Double-frequency differential band-pass filter based on branch load resonator
A resonator and filter technology, applied in the microwave and radio frequency fields, can solve the problems of low selectivity, the center frequency of the filter cannot be adjusted independently, and the insertion loss is large, so as to achieve enhanced flexibility and convenience, and good common mode rejection characteristics. , the effect of reducing insertion loss
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
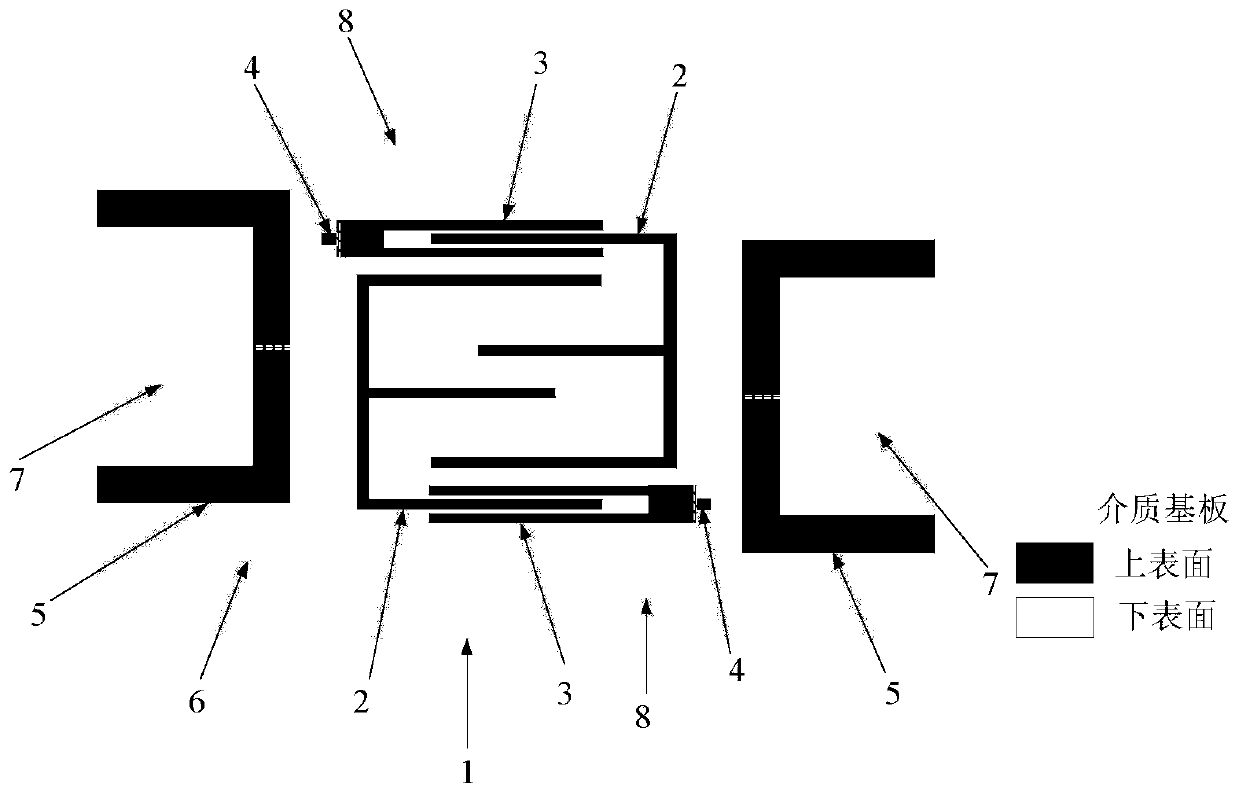
[0027] With the continuous development of the communication field, the communication system is becoming more and more complex. As an indispensable device in the radio frequency transceiver, the filter becomes particularly important. The performance of the filter is related to the normal operation of the entire communication system. The high-frequency system is particularly complex, which requires the filter to have stronger anti-interference ability, and the differential filter came into being. In recent years, many differential filters have been invented and proposed, but most of them cannot satisfy multi-band, low insertion loss, high selectivity and design flexibility at the same time. In view of these shortcomings, the present invention designs a dual filter based on stub load resonators. frequency difference filter for high selectivity and design flexibility.
[0028] The present invention is a dual-frequency differential bandpass filter based on stub load resonators, see...
Embodiment 2
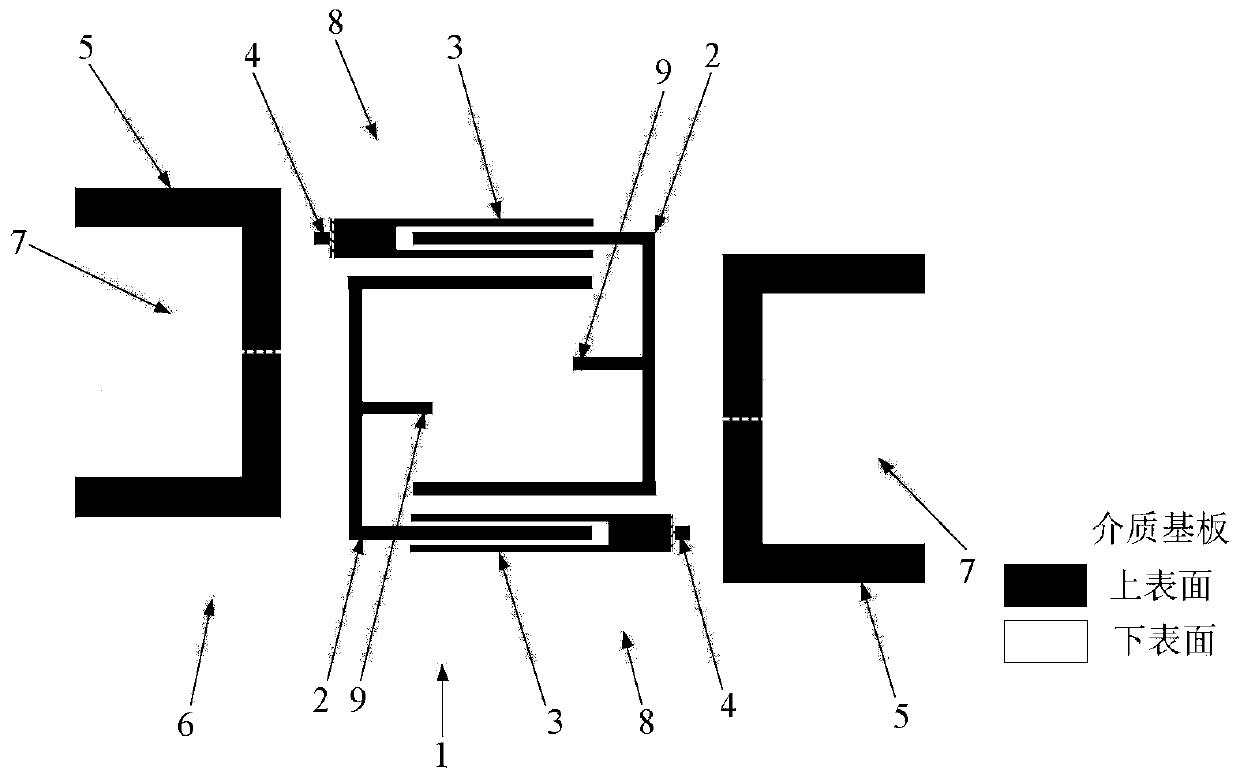
[0036] The overall composition and specific structure of the dual-frequency differential bandpass filter based on stub load resonators are the same as in Embodiment 1, see figure 1 , figure 2 , the opening directions of the two stub load resonators 2 that are symmetrical about the center of the dielectric substrate of the present invention are opposite, see Figure 4 and Figure 5 , that is, the openings of the two E-type stub load resonators 2 face each other, and the coupling mode is quasi-interdigitated coupling. The stubs loaded in the microstrip resonator 2 are either open-circuit stubs or short-circuit stubs, all located at the very center of the C-shaped microstrip line formed by the E-shaped frame. The stub-loaded microstrip resonator 2 includes a C-type microstrip line folded into three sections and a section of stub loaded at the center of the C-type microstrip line. The size of the microstrip resonator is reduced by folding, and multiple frequency bands and It i...
Embodiment 3
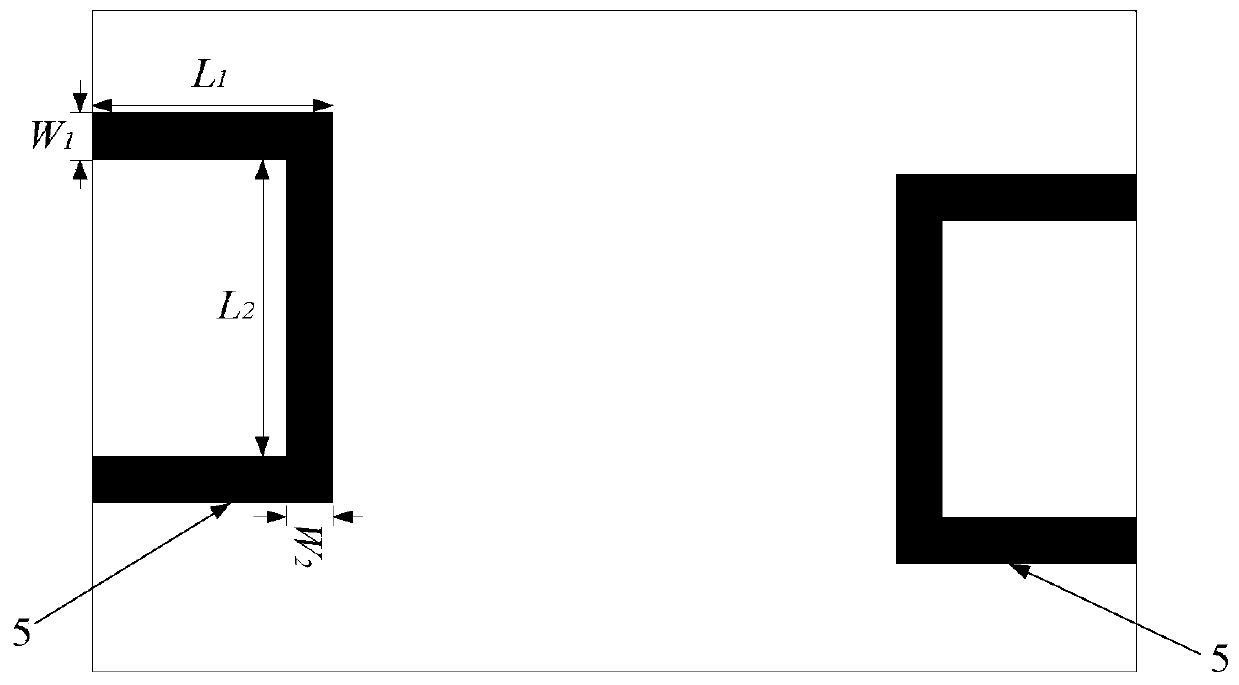
[0041] The overall composition and specific structure of the dual-frequency differential bandpass filter based on stub load resonators are the same as those in Embodiment 1-2, see figure 1 , figure 2 , Figure 4 and Figure 5 , the stepped impedance microstrip line 3 of the present invention is formed by connecting a smaller rectangular high-impedance microstrip line and a larger rectangular low-impedance microstrip line, and the end of the high-impedance microstrip line is grounded through a metallized via hole 4 and exceeds The bottom slot line is a quarter of the waveguide wavelength of the microstrip line to achieve a good transition of the differential mode signal from the slot line to the microstrip line. The two microstrip lines are parallel to the long side of the dielectric board 1 , and to achieve a smaller size, the two stepped impedance microstrip lines 3 are symmetrical about the center point of the dielectric substrate.
[0042] see Figure 4 , when the stub...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com