Analysis detection method for chromium metal element in solid food sample
A detection method and technology for metal elements, which are used in the preparation of test samples, analysis of materials, and material analysis by optical means, etc., can solve the problems of low heavy metal ion content, damage, complex composition, etc. The effect of eliminating interference, eliminating safety and environmental pollution problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] Embodiment 1 preparation solution
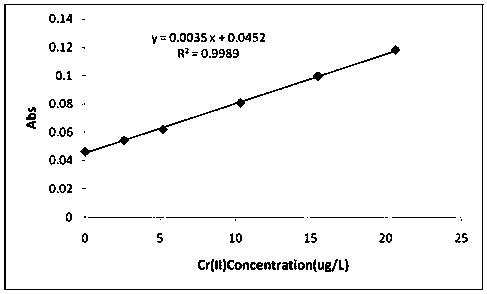
[0039] Mixed standard stock solution: pipette 2mL multi-element mixed standard solution (GBW08607: where the Cr concentration is 0.516μg / g). Dissolve in 25mL deionized water, shake well to obtain a mixed standard stock solution with a Cr concentration of 41.28 μg / L.
Embodiment 2
[0040] Example 2 Using ionic liquid and nitric acid to sample pretreatment
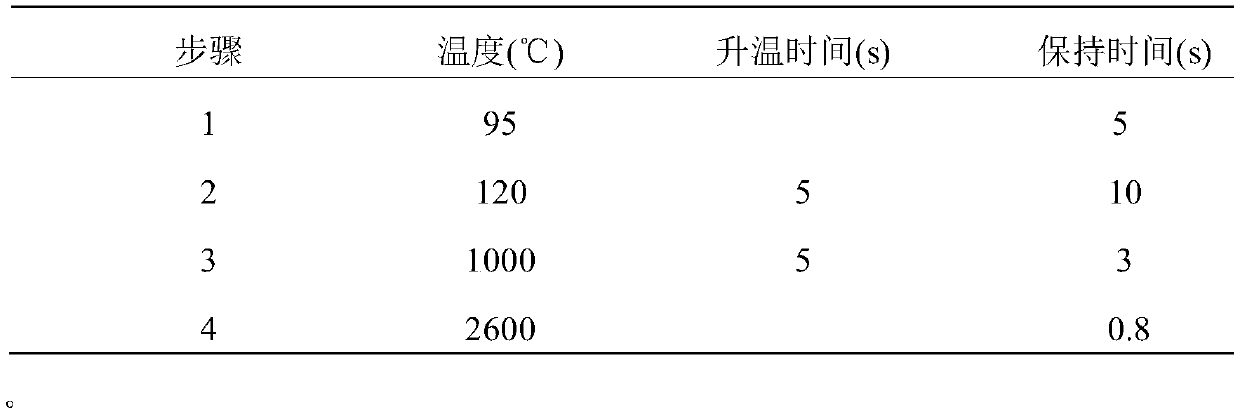
[0041] Accurately weigh 3g of ionic liquid [Bmim]-Cl and place it in a beaker, heat the beaker to 90°C to melt the ionic liquid [Bmim]-Cl crystals, remove and cool after completely melting, and accurately weigh 0.2g of sample powder into the beaker , the sample was evenly dispersed on the liquid surface, and 0.5mL concentrated HNO was added 3 , heated to 160°C, dissolved for 5 minutes, added deionized water to precipitate the cellulose, and set the volume to 50mL. After the precipitated cellulose naturally settled, take part of the upper clear night, and use the graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry to detect it.
Embodiment 3
[0042] The selection of embodiment 3 ashing temperature
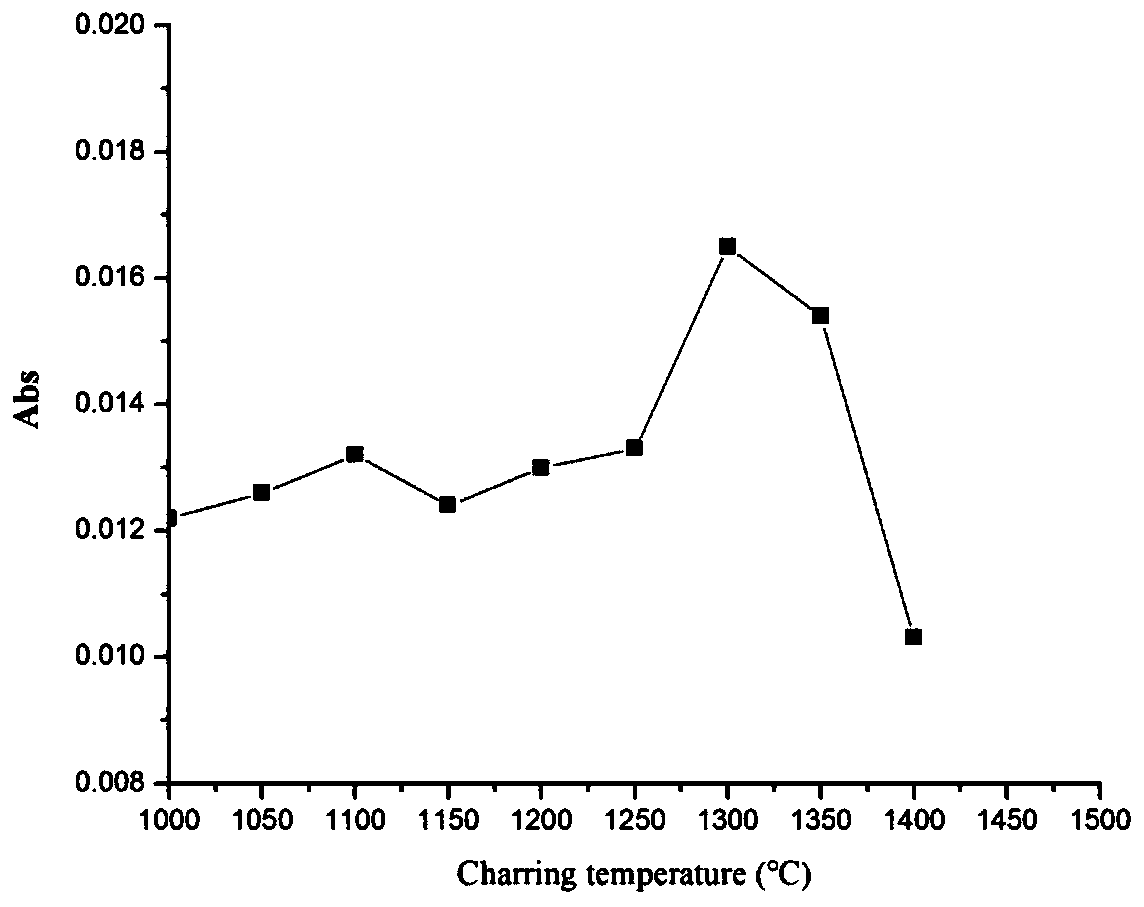
[0043] Since the aqueous solution of the ionic liquid [Bmim]-Cl contains organic matter, it is difficult to ash the organic matter completely when using a lower ashing temperature, which will interfere with the detection. When the ashing temperature is in the range of 1000℃~1400℃, the measured absorbance value of Cr element is shown in the attached figure 1 . It can be seen from the figure that when the ashing temperature is lower than 1300 °C when the Cr element is detected, the ionic liquid [Bmim]-Cl has an inhibitory effect on the detection signal, and when the ashing temperature reaches 1300 °C, the detection signal reaches the maximum value. It can be seen that the optimum ashing temperature is 1300°C.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com