High-speed large-range continuous tunable method for DFB array
A large-scale, array technology, applied to the structure of the optical resonant cavity, etc., can solve problems such as limitations, inability to scan the frequency range without interval splicing and coverage, and severe temperature fluctuations of the target
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
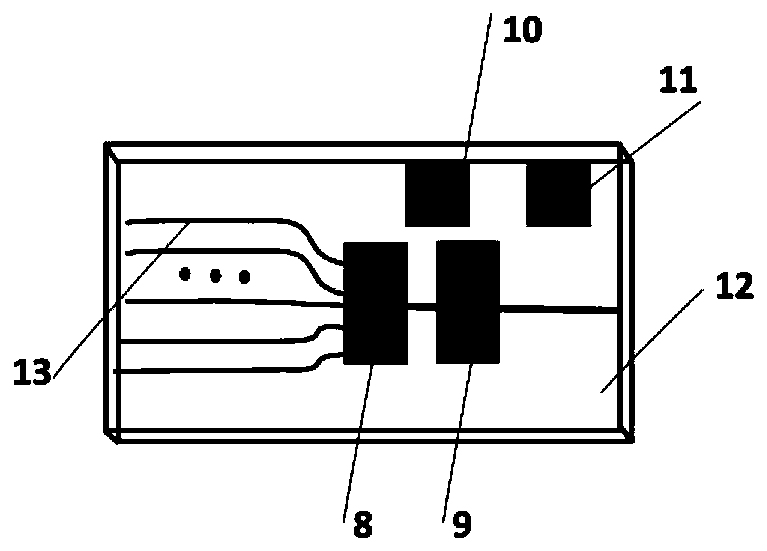
[0023] figure 1 It is a schematic diagram of the structure of a typical DFB array laser. Usually, it is composed of parallel laser diodes and a multimode interference coupler. For the D66 laser of Japan's FITEL company, it consists of 12 diodes with a wavelength spacing of 3.5nm. constitute. Temperature is typically used in its application to tune each diode to sweep across the 3.5 nm wavelength range. However, the current tuning sensitivity of this laser is very low, and only about 1nm can be tuned within its safe current range. However, in the solution proposed in this patent, temperature tuning is not used. Instead, current tuning is performed on each single tube and an attempt is made to expand the single tube frequency to achieve a single tube tuning range beyond the inherent wavelength spacing of adjacent diodes. For the D66 model For lasers, this value is 3.5nm.
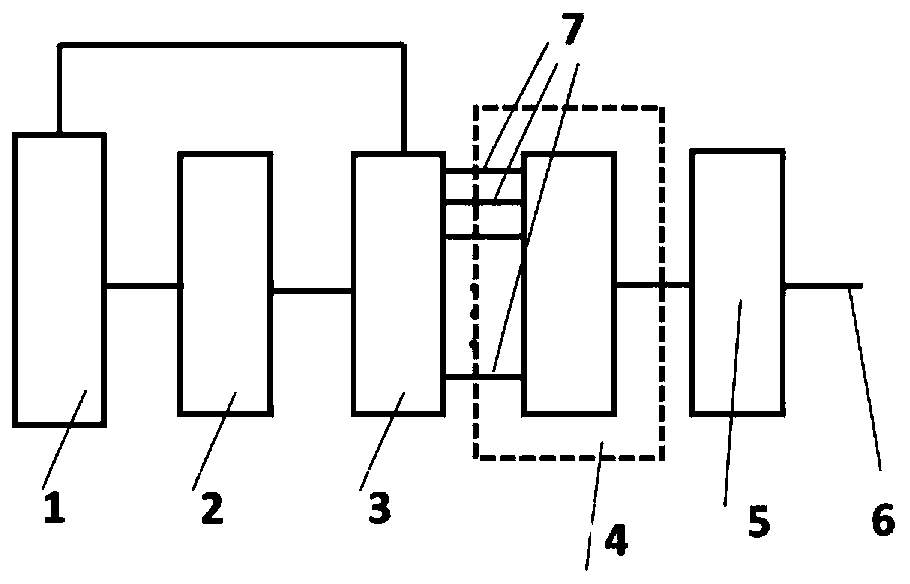
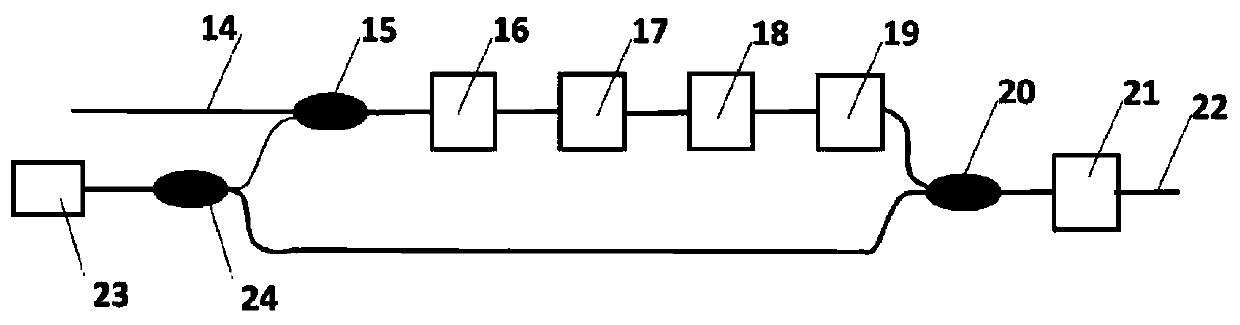
[0024] figure 2 It is the core process of the high-speed and large-range continuous tunable method of ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com