Novel semiconductor field-effect positive feedback transistor based on bulk silicon substrate and method thereof
A bulk silicon substrate and semiconductor technology, which is applied in the manufacture of transistors, semiconductor devices, semiconductor/solid-state devices, etc., can solve problems such as high price, increased process difficulty and cost, and incompatibility of bulk silicon materials, achieving low process difficulty, The effect of low process cost and high price
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
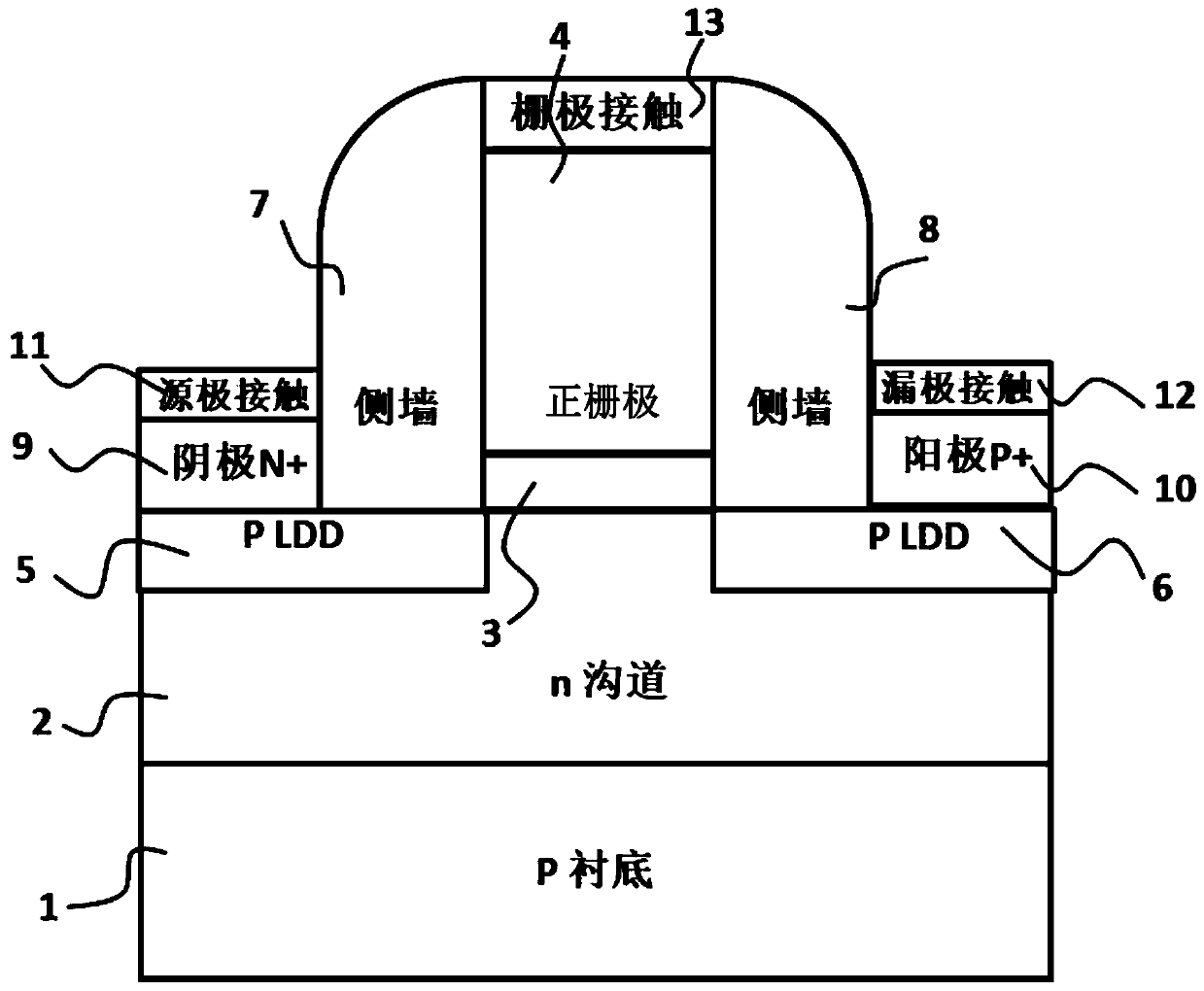
[0053] Such as figure 1 As shown, the novel semiconductor field effect positive feedback transistor based on a bulk silicon substrate of the present invention includes a substrate 1, an epitaxial channel layer 2, a gate oxide layer 3 covering the channel layer, and a positive gate 4 arranged sequentially from bottom to top; Specifically, the channel layer 2 is located on the substrate 1 , the gate oxide layer 3 is located on the channel layer 2 , and the positive gate 4 is located on the gate oxide layer 3 .
[0054] The substrate 1 is undoped or weakly doped, and the substrate 1 and the channel layer 2 are inversely doped, that is, one side is n-type doped while the other side is p-type doped. In the first embodiment, the substrate 1 is weakly p-type doped, and the channel layer 2 is n-type doped.
[0055] A low-drain doped region 5 (LDD) and a low-drain doped region 6 (LDD) are respectively provided on both sides of the positive gate 4, and both the low-drain doped region 5...
Embodiment 2
[0081] Such as figure 2 As shown, the device structure and method of Embodiment 2 are similar to Embodiment 1, the difference is that Embodiment 2 is a p-type device, while Embodiment 1 is an n-type device. Specifically: the substrate 1 in the second embodiment is n-type doped, the low-drain doped region 5 and the low-drain doped region 6 are both n-type doped, and the channel layer 2 is p-type doped.
[0082] The realization of the structure of the second embodiment only needs to replace the substrate 1 with n-type doping, the channel layer 2 with p-type doping, and the ion implantation of LDD with n-type on the basis of the first embodiment. Specifically: the substrate doping is weak n-type doping, and the doping concentration is 10 15 cm -2 to 10 19 cm -2 between. On the original silicon wafer, a p-type doped channel layer is epitaxially, and its doping concentration is 10 15 cm -2 to 10 19 cm -2 Between, and the thickness is between 50nm and 1000nm. In addition,...
Embodiment 3
[0084] Such as image 3 As shown, the device structure and method of the third embodiment are similar to the structure of the first embodiment, the difference lies in the formation of the cathode and anode regions. Among them, in the third embodiment, the epitaxy of the cathode region 9 and the anode region 10 does not require in-situ doping, nor does it require a mask; after the epitaxy, combined with photolithography and ion implantation, selectively Form the doping of n+ and p+; the specific steps are similar to the first embodiment, the difference is that step S6 and step S7 are replaced by the following steps: an epitaxial silicon layer with a thickness between 10nm and 100nm; Open the cathode area engraved, inject arsenic or phosphorus, the dose is 10 14 cm -2 to 10 16 cm -2 The energy is between 1keV and 10keV; the anode area is opened by photolithography, and boron or BF2 is implanted with a dose of 10 14 cm -2 to 10 16 cm -2 Between, the energy is between 1keV...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com