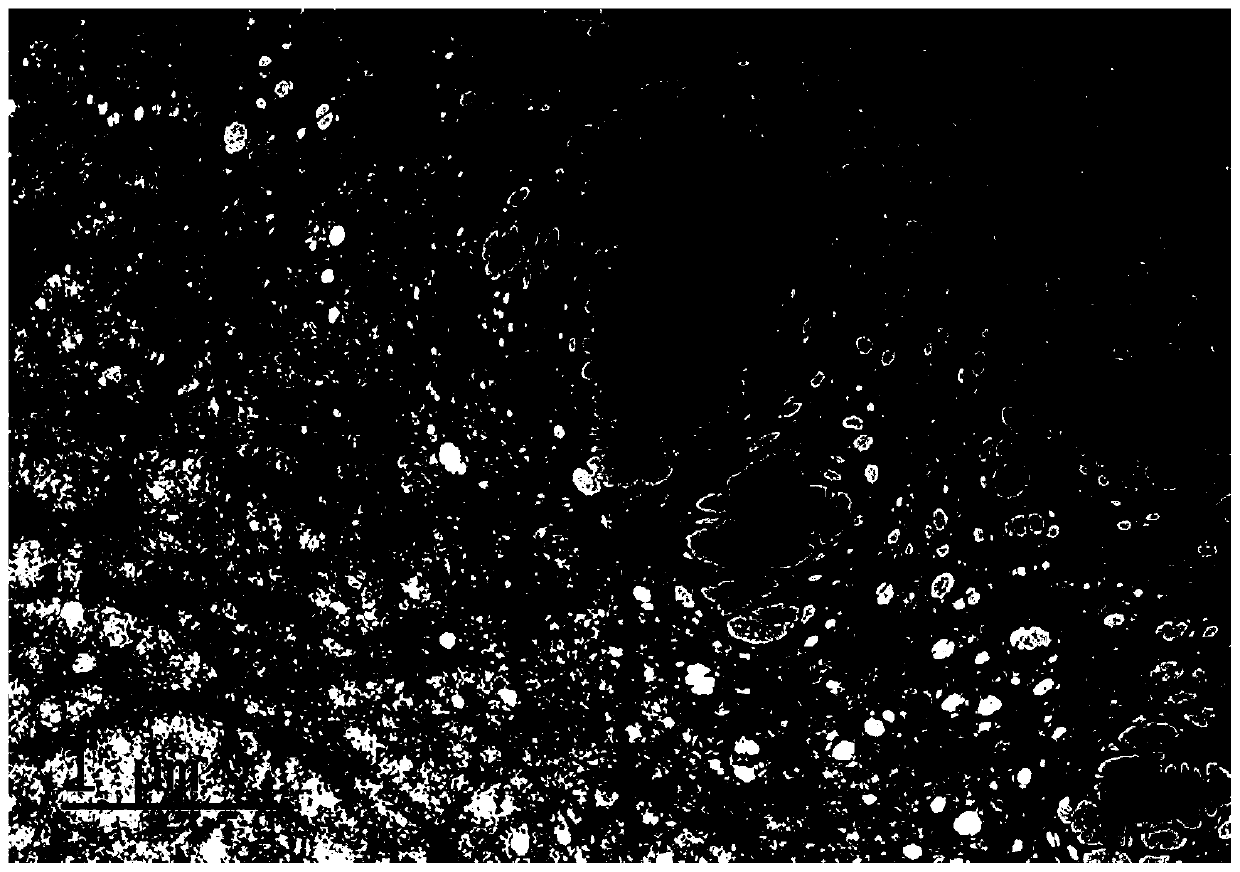
Method for preparing superhydrophobic coating by taking nano-cellulose and nano-particle as raw materials and modifying raw materials in aqueous solution with fluoride-free modifier
A technology of nano-cellulose and super-hydrophobic coatings, applied in cellulose coatings, coatings, etc., can solve problems such as poor mechanical stability and environmental impact, and achieve the effects of mild reaction conditions, high feasibility, and good hydrophobic properties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0035] Specific embodiment one: present embodiment is a kind of method that uses nanocellulose and nanoparticle as raw material in aqueous solution without fluorine modifier modification to prepare superhydrophobic coating, and it is carried out according to the following steps:
[0036] 1. Disperse nanocellulose into deionized water, and then add γ-aminopropyltriethoxysilane and fluorine-free modifier in sequence under magnetic stirring at a speed of 50r / min to 1000r / min to obtain modified Nanocellulose solution;
[0037] The mass ratio of the nanocellulose to deionized water is 1g:(100~500)mL; the mass ratio of the nanocellulose to γ-aminopropyltriethoxysilane is 1:(0.1 ~5); The mass ratio of described nanocellulose and fluorine-free modifier is 1:(0.25~10);
[0038] 2. Disperse the nanoparticles into deionized water, and then add hexadecyltrimethoxysilane and formic acid with a mass percentage of 15% to 88% under magnetic stirring with a rotating speed of 50r / min to 1000r / ...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0050] Embodiment 2: This embodiment is different from Embodiment 1 in that: the particle size of the nanoparticles described in Step 2 is 7nm-40nm. Others are the same as in the first embodiment.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0051] Specific embodiment three: This embodiment differs from specific embodiment one or two in that the nanoparticles described in step two are nano-silicon dioxide, nano-titanium dioxide, nano-ferric oxide, nano-calcium carbonate, nano-kaolin or nano- alumina. Others are the same as in the first or second embodiment.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com