Preparation method of high-quality anhydrous rare earth chloride and bromide
A rare earth chloride and bromide technology, applied in the fields of rare earth metal compounds, chemical instruments and methods, inorganic chemistry, etc., can solve the problems of easy deliquescence, high cost, and difficult dehydration of finished products, and achieve easy industrial production, avoid pollution, and reduce process costs low effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] Weigh 1 kg of lanthanum bromide heptahydrate, heat it to 180°C under the protection of flowing nitrogen, and keep it for 3h; vacuumize the system, continue to heat up to 245°C and keep it for 5h, to obtain crude anhydrous lanthanum bromide; Transfer to a vacuum distillation device, after vacuuming (the vacuum pressure is 120Pa at this time), heat up to 260°C for 5h, continue to heat up to 500°C for 4h, continue to heat up to 820°C for 5h, continue to heat up to 900°C, and heat for 15h. And receive the distilled lanthanum bromide to obtain high-purity anhydrous lanthanum bromide. After testing, the oxygen content in the high-purity anhydrous lanthanum bromide product of this example is 36 ppm, and the water content is 18 ppm.
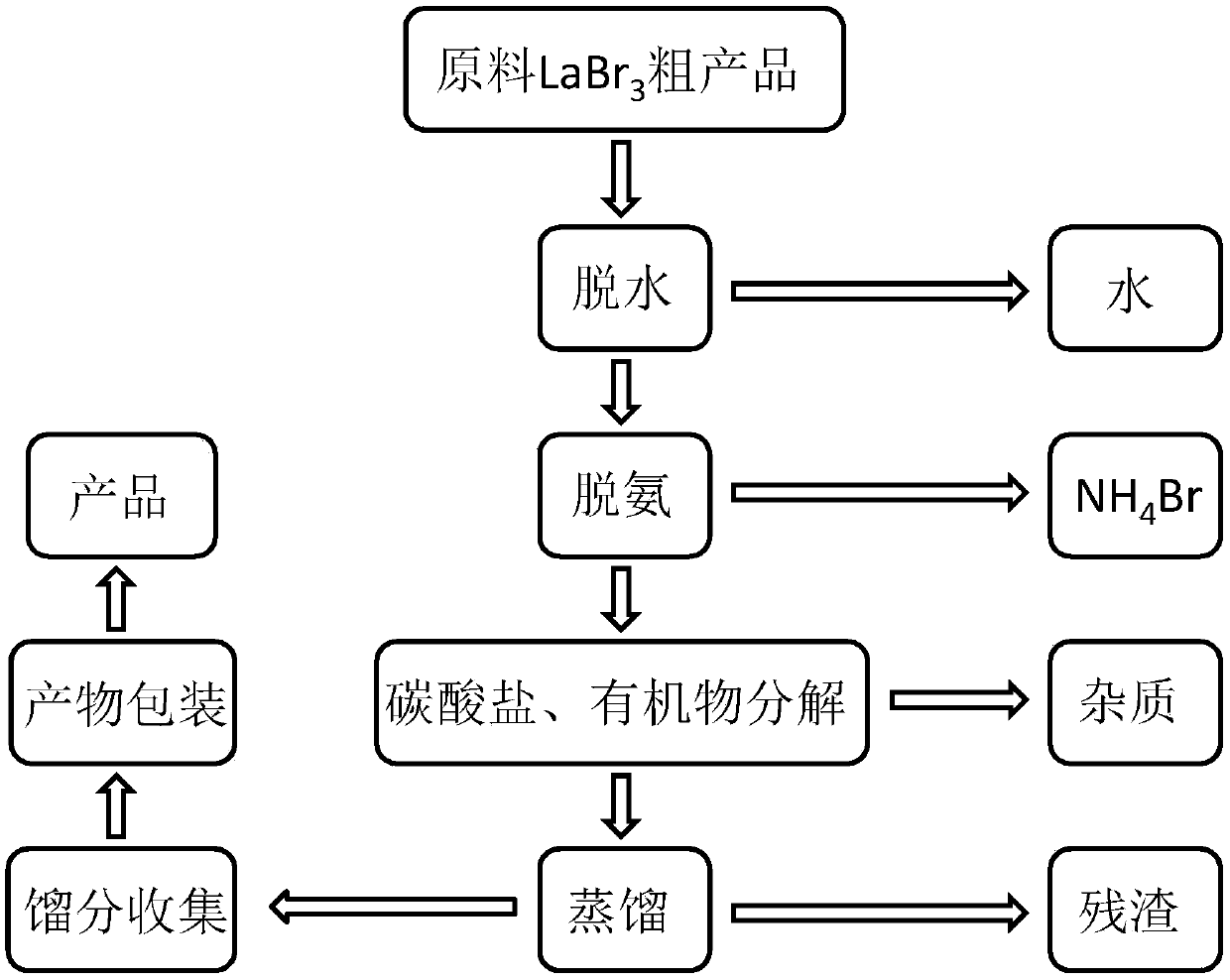
[0034] The process flow diagram of this embodiment after obtaining thick anhydrous lanthanum bromide is shown in figure 1 .
Embodiment 2
[0036] Weigh 1 kg of cerium carbonate, add it gradually and completely dissolve it in a certain amount of commercially available concentrated hydrochloric acid (cerium carbonate and concentrated hydrochloric acid are added in a stoichiometric ratio), until the pH of the solution is 5-7, heat to 130°C to concentrate and crystallize Obtain cerium chloride hydrate crystals, transfer the obtained cerium chloride hydrate crystals to a vacuum device, and treat at 250°C for 10 hours to obtain crude anhydrous cerium chloride; transfer the crude anhydrous cerium chloride to a vacuum distillation device, and vacuumize Afterwards (vacuum pressure is 1100Pa at this moment) be warming up to 230 DEG C of insulation 5h, continue to heat up to 500 DEG C of insulation 4h, continue to heat up to 835 DEG C of insulation 5h, continue to heat up to 940 DEG C, insulation 15h, and receive distilled cerium chloride, Obtain high-purity anhydrous cerium chloride. After testing, the oxygen content in th...
Embodiment 3
[0038] Weigh 1.5kg of lanthanum oxide, add it gradually and completely dissolve it in a certain amount of commercially available concentrated hydrochloric acid (adding lanthanum oxide and concentrated hydrochloric acid according to the stoichiometric ratio), until the pH of the solution is 5-7, heat to 135°C Concentrate and crystallize to obtain hydrated lanthanum chloride crystals, transfer the obtained hydrated lanthanum chloride crystals to a vacuum device, protect the flow of Ar gas, and treat at 260 ° C for 10 hours to obtain crude anhydrous lanthanum chloride; transfer the crude anhydrous lanthanum chloride to In the vacuum distillation device, after vacuuming (at this time, the vacuum pressure is 12Pa), the temperature is raised to 300°C for 5 hours, and then the temperature is raised to 550°C for 3.5 hours, and then the temperature is raised to 865°C for 5 hours, and the temperature is continued to 1000°C for 18 hours. Receive the distilled lanthanum chloride to obtain ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com