Piezoelectric driving mutual shielding electrode micro electric field sensor
An electric field sensor, driving electrode technology, applied in electrostatic field measurement and other directions, can solve the problems of inability to ensure that the electrode works in a resonant state, difficult to integrate and mass production, low resolution and sensitivity, avoiding direct interference and easy assembly. , the effect of improving the induction efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0053] Embodiment 1 introduces a structural example of a piezoelectrically driven mutual shielding electrode miniature electric field sensor using strip-shaped sensing electrodes.
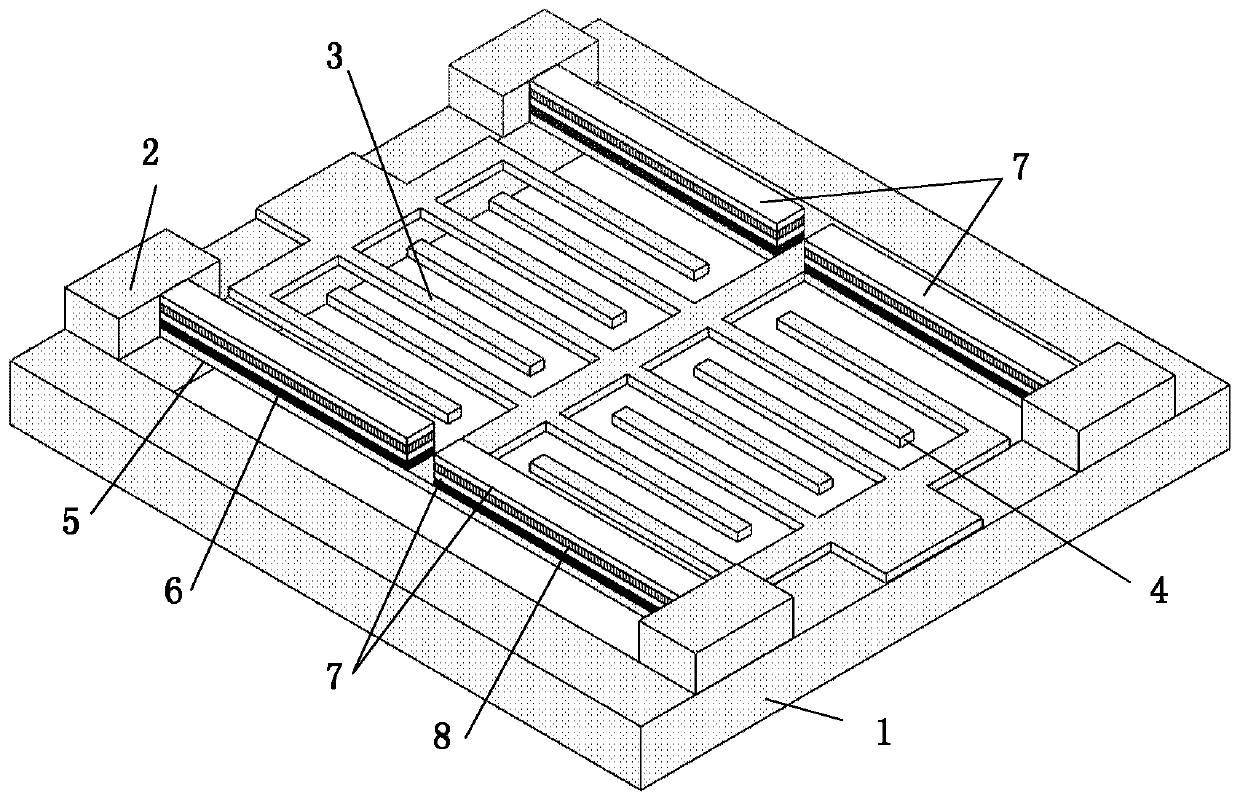
[0054] figure 1 It is a schematic structural diagram of a piezoelectrically driven mutual shield electrode miniature electric field sensor shown in Embodiment 1 of the present invention. refer to figure 1 As shown, in this embodiment, the piezoelectrically driven mutual shield electrode miniature electric field sensor includes: a substrate 1, a pillar 2, a fixed electrode 3, a movable electrode 4, an elastic beam 5, an insulating layer 6 and a driving structure.
[0055] In this embodiment, the movable electrodes 4 are arranged in two groups, and the fixed electrodes 3 are arranged in two groups; the pillars 2 are arranged in six groups, fixed on the substrate 1, for supporting and connecting the fixed electrodes 3 and the substrate 1, and elastic beams 5 and the substrate 1; the movable electrod...
Embodiment 2
[0060] Embodiment 2 introduces a structural example of a piezoelectrically driven mutual shielding electrode miniature electric field sensor using comb-teeth sensing electrodes.
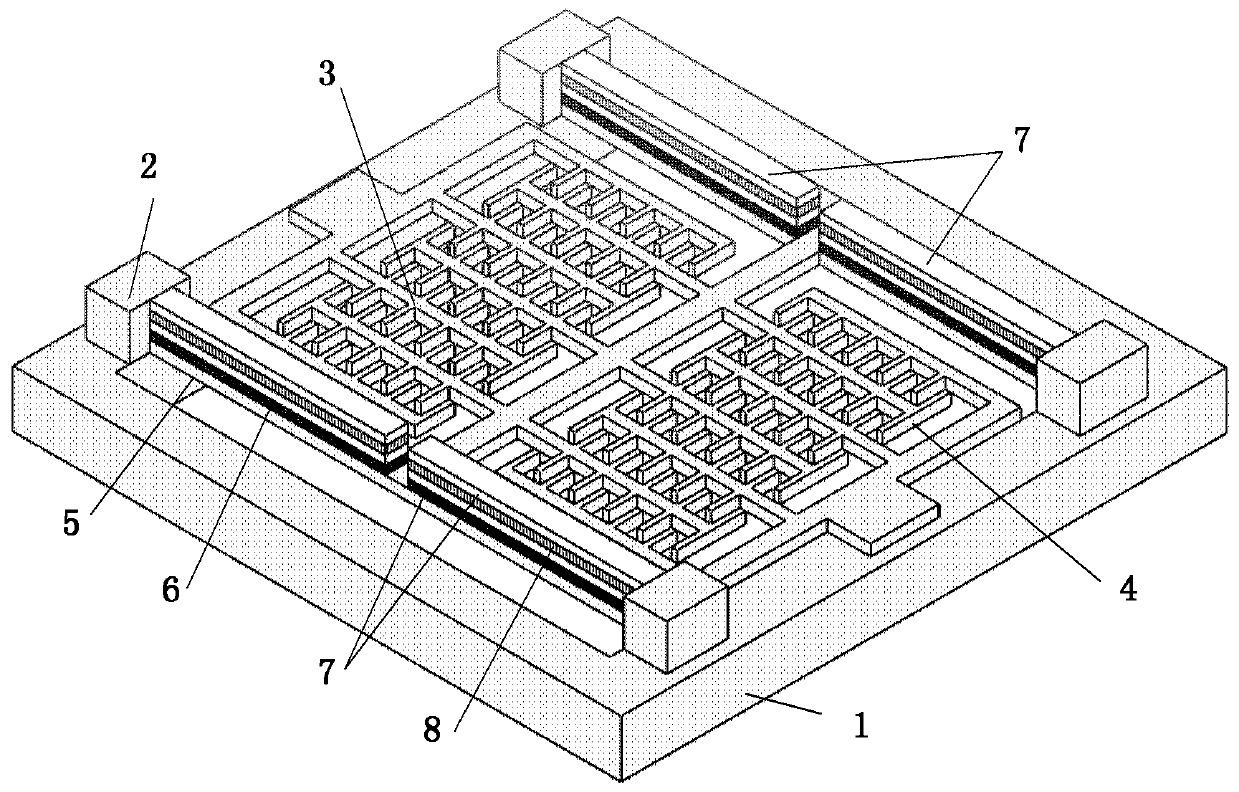
[0061] image 3 It is a structural schematic diagram of a piezoelectrically driven mutual shield electrode miniature electric field sensor shown in Embodiment 2 of the present invention. refer to image 3 As shown, the working principle of this embodiment 2 is consistent with that of embodiment 1. The piezoelectrically driven mutual shielding electrode miniature electric field sensor includes two sets of fixed electrodes 3 and two sets of movable electrodes 4; but the difference lies in: this embodiment Among them, the fixed electrodes 3 and the movable electrodes 4 are intersected by a comb structure.
Embodiment 3
[0063] Embodiment 3 introduces a structural example of a piezoelectrically driven miniature electric field sensor with mutually shielded electrodes using a serpentine composite elastic beam.
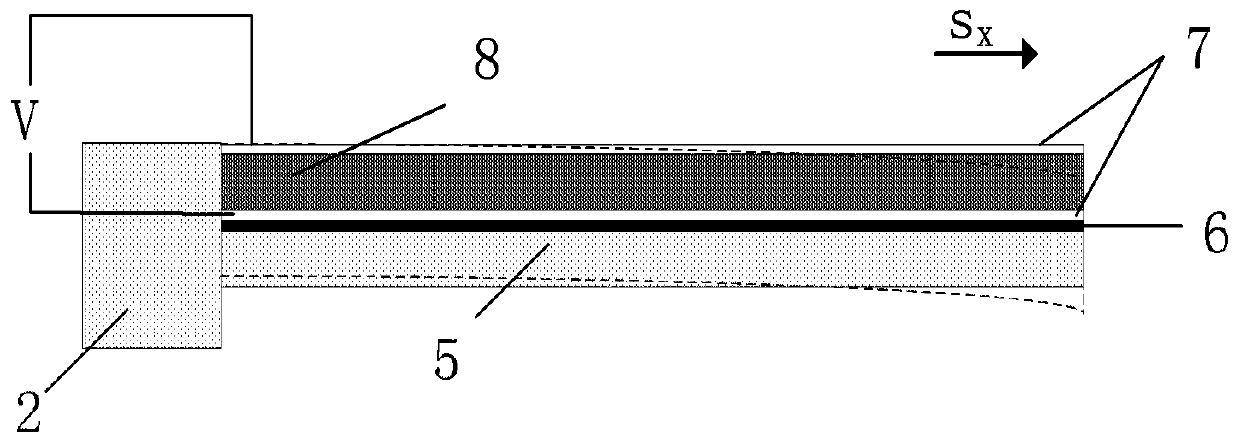
[0064] image 3 It is a structural schematic diagram of a piezoelectrically driven mutual shield electrode miniature electric field sensor shown in Embodiment 3 of the present invention. refer to Figure 4 As shown, the working principle of Embodiment 3 is consistent with that of Embodiment 1. The piezoelectrically driven mutual shielding electrode miniature electric field sensor includes two groups of fixed electrodes 3 and two groups of movable electrodes 4; the pillars are set to four groups; the driving structure is two group, located above the plane where the movable electrode 4 is located through the insulating layer 6 .
[0065] In this embodiment, the fixed electrodes 3 and the movable electrodes 4 are strip-shaped structures, arranged crosswise in the same plane; the elastic b...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com