Method for preparing porous fiber from natural polymers and product and application thereof
A technology of natural polymers and porous fibers, which is applied in the field of preparing porous fibers from natural polymers. It can solve the problems of inability to realize continuous large-scale preparation and limit the application of porous fibers, and achieve the effects of simple preparation methods, low cost and wide sources.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] (1) Dissolve 0.2 g of sodium carboxymethyl cellulose powder in 10 ml of deionized water, and after dissolving completely, prepare a sodium carboxymethyl cellulose solution with a mass fraction of 2%.
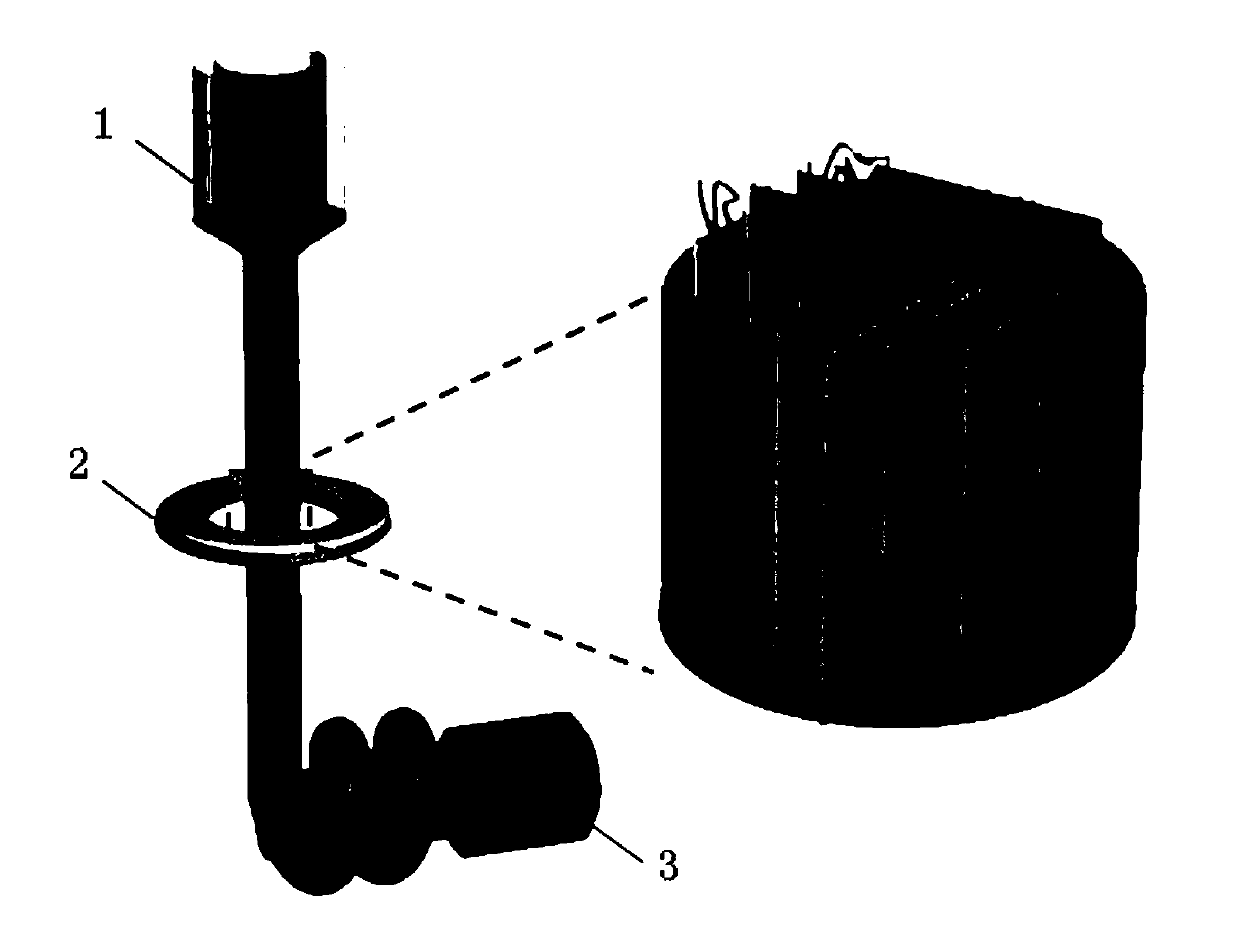
[0039] (2) Put the solution in the syringe, extrude the solution through the extrusion pump, place the copper ring in a low-temperature reaction bath, the temperature of the copper ring is -90 ° C, the solution passes through the copper ring for freezing-spinning process, and freezes The final fiber is collected by motor.
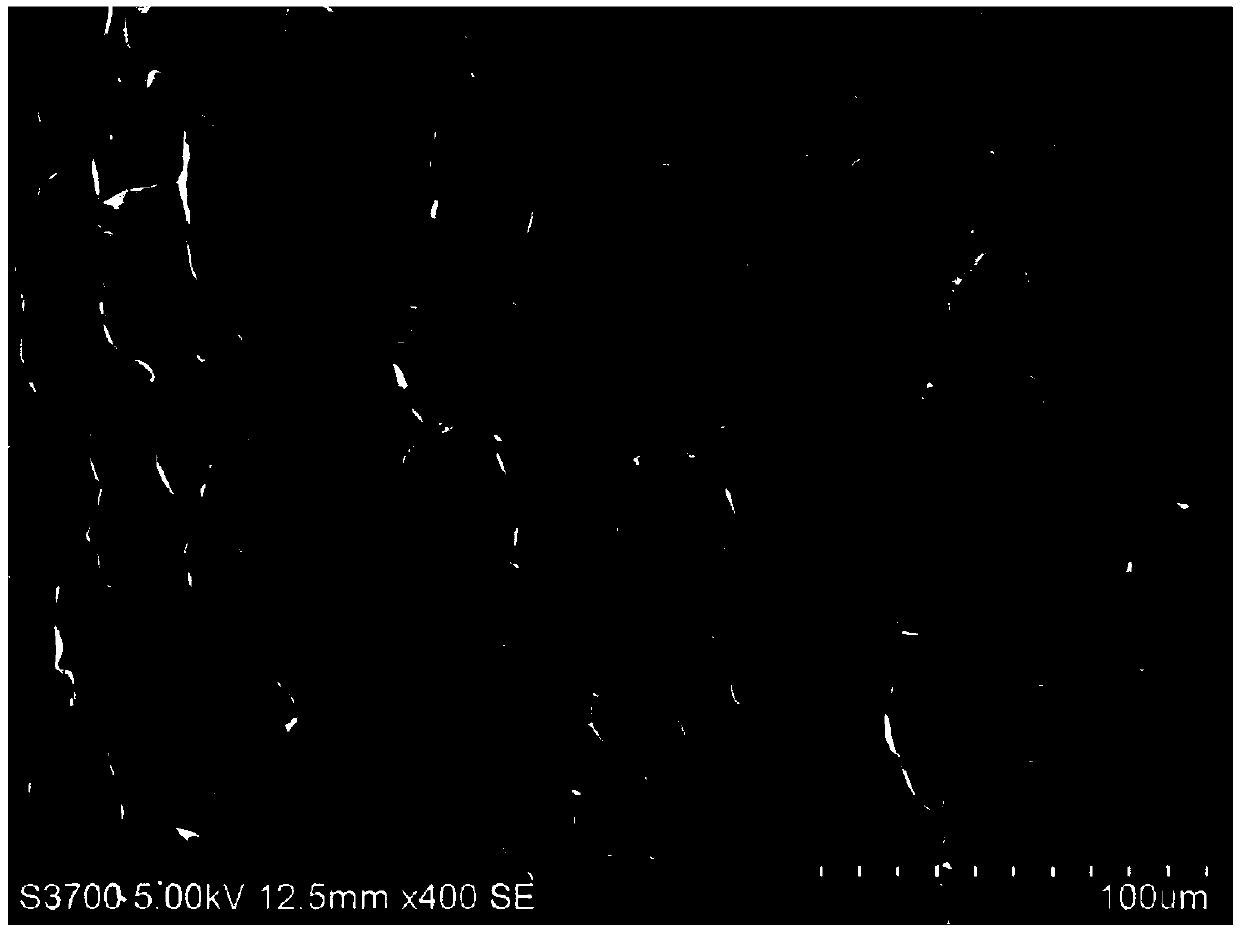
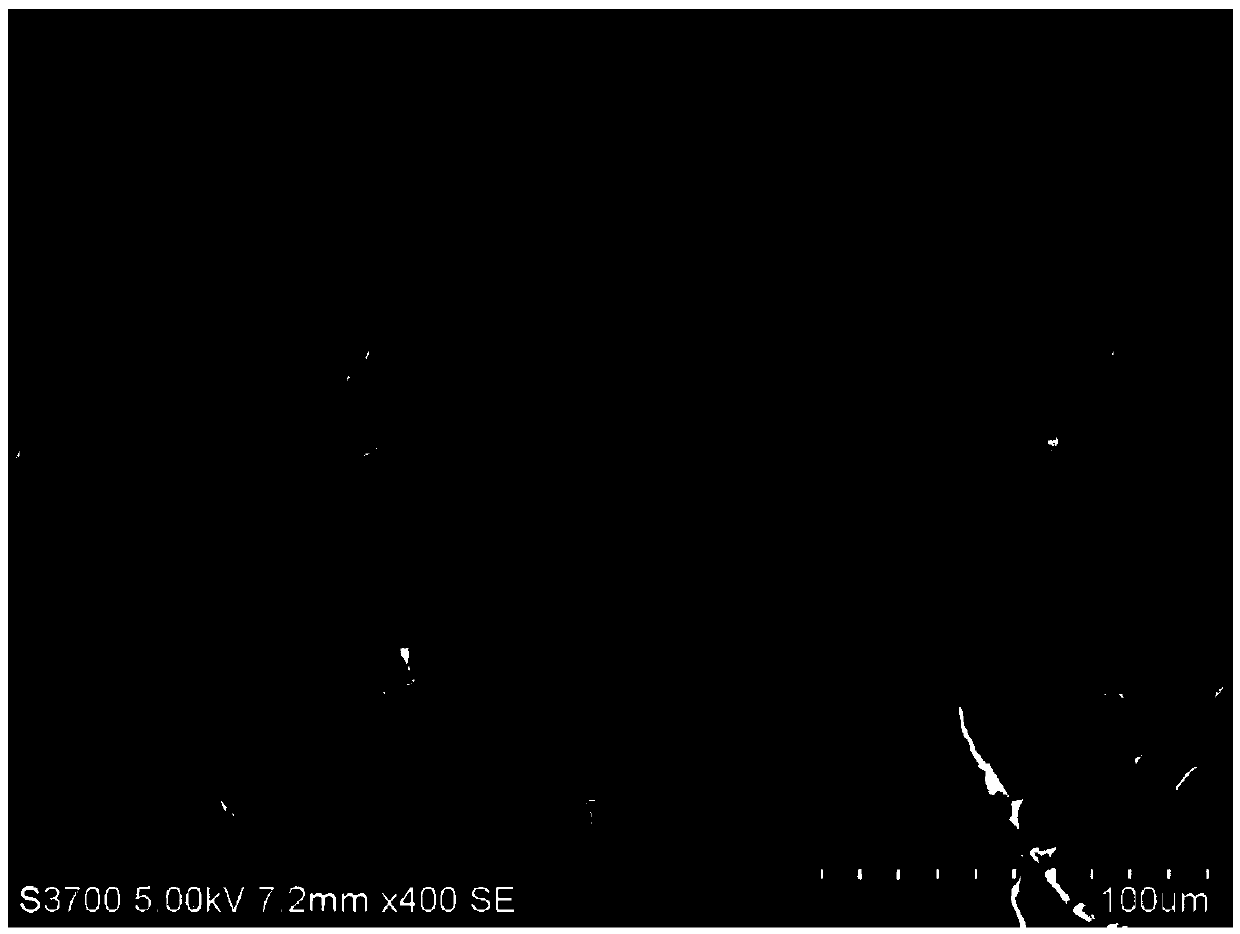
[0040] (3) Freeze-drying the frozen fiber obtained in step (2) for 24 hours to remove the solvent to obtain a porous fiber with an oriented porous structure.
[0041] (4) Weaving the porous fiber obtained in step (3) into a fabric.
Embodiment 2
[0043](1) Dissolve 1 g of sodium carboxymethyl cellulose powder in 10 ml of deionized water, and after dissolving completely, make a sodium carboxymethyl cellulose solution with a mass fraction of 10%.
[0044] (2) Put the solution in the syringe, extrude the solution through the extrusion pump, place the copper ring in a low-temperature reaction bath, the temperature of the copper ring is -50 ° C, the solution passes through the copper ring for freezing-spinning process, and freezes The final fiber is collected by motor.
[0045] (3) Freeze-drying the frozen fiber obtained in step (2) for 24 hours to remove the solvent to obtain a porous fiber with an oriented porous structure.
[0046] (4) Weaving the porous fiber obtained in step (3) into a fabric.
Embodiment 3
[0048] (1) Dissolve 0.5 g of sodium carboxymethyl cellulose powder in 10 ml of deionized water, and after dissolving completely, prepare a sodium carboxymethyl cellulose solution with a mass fraction of 5%.
[0049] (2) Put the solution in the syringe, squeeze out the solution through the extrusion pump, place the copper ring in a low-temperature reaction bath, the temperature of the copper ring is -100 ° C, the solution passes through the copper ring for freezing-spinning process, and freezes The final fiber is collected by motor.
[0050] (3) Freeze-drying the frozen fiber obtained in step (2) for 24 hours to remove the solvent to obtain a porous fiber with an oriented porous structure.
[0051] (4) Weaving the porous fiber obtained in step (3) into a fabric.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| quality score | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com