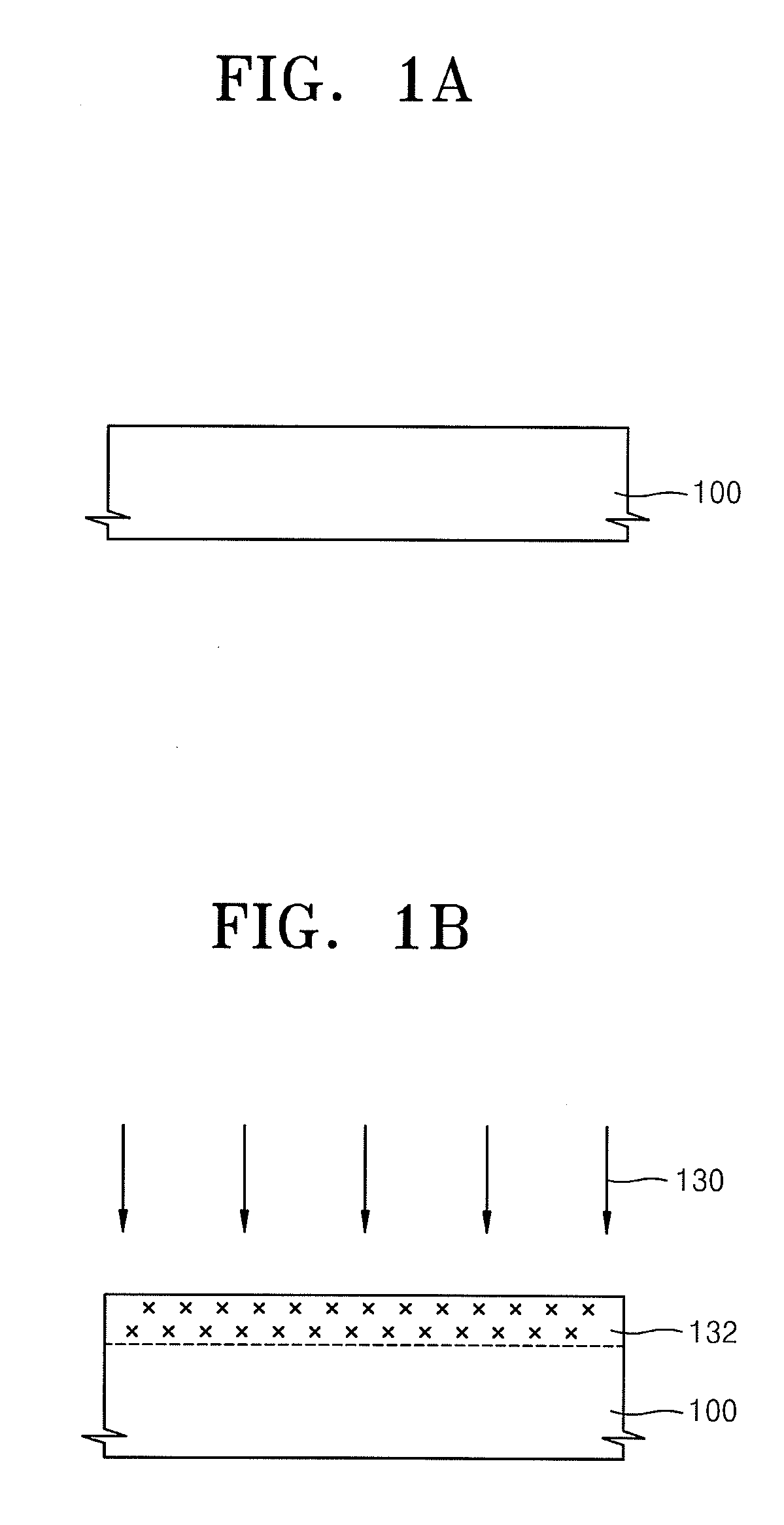
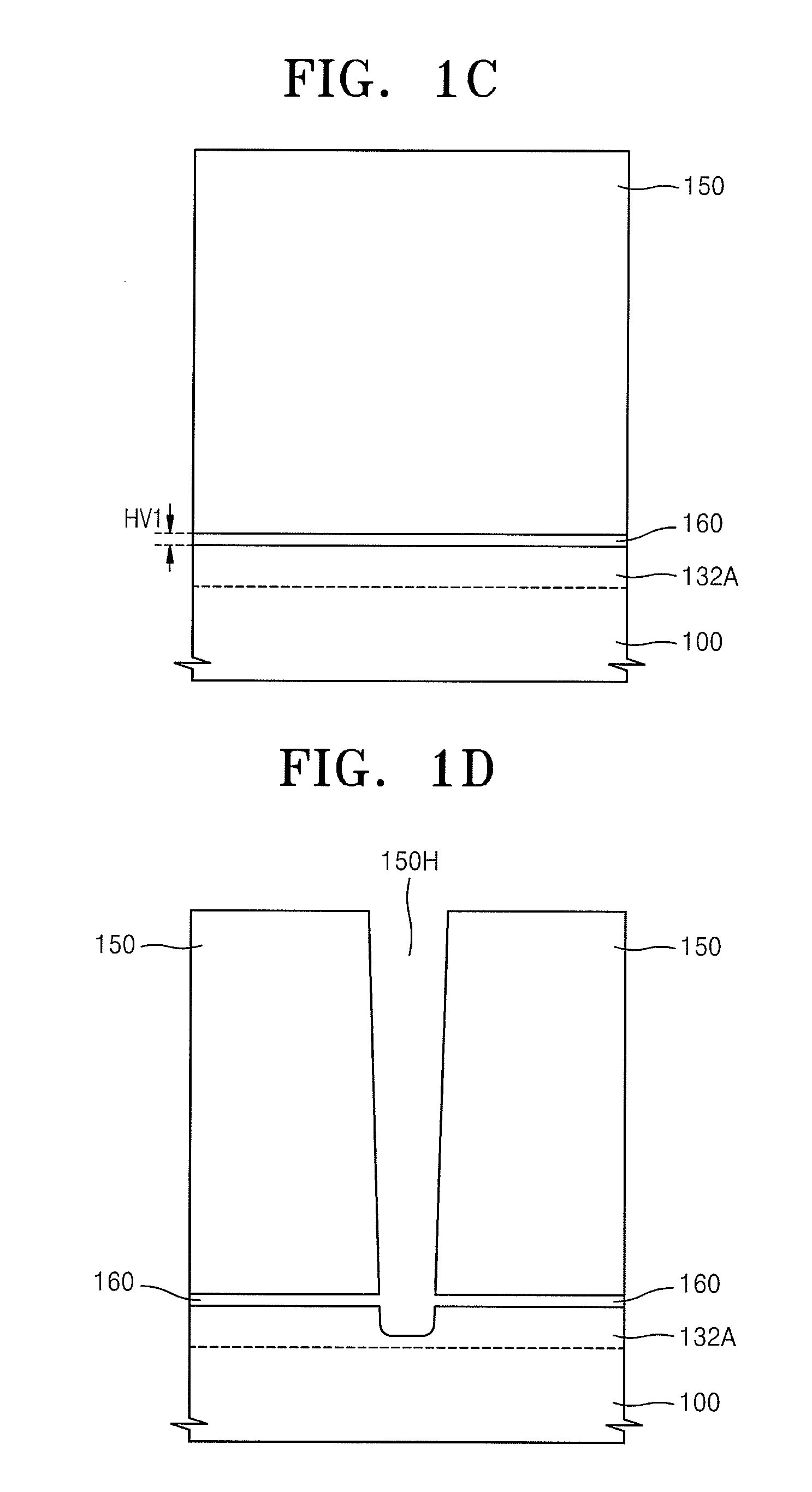
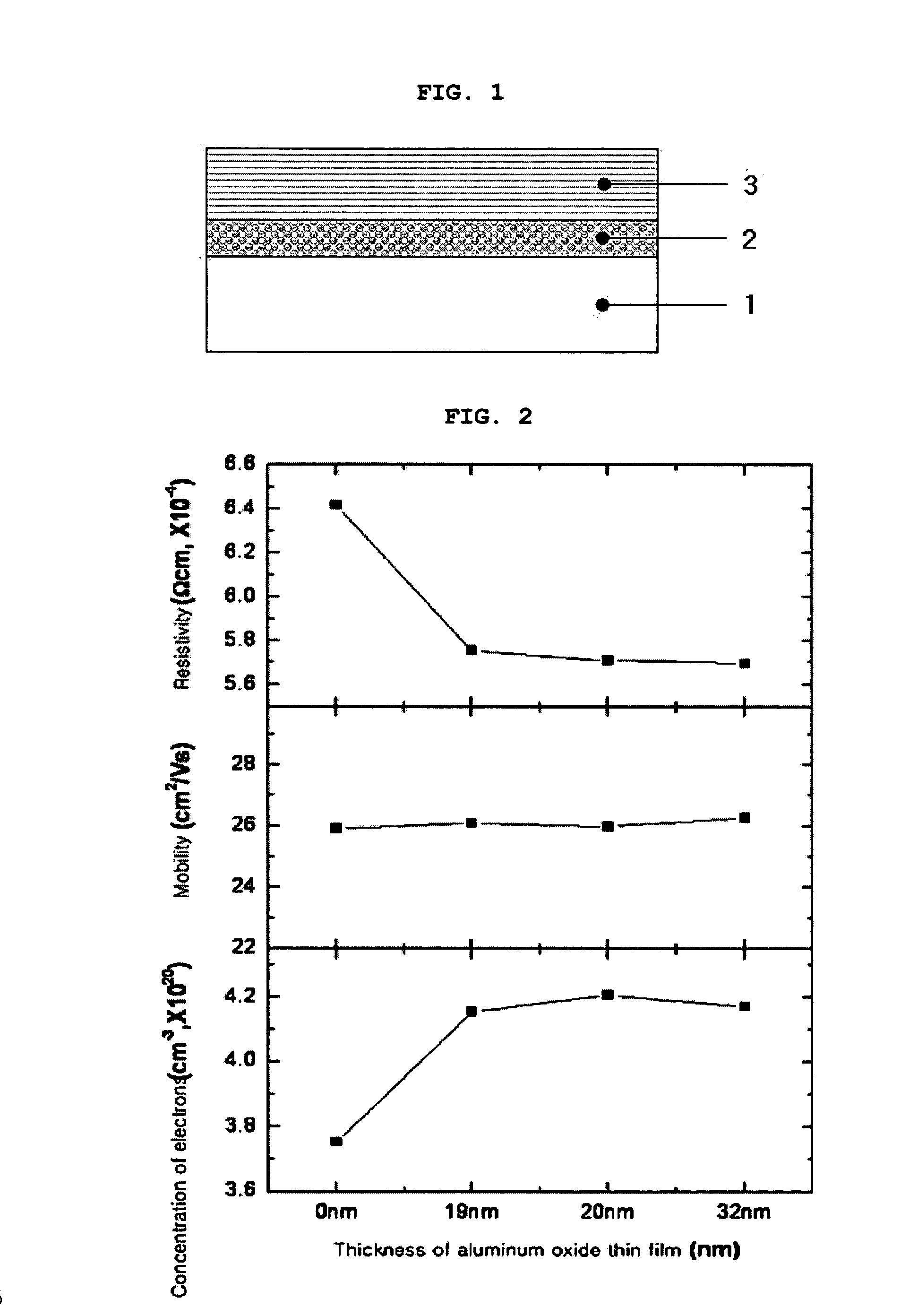
Patents
Literature
40 results about "Substrate doping" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
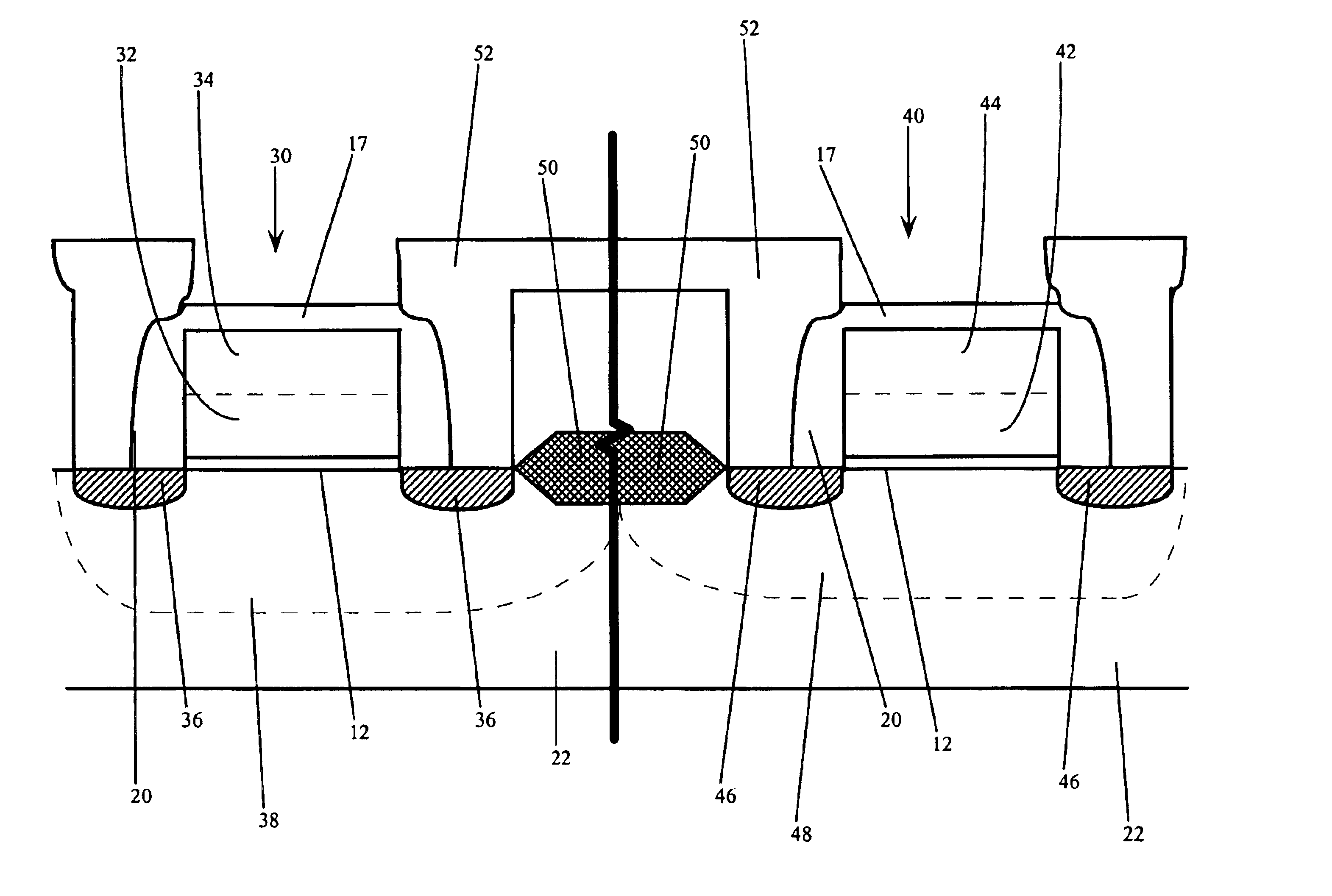
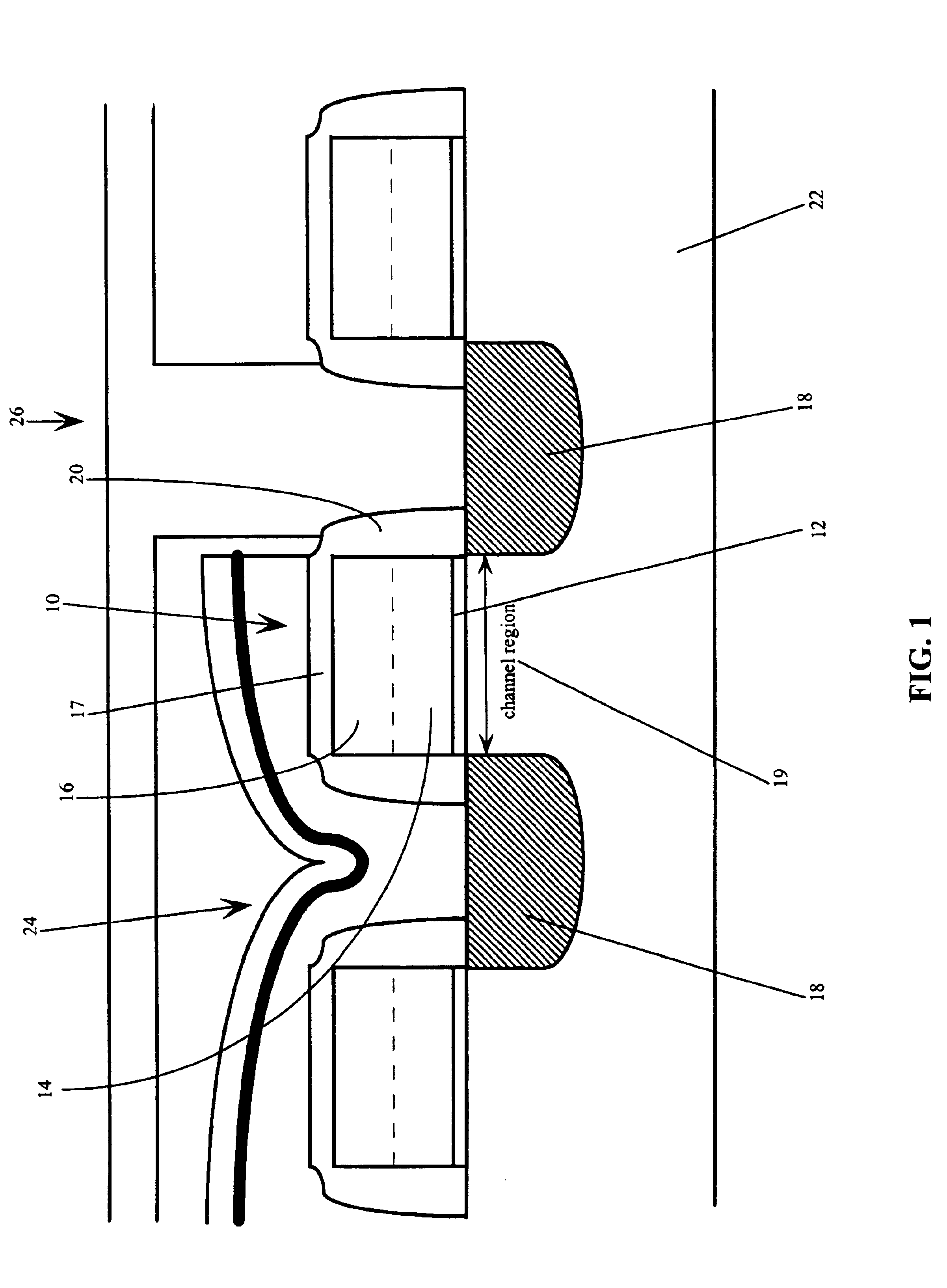
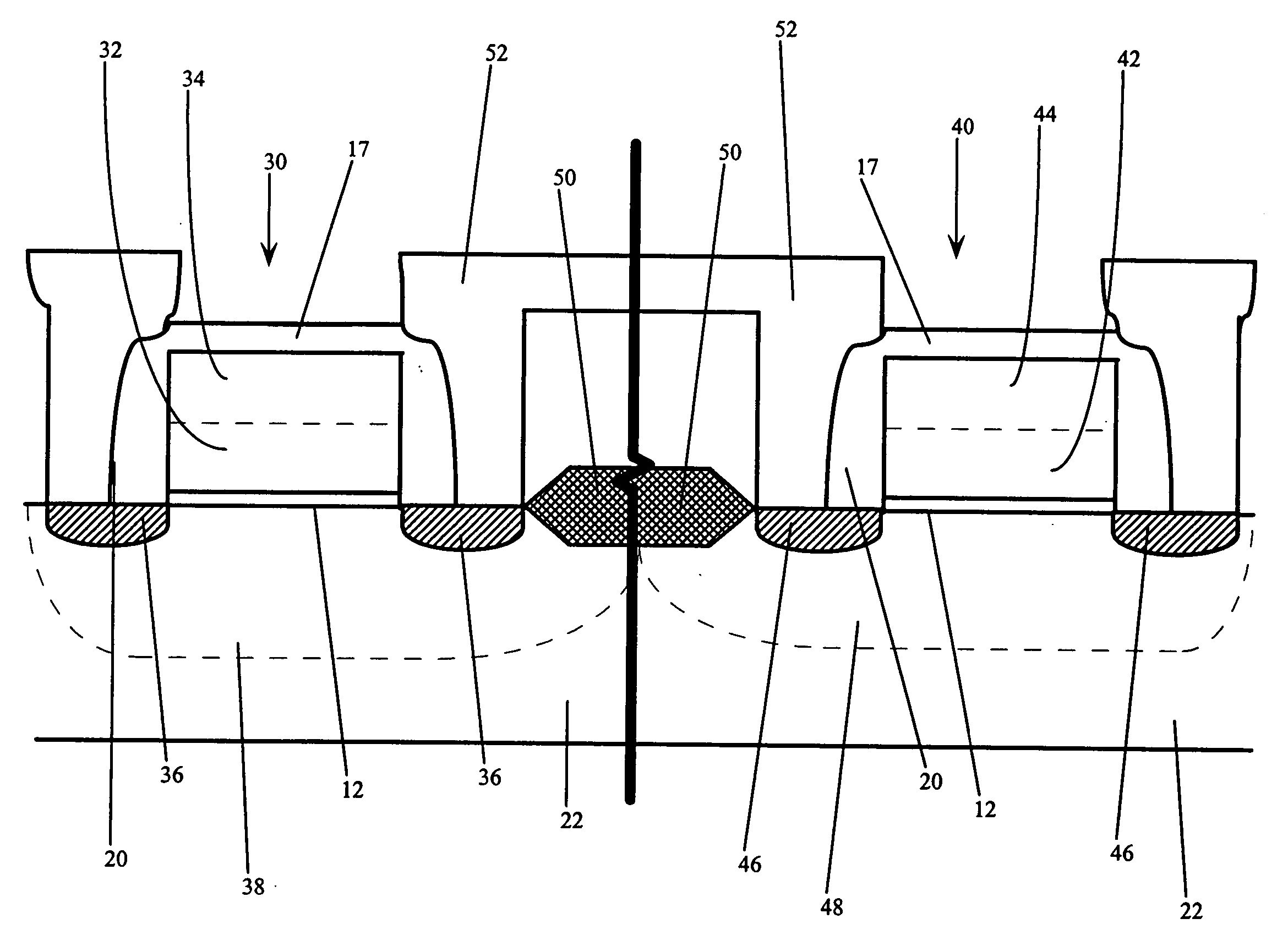
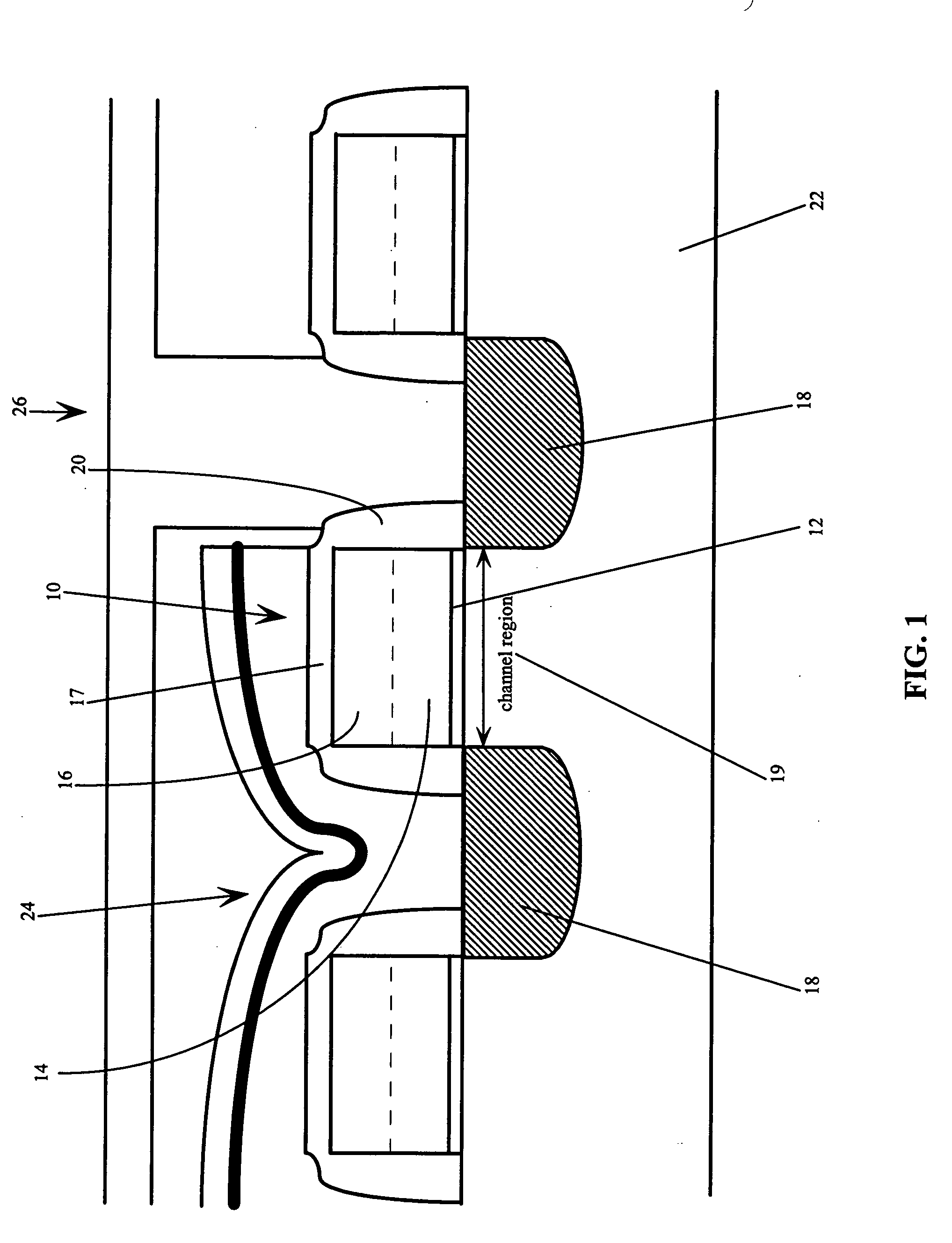
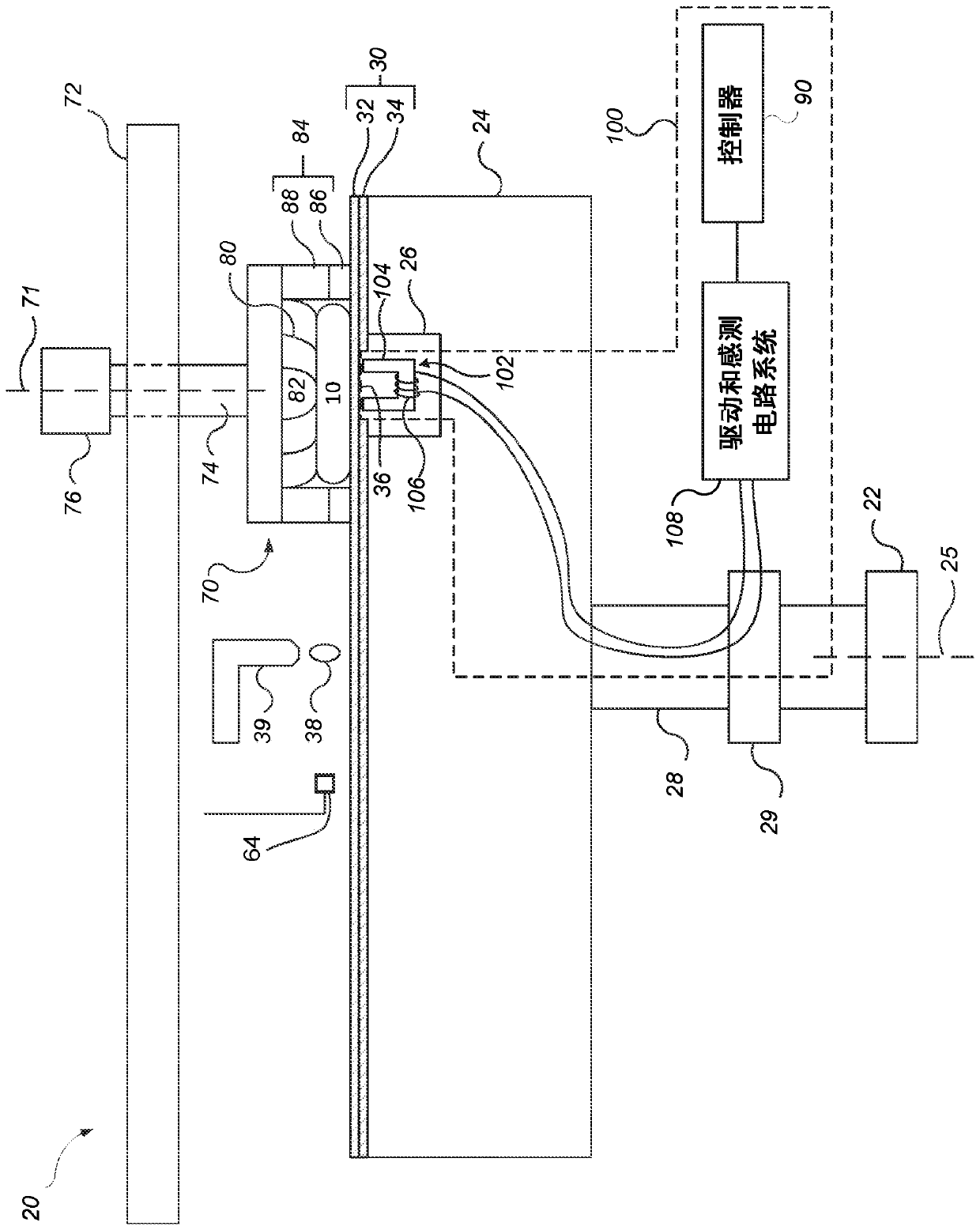
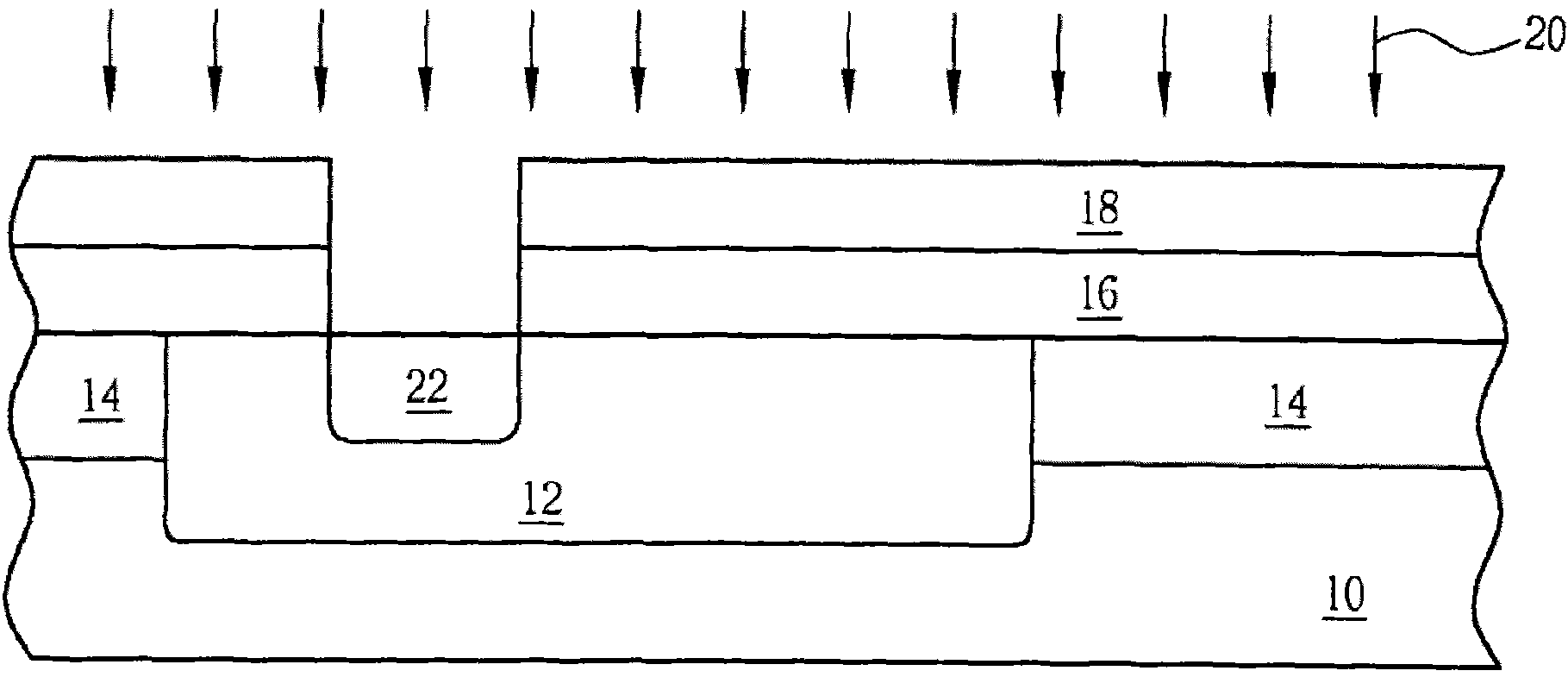
Use of gate electrode workfunction to improve DRAM refresh
InactiveUS6924190B2Reduce decreaseReduced channel region substrate dopingTransistorSolid-state devicesSubstrate dopingEngineering
This invention relates to a method and resulting structure, wherein a DRAM may be fabricated by using silicon midgap materials for transistor gate electrodes, thereby improving refresh characteristics of access transistors. The threshold voltage may be set with reduced substrate doping requirements. Current leakage is improved by this process as well.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON CONSUMER COPANIES
Semiconductor device including metal silicide layer and method for manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20110084320A1Improve production efficiencyShorten manufacturing timeTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSurface layerDevice material
A device formed from a method of fabricating a fine metal silicide layer having a uniform thickness regardless of substrate doping. A planar vacancy is created by the separation of an amorphousized surface layer of a silicon substrate from an insulating layer, a metal source enters the vacancy through a contact hole through the insulating later connecting with the vacancy, and a heat treatment converts the metal in the vacancy into metal silicide. The separation is induced by converting the amorphous silicon into crystalline silicon.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Conductive laminated body and method for preparing the same
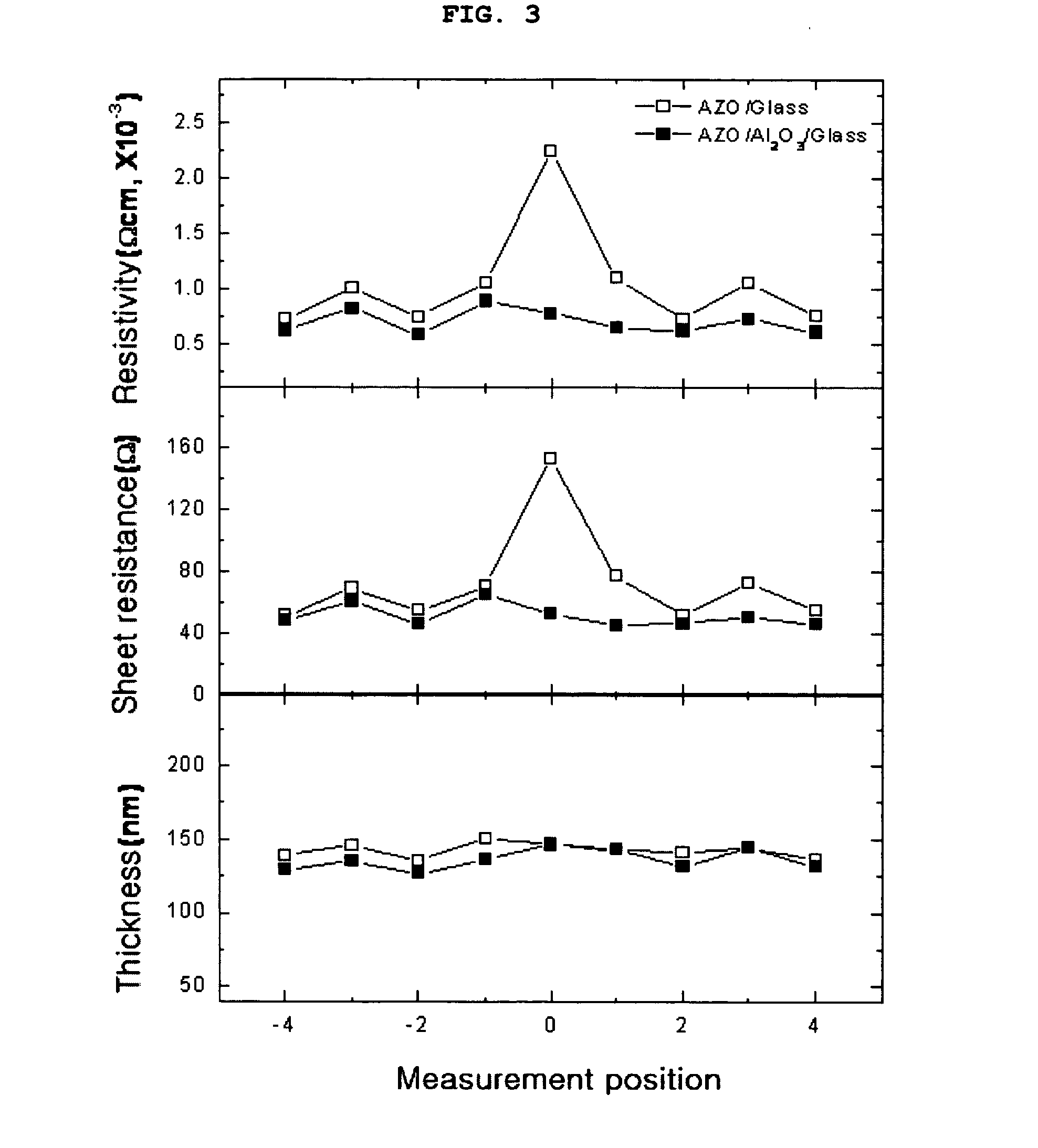
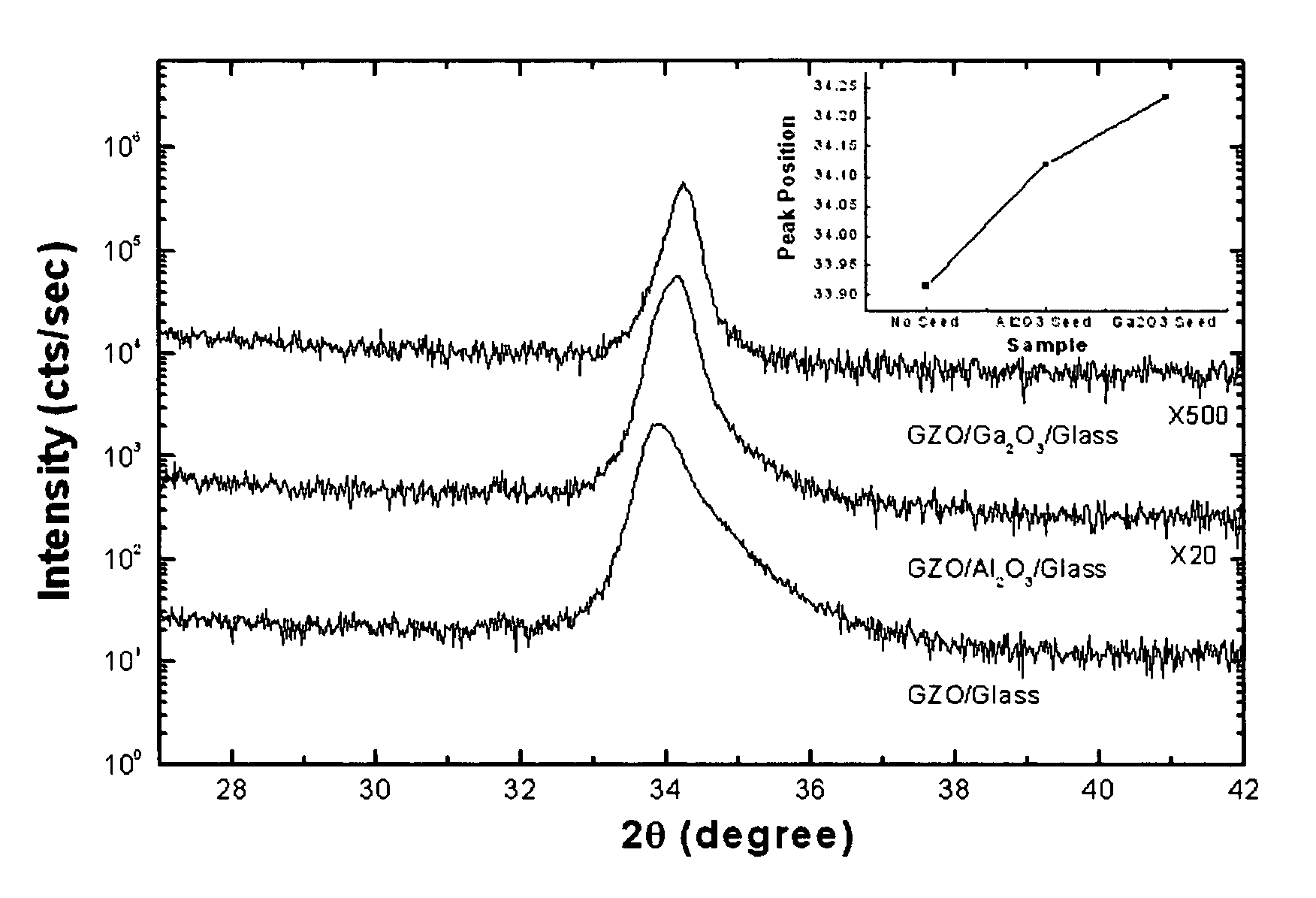
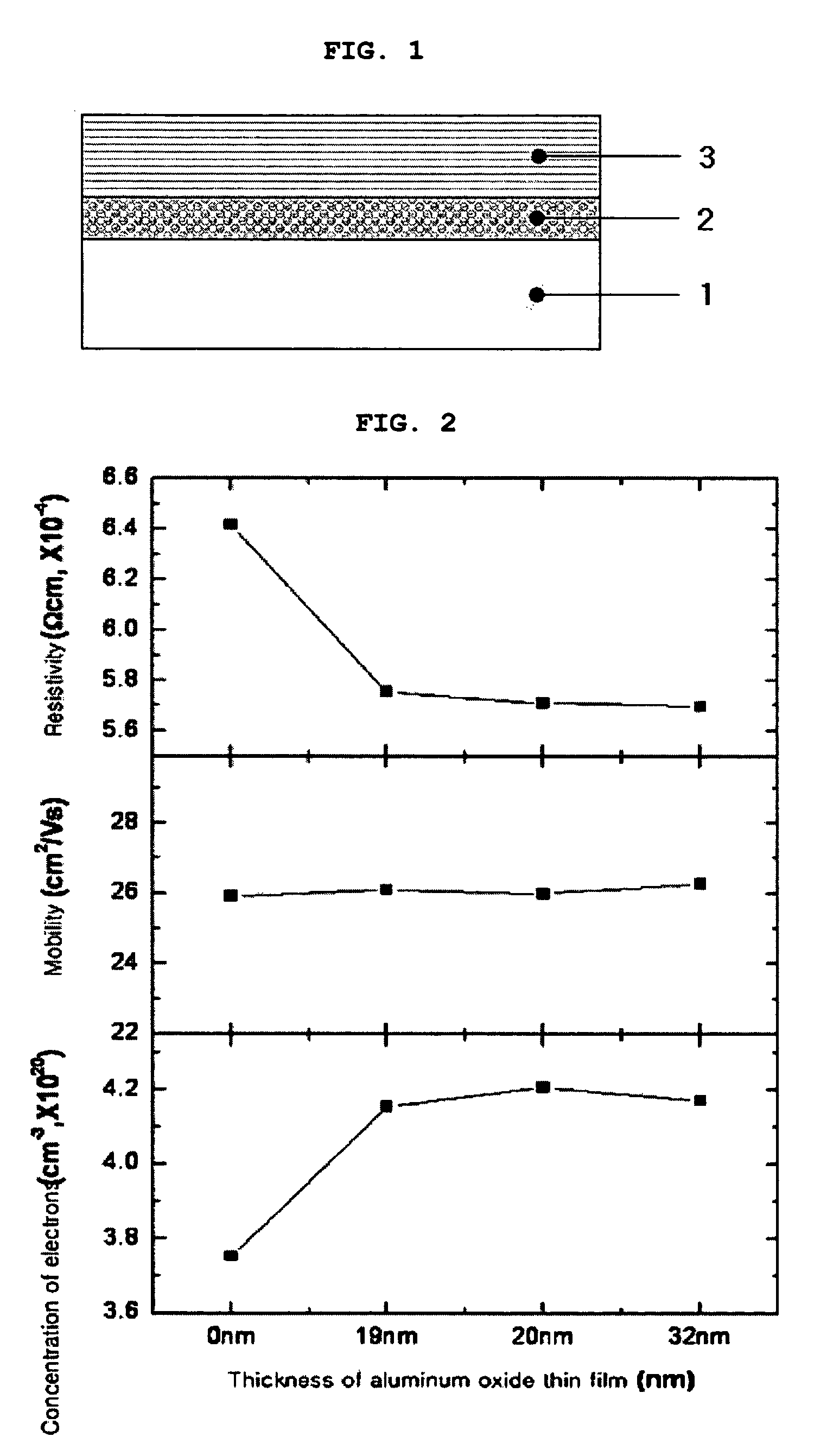
ActiveUS20100089623A1Increase electron concentrationLow mobilityConductive materialVacuum evaporation coatingHydrogenHeat resistance
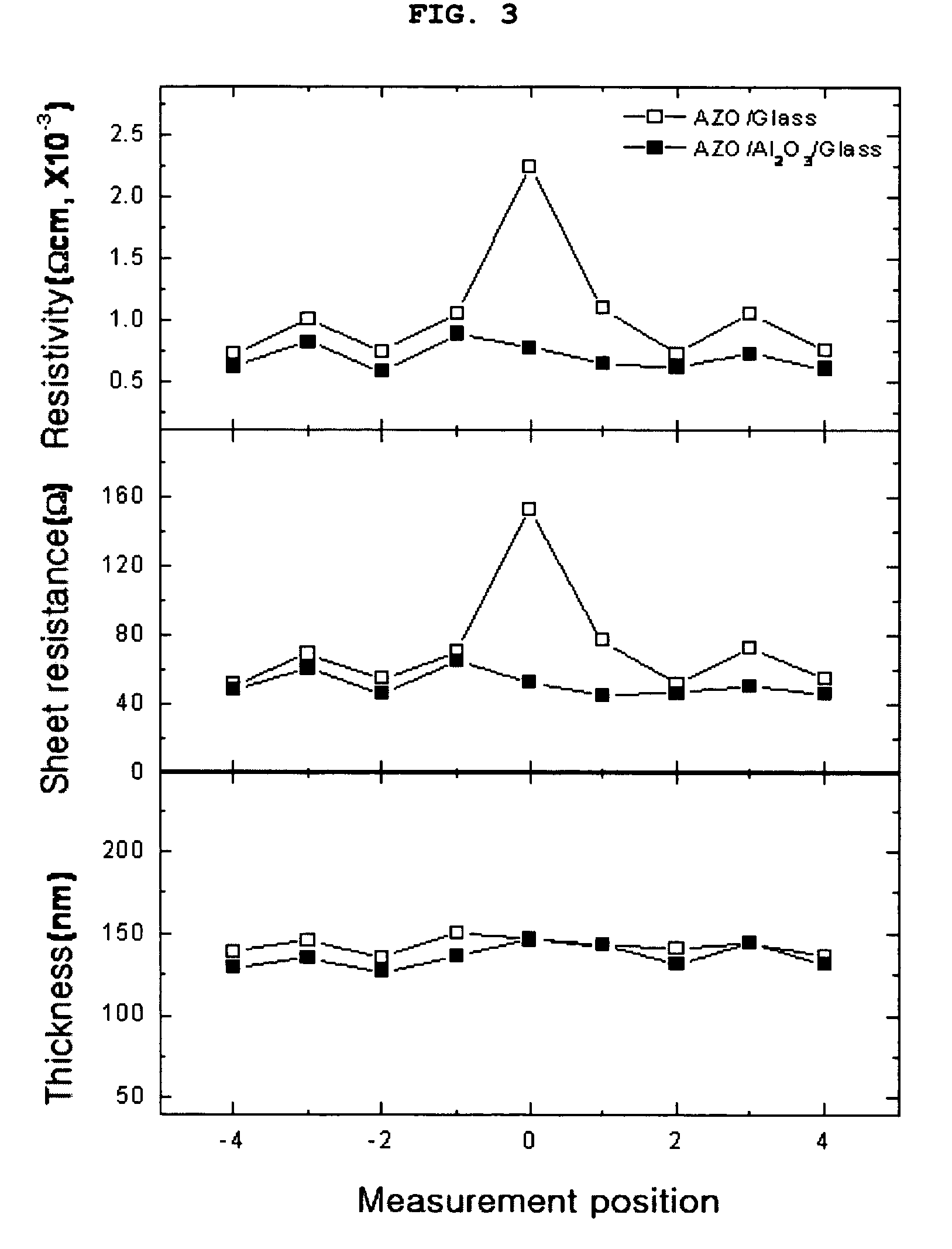
Disclosed is a conductive laminated body, and a method for preparing the same, wherein the conductive laminated body including: a substrate; a zinc oxide-based thin film doped with an element M; and an interlayer including an oxide M′2O3, which is interposed between the substrate and the zinc oxide-based thin film. The disclosed conductive laminated body includes a metal oxide interlayer of an oxidation number +3, between a substrate and a zinc oxide layer. Therefore, it is possible to improve electrical properties of a transparent conductive thin film, especially, a resistivity property, and to minimize the unevenness in electrical properties between a middle portion and a circumferential portion on the surface of the thin film in sputtering deposition. Also, in deposition of a zinc oxide film, in addition to inert gas such as argon gas, the use of hydrogen gas can improve the concentration of electrons, and herein, the interposition of an interlayer including a metal oxide, between the substrate and the zinc oxide-based transparent conductive film, allows the heat-resistance / moisture-resistance stability and the uniformity of electrical properties.
Owner:LG CHEM LTD
Power LDMOS device with junction field plate
InactiveCN103268890AImprove breakdown characteristicsLower on-resistanceDiodeEngineeringHigh pressure
The invention relates to a power LDMOS device with a junction field plate, and belongs to the technical field of power semiconductor devices. According to the power LDMOS device with the junction field plate, a buried layer opposite to a substrate doping type is formed on a substrate of a conventional LDMOS device, and the junction field plate formed by a PN junction is formed in the surface of a device drifting area. The power LDMOS device with the junction field plate uses PN junction electric field distribution in the junction field plate for modulating a device surface electric field, the distribution of the device surface electric field is made to be more even, the insufficiency of a peak of a tail end electric filed of a metal field plate can be effectively avoided, and breakdown performance of the device is improved. Under the reverse blocking state, the junction field plate has an auxiliary exhaustion function for the drifting area, the doping level of the drifting area can be improved to a large extent, and the on-resistance of the device is reduced. Meanwhile, reverse currents are small when reverse bias of the PN junction in the junction field plate occurs, the fact that leakage currents in the field plate are reduced is benefited, and the buried layer in the substrate can effectively improve the voltage endurance property of the device. The device has the advantages of being high in voltage, low in power consumption, low in cost and easy to integrate, and is suitable for power integrated circuits and radio frequency power integrated circuits.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA +1
Semiconductor device including metal silicide layer and method for manufacturing the same
ActiveUS8304819B2Uniform thicknessFew stepsTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsDevice materialMetal silicide
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Array substrate doping method and doping equipment
InactiveCN104485278ASimple processLow costSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSubstrate dopingPhotoresist
The invention discloses an array substrate doping method and doping equipment. The method includes the following steps: providing an array substrate on which a region to be heavily doped, a region to be lightly doped and a channel region to be doped are defined; forming a photoresist layer on the array substrate through a photolithography process, wherein a first photoresist part is formed on the photoresist layer corresponding to the region to be heavily doped, a second photoresist part is formed on the photoresist layer corresponding to the region to be lightly doped, a third photoresist part is formed on the photoresist layer corresponding to the channel region to be doped, the first photoresist part is thinner than the second photoresist part, and the second photoresist part is thinner than the third photoresist part; carrying out a one-time doping in the region to be heavily doped, the region to be lightly doped and the channel region to be doped via the photoresist layer, so as to form a heavily doped region, a lightly doped region and a doped channel region at a time respectively corresponding to the region to be heavily doped, the region to be lightly doped and the channel region to be doped. With the steps, one-time doping is realized in the region to be heavily doped, the region to be lightly doped and the channel region to be doped on the array substrate; the process is simplified; the cost is reduced.
Owner:TCL CHINA STAR OPTOELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
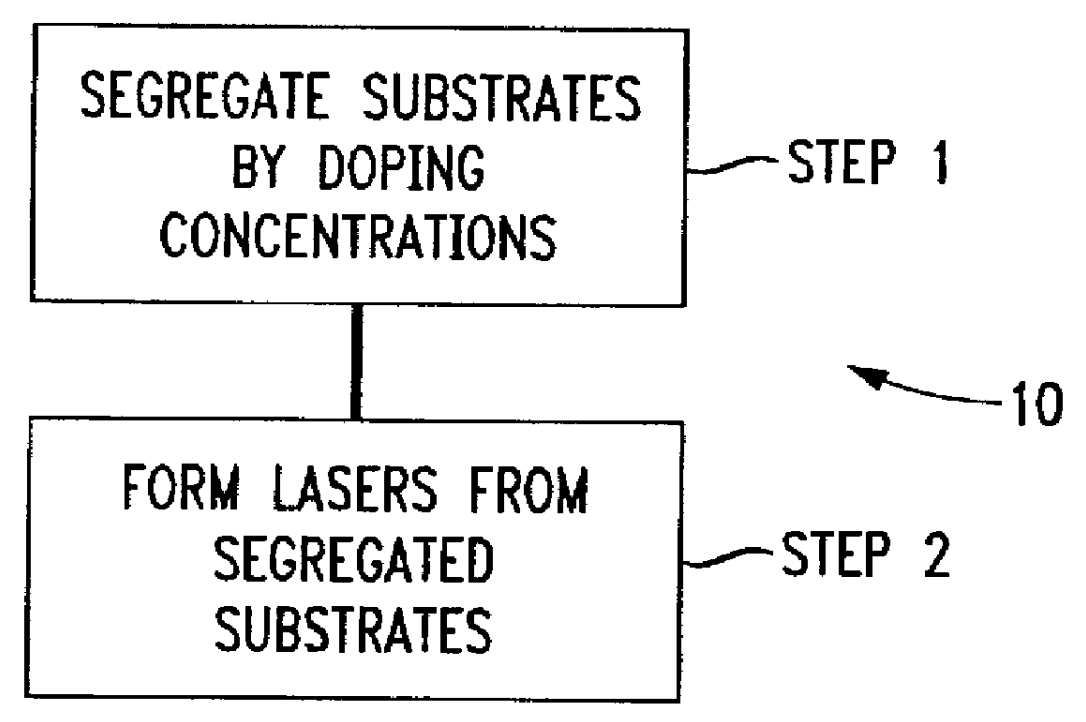
Method of improving laser yield for target wavelengths in epitaxial InGaAsP lasers based upon the thermal conductivity of the InP substrate
A method of producing a batch of MQW lasers from a plurality of wafers having doping concentrations within a concentration range. The MQW lasers are produced by epitaxially growing an InGaAsP quaternary layer on the substrates in a metal-organic chemical vapor deposition (MOCVD) reactor. The method includes the steps of segregating the substrates into groups based upon the substrate doping concentrations and batch producing the lasers at specific target wavelengths for each segregated substrate group.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
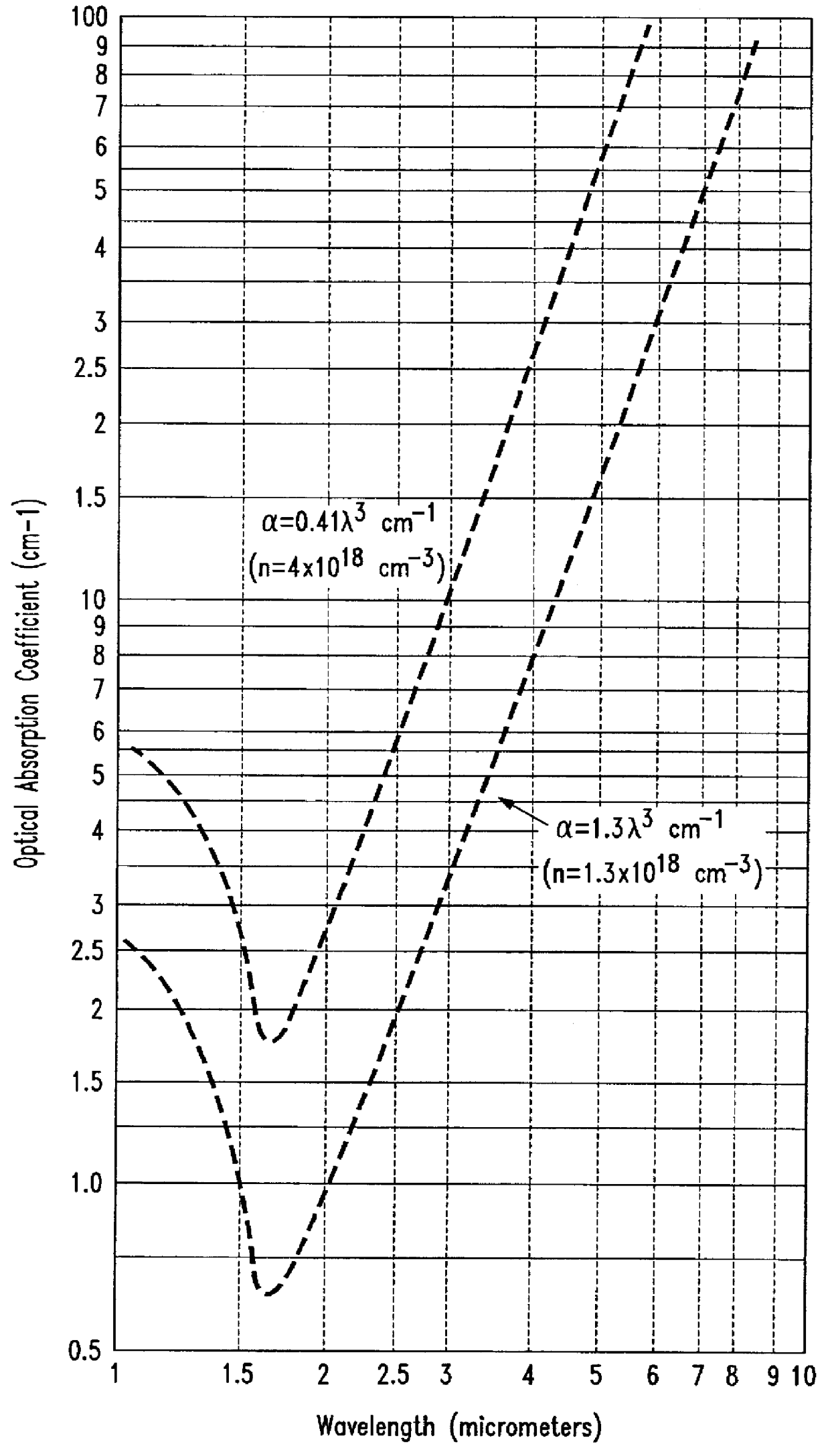
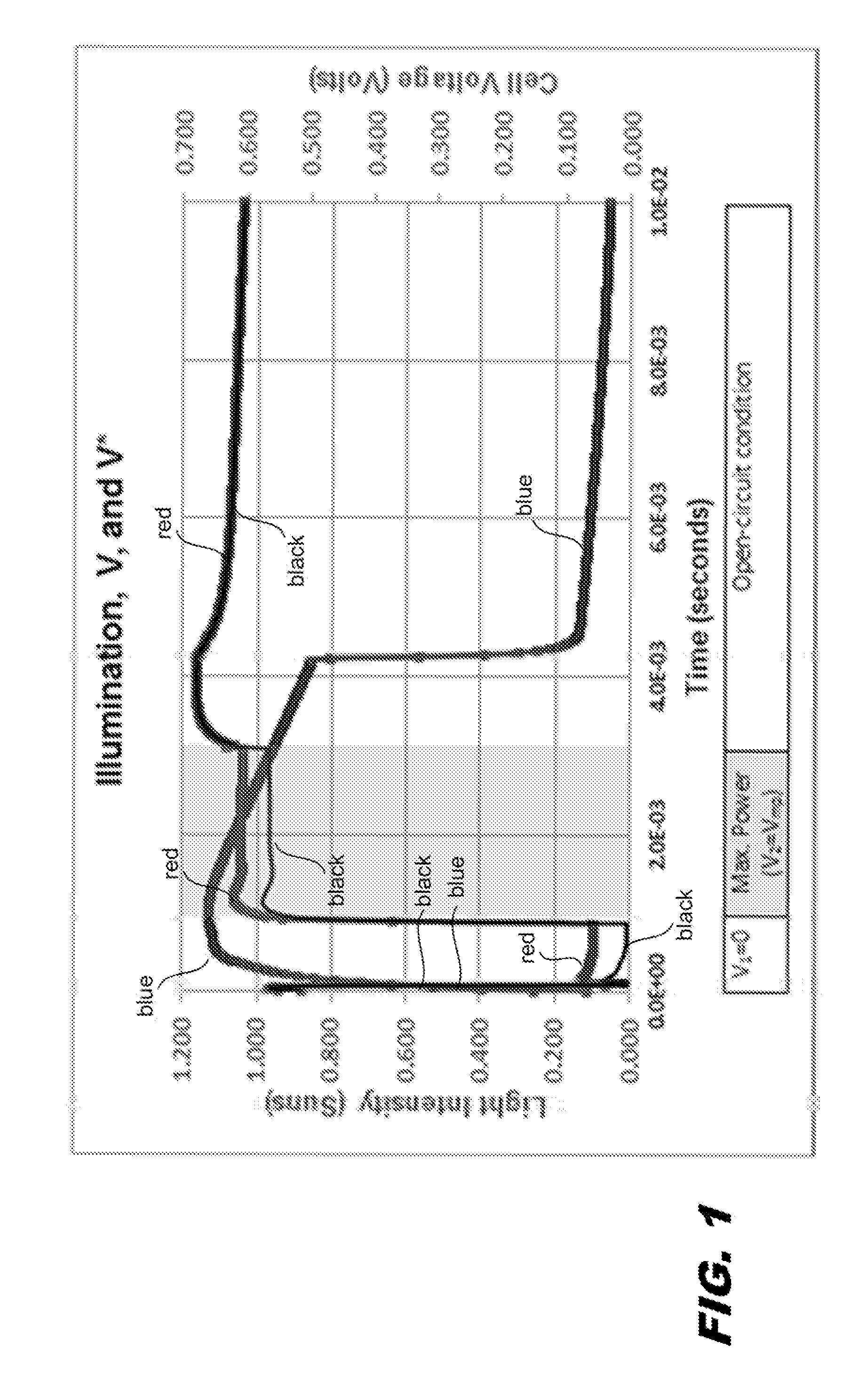
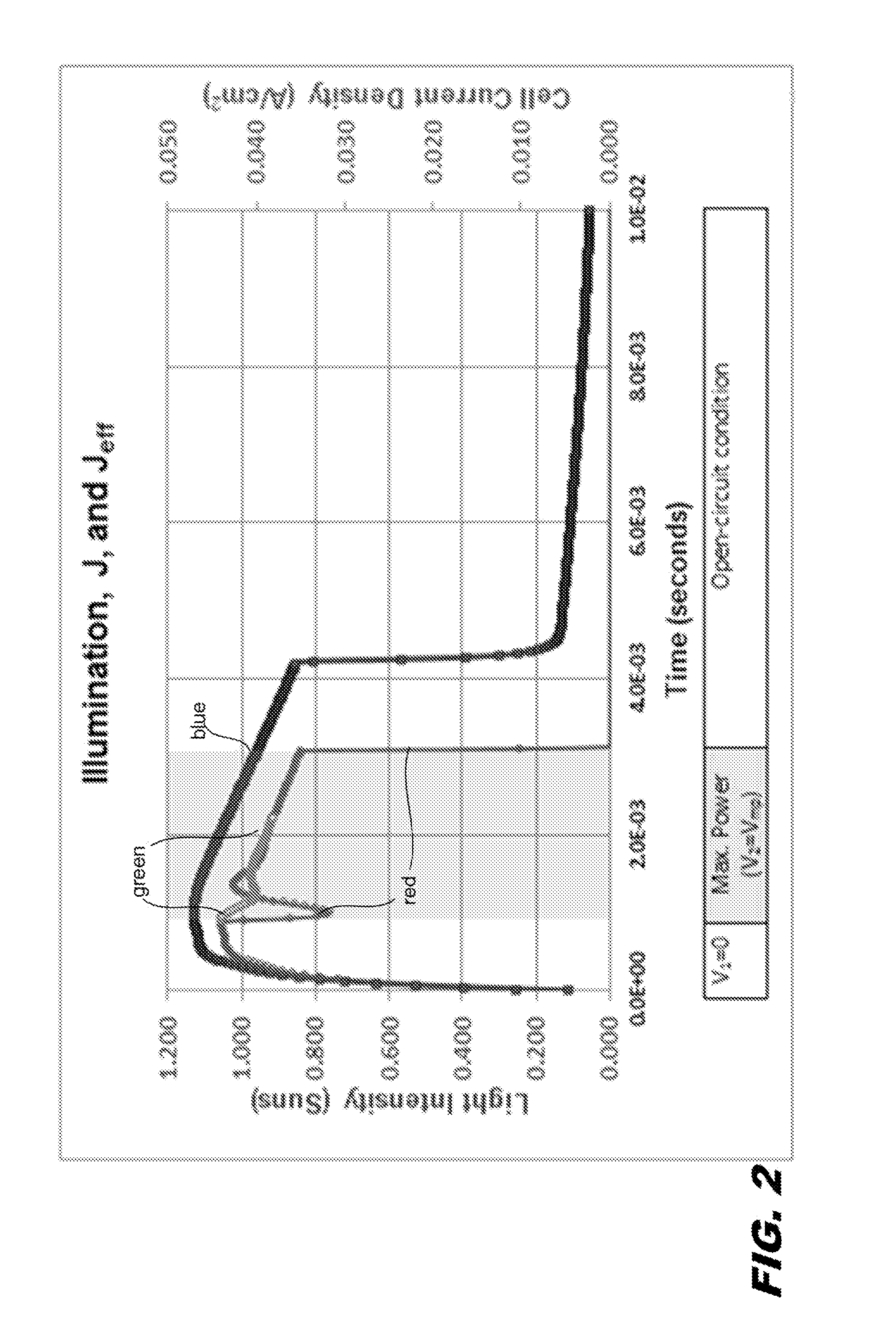
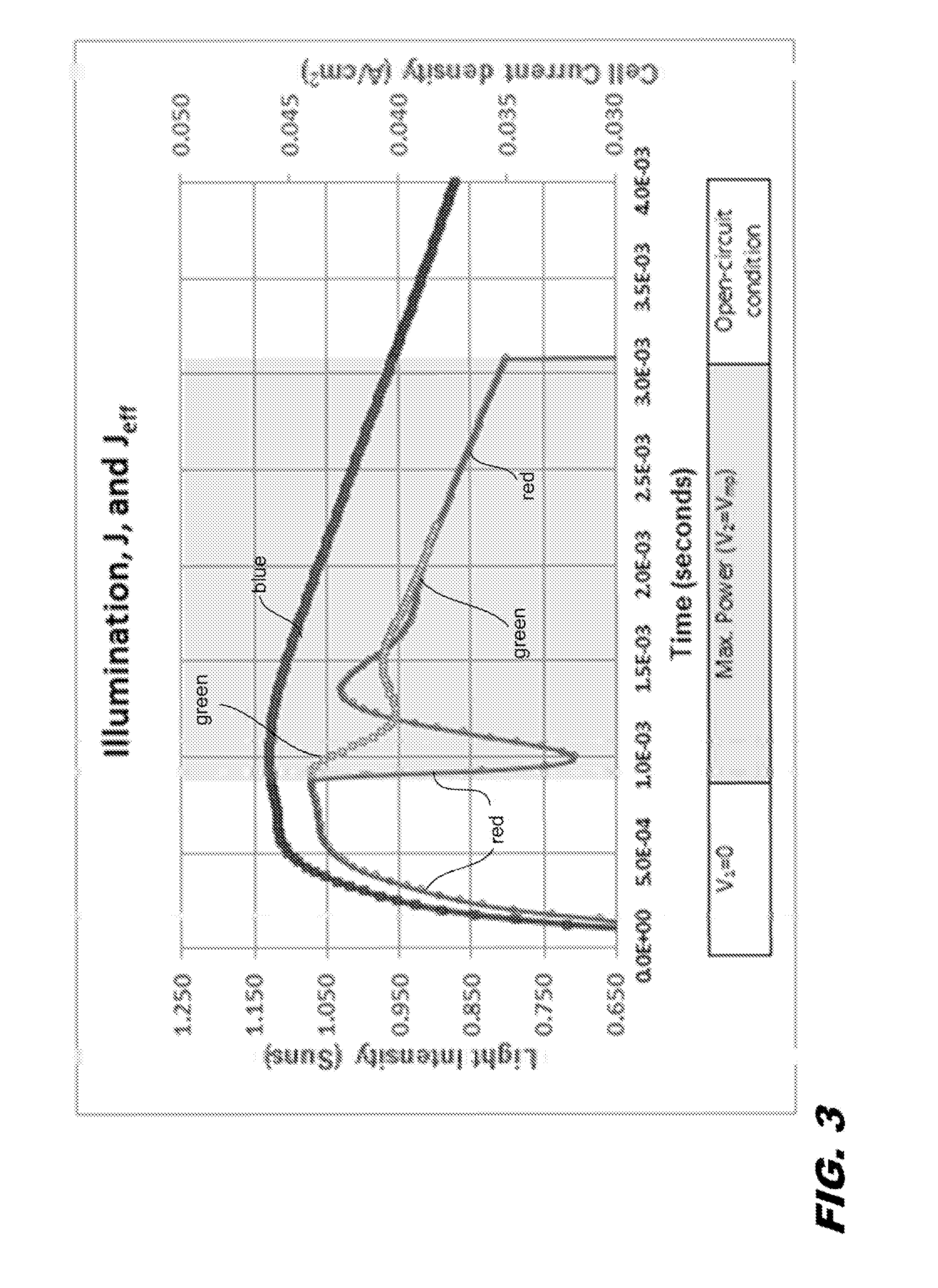
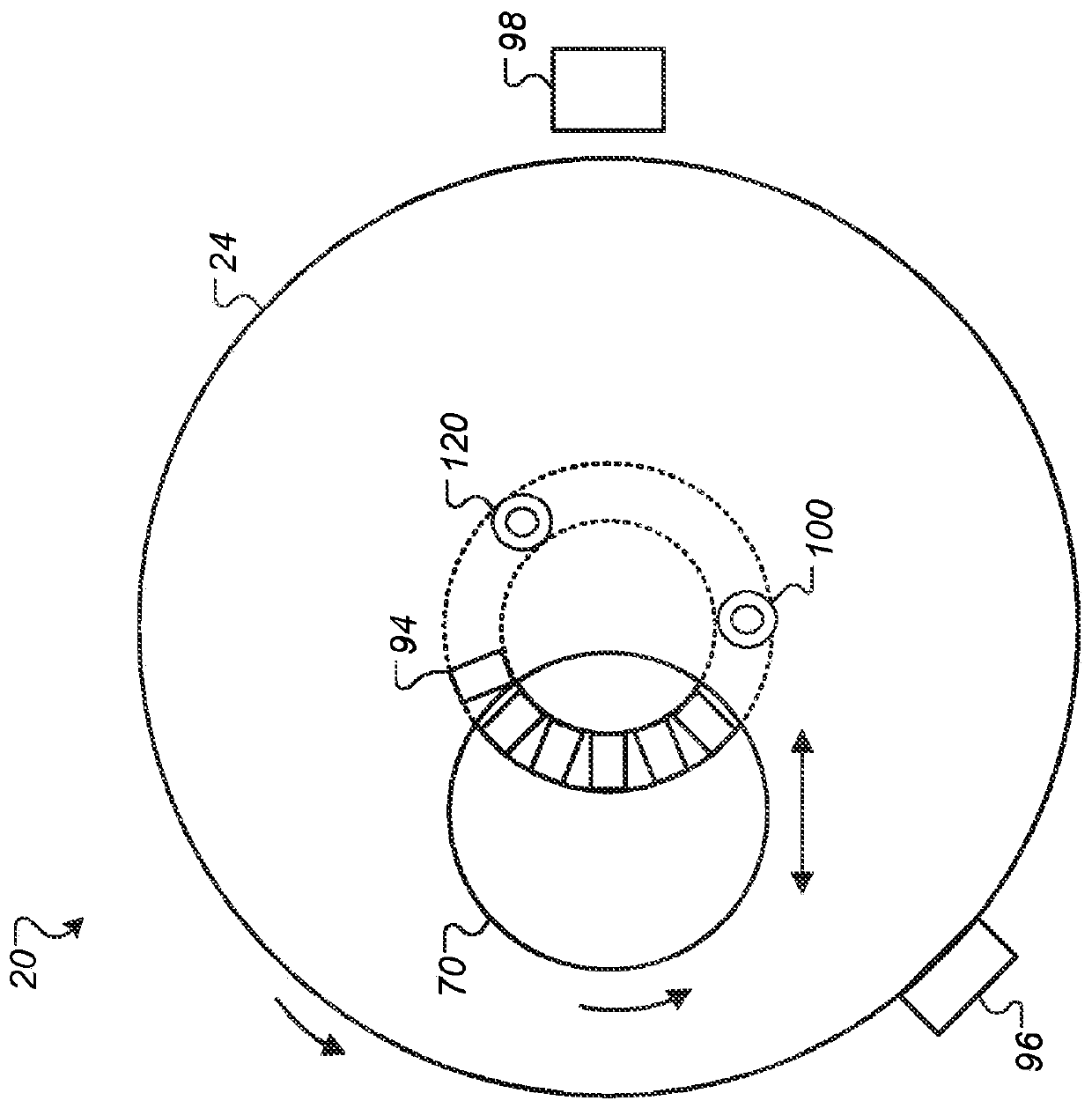
Characterization of substrate doping and series resistance during solar cell efficiency measurement
ActiveUS20140333319A1Photovoltaic monitoringResistance/reactance/impedenceSingle flashOperating point
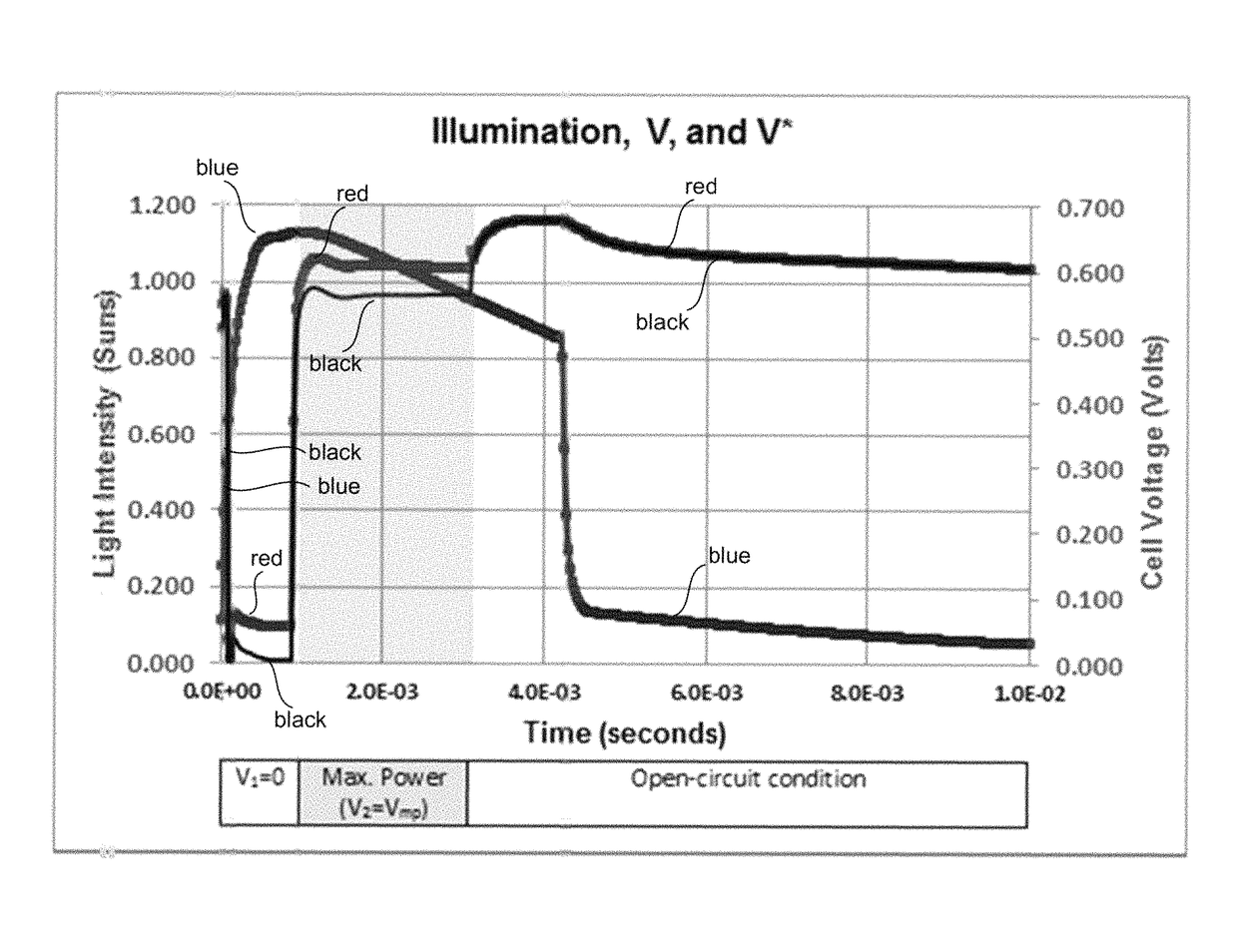
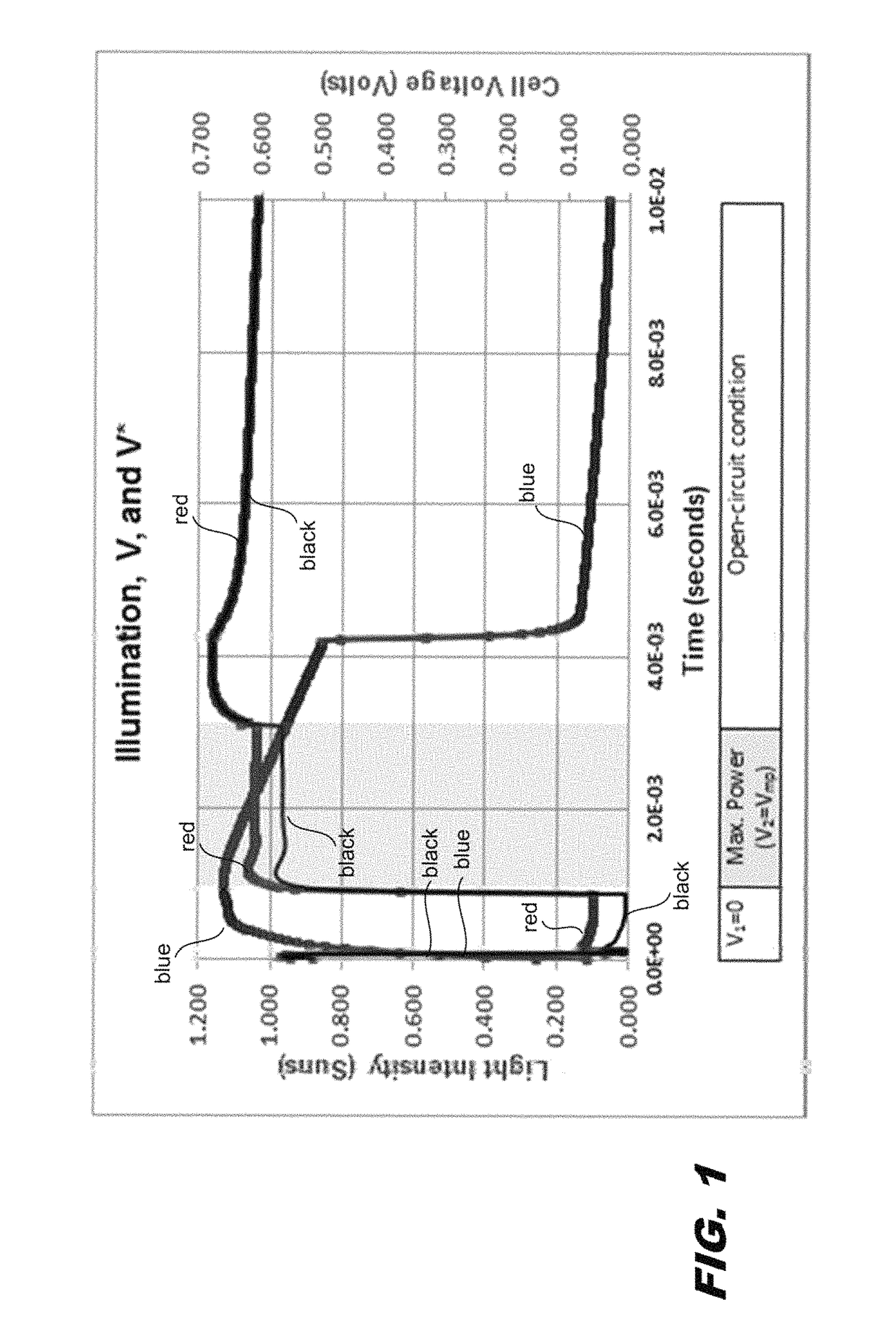
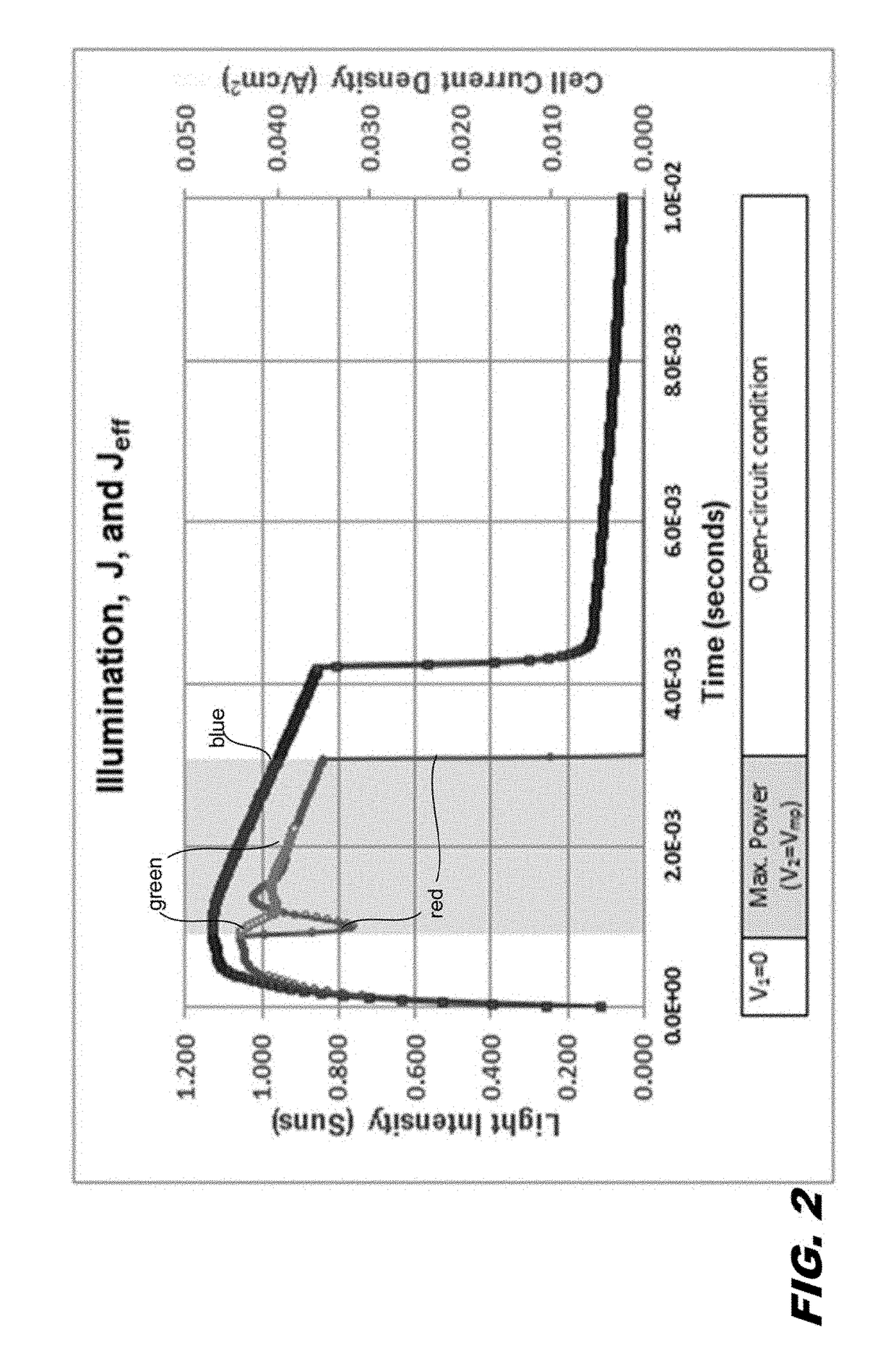
Short-circuit current, maximum power, and open circuit voltage during a single flash are determined by varying intensity, voltage, and current. An apparatus determines the substrate doping and the series resistance of the solar cell. The series resistance of the cell is determined from a voltage step from the maximum power voltage operating point to the open-circuit condition. Methods are described for determining the substrate doping from stepping or sweeping the voltage. The first uses a voltage step and finds the change in charge that results. This determines a unique doping if the series resistance is known. The second uses data for a case of varying current, voltage, and light intensity, and compares this data to the case of varying voltage and intensity with no current. By transposing both cases into the steady state, agreement between the two data sets is found for unique doping and series resistance values.
Owner:SINTON CONSULTING
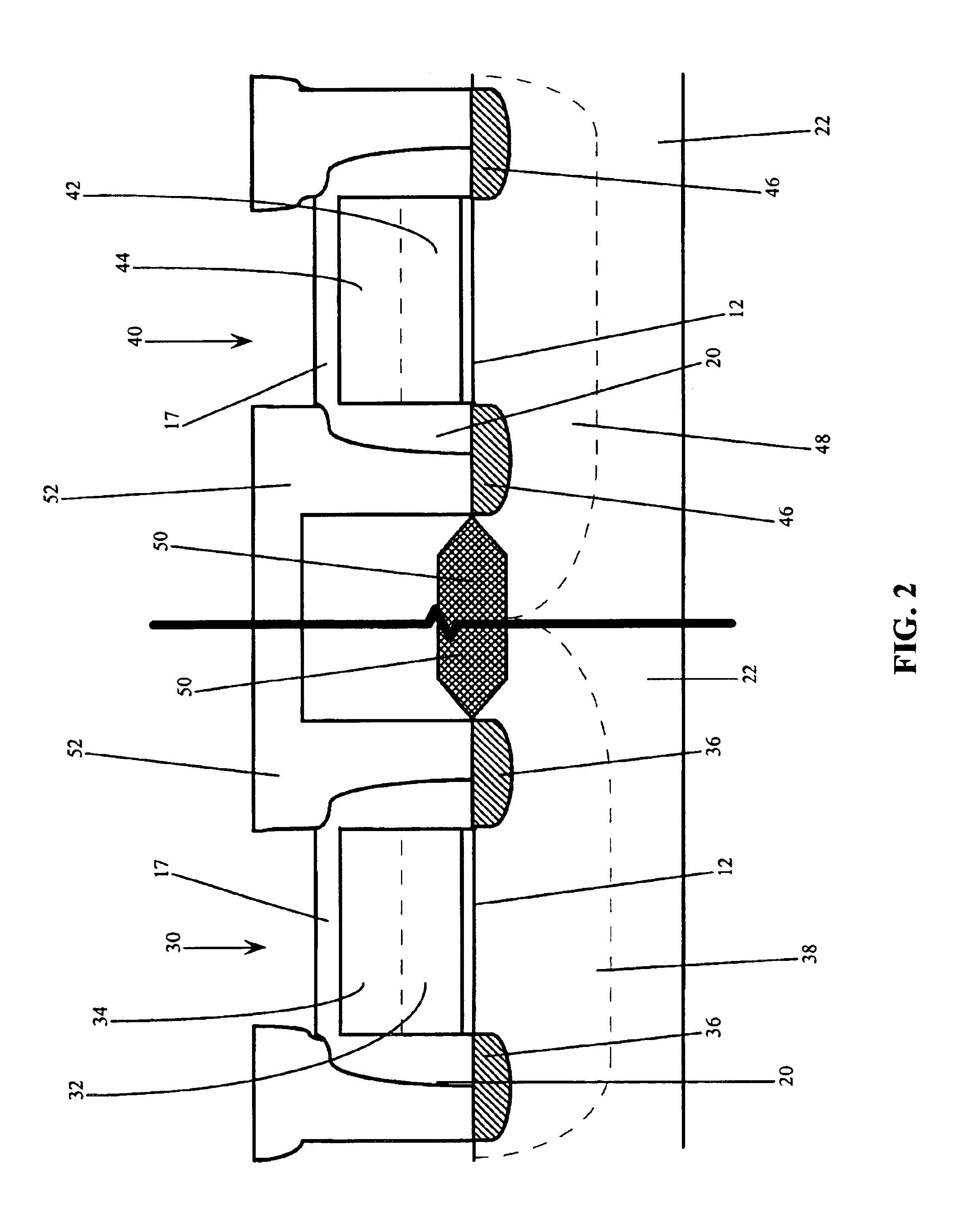
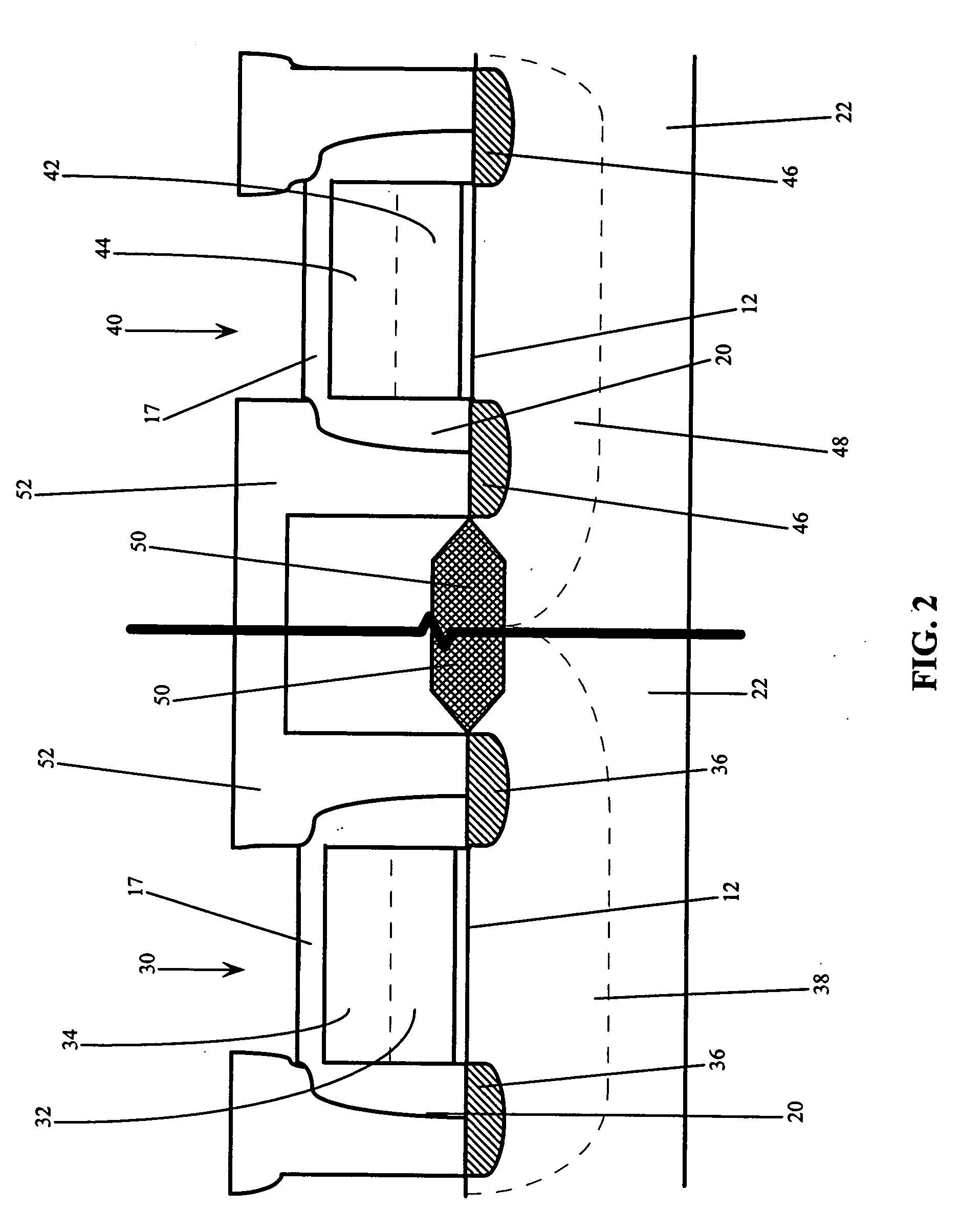
Use of gate electrode workfunction to improve DRAM refresh
InactiveUS20050173746A1Improve refresh featureLower requirementTransistorSolid-state devicesSubstrate dopingEngineering
This invention relates to a method and resulting structure, wherein a DRAM may be fabricated by using silicon midgap materials for transistor gate electrodes, thereby improving refresh characteristics of access transistors. The threshold voltage may be set with reduced substrate doping requirements. Current leakage is improved by this process as well.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Method for extracting gate-oxide thickness and substrate doping concentration of field effect transistor
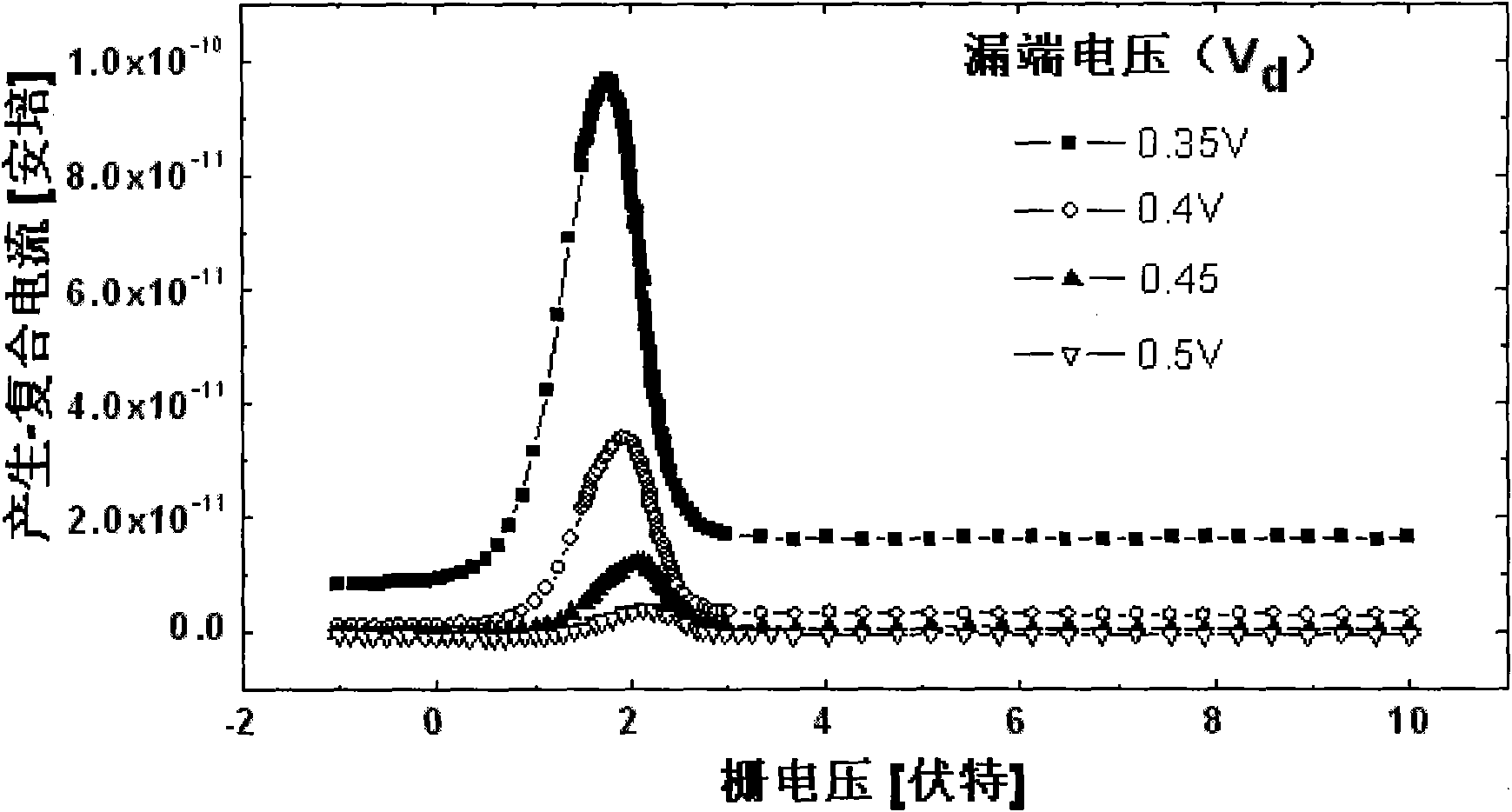
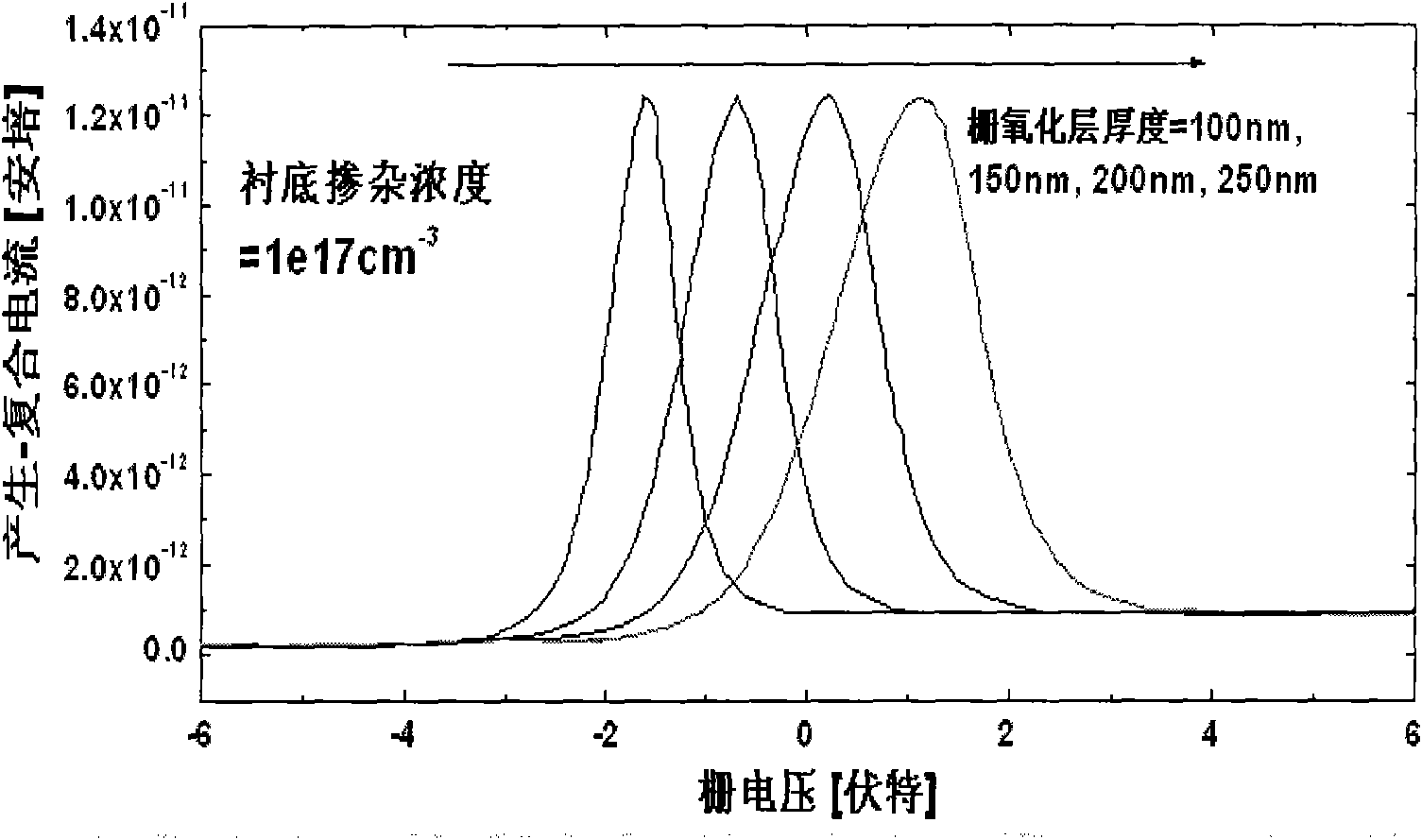
InactiveCN102042799ASensitive and accurate extractionImprove accuracyMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansElectrical/magnetic thickness measurementsRecombination currentPower flow
The invention provides a method for extracting gate oxide thickness and substrate doping concentration of a field effect transistor, which is characterized by comprising the following steps of: grounding a source electrode and a drain electrode of a device, connecting a substrate with smaller positive bias to enable a drain-body diode to be in positive bias and not conducted, scanning gate voltage from negative voltage to a positive voltage, measuring the relation curve of a generation-recombination current of the substrate and the gate voltage, and accurately extracting the gate oxide thickness and the substrate doping concentration of the field effect transistor by utilizing the position shift of the generation-recombination current peak of the positively-biased diode. In the method, a required measuring structure is simple and has high sensitivity and can be used for accurately reflecting the dependence of the gate oxide thickness on the substrate doping concentration.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
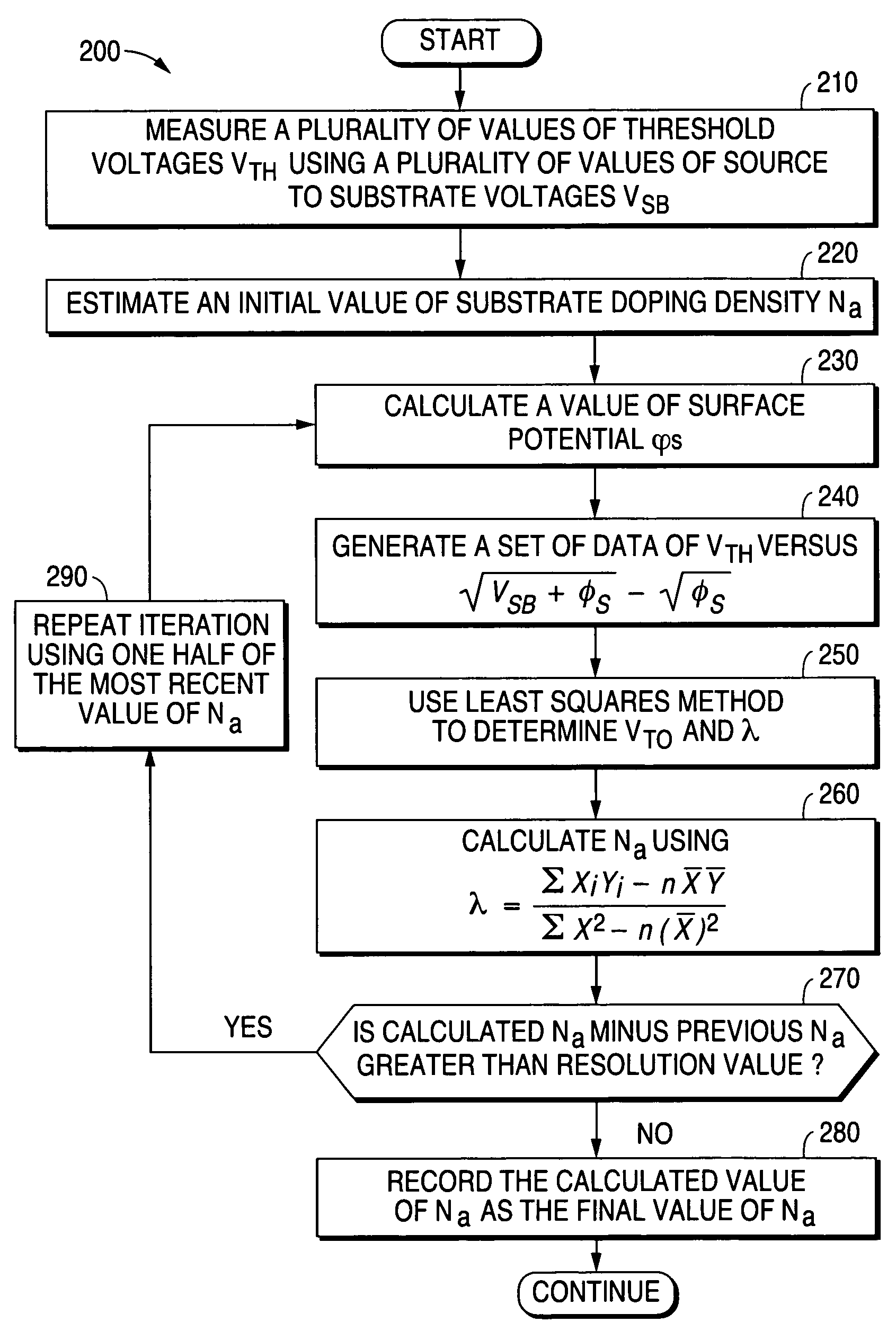
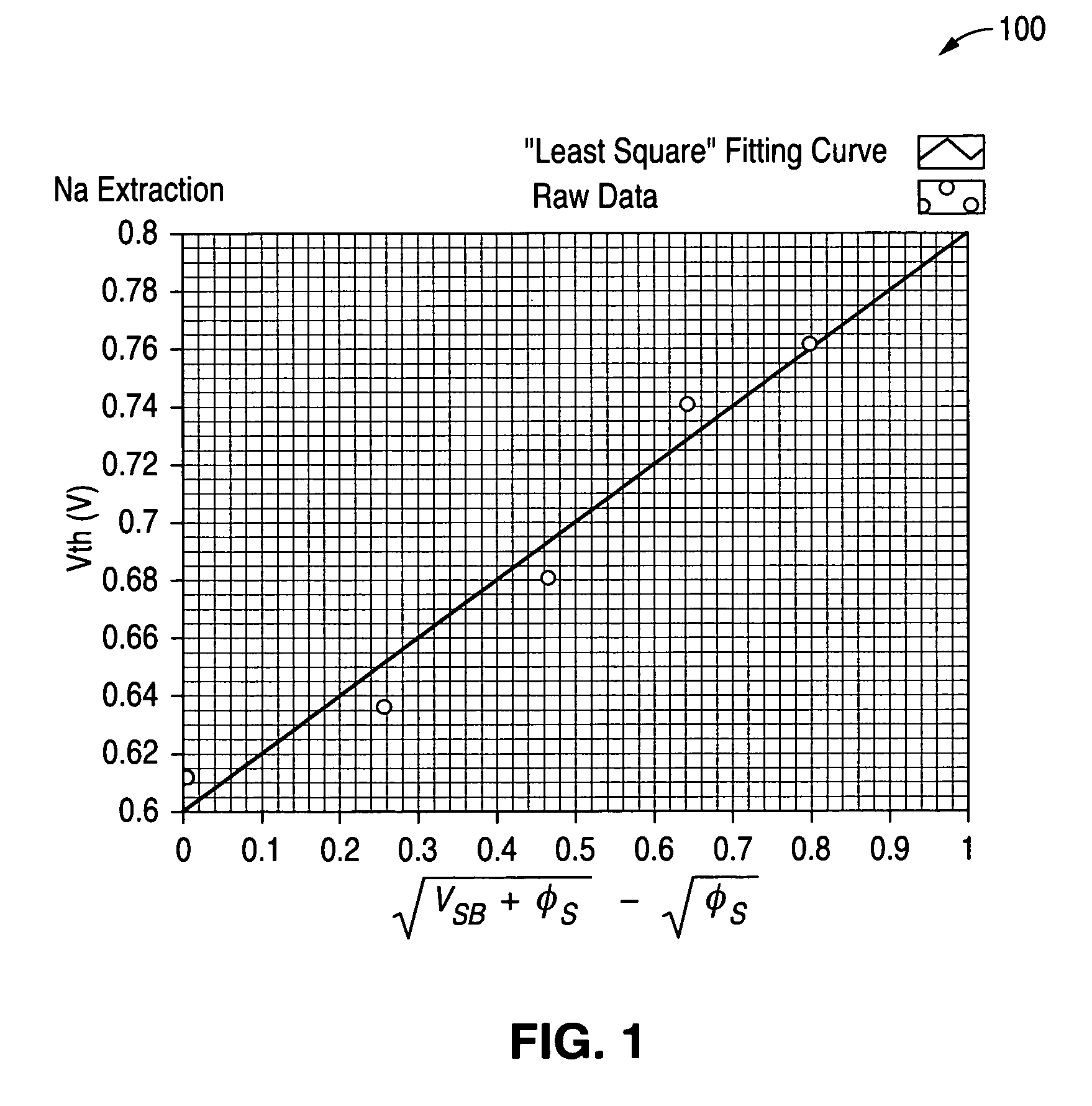
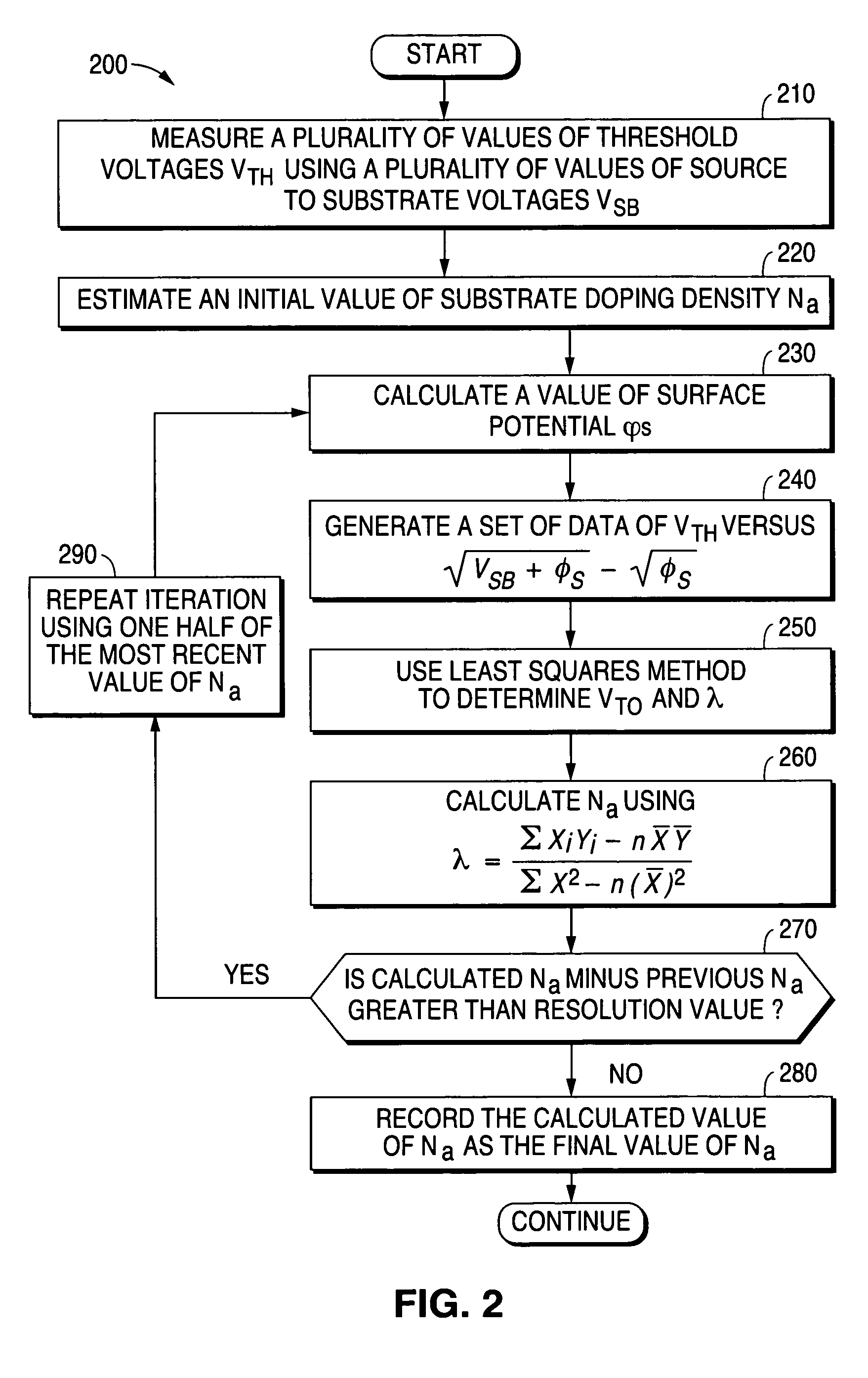
System and method for determining substrate doping density in metal oxide semiconductor devices
ActiveUS7512499B1Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementDigital computer detailsLinear relationshipSubstrate doping
A system and method are disclosed for very accurately determining a value of a substrate doping density in a metal oxide semiconductor device. A plurality of values of threshold voltage of a device under test are measured using a plurality of different values of source to substrate bias voltage. Then a linear relationship is determined between the plurality of values of threshold voltage and a plurality of different values of an expression that is a function of the source to substrate bias voltage and a function of a surface potential of the device. A very accurate value of the substrate doping density is reiteratively calculated from the linear relationship without assuming that the surface potential of the device has a constant value.
Owner:NAT SEMICON CORP
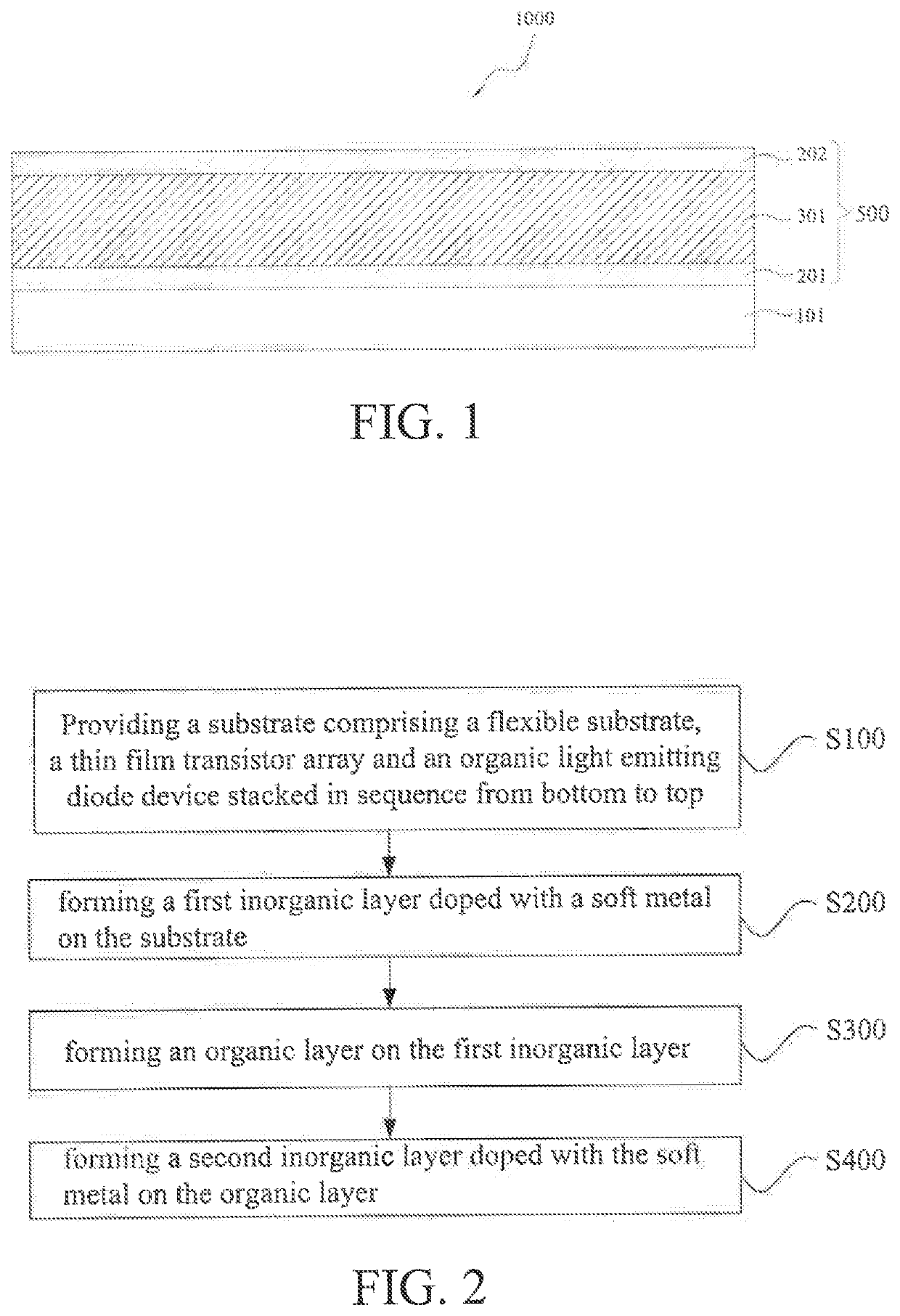
Flexible organic light emitting diode display panel and method for fabricating same
ActiveUS20210408453A1Improve toughnessAvoid breakingFinal product manufactureSolid-state devicesFlexible organic light-emitting diodeTransistor array
The present disclosure provides a flexible organic light emitting diode display panel and a method for fabricating the same. The flexible organic light emitting diode display panel includes a substrate, a first inorganic layer doped with a soft metal, an organic layer, and a second inorganic layer doped with the soft metal. The substrate comprises a flexible substrate, a thin film transistor array and an organic light emitting diode device stacked in sequence from bottom to top. The first inorganic layer doped with a soft metal is disposed on the substrate. The organic layer is disposed on the first inorganic layer. The second inorganic layer doped with the soft metal is disposed on the organic layer. The present invention can improve bending performance of the flexible organic light emitting diode display panel.
Owner:WUHAN CHINA STAR OPTOELECTRONICS SEMICON DISPLAY TECH CO LTD
Compensation for substrate doping in edge reconstruction for in-situ electromagnetic inductive monitoring
PendingCN111886686AAvoid undergrindingReduce unevennessSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNerve networkWafering
A method of compensating for a contribution of conductivity of the semiconductor wafer to a measured trace by an in-situ electromagnetic induction monitoring system includes storing or generating a modified reference trace. The modified reference trace represents measurements of a bare doped reference semiconductor wafer by an in-situ electromagnetic induction monitoring system as modified by a neutral network. The substrate is monitored with an in-situ electromagnetic induction monitoring system to generate a measured trace that depends on a thickness of the conductive layer, and at least a portion of the measured trace is applied to a neural network to generate a modified measured trace. An adjusted trace is generated, including subtracting the modified reference trace from the modifiedmeasured trace.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
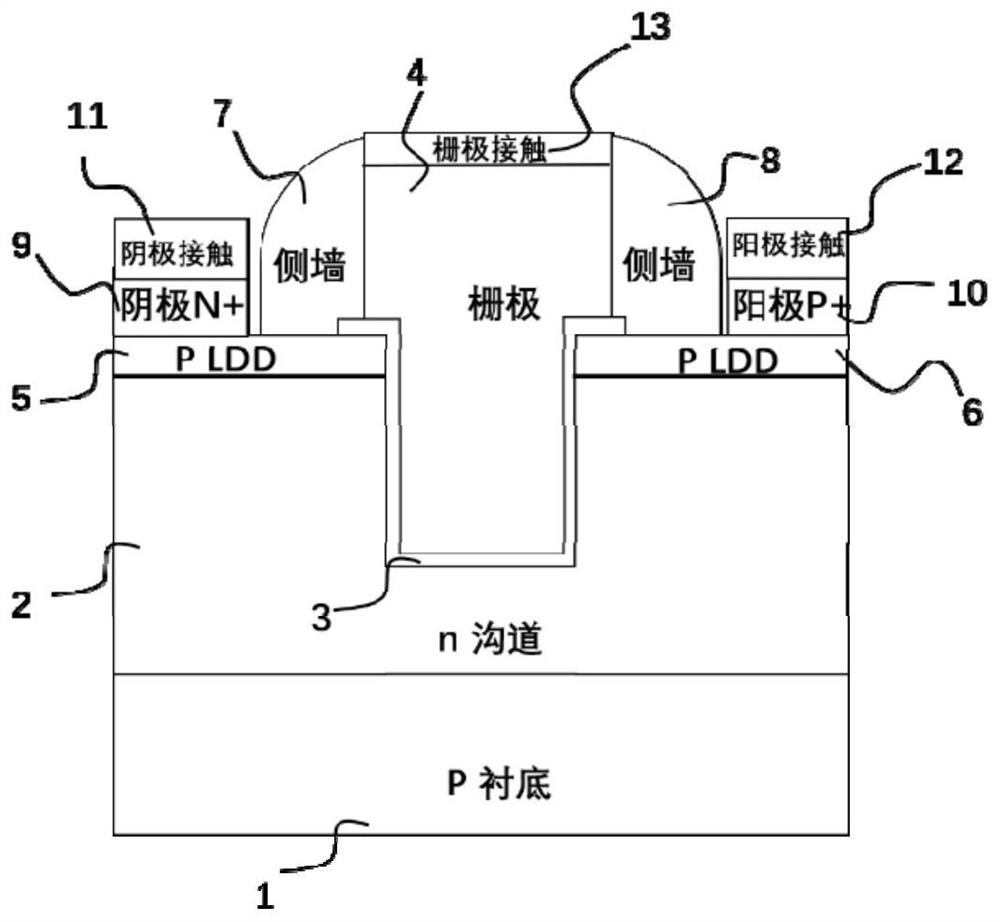
Novel semiconductor field-effect positive feedback transistor based on bulk silicon substrate and method thereof
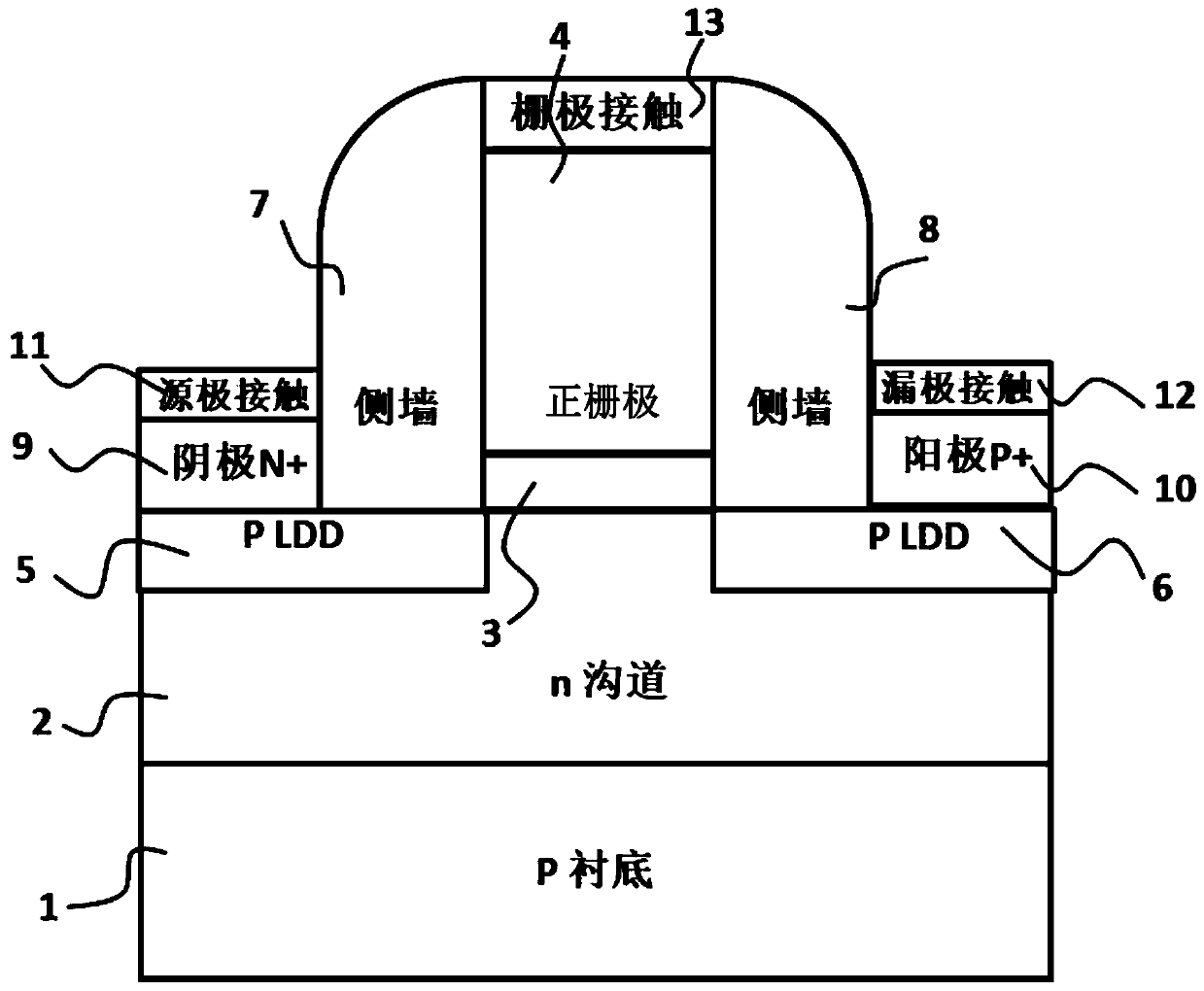
ActiveCN110634955AReduce processing costsReduce processing difficultyTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSub thresholdSubstrate doping
The invention discloses a novel semiconductor field-effect positive feedback transistor based on a bulk silicon substrate and a method thereof. Source and drain electrodes of the transistor are in reverse heavy doping, wherein one side is in p<+> type doping, and the other side is in n<+> type doping; a channel is in weak doping; a low-drain doped region (LDD) defined by grid side walls is close to the channel; and the substrate is doped opposite to the channel in doping type. A traditional field-effect positive feedback device, such as a Z<2>-FET, is established on a silicon-on-insulator (SOI) substrate, so that the traditional field-effect positive feedback device is high in price and asymmetric in structure and is incompatible with a common bulk silicon CMOS process and a device structure; and by introducing the key LDD, channel and substrate doping, the structure-symmetry novel semiconductor field-effect positive feedback transistor is formed on the bulk silicon substrate. The novel device provided by the invention is lower in process cost and smaller in process difficulty, and can be widely applied to the fields of high-performance dynamic and static memories (DRAM and SRAM),low sub-threshold swing switches and electrostatic protection and sensing and the like.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Compensation for substrate doping for in-situ electromagnetic inductive monitoring
PendingCN111511503AReduce inaccuracyReduce non-uniformityLapping machinesGrinding feed controlWaferingSubstrate doping
A method of chemical mechanical polishing includes bringing a substrate having a conductive layer disposed over a semiconductor wafer into contact with a polishing pad, generating relative motion between the substrate and the polishing pad, monitoring the substrate with an in-situ electromagnetic induction monitoring system as the conductive layer is polished to generate a sequence of signal values that depend on a thickness of the conductive layer, determining a sequence of thickness values for the conductive layer based on the sequence of signal values, and at least partially compensating for a contribution of conductivity of the semiconductor wafer to the signal values.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Double-conduction semiconductor component and manufacturing method thereof
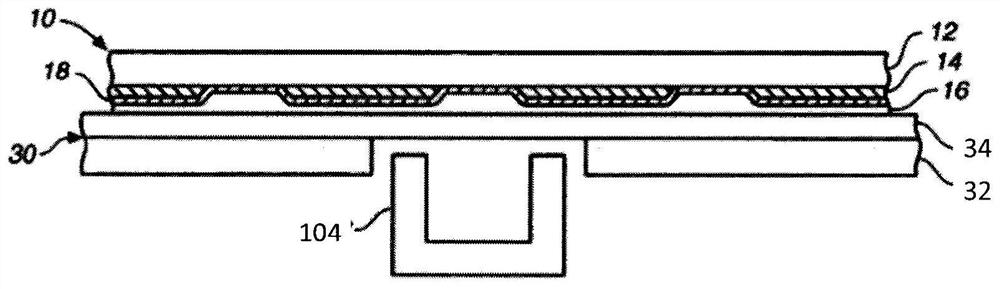
InactiveCN102956640AImprove pressure resistanceTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingInsulation layerSubstrate doping
The invention discloses a double-conduction semiconductor component. The double-conduction semiconductor component comprises a semiconductor substrate, a first substrate doping area, a second substrate doping area and a grid insulation layer, wherein the semiconductor substrate is provided with a first conduction type, and both the first substrate doping area and the second substrate doping area are provided with second conduction types. The semiconductor substrate is provided with a first groove, the first substrate doping area and the second substrate doping area are respectively arranged in the semiconductor substrate on two sides of the first groove, the grid insulation layer covers the surface of the first groove and is provided with a first part, a second part and a third part, wherein the first part is adjacent to the first substrate doping area, the second part is adjacent to the second substrate doping area, and the third part is arranged at a turning position of the bottom and the side wall of the first groove. The thickness of each of the first part and the second part is smaller than that of the third part. Therefore, withstand voltage of the double-conduction semiconductor component can be increased.
Owner:SINOPOWER SEMICON
Conductive laminated body and method for preparing the same
ActiveUS8303856B2Increase electron concentrationLow mobilityConductive materialVacuum evaporation coatingElectric propertiesInert gas
Disclosed is a conductive laminated body, and a method for preparing the same, wherein the conductive laminated body including: a substrate; a zinc oxide-based thin film doped with an element M; and an interlayer including an oxide M′2O3, which is interposed between the substrate and the zinc oxide-based thin film. The disclosed conductive laminated body includes a metal oxide interlayer of an oxidation number +3, between a substrate and a zinc oxide layer. Therefore, it is possible to improve electrical properties of a transparent conductive thin film, especially, a resistivity property, and to minimize the unevenness in electrical properties between a middle portion and a circumferential portion on the surface of the thin film in sputtering deposition. Also, in deposition of a zinc oxide film, in addition to inert gas such as argon gas, the use of hydrogen gas can improve the concentration of electrons, and herein, the interposition of an interlayer including a metal oxide, between the substrate and the zinc oxide-based transparent conductive film, allows the heat-resistance / moisture-resistance stability and the uniformity of electrical properties.
Owner:LG CHEM LTD
Characterization of substrate doping and series resistance during solar cell efficiency measurement
Short-circuit current, maximum power, and open circuit voltage during a single flash are determined by varying intensity, voltage, and current. An apparatus determines the substrate doping and the series resistance of the solar cell. The series resistance of the cell is determined from a voltage step from the maximum power voltage operating point to the open-circuit condition. Methods are described for determining the substrate doping from stepping or sweeping the voltage. The first uses a voltage step and finds the change in charge that results. This determines a unique doping if the series resistance is known. The second uses data for a case of varying current, voltage, and light intensity, and compares this data to the case of varying voltage and intensity with no current. By transposing both cases into the steady state, agreement between the two data sets is found for unique doping and series resistance values.
Owner:SINTON CONSULTING
Method for measuring size of nonbonding area on bonding device structure
InactiveCN103887197ANo damageAccurate measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSubstrate dopingOptical measurements
The invention discloses a method for measuring the size of a nonbonding area on a bonding device structure. According to the method, light capable of penetrating through the bonding device structure to be measured is adopted to shine on the bonding device structure to be measured so that a Newton ring can be formed at the position corresponding to the nonbonding area in the light incidence direction, then the width, in the direction perpendicular to the light incidence direction, of the Newton ring is measured by means of an optical measuring microscope, and then the width, in the direction perpendicular to the light incidence direction, of the nonbonding area is obtained. According to the method, the measurement of the size of the nonbonding area on the bonding device structure is achieved by means of the Newton ring principle, an accurate measurement result can be obtained, no damage can be caused to the bonding device structure to be measured serving as a sample during measurement, and then production cost is reduced. Furthermore, the method can be applied to bonding device structures formed by bonding of wafers the thickness of each of which is o micron - 775 microns, or chips or other silicon substrates, the method supports substrate doping, the application range is wide, and practicality is high.
Owner:WUHAN XINXIN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Transverse electric-injection luminescent device of indirect gap semiconductor material controlled by phonon
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
A power ldmos device with junction field plate
InactiveCN103268890BImprove breakdown characteristicsLower on-resistanceDiodeEngineeringHigh pressure
The invention relates to a power LDMOS device with a junction field plate, and belongs to the technical field of power semiconductor devices. According to the power LDMOS device with the junction field plate, a buried layer opposite to a substrate doping type is formed on a substrate of a conventional LDMOS device, and the junction field plate formed by a PN junction is formed in the surface of a device drifting area. The power LDMOS device with the junction field plate uses PN junction electric field distribution in the junction field plate for modulating a device surface electric field, the distribution of the device surface electric field is made to be more even, the insufficiency of a peak of a tail end electric filed of a metal field plate can be effectively avoided, and breakdown performance of the device is improved. Under the reverse blocking state, the junction field plate has an auxiliary exhaustion function for the drifting area, the doping level of the drifting area can be improved to a large extent, and the on-resistance of the device is reduced. Meanwhile, reverse currents are small when reverse bias of the PN junction in the junction field plate occurs, the fact that leakage currents in the field plate are reduced is benefited, and the buried layer in the substrate can effectively improve the voltage endurance property of the device. The device has the advantages of being high in voltage, low in power consumption, low in cost and easy to integrate, and is suitable for power integrated circuits and radio frequency power integrated circuits.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA +1
Manufacturing method of laterally diffused metal oxide semiconductor element
InactiveCN102044441ALength will not be affectedLength effectSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLDMOSSubstrate doping
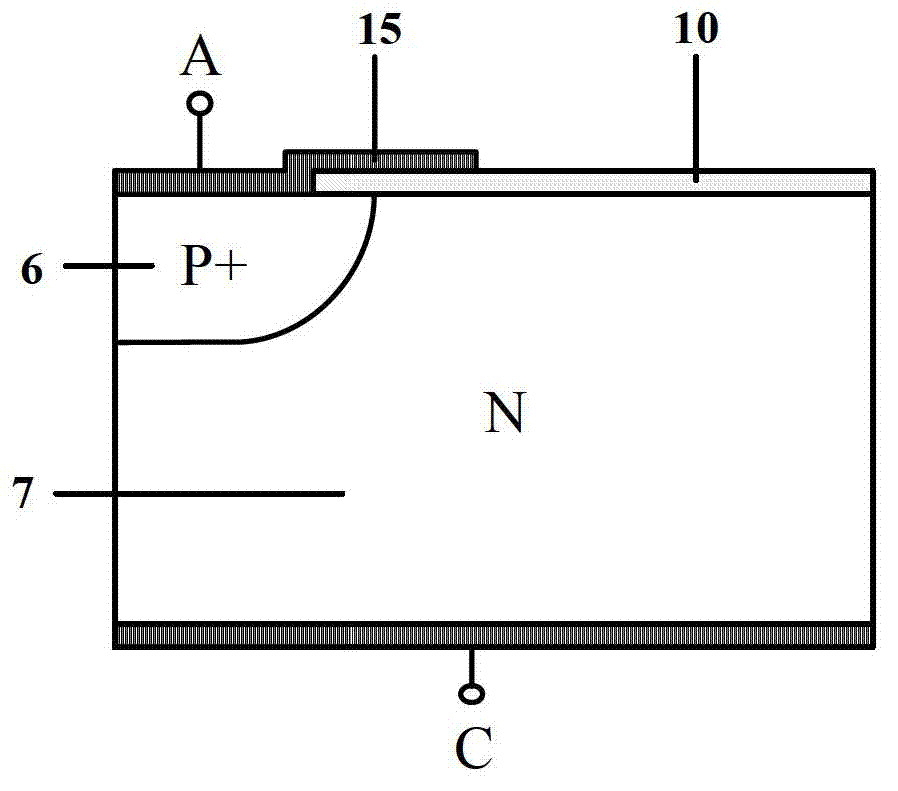
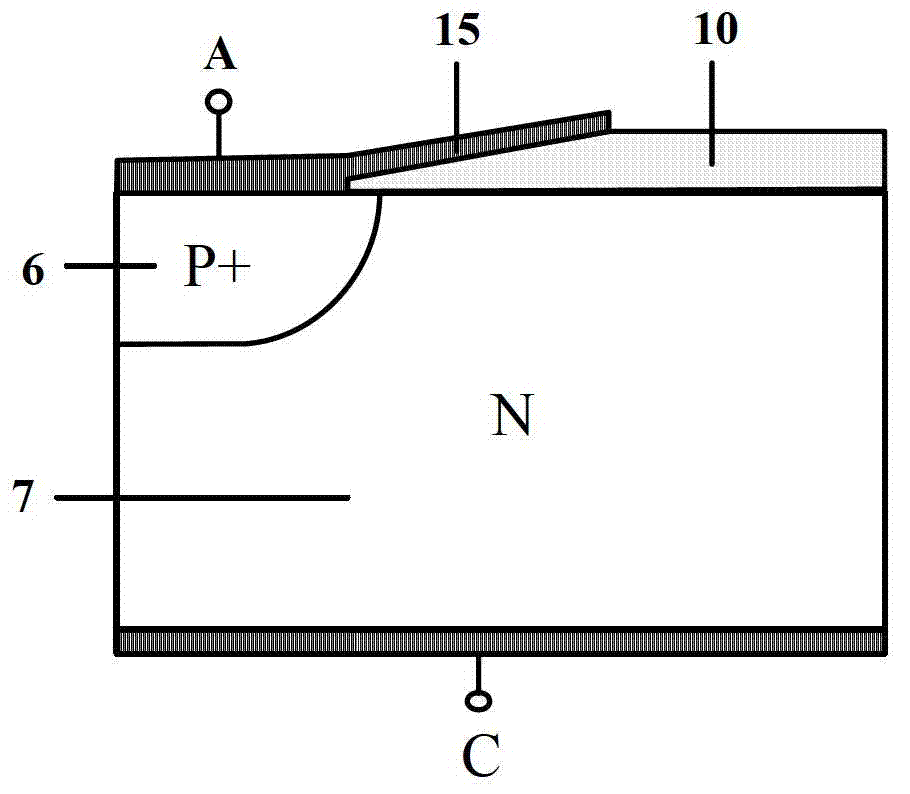
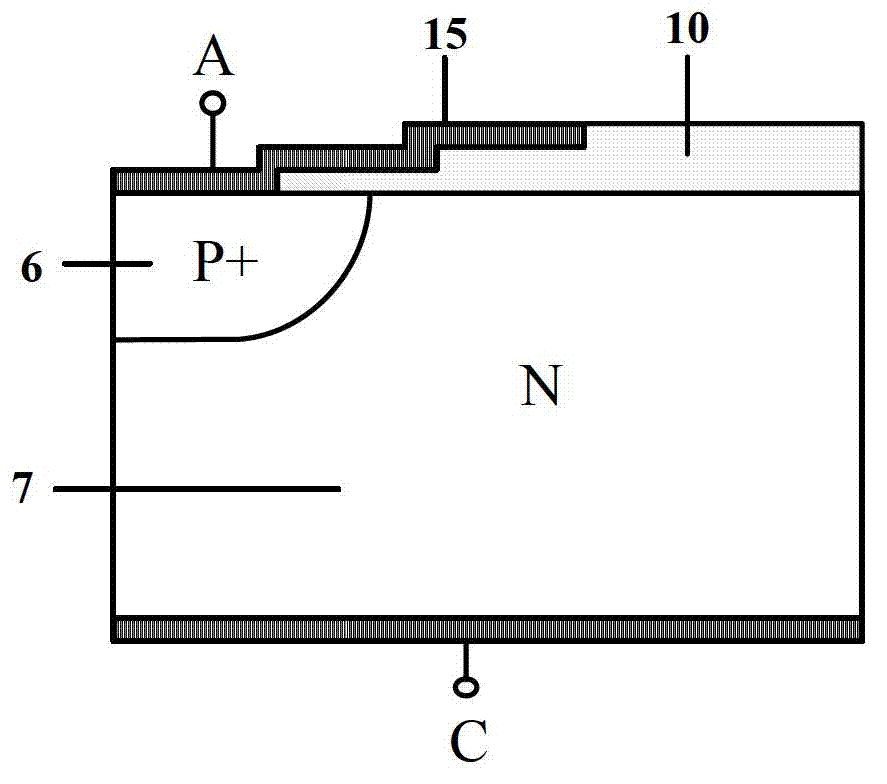
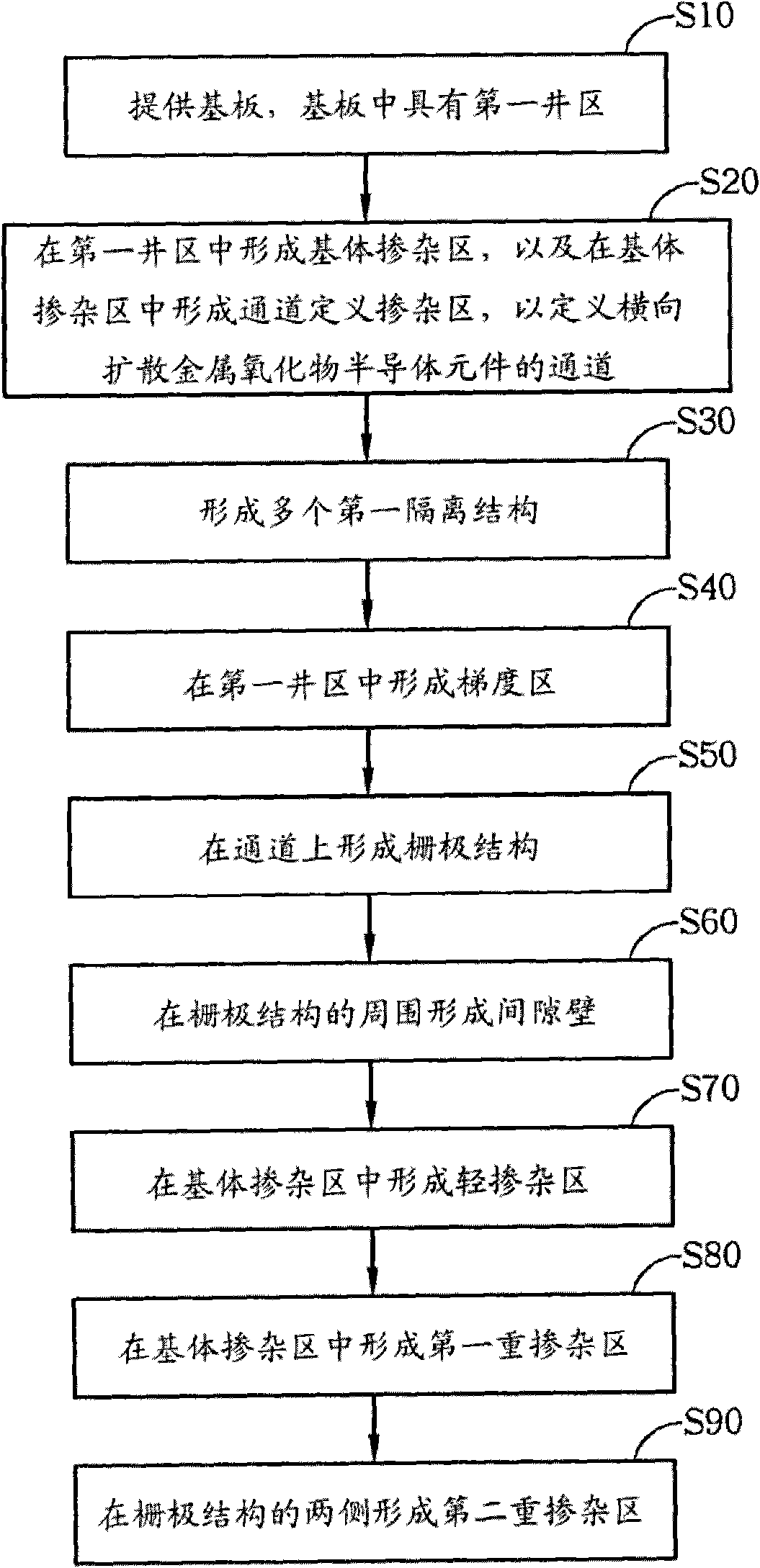
The invention discloses a manufacturing method of a laterally diffused metal oxide semiconductor element. The manufacturing method is as follows: a providing a substrate with a first conduction type, wherein the substrate is internally provided with a well area with a second conduction type; then, forming a substrate doping area in the well area and forming a channel definition doping area in the substrate doping area, wherein the substrate doping area is provided with the first conduction type, and the channel definition doping area is provided with the second conduction type; utilizing the substrate doping area which is positioned between the channel definition doping area and the well area and is not covered by the channel definition doping area to form a channel of the laterally diffused metal oxide semiconductor element; and then, forming a grid structure on the channel. Therefore, by utilizing the manufacturing method, the channel change due to displacement of the grid structure can be avoided.
Owner:UNITED MICROELECTRONICS CORP
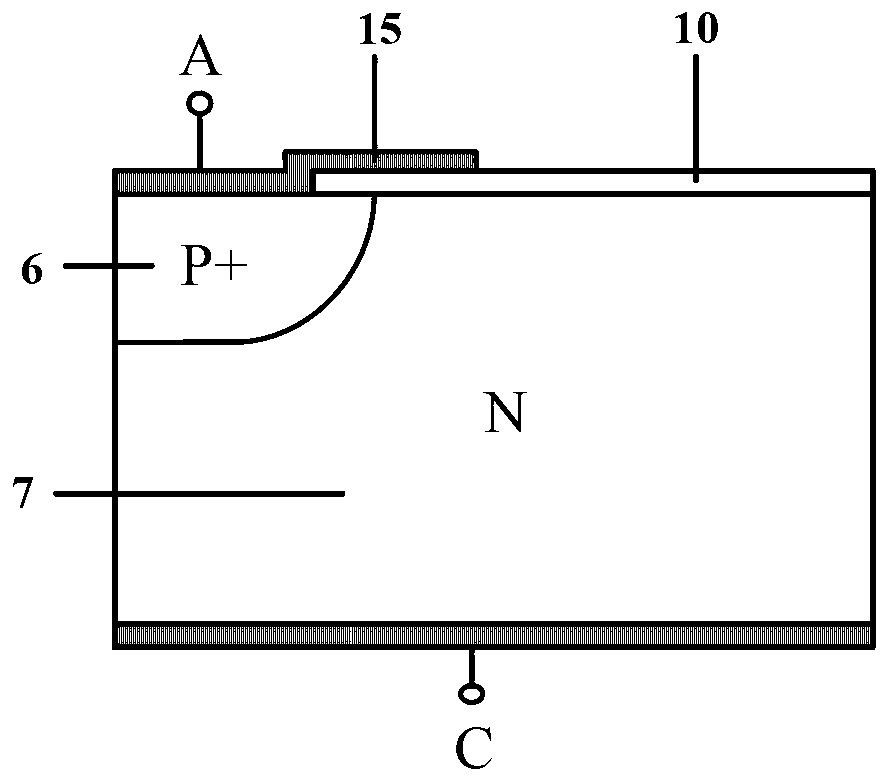
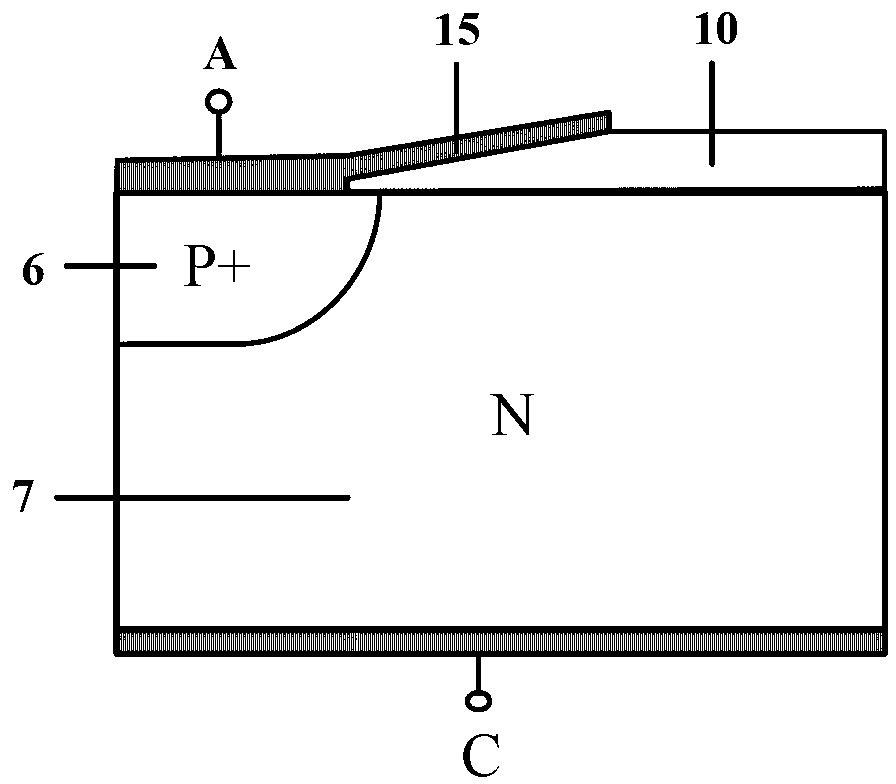
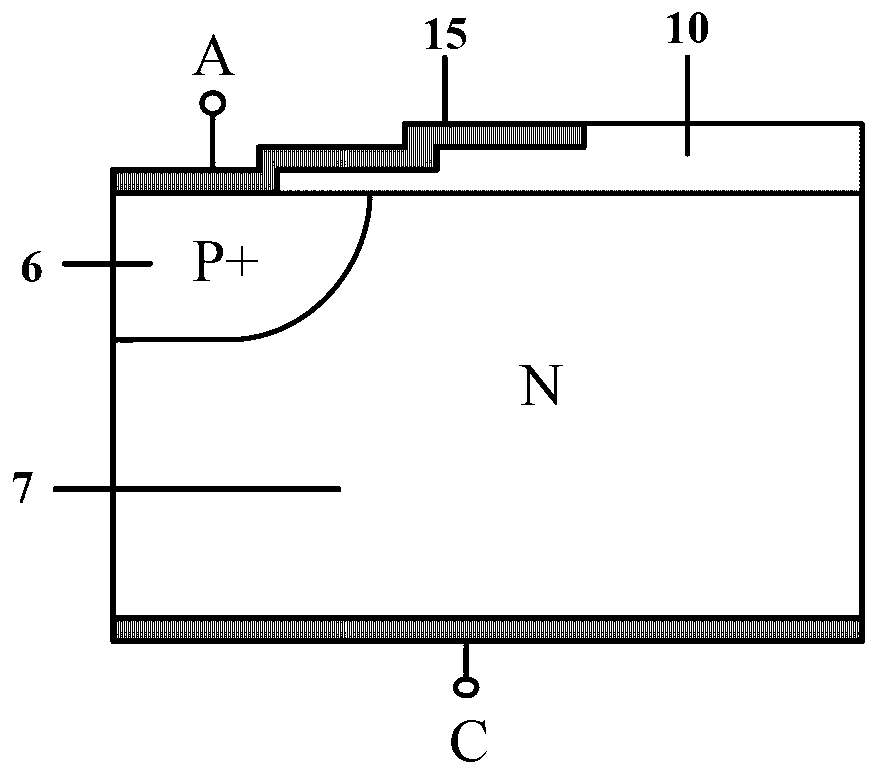
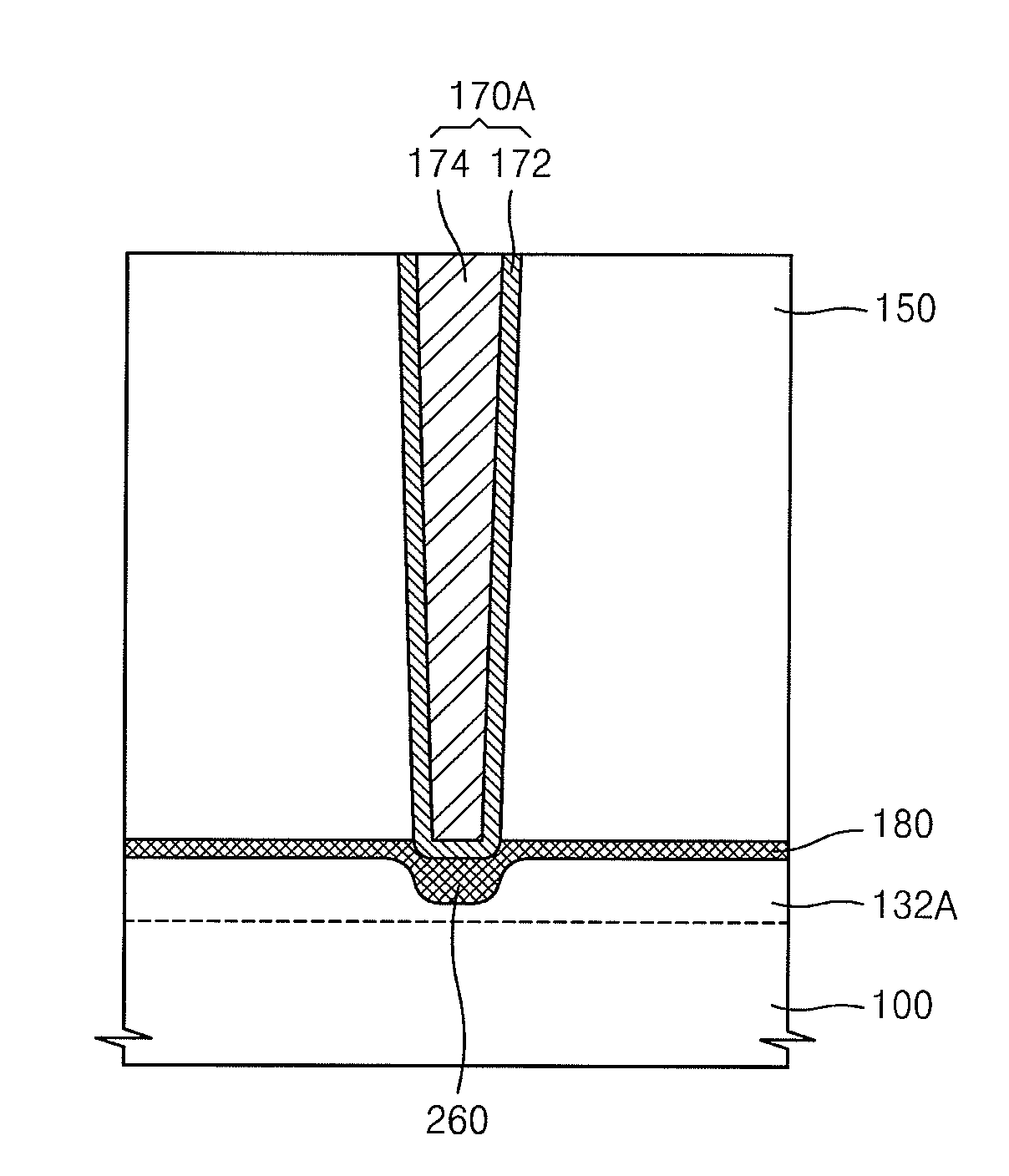
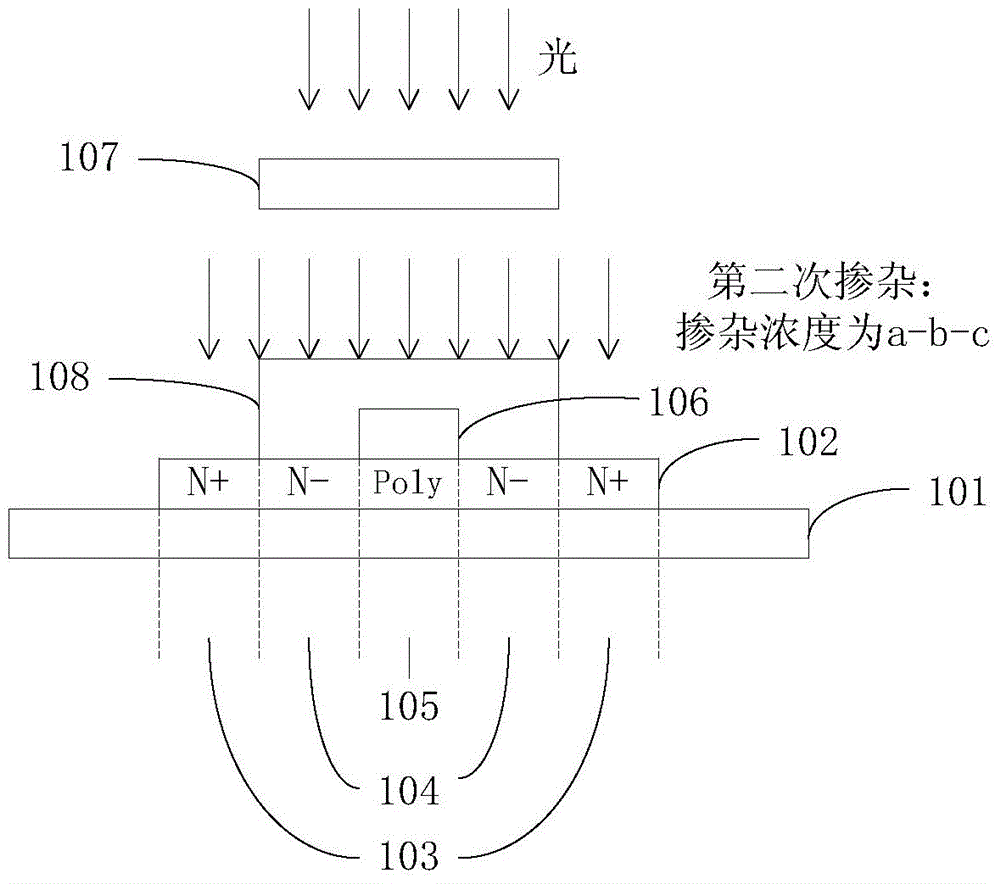
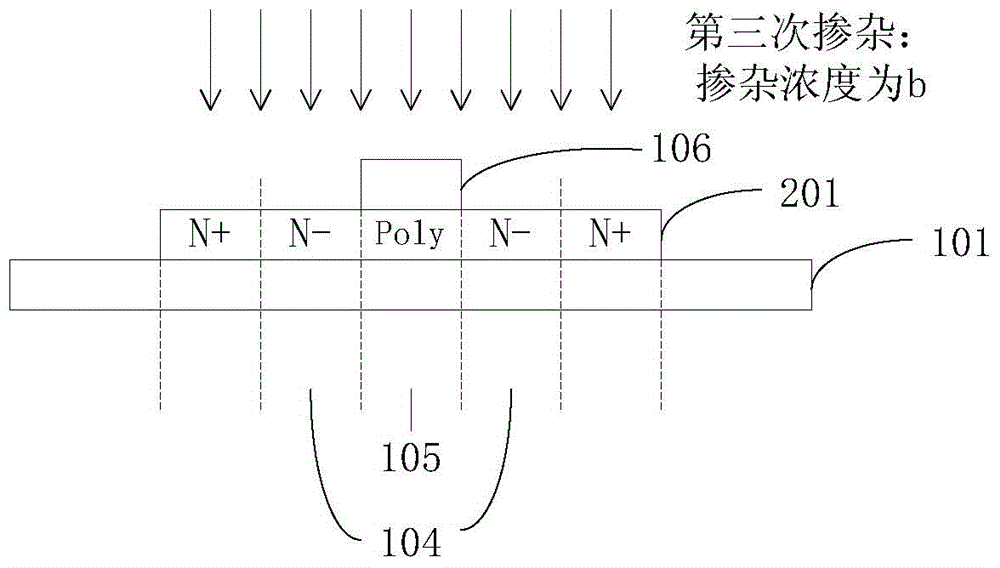
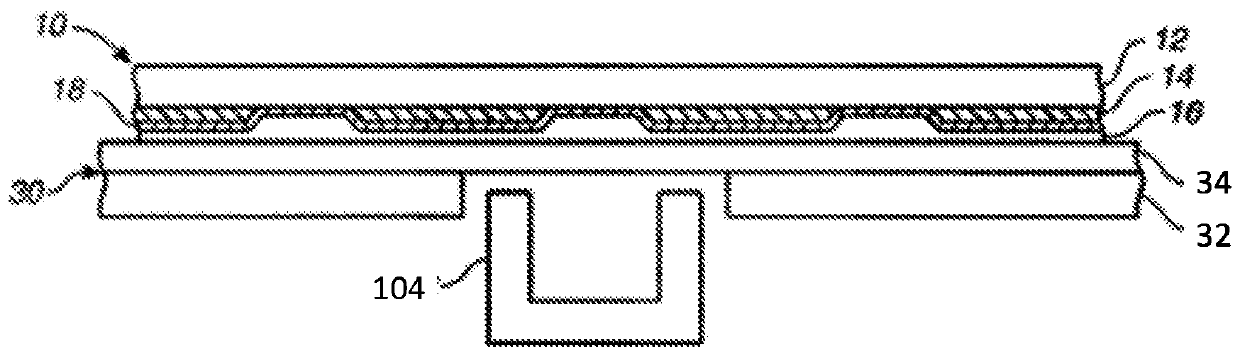
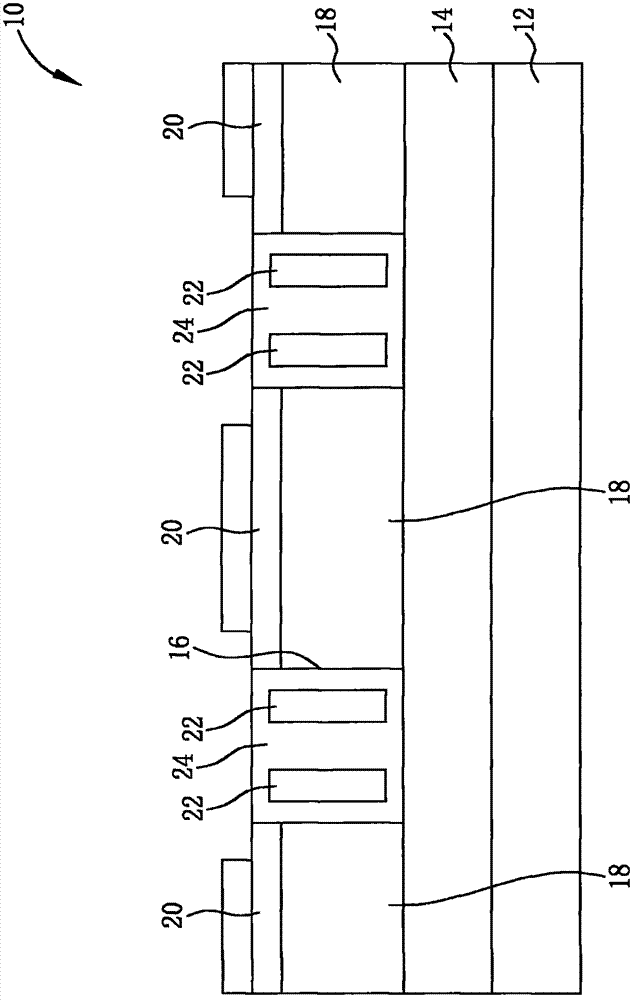
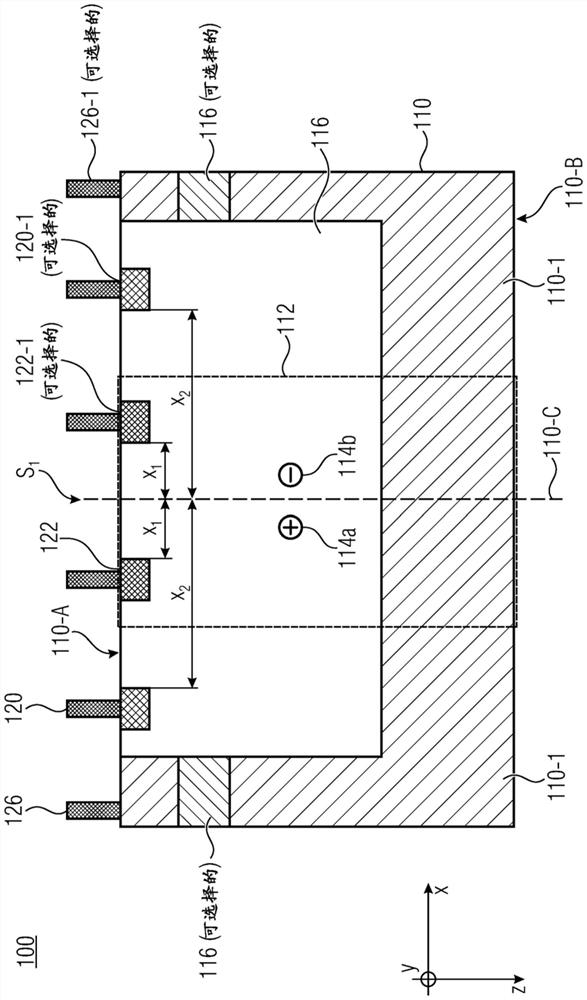
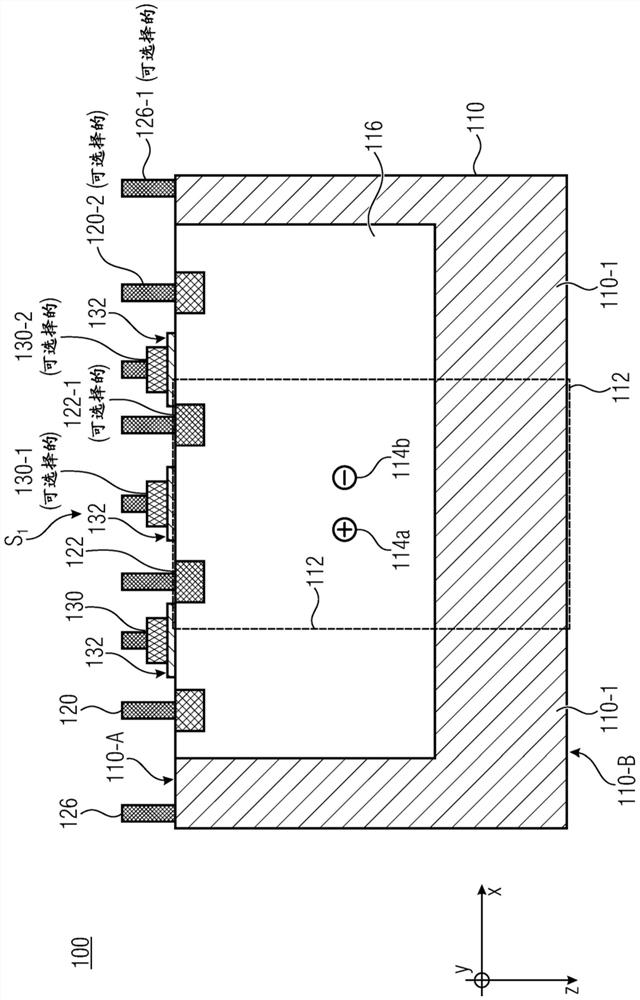
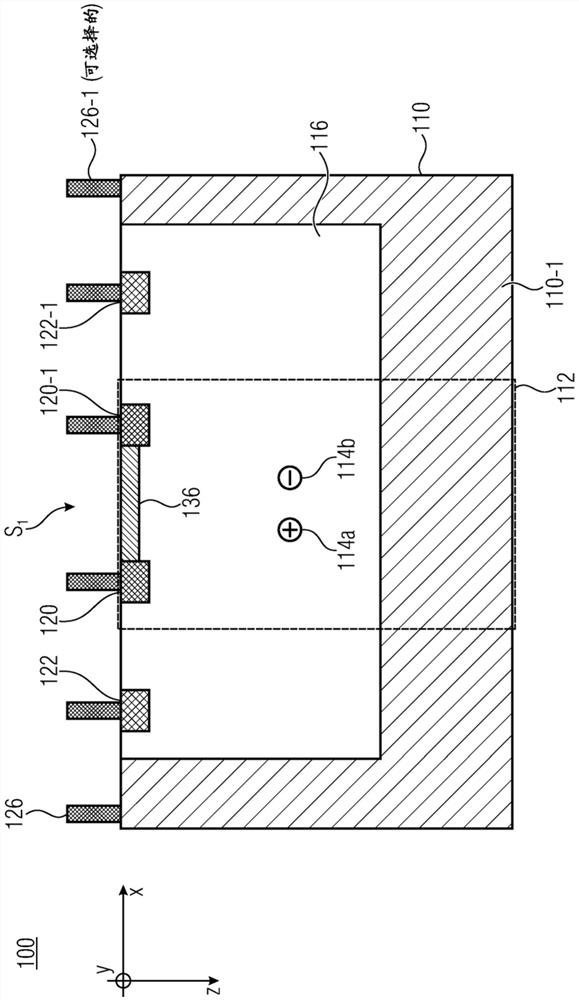
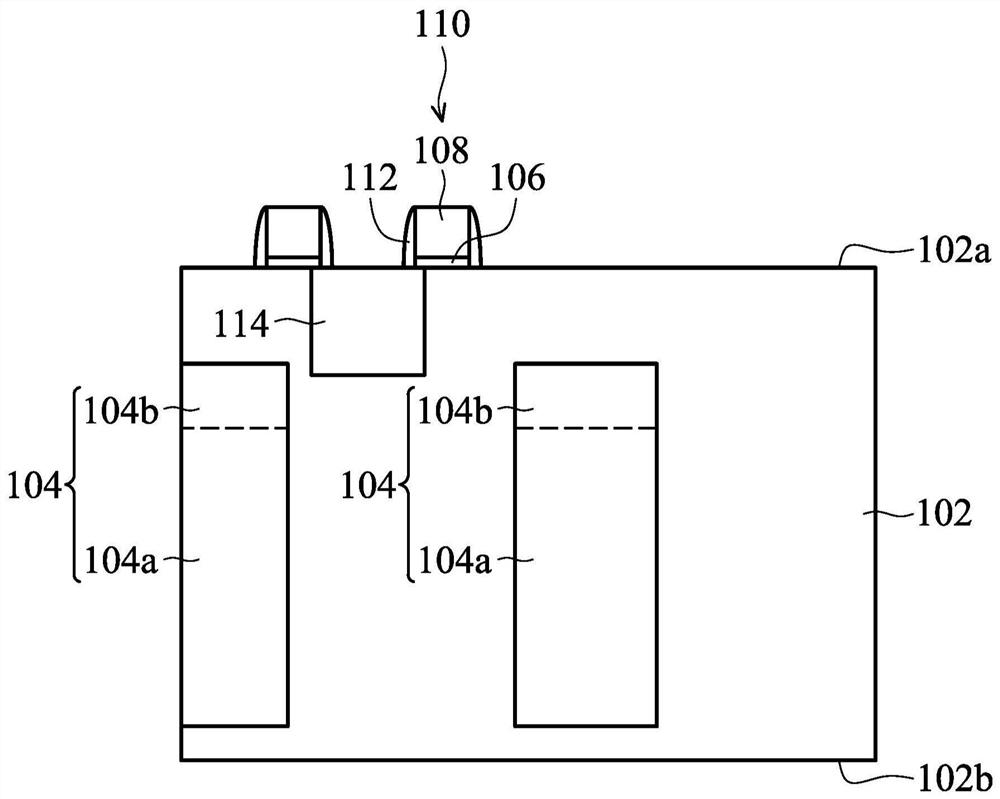
Substrate doping structure and method for forming the same
ActiveCN108615675BReduce leakage currentImprove performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesChemical physicsSubstrate doping
The invention relates to a substrate doping structure and a formation method thereof. The method comprises steps of providing a substrate including an isolation region and a first doping well region;forming first graphical mask layers which are exposed to the isolation region and the first doping well region on the surface of the substrate; by taking the first graphical mask layers as masks, carrying out field injection on the substrate and forming doping regions in the isolation region and the first doping well region; by taking the first graphical mask layers as masks, carrying out first doping ion injection on the substrate and forming first doping regions in the isolation region and the first doping well region; forming second graphical mask layers exposed to the first doping well region on the surface of the substrate; and by taking the second graphical mask layers as masks, carrying out second doping ion injection on the substrate and forming second doping regions in the first doping well region, wherein the first doping regions are arranged in the second doping regions. According to the invention, device performance can be improved with no need to increase the quantity of light covers.
Owner:YANGTZE MEMORY TECH CO LTD
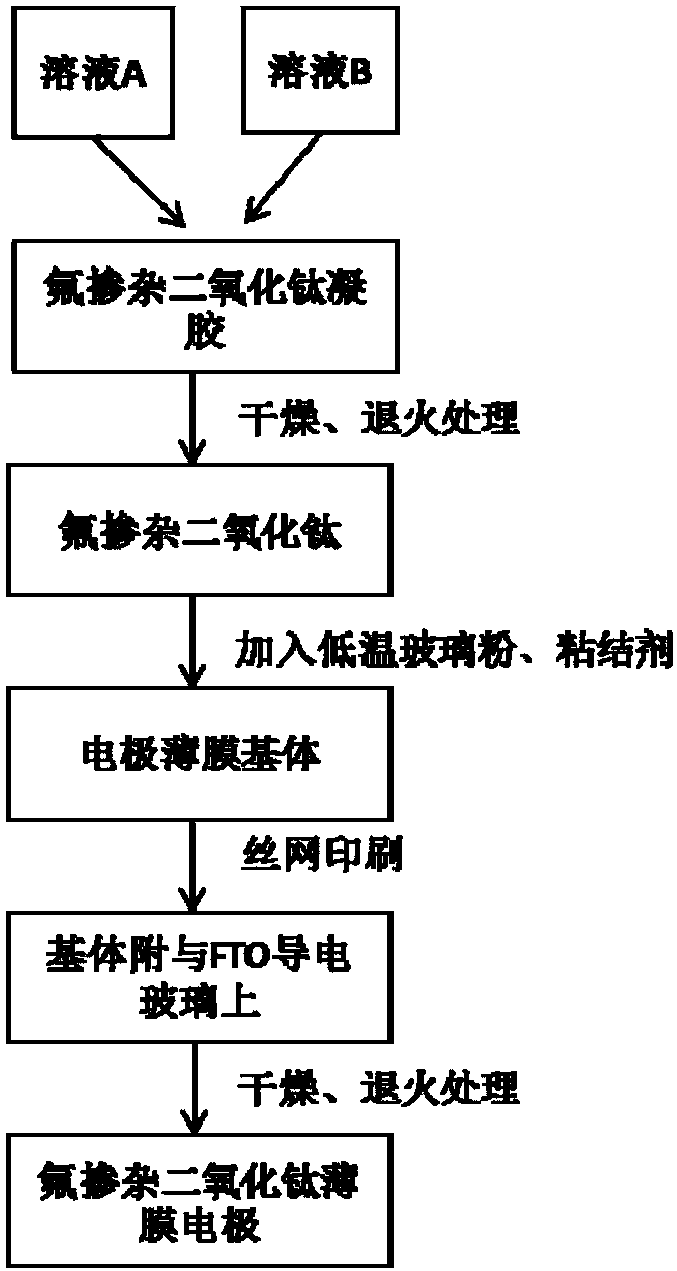
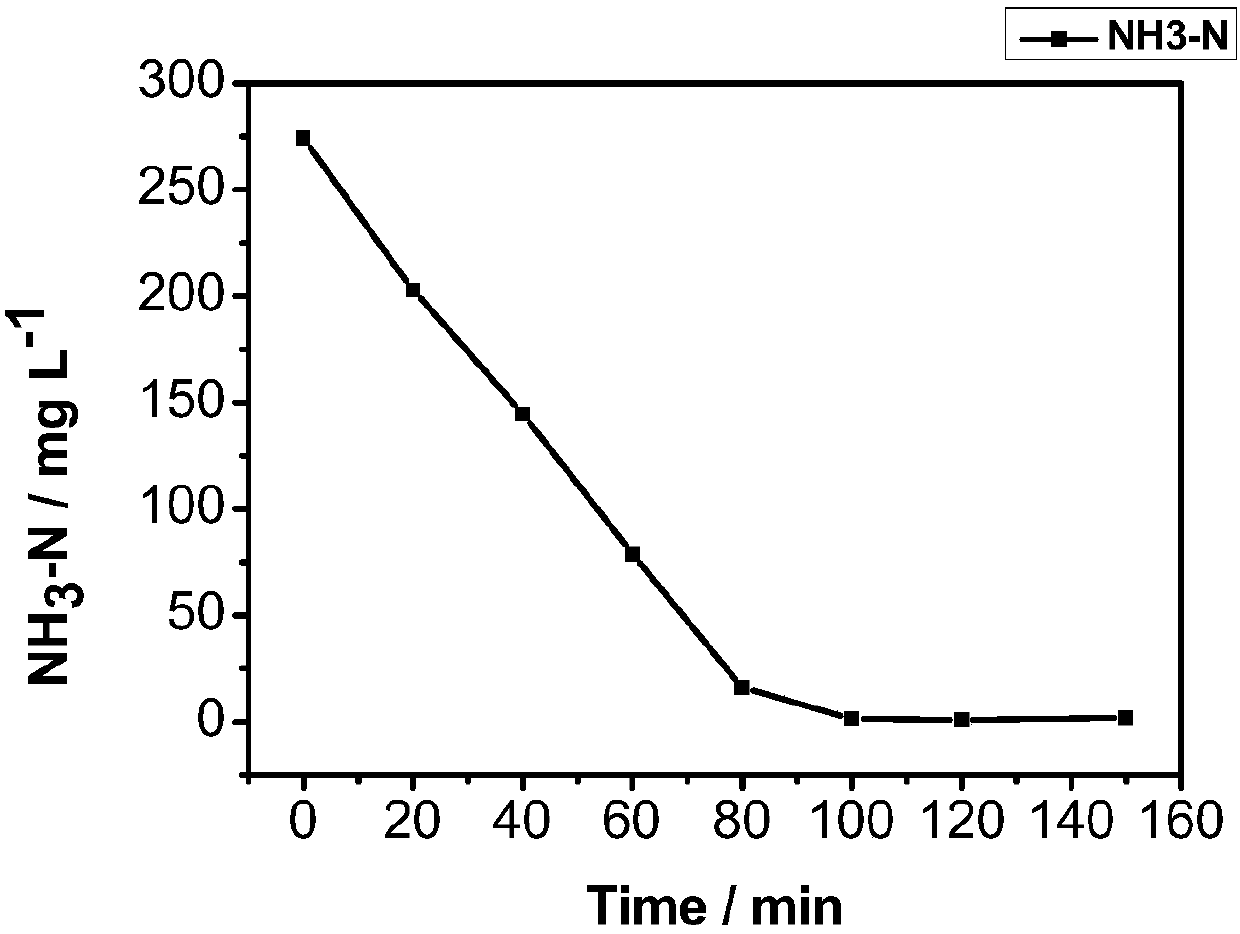
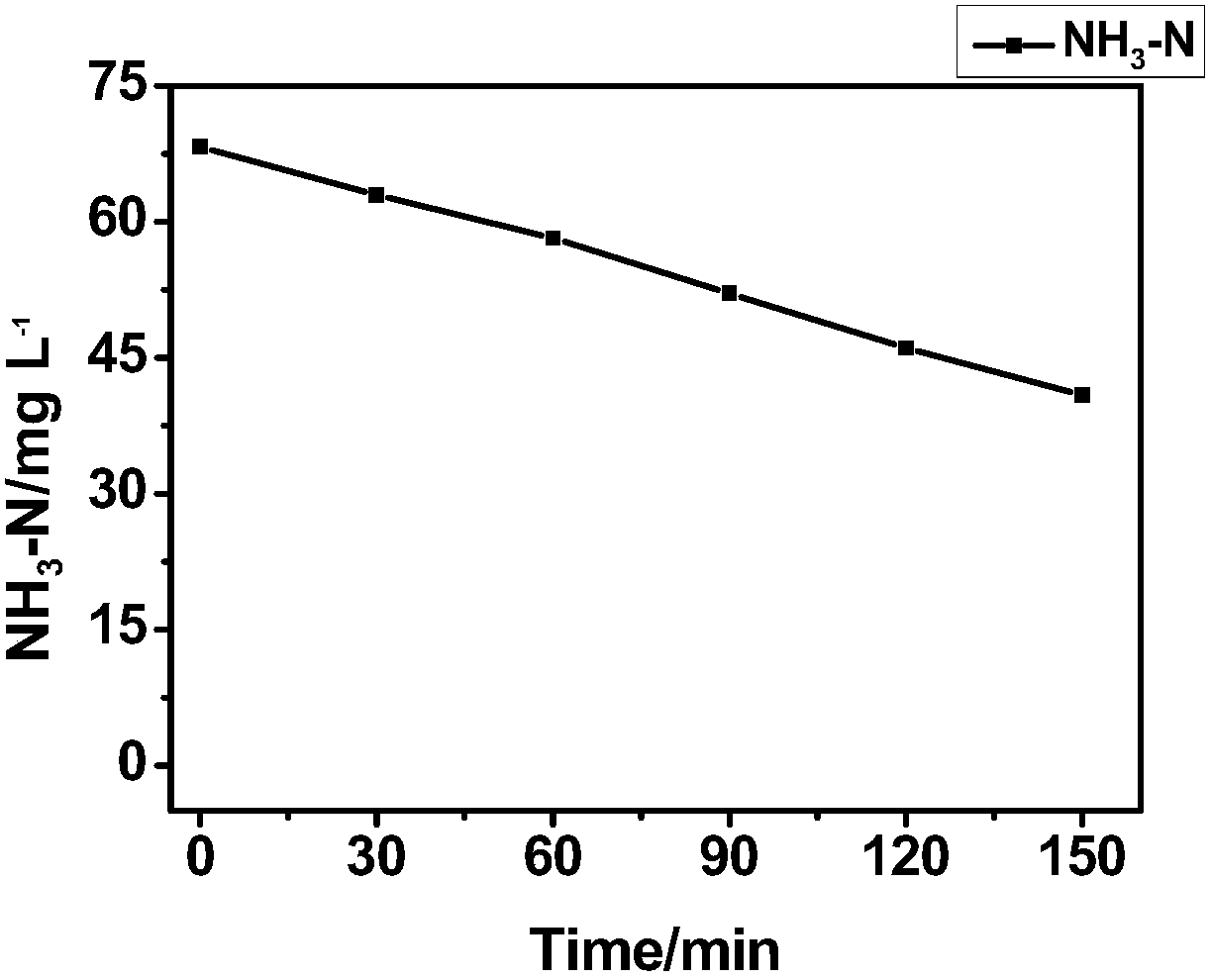
A preparation method of nano-oxide thin film electrode for treating ammonia nitrogen wastewater
ActiveCN105692777BChange usageEasy to cleanPhysical/chemical process catalystsWater/sewage treatment by irradiationHazardous substanceTurpentine
The invention relates to the technical field of environmental engineering, in particular to a preparation method of a nano-oxide film electrode for treating ammonia nitrogen wastewater. A preparation method of a nano-oxide film electrode for treating ammonia nitrogen wastewater, characterized in that: the preparation method is as follows, step 1, preparation of fluorine-doped titanium dioxide nanoparticles; step 2, pretreatment of FTO conductive glass; step 3 , preparation of turpentine permeating alcohol binder; step 4, preparation of fluorine-doped titanium dioxide electrode film substrate; step 5, preparation of fluorine-doped titanium dioxide film electrode; step 6, construction of photoelectrocatalytic thin film electrode group. Compared with the existing technology, the preparation process is simple, and it is easy to realize large-scale production; it has a good removal effect on most ammonia nitrogen wastewater, and at the same time, no other harmful substances are produced during the treatment process, and no secondary pollution is caused; the electrode module In the sewage treatment process, only a certain amount of electric energy needs to be provided as a bias voltage and light source, and the energy consumption is small.
Owner:上海纳晶科技有限公司
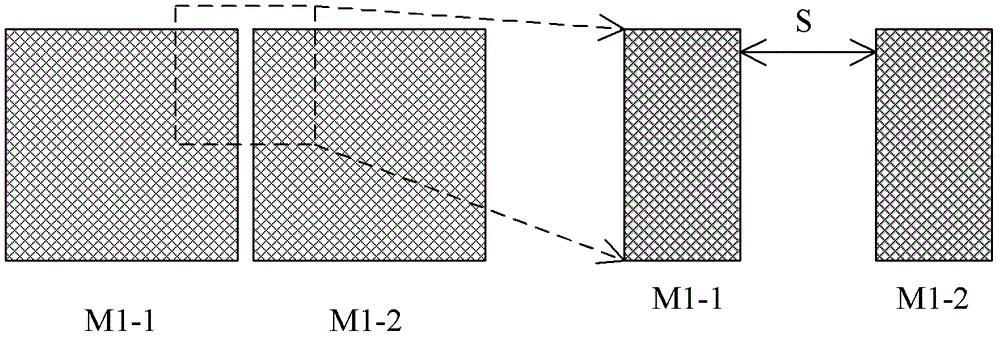
Monitoring semiconductor substrate test structures and test methods for integrated passive devices
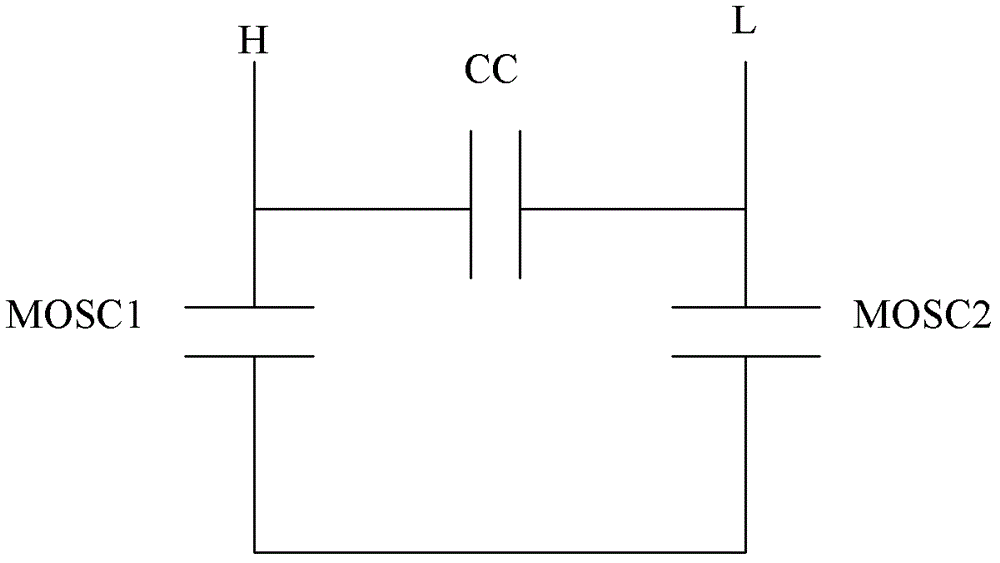
ActiveCN102509725BResistance/reactance/impedenceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsCapacitanceSubstrate doping
The invention provides a semiconductor substrate testing structure and testing method for monitoring integrated passive devices. The test structure for monitoring a semiconductor substrate for integrating passive devices according to the present invention includes: the two ends of the semiconductor circuit on the semiconductor substrate that are connected to the two ends of the inductance, capacitance and resistance tester are separated by a specific distance. The first metal wire and the second metal wire, wherein a test signal is added to one end of the LCR tester to obtain a C-V curve, and the doping concentration of the semiconductor substrate is determined through the C-V curve. According to the test structure for monitoring semiconductor substrates used for integrated passive devices, the C-V curves reflect the characteristics of metal-oxide-substrate capacitors, and the characteristics of metal-oxide-substrate capacitors are as the semiconductor substrate is doped. The C-V curve reflects the doping concentration of the semiconductor substrate. Furthermore, the change of the resistivity of the semiconductor substrate can be judged by the doping concentration of the semiconductor substrate.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUAHONG GRACE SEMICON MFG CORP
Semiconductor optical detector structure
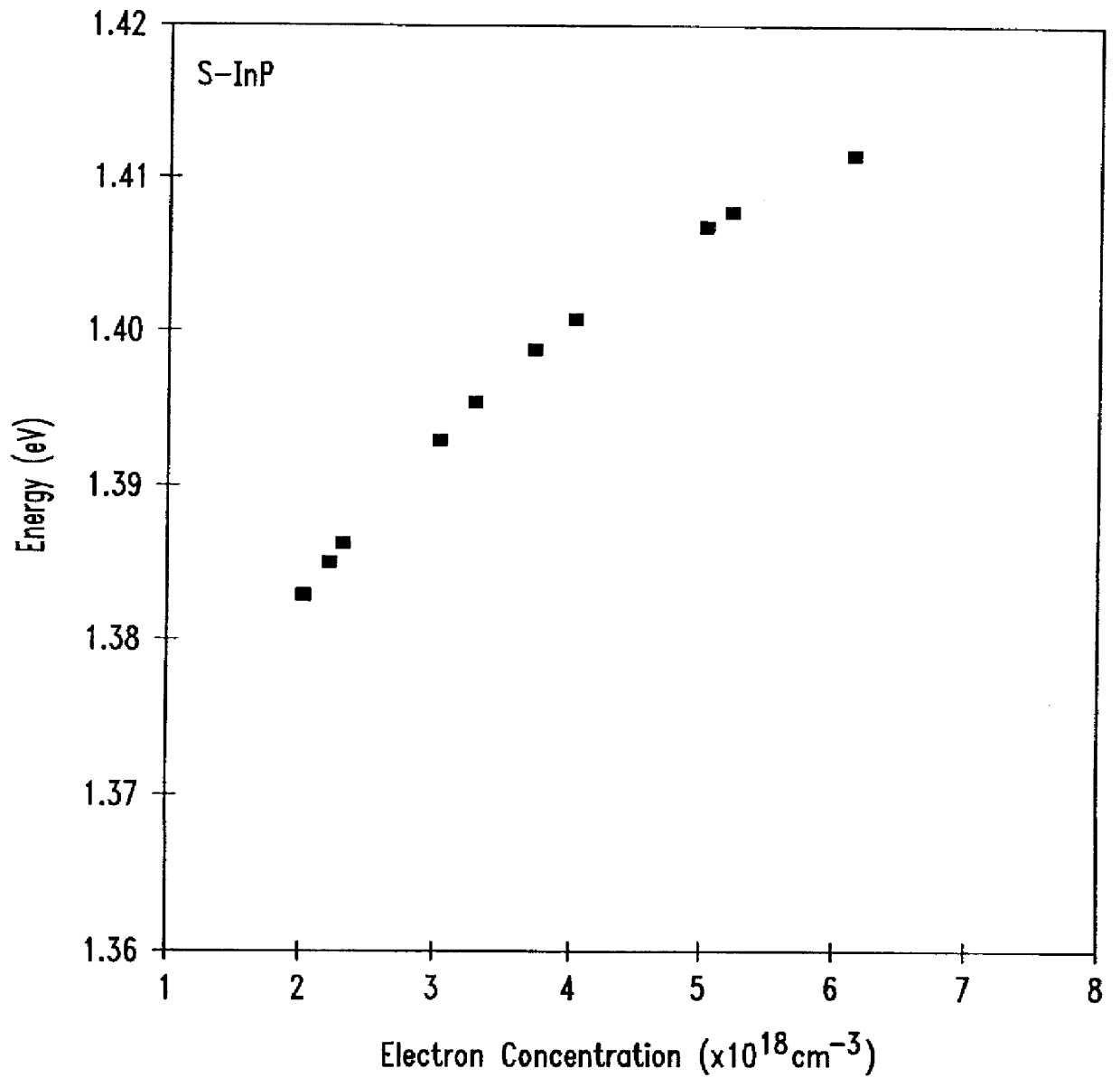
InactiveCN102804392AFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationAmorphous siliconSubstrate doping
A semiconductor is disclosed with a substrate doped with a substrate doping. There is a crystalline semiconductor layer disposed on a front side of the substrate. The crystalline semiconductor layer has a layer doping. The substrate doping changes to the layer doping within a 100 angstrom transition region. In alternative embodiments, the layer doping has novel profiles. In other alternative embodiments, the substrate has a crystalline semiconductor layers disposed on each of a front and a back side of the substrate. Each of the crystalline semiconductor layers has a respective layer doping and each of these layer dopings changes to the substrate doping within a respective transition region less than 100 angstroms thick. In still other embodiments of this invention, an amorphous silicon layer is disposed on a side of the crystalline semiconductor layer opposite the substrate.; The amorphous silicon layer has an amorphous doping so that a tunnel junction is formed between the doped crystalline semiconductor layer and the amorphous layer. Manufacturing these structures at below 700 degrees Centigrade enables the narrow transition regions of the structures.
Owner:IBM CORP
Inverted organic light-emitting diode device and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN112397665AImprove injection abilityHigh electron mobilitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectron injectionMaterials science
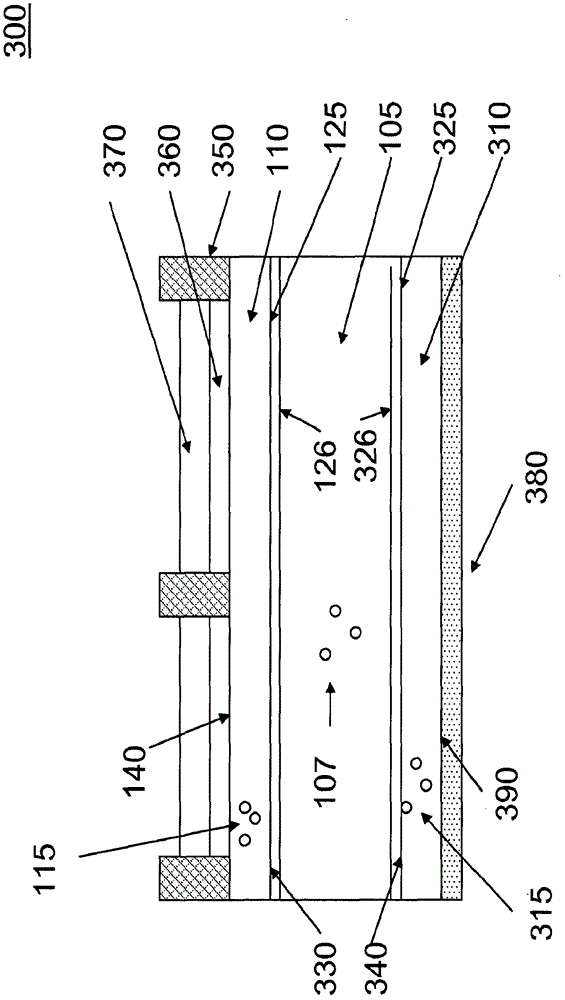
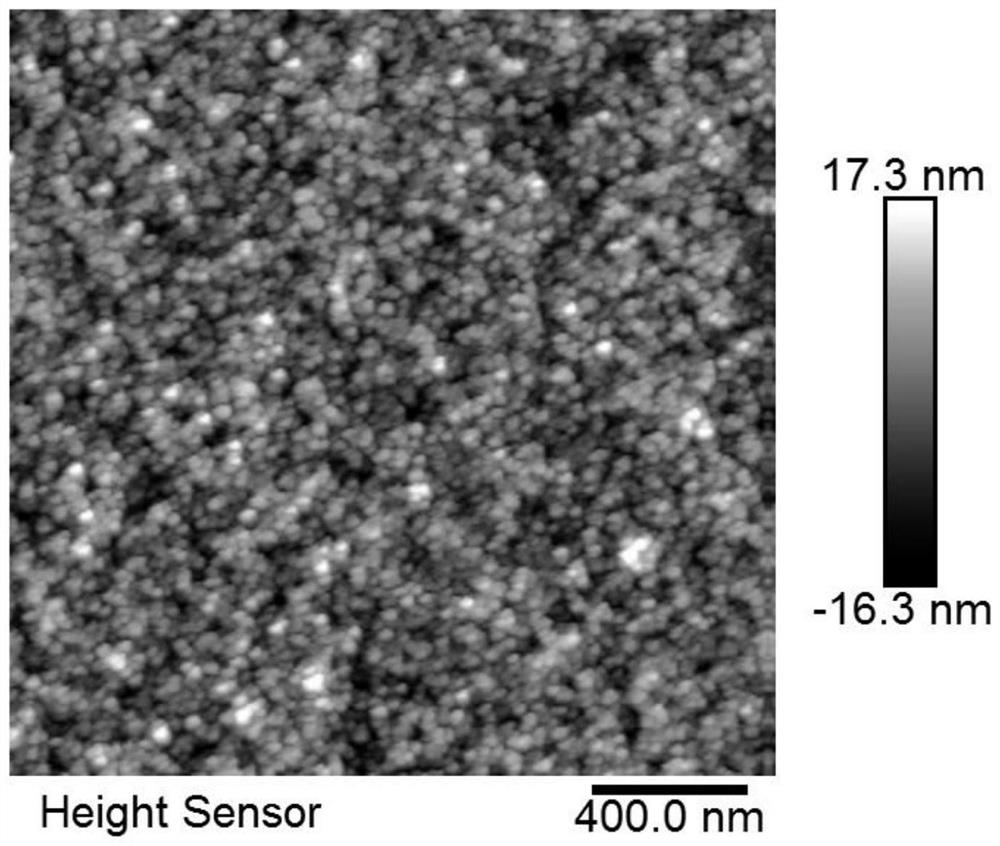
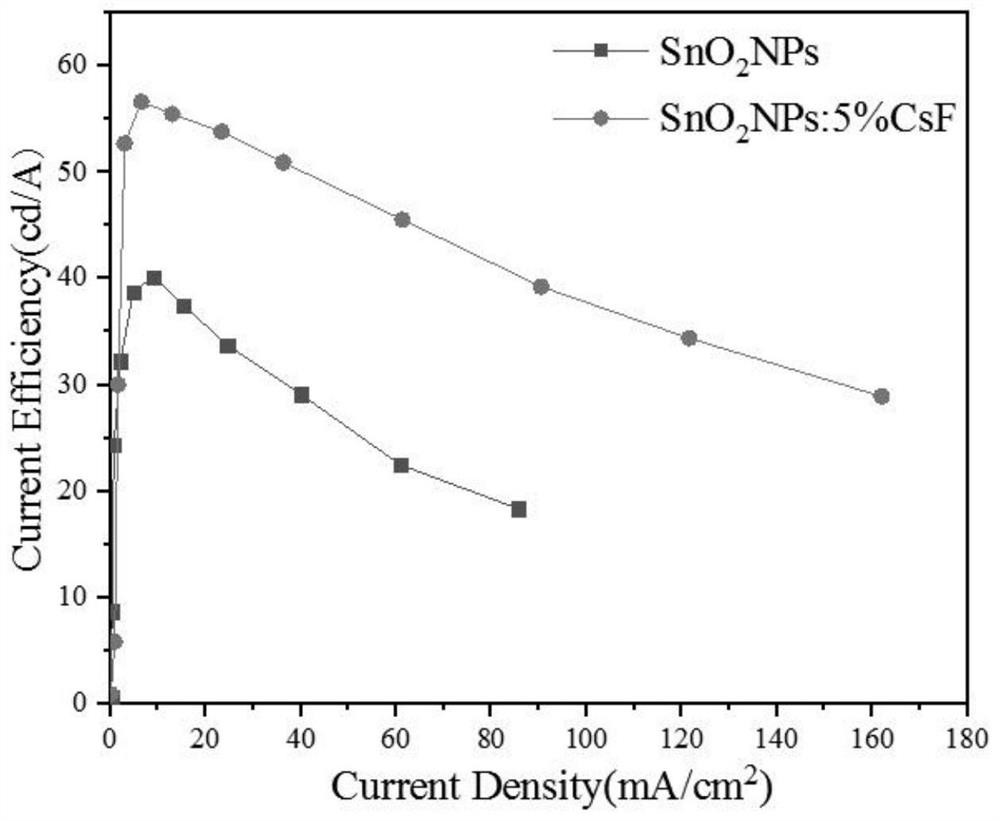
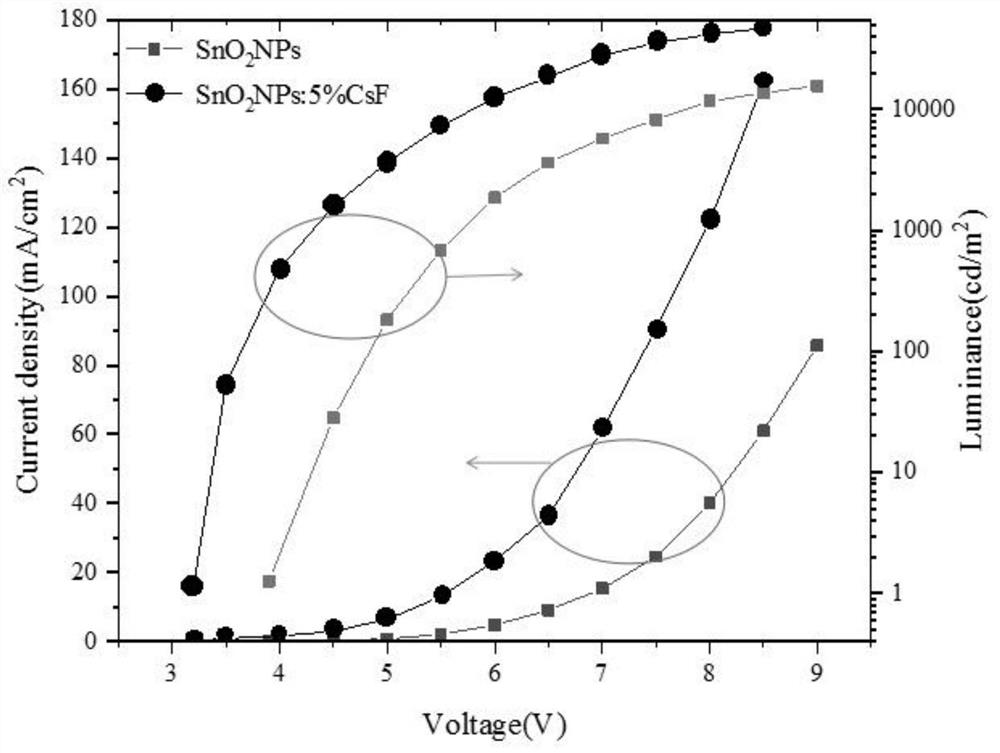
The invention discloses an inverted organic light-emitting diode device and a preparation method thereof. The performance of the inverted organic light-emitting diode device is improved by enhancing electron injection. The inverted organic light-emitting diode device structure comprises an ITO substrate, a doped electron injection layer, an energy level matching layer, a hole blocking layer, a light-emitting layer, a hole transport layer, a hole injection layer and an anode layer; according to the preparation method, a methanol solution of cesium fluoride is used for treating a stannic oxide solution through a solution process, and the electron mobility of the prepared cesium fluoride doped stannic oxide nanoparticle film is improved compared with that of an untreated stannic oxide film. The stannic oxide film is used as an electron injection layer of an inverted organic light-emitting diode device, so that compared with a device in which an untreated stannic oxide film is used as theelectron injection layer, the electronic current of the device is increased, and the driving voltage is reduced. The doped electron injection layer is prepared by a solution method with a simple process, and an effective scheme is provided for realizing inverted solution processing of an OLED device with low driving voltage and high efficiency.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Time of flight sensor device and time of flight sensor arrangement
PendingCN111725246ASolid-state devicesRadiation controlled devicesTime of flight sensorCharge carrier
The disclosure relates to a time of flight sensor device and a time of flight sensor arrangement. According to an embodiment, The time of flight sensor device comprises: a semiconductor substrate comprising a conversion region to convert an electromagnetic signal in photo-generated charge carriers, and comprising a substrate doping region having a n doping type, wherein the substrate doping regionextends from a first main surface region of the semiconductor substrate into the semiconductor substrate, wherein the semiconductor substrate has adjacent to the substrate doping region doped region,and wherein the substrate doping region at least partially forms the conversion region in the semiconductor substrate, a readout node arranged in the semiconductor substrate within the substrate doping region and having the n-doping type, wherein the readout node is configured to readout the photo generated charge carriers; and a control electrode arranged in the substrate doping region of the semiconductor substrate and in the substrate doping region and having the p-doping type.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
Image sensor device structure and method for forming the same
Embodiments of the present application provide an image sensor device structure and a forming method thereof. The image sensor device structure includes a substrate, and the substrate is doped with impurities of a first conductivity type. The image sensor device structure includes a photo-sensing region formed in the substrate, and the photo-sensing region is doped with impurities of a second conductivity type different from the first conductivity type. The image sensor device structure further includes a doping region extending into the photo-sensing region, and the doping region is doped with impurities of the first conductivity type. The image sensor device structure also includes a plurality of color filters formed on the doped regions.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Grooved Field Effect Positive Feedback Transistor Based on Semiconductor Substrate and Fabrication Method
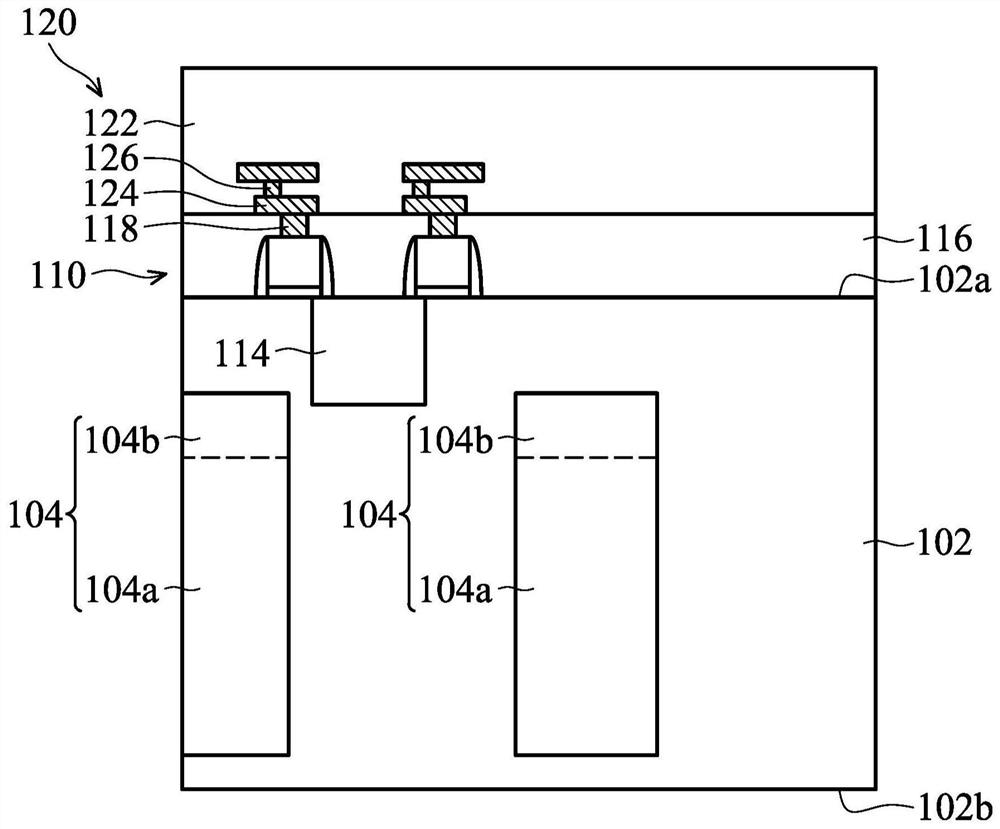
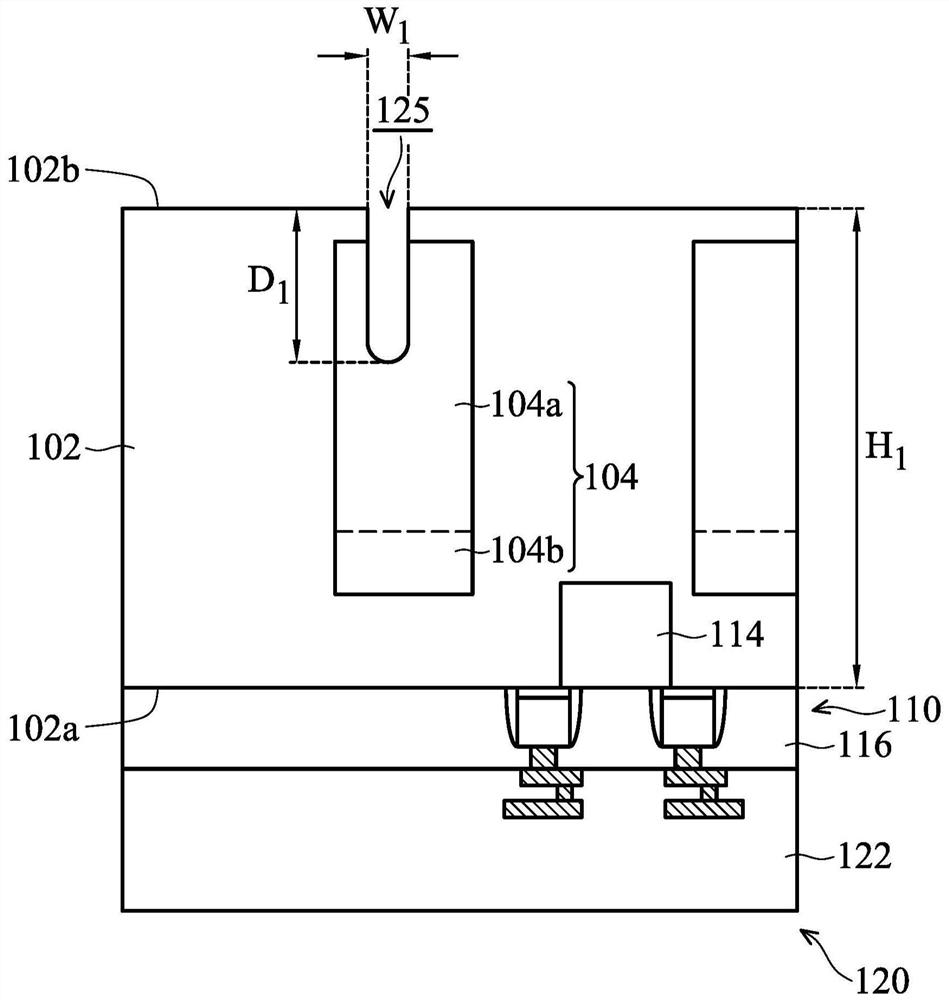
ActiveCN111477685BImprove defectsThe process conditions are simple and matureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesMOSFETCapacitance
The invention discloses a groove type field effect positive feedback transistor based on a semiconductor substrate and a preparation method thereof. The positive feedback transistor uses a groove type gate oxide layer structure to improve the defects of the planar gate oxide layer positive feedback transistor. By introducing key The doping of the channel region and the inverse substrate doping and low drain doping region of the channel region form the special energy band structure required by the positive feedback mechanism, thereby achieving electrical properties similar to ordinary positive feedback transistors In addition, the positive feedback transistor has a symmetrical physical structure similar to that of a MOSFET, and can be formed on the channel region by a self-aligned ion implantation process similar to a MOSFET under the masking effect of the positive gate and the gate spacer Low drain doping region and cathode region / anode region doping; the positive feedback transistor preparation process of the present invention is compatible with traditional CMOS, increases gate oxide layer capacitance, increases charge retention time, prolongs data storage time, and improves the Device performance as memory.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com