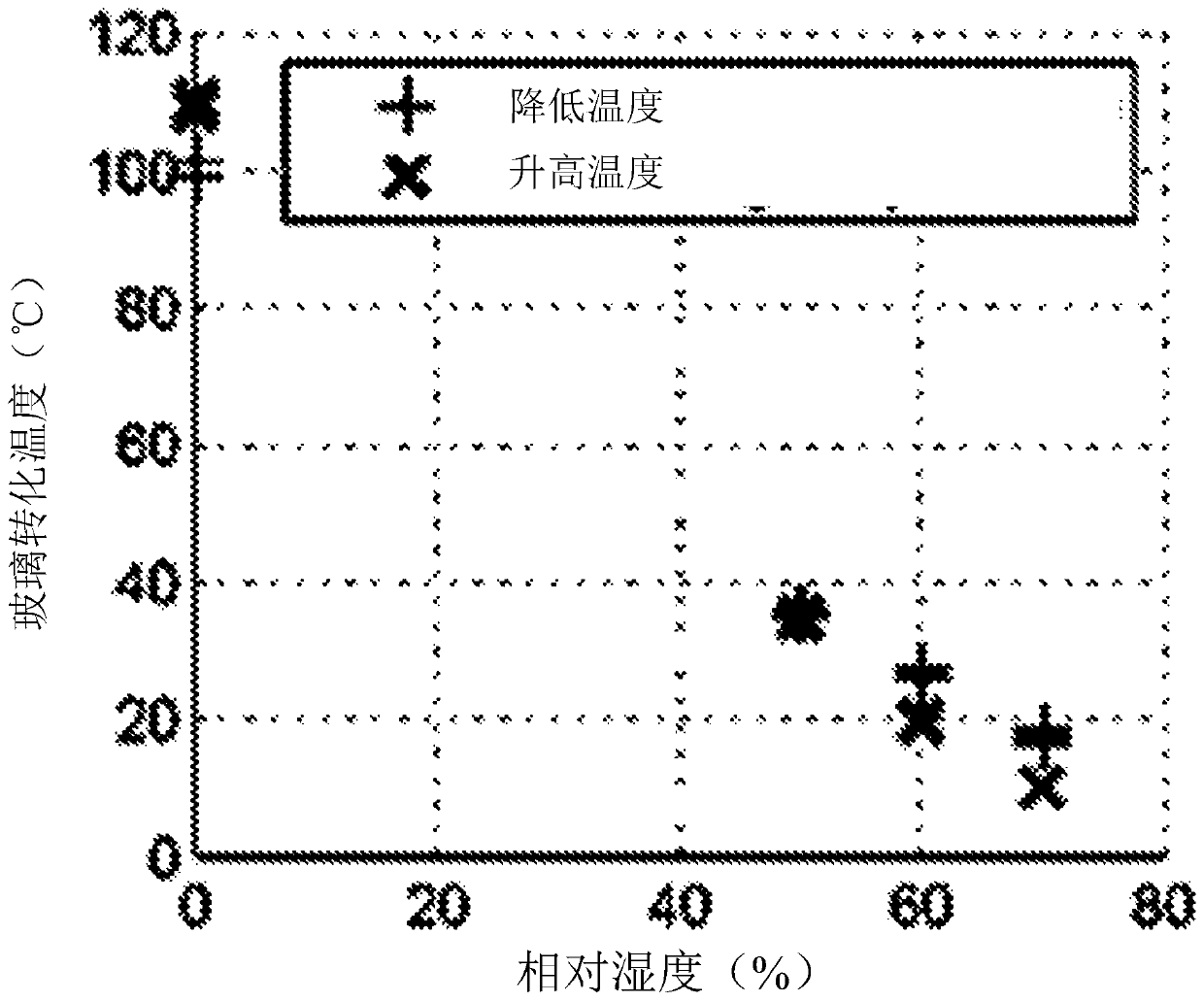
[0084] To better understand the wet mechanical and thermomechanical properties of modified cellulose, dynamic mechanical thermal analysis (DMTA) was performed at selected amounts of relative humidity. All DMTA tests were performed in a controlled environment using a Q800DMTA from TA Instruments with a humidity and temperature controlled chamber. During each test, an approximately constant (±2.5% for all data points in this manuscript, except for the DMTA results at 113°C and high humidity, which had a maximum error of ±12% in humidity) relative humidity (0%, 50%, 60% and 70% RH). The desired relative humidity and temperature of 10°C are obtained and then maintained for the first 120 minutes of the test. After 120 minutes had elapsed, the temperature was swept from 10°C to 113°C (this process lasted 206 minutes), held at 113°C for 30 minutes, scanned from 113°C to 10°C (this process lasted 206 minutes), and then at 10 °C for 30 minutes. This temperature cycle is performed th...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com