Transcatheter interventional artificial valve
A catheter intervention and valve technology, which is applied in catheters, heart valves, balloon catheters, etc., can solve the problems of affecting valve performance, balloon rupture, and insufficient regurgitation efficacy, so as to improve safety, reliability and service life. Small paravalvular leakage, the effect of preventing regurgitation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
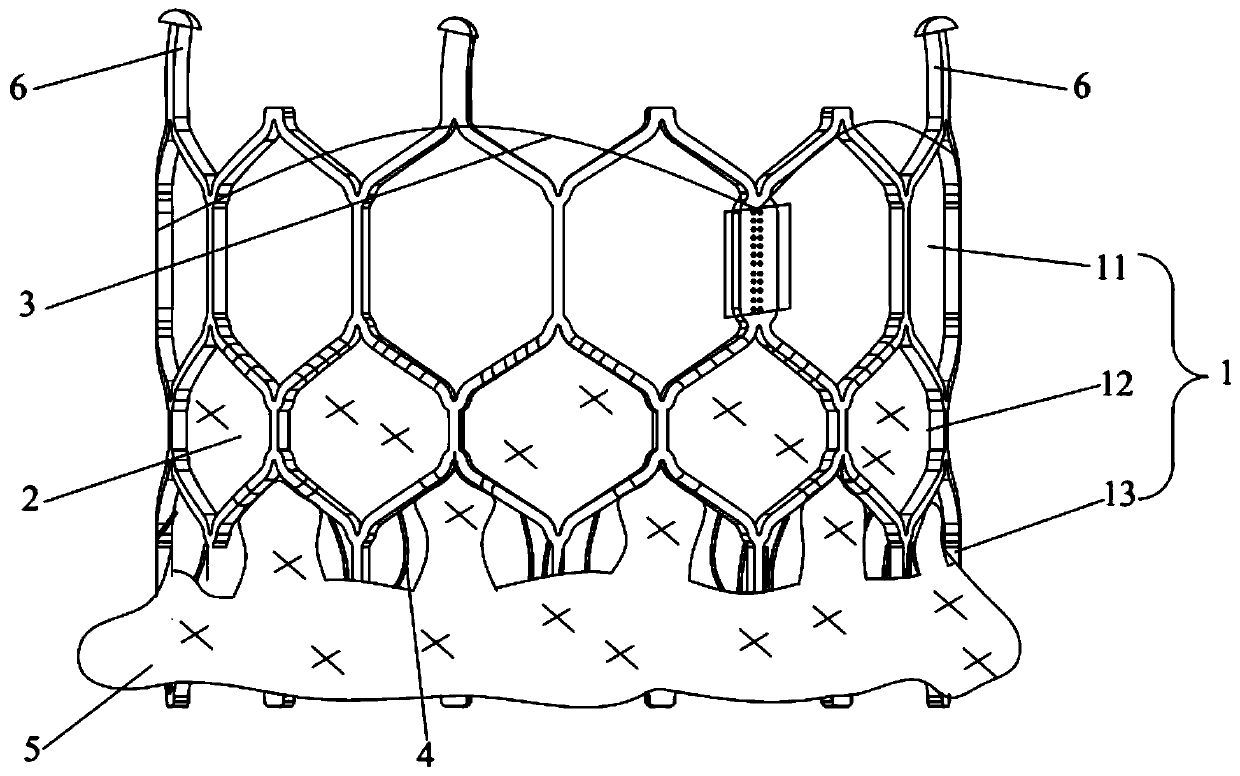
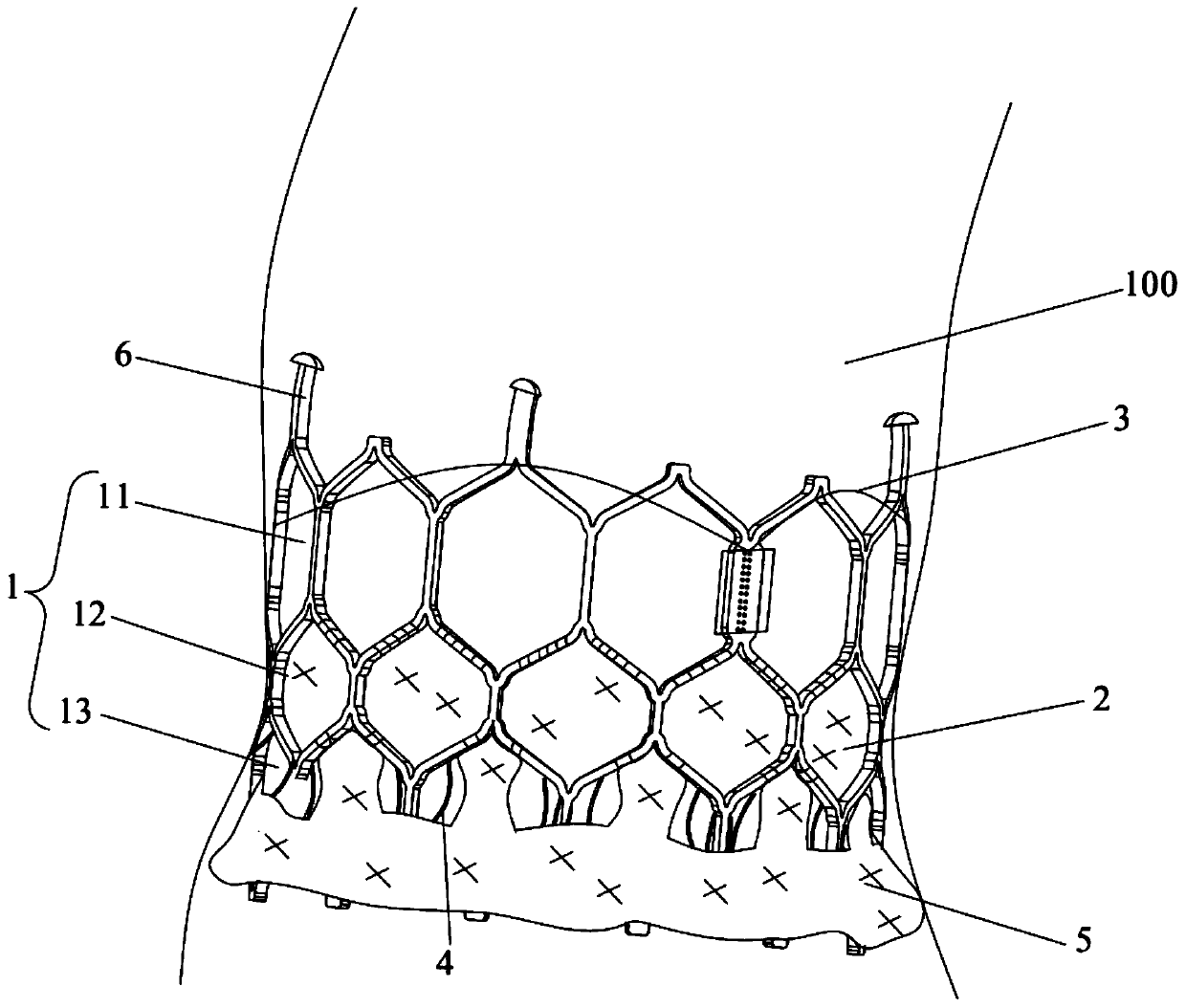
[0033] figure 1 It is a structural diagram of the transcatheter interventional artificial valve provided in this embodiment; figure 2 It is a structural diagram of a stent and a skirt frame in the transcatheter interventional artificial valve provided in this embodiment; image 3 It is a schematic diagram of the transcatheter interventional artificial valve implanted in the left ventricular outflow tract provided in this embodiment.
[0034] Such as Figure 1-Figure 3 As shown, the present embodiment provides a transcatheter interventional artificial valve, including a stent 1, a sealing membrane 2, a tissue leaflet 3, a skirt frame 4 and an outer skirt 5, wherein the stent 1 is capable of contracting radially and automatically The ring structure is expanded; the sealing membrane 2 is arranged on the inner surface of the stent 1, and the sealing membrane 2 is sutured and connected with the stent 1; The outer edge of the leaflet 3 is sutured to the inner surface of the seal...
Embodiment 2
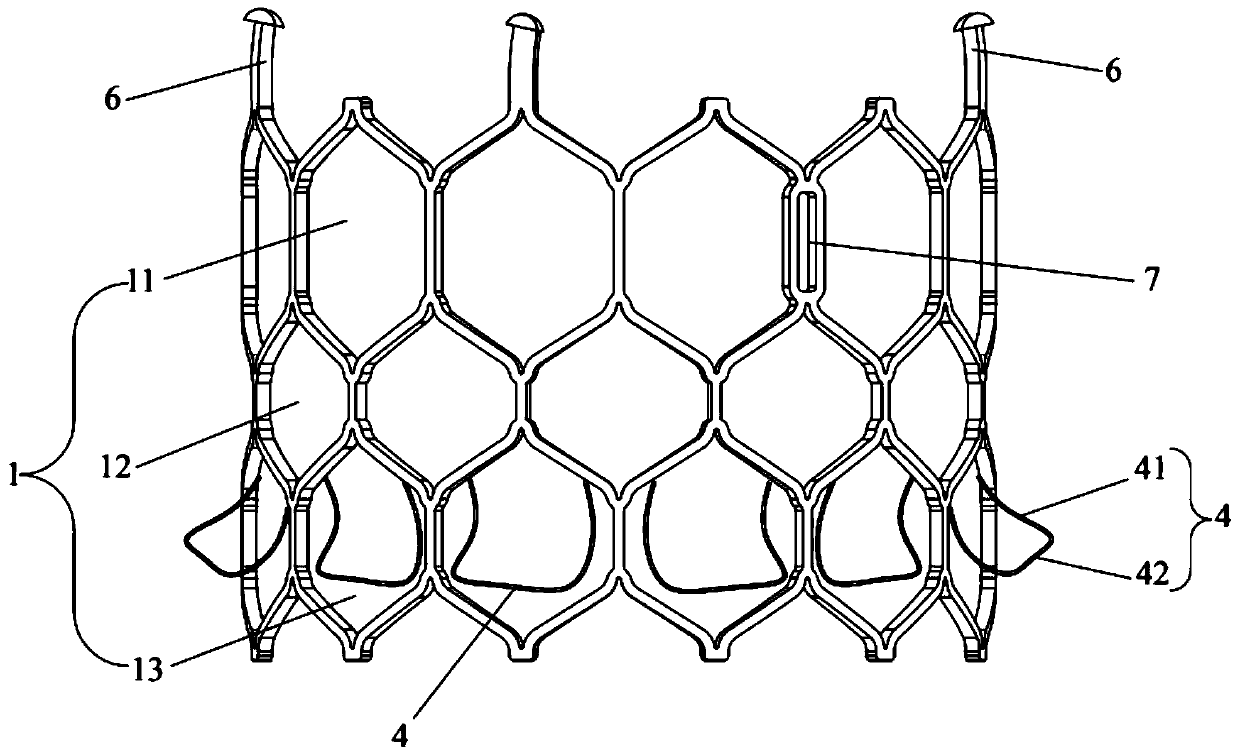
[0043] This embodiment discloses a transcatheter interventional artificial valve, which is basically the same in structure as that in Embodiment 1, the difference being that the arrangement of the skirt frame 4 is different.
[0044] Figure 4 It is a structural diagram of the stent and the skirt frame in the transcatheter interventional artificial valve provided in this embodiment. Such as Figure 4 As shown, the skirt frame 4 is formed by turning down the tops of successively spaced hexagonal grids in the third grid group 13, that is, the two upper oblique bars of the hexagonal grids are turned down to As a skirt rack4. Similar to Embodiment 1, the skirt frame 4 is also processed by heat setting after the bracket 1 is cut out; after folding, the angle between the skirt frame 4 and the outer surface of the bracket 1 10° to 50°, preferably 25° to 35°. This embodiment uses spaced hexagonal grids to fold down to form the skirt frame 4, which can achieve the same effect as th...
Embodiment 3
[0047] This embodiment discloses a transcatheter interventional artificial valve, which has basically the same structure as that in Embodiment 2, the difference being that a waist drum frame 8 is added in this embodiment.
[0048] Figure 5 It is a structural diagram of the transcatheter interventional artificial valve provided in this embodiment; Figure 6 It is a structural diagram of the stent, the skirt frame and the waist drum frame in the transcatheter interventional artificial valve provided in this embodiment; Figure 7 It is a top view of the transcatheter interventional artificial valve provided in this embodiment. Such as Figure 5-Figure 7 As shown, the stent 1 of this embodiment is also provided with a waist drum frame 8 for fixing the artificial valve on the calcified original valve leaflet. Preferably, the waist drum stand 8 is V-shaped, and its two upper ends are respectively connected to the upper slanting bars of the hexagonal grid in the second grid group...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com